Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inflammation
Inflammation
Uploaded by
محیظ ملک0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
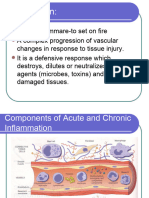
10 views1 pageInflammation is the body's response to tissue damage, involving changes in blood flow and permeability that allow fluid, proteins, and white blood cells to reach the injured site. Acute inflammation results from trauma, toxins, or microbes and aims to heal damage, while chronic inflammation involves prolonged activity of macrophages and T-cells that cause ongoing tissue destruction. Acute inflammation is evident in scabbing, redness, pus and swelling and aims to heal, whereas chronic inflammation features constantly dilated blood vessels and an overactive immune system in the absence of the body's natural healing process.
Original Description:
Original Title
Inflammation.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInflammation is the body's response to tissue damage, involving changes in blood flow and permeability that allow fluid, proteins, and white blood cells to reach the injured site. Acute inflammation results from trauma, toxins, or microbes and aims to heal damage, while chronic inflammation involves prolonged activity of macrophages and T-cells that cause ongoing tissue destruction. Acute inflammation is evident in scabbing, redness, pus and swelling and aims to heal, whereas chronic inflammation features constantly dilated blood vessels and an overactive immune system in the absence of the body's natural healing process.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageInflammation
Inflammation
Uploaded by
محیظ ملکInflammation is the body's response to tissue damage, involving changes in blood flow and permeability that allow fluid, proteins, and white blood cells to reach the injured site. Acute inflammation results from trauma, toxins, or microbes and aims to heal damage, while chronic inflammation involves prolonged activity of macrophages and T-cells that cause ongoing tissue destruction. Acute inflammation is evident in scabbing, redness, pus and swelling and aims to heal, whereas chronic inflammation features constantly dilated blood vessels and an overactive immune system in the absence of the body's natural healing process.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Inflammation, a response triggered by damage to living tissues. ...
The response consists of
changes in blood flow, an increase in permeability of blood vessels, and the migration of fluid,
proteins, and white blood cells (leukocytes) from the circulation to the site of tissue damage.
Acute inflammation is induced by tissue damage due to trauma, noxious compounds,
or microbial invasion. ... In chronic inflammation, the primary immune cells are
macrophages and T lymphocytes, which produce cytokines and enzymes that cause
more lasting damage to cells.
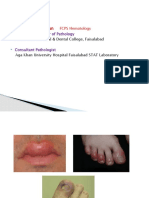
Acute vs Chronic Inflammation. ... Evidence of acute inflammation can be seen in scabbing,
redness, pus, and swelling. Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, is not part of the body's
natural healing process. Chronic inflammation is a condition where dilated blood vessels and
a hyped up immune system become the new norm.
You might also like
- Inflammation. Etiology. Vascular Changes. Cellular Events in Inflammation. Acute Inflammation. Morphologic PatternsDocument57 pagesInflammation. Etiology. Vascular Changes. Cellular Events in Inflammation. Acute Inflammation. Morphologic PatternsZauzaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4.1Document8 pagesUnit 4.1Bloody MarieNo ratings yet
- Inflammation Is Part of The Complex Biological Response of Vascular Tissues To Harmful StimuliDocument2 pagesInflammation Is Part of The Complex Biological Response of Vascular Tissues To Harmful StimuliGabitza GabiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Inflammation, Tissue Repair & FeverDocument8 pagesChapter 6 - Inflammation, Tissue Repair & FeverChrista CastorNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic InflammationDocument22 pagesAcute and Chronic InflammationRedhwan85No ratings yet
- Acute InflammationDocument64 pagesAcute InflammationSuleiman KikulweNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic InflammationDocument40 pagesAcute and Chronic InflammationIqra ChNo ratings yet
- Thanavala 2-23-17 Mir 508 Adv Immunol Yt Inflammation 2017Document27 pagesThanavala 2-23-17 Mir 508 Adv Immunol Yt Inflammation 2017kaoutherboublatNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Acute InflammationDocument70 pages2.1 Acute InflammationRawa Muhsin100% (1)
- لقطة شاشة ٢٠٢٣-١١-٠٩ في ٨.٥٣.٥٠ صDocument7 pagesلقطة شاشة ٢٠٢٣-١١-٠٩ في ٨.٥٣.٥٠ صmo44hh44No ratings yet
- Inflammation: Inflammation Is A Protective Response, The Goal of Which Is To EliminateDocument26 pagesInflammation: Inflammation Is A Protective Response, The Goal of Which Is To EliminateDavid Cahyo WibisonoNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Inflammation: Yacob Alemu (MD) May 2021Document89 pagesAcute and Chronic Inflammation: Yacob Alemu (MD) May 2021Tazeb AyeleNo ratings yet
- انواع السعال واختيار الدواء المناسبDocument3 pagesانواع السعال واختيار الدواء المناسبOmer AlsameiNo ratings yet
- Group No 3Document19 pagesGroup No 3محمد نعیم اقبالNo ratings yet
- InflammationDocument2 pagesInflammationSujan BoseNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio;Ogy of Inflammation تم حفظه تلقائياDocument59 pagesPathophysio;Ogy of Inflammation تم حفظه تلقائياbebba habdouNo ratings yet
- InflammationDocument83 pagesInflammationpriyaNo ratings yet
- Chetna NewDocument8 pagesChetna NewRAVINDER YADAVNo ratings yet
- 3 Inflammation and RepairDocument14 pages3 Inflammation and RepaircedonuliNo ratings yet
- Mimiproject Anti InfiamationDocument69 pagesMimiproject Anti Infiamationmukeshcilaveni18No ratings yet
- Workshop 1.2 Inflammation1Document30 pagesWorkshop 1.2 Inflammation1nganleo5801No ratings yet
- 6.role of Complement System in Acute InflammationDocument42 pages6.role of Complement System in Acute InflammationDR.NITHA WILLYNo ratings yet
- Short Notes InflammationDocument3 pagesShort Notes InflammationDr-Rukhshanda RamzanNo ratings yet
- 2.4 2.5 Radang Akut Kronik Dan MorfologiDocument51 pages2.4 2.5 Radang Akut Kronik Dan MorfologimeNo ratings yet
- Inflammation CompleteDocument56 pagesInflammation CompletePunjabi Culture KhushabNo ratings yet
- Sworts Immunology Inflammation-And-Wound-HealingDocument68 pagesSworts Immunology Inflammation-And-Wound-HealingꕶᗋᏦᎥꕗNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Usman: Associate Professor of Pathology Consultant PathologistDocument89 pagesMuhammad Usman: Associate Professor of Pathology Consultant PathologistSmithNo ratings yet
- Inflammation & Immune ResponseDocument68 pagesInflammation & Immune Responsesuday sunday100% (1)
- Inflammation & Immune ResponseDocument68 pagesInflammation & Immune ResponseAgata Krisensia Putri100% (1)
- Inflammation 30.08.2022Document39 pagesInflammation 30.08.2022Abdur RaquibNo ratings yet
- InflammationDocument22 pagesInflammationAhmad Khan GhoriNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPathophysiologySarahlaine BrazasNo ratings yet
- InflammationDocument48 pagesInflammationTewodros TeshomeNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and Tissue Repair: July 2021Document54 pagesInflammation and Tissue Repair: July 2021EdenNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and RepairDocument34 pagesInflammation and Repairanshum guptaNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and Inflammatory MediatorsDocument28 pagesInflammation and Inflammatory Mediatorsla.instagramawaNo ratings yet
- Dangerous Malware Trojan Dont ClickDocument4 pagesDangerous Malware Trojan Dont ClickAdam HendersonNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and RepairDocument2 pagesInflammation and RepairSha BtstaNo ratings yet
- Inflamasi Akut Dan KronikDocument60 pagesInflamasi Akut Dan KronikMunawir_Syam91No ratings yet
- Inflammation and RepairDocument77 pagesInflammation and RepaironyekaNo ratings yet
- Acute InflammationDocument16 pagesAcute InflammationNoman AnwarNo ratings yet
- 1 Acute InflammationDocument6 pages1 Acute InflammationNauzaina IjazNo ratings yet
- IVMS - General Pathology, Inflammation NotesDocument19 pagesIVMS - General Pathology, Inflammation NotesMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.No ratings yet
- InflammationDocument55 pagesInflammationvabinh.dd2022No ratings yet
- 07 InflammationDocument69 pages07 InflammationSangameswaran B.BNo ratings yet
- Amo PathologyDocument10 pagesAmo PathologyOtema JamesNo ratings yet
- Skenario IDocument12 pagesSkenario IRajasa FathahilllahNo ratings yet
- Combine Class Chronic Inflammation & Wound Healing (Power Point)Document35 pagesCombine Class Chronic Inflammation & Wound Healing (Power Point)Suleiman KikulweNo ratings yet
- Inflammation KundieDocument4 pagesInflammation KundieTadiwanashe ManyandeNo ratings yet
- Inflamasi Akut Dan KronikDocument60 pagesInflamasi Akut Dan KronikDhea Resty PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Inflammation (: Latin Vascular PathogensDocument1 pageInflammation (: Latin Vascular PathogensSharmaine Grace FlorigNo ratings yet
- Chronic InflammationDocument24 pagesChronic InflammationTommys100% (1)
- Summer of Patho.t PDFDocument10 pagesSummer of Patho.t PDFحسن محمد سعيد جاسمNo ratings yet
- Immunology of Inflammation - SlidesDocument22 pagesImmunology of Inflammation - SlidesEssington BeloNo ratings yet
- InflammationDocument8 pagesInflammationGhazi Uddin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Study-Notes - Inflammation-And-Repair (1) 88Document17 pagesStudy-Notes - Inflammation-And-Repair (1) 88jjjkkNo ratings yet
- Cell InflammationDocument17 pagesCell InflammationSwetha reddyNo ratings yet
- Vascularized Tissue To Injurious Agent A Protective ResponseDocument13 pagesVascularized Tissue To Injurious Agent A Protective ResponseBravan AliennNo ratings yet
- Inflammation: Presenter: Priyanka Shah Junior Resident Department of Pedodontics and Preventive DentistryDocument73 pagesInflammation: Presenter: Priyanka Shah Junior Resident Department of Pedodontics and Preventive DentistryBibek RajNo ratings yet
- Open 5Document1 pageOpen 5محیظ ملکNo ratings yet
- Gobby: Project Page Source Code Gplv2+ Isc GobbyDocument1 pageGobby: Project Page Source Code Gplv2+ Isc Gobbyمحیظ ملکNo ratings yet
- Free Project Management SoftwareDocument1 pageFree Project Management Softwareمحیظ ملکNo ratings yet
- Admin 10456 - Ad 10789 - DD 101234 - Deo: PasswordDocument2 pagesAdmin 10456 - Ad 10789 - DD 101234 - Deo: Passwordمحیظ ملکNo ratings yet