Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Centrifugal Pump Performance Test
Centrifugal Pump Performance Test
Uploaded by
VirneDalisayOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Centrifugal Pump Performance Test
Centrifugal Pump Performance Test
Uploaded by
VirneDalisayCopyright:
Available Formats
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY 2
Centrifugal Pump Performance Test
Centrifugal pumps are among the important equipment in any process plant. In any refinery they are
considered to be equivalent to heart of a refinery, as they keep the flow running with a certain pressure and
quantity from one place to another, each pump has its own pump performance curve.
Pump performance curve
A performance curve is plotted to indicate the variation of pump differential head against volumetric flow
(gpm) of a liquid at an indicated rotational speed or velocity, while consuming a specific quantity of
horsepower (BHP). The performance curve is actually four curves relating with each other on a common
graph. These four curves are:
1. The Head-Flow Curve. It is called the H-Q Curve.
2. The Efficiency Curve.
3. The Energy Curve. It records Brake Horsepower, BHP.
4. The Pump’s Minimum Requirement Curve. It’s called Net Positive Suction Head required,
NPSHr.
Typical Procedure of Pump Performance Test
The purpose of pump performance test is to ensure that the actual performance of a pump is typical to that
set by supplier. Typical steps to be followed to conduct a pump performance test are outlined below.
1. Prepare the original pump curve sent by supplier.
2. Make sure that the suction strainer is clean and the suction valve is fully open.
ENGR. VIRNE B. DALISAY 1
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY 2
3. Ensure that discharge valve is fully closed.
4. Start the centrifugal pump take the reading of the discharge pressure, flow rate, suction
pressure and pump Ampere. (Finish this procedure in less than 1 min. As not to damage
the internal parts of the pump)
5. Open the discharge valve slightly till the flow rate reaches the first value indicated in pump
performance curve provided by pump supplier.
6. Write down the discharge pressure, flow rate, suction pressure and pump Ampere.
7. Increase the opening of the discharge valve till you reach the next value indicated in pump
performance curve provided by pump supplier.
8. Open the discharge valve in small increments until it is fully open and take the readings of
the discharge pressure, flow rate, suction pressure and pump Ampere at each of the steps.
ACTUAL PUMP DATA OBSERVED DATA
Data 1 2 3 4 5
Q, m3/hr
SUCTION PRESSURE, kPa
DISCHARGE Pressure, kPa
DIFFERENTIAL HEAD, meter
CURRENT RATING, ampere
THEORETICAL PUMP DATA OBSERVED DATA
Data 1 2 3 4 5
Q, m3/hr
SUCTION PRESSURE, kPa
DISCHARGE Pressure, kPa
DIFFERENTIAL HEAD, meter
CURRENT RATING, ampere
SUPPLIER’S PUMP DATA OBSERVED DATA
Data 1 2 3 4 5
Q, m3/hr
SUCTION PRESSURE, kPa
DISCHARGE Pressure, kPa
DIFFERENTIAL HEAD, meter
CURRENT RATING, ampere
ENGR. VIRNE B. DALISAY 2
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY 2
SUPPLIER’S PUMP DATA
Compare the curve plotted from pump performance test readings (table) with the performance curve sent
by supplier and observe for any differences. If you witness any deviation try to locate the problem and fix
it then repeat the test and compare the results.
ENGR. VIRNE B. DALISAY 3
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY 2
Source: www.blagdonpump.com
ENGR. VIRNE B. DALISAY 4
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY 2
Source: www.vertiflopump.com
Source: Plast-O-Matic Valves, Inc.
ENGR. VIRNE B. DALISAY 5
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY 2
Figure 1. Centrifugal Pump Parts
ENGR. VIRNE B. DALISAY 6
You might also like
- Large Diameter Manhole Sizing GuidelineDocument1 pageLarge Diameter Manhole Sizing Guidelinemirza_adil99No ratings yet
- Is 13349 (Penstock)Document16 pagesIs 13349 (Penstock)praval84100% (1)
- Unit 2 Section 2.1 Earth Inside and OutDocument5 pagesUnit 2 Section 2.1 Earth Inside and OutMercedes Muñoz GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum For Beautician: 6-Months (Certificate Course)Document19 pagesCurriculum For Beautician: 6-Months (Certificate Course)starwar111No ratings yet
- Earthing Schematic Office R3 (04.01.2022) OUR ScopeDocument1 pageEarthing Schematic Office R3 (04.01.2022) OUR ScopeRZK AbbadonNo ratings yet
- Reaffirmed 2018Document36 pagesReaffirmed 2018TessaNo ratings yet
- Composite Elevated Water Storage Tank SpecificationsDocument9 pagesComposite Elevated Water Storage Tank SpecificationsArputharaj Maria LouisNo ratings yet
- Medium Voltage Metal Clad Switchgear CatalogDocument24 pagesMedium Voltage Metal Clad Switchgear CatalogRobert John ToledoNo ratings yet
- j20 014 Permit Electrical 210604Document8 pagesj20 014 Permit Electrical 210604Art AV B LimNo ratings yet
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument28 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationAMIAMINo ratings yet
- IS3042 S.gatesDocument25 pagesIS3042 S.gatessheikhyasir11No ratings yet
- Philips Office Lighting BrochureDocument77 pagesPhilips Office Lighting BrochureTaiyeb Mohammed100% (1)
- I4 Industrial UPS Catalogue (Domestic)Document8 pagesI4 Industrial UPS Catalogue (Domestic)p41005679No ratings yet
- 11kv 3 Unit 350MVA Kiosk With 2700kVA TransformerDocument35 pages11kv 3 Unit 350MVA Kiosk With 2700kVA Transformer10derNo ratings yet
- Tyco Vanessa DatasheetDocument16 pagesTyco Vanessa DatasheetJack ChavanNo ratings yet
- MK Giridharan Latest EditionDocument2 pagesMK Giridharan Latest EditionBenadict JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument20 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationpkumarmysNo ratings yet
- Specification For 1000 KV TransformerDocument1 pageSpecification For 1000 KV TransformerSandeep SoniNo ratings yet
- Hoa Thang Genset Installation GuidelineDocument8 pagesHoa Thang Genset Installation GuidelineUsman FaarooquiNo ratings yet
- ICS61800 Part1 R2007 PDFDocument9 pagesICS61800 Part1 R2007 PDFpata nahi hai mujeNo ratings yet
- UPS Sizing Calculations PDFDocument2 pagesUPS Sizing Calculations PDFManglesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Catálogo - Cubículos 8DH10 PDFDocument44 pagesCatálogo - Cubículos 8DH10 PDFRicardo Nunes Pereira JuniorNo ratings yet
- BS EN 1092-1 PN 16 DimensionsDocument3 pagesBS EN 1092-1 PN 16 DimensionsCheerag100% (1)
- Final ProjectDocument45 pagesFinal Projectrahulshandilya2k100% (1)
- Variable Flow Cooling Tower-FlyerDocument2 pagesVariable Flow Cooling Tower-FlyerManik Singh100% (1)
- Apfc PanelDocument2 pagesApfc Paneli_m_pranayNo ratings yet
- SP6 6hand Book of Structural EngineersDocument76 pagesSP6 6hand Book of Structural EngineerstrmpereiraNo ratings yet
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument14 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationKatie RamirezNo ratings yet
- Structural Calculation of Driven Pipes: German Atv Rules and StandardsDocument92 pagesStructural Calculation of Driven Pipes: German Atv Rules and Standardsgarisa1963No ratings yet
- Variable Speed Drive For Converter Fed Synchronous Machine - PCS 8000 Variable-Speed Converter - (Converters For Pumped Storage Plants - ) - ABBDocument3 pagesVariable Speed Drive For Converter Fed Synchronous Machine - PCS 8000 Variable-Speed Converter - (Converters For Pumped Storage Plants - ) - ABBDeepak GehlotNo ratings yet
- Iec 62494-1-2008Document44 pagesIec 62494-1-2008latifNo ratings yet
- Ductile Iron Gate Valve PN16. BS EN 1171:2002 PN16Document8 pagesDuctile Iron Gate Valve PN16. BS EN 1171:2002 PN16Emil AbdoNo ratings yet
- Crompton - LED Fitting PDFDocument52 pagesCrompton - LED Fitting PDFwritetorahulsinha9028No ratings yet
- ABB MAG Flow DN400 Water Master SeriesDocument52 pagesABB MAG Flow DN400 Water Master SeriesNad EemNo ratings yet
- 22kv Simosec EngDocument44 pages22kv Simosec Engmimran18No ratings yet
- AVK Dam Reservoir Applications Glenfield PDFDocument16 pagesAVK Dam Reservoir Applications Glenfield PDFsexmanijakNo ratings yet
- IS 1570 Part 3Document19 pagesIS 1570 Part 3Sheetal JindalNo ratings yet
- Catalogo 13 Eng - Nuovo Needle ValvesDocument8 pagesCatalogo 13 Eng - Nuovo Needle ValvesDheeraj ThakurNo ratings yet
- BS 1965-1Document19 pagesBS 1965-1Fenner ElectromechanicalNo ratings yet
- Awwa Standard For Pilot Operated Control ValvesDocument32 pagesAwwa Standard For Pilot Operated Control ValvesAbhishek Kumar SinhaNo ratings yet
- Sikkim Hydro InitiativesDocument4 pagesSikkim Hydro InitiativesVishnu VasanthNo ratings yet
- KSB Butterfly Valve Boax-B SeriesDocument20 pagesKSB Butterfly Valve Boax-B SeriesswcciqbalNo ratings yet
- Valves & ControlsDocument16 pagesValves & ControlseborresonNo ratings yet
- Parameter: Data Sheet For 3 Phase TransformerDocument1 pageParameter: Data Sheet For 3 Phase Transformermkbhat17kNo ratings yet
- Cable Operating TemperatureDocument3 pagesCable Operating TemperaturedusktodawnNo ratings yet
- L&T CatalogueDocument246 pagesL&T CatalogueSajid AkhterNo ratings yet
- T83840en PDFDocument6 pagesT83840en PDFshareyhou100% (1)
- Relay Coordination Preliminary Report Draft-BDocument4 pagesRelay Coordination Preliminary Report Draft-Bramesh1950No ratings yet
- Basic Valve & SizingDocument8 pagesBasic Valve & SizingRio Ananda PutraNo ratings yet
- Motor Data CalculatorDocument6 pagesMotor Data CalculatorSebastian R.No ratings yet
- Abb SKDocument27 pagesAbb SKtonNo ratings yet
- Nepal Authority PDFDocument8 pagesNepal Authority PDFManu MouryaNo ratings yet
- Water Hammers PDI PDFDocument38 pagesWater Hammers PDI PDFkarthickNo ratings yet
- Is 6392Document60 pagesIs 6392Yogesh NadgoudaNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Turbo Machinery Lab ManualDocument10 pagesFluid and Turbo Machinery Lab ManualAnkush Shankar PujariNo ratings yet
- Paper Tekpro Ii - Kelompok 8-DikonversiDocument6 pagesPaper Tekpro Ii - Kelompok 8-DikonversiSilvi AmaliaNo ratings yet
- 6910-Article Text-26607-1-10-20210930Document12 pages6910-Article Text-26607-1-10-20210930dile garciaNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of A Selected Pump and FanDocument2 pagesPerformance Evaluation of A Selected Pump and Fanashier dave calulotNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pumps R7Document9 pagesCentrifugal Pumps R7b.jefferson4738123No ratings yet
- Lab Manual - FM and M LabDocument64 pagesLab Manual - FM and M LabRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan12 ESP 04042016 13042016Document192 pagesPertemuan12 ESP 04042016 13042016Priozky Pratama Purba100% (1)
- How to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesFrom EverandHow to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Gear DesignDocument2 pagesGear DesignVirneDalisayNo ratings yet
- Bookquick Marketing: Summary of Selected Foreign Journals From Book Fair 2017Document1 pageBookquick Marketing: Summary of Selected Foreign Journals From Book Fair 2017VirneDalisayNo ratings yet
- SUWECODTRDocument1 pageSUWECODTRVirneDalisayNo ratings yet
- Abo It Iz Power ConfirmationDocument1 pageAbo It Iz Power ConfirmationVirneDalisayNo ratings yet
- Abstract Air Con Trainer UnitDocument11 pagesAbstract Air Con Trainer UnitVirneDalisayNo ratings yet
- Pasuc Cdio Training For Engineering CurriculumDocument1 pagePasuc Cdio Training For Engineering CurriculumVirneDalisayNo ratings yet
- TOS Sample For 100 Item Midterm Examination in Thermo1Document1 pageTOS Sample For 100 Item Midterm Examination in Thermo1VirneDalisayNo ratings yet
- Certificate Appearnce o JT 2015Document1 pageCertificate Appearnce o JT 2015VirneDalisayNo ratings yet
- Matl Science Final 2015Document4 pagesMatl Science Final 2015VirneDalisayNo ratings yet
- Automotive Engineering Completion: (10 PTS) Complete Each Statement by Filling Up With Correct Answer The Underlined SpaceDocument3 pagesAutomotive Engineering Completion: (10 PTS) Complete Each Statement by Filling Up With Correct Answer The Underlined SpaceVirneDalisayNo ratings yet
- Information Dissemination Re: Fieldtrip & ToursDocument17 pagesInformation Dissemination Re: Fieldtrip & ToursVirneDalisayNo ratings yet
- Toyota Production SystemDocument8 pagesToyota Production SystemVirneDalisayNo ratings yet
- Dr. Elvin F. Gaac: Vpaa This UniversityDocument1 pageDr. Elvin F. Gaac: Vpaa This UniversityVirneDalisayNo ratings yet
- Sample Letter Medical CertificateDocument1 pageSample Letter Medical CertificateVirneDalisayNo ratings yet
- 140 160 F (X) 2x + 50 R 1 Y Linear (Y)Document4 pages140 160 F (X) 2x + 50 R 1 Y Linear (Y)VirneDalisayNo ratings yet
- Munggo ShellerDocument1 pageMunggo ShellerVirneDalisayNo ratings yet
- Project Execution PlanDocument1 pageProject Execution PlanVirneDalisayNo ratings yet
- Certificate of AppearanceDocument1 pageCertificate of AppearanceVirneDalisayNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 ImineDocument10 pagesLab 5 ImineCheng FuNo ratings yet
- Mental AltitudeDocument16 pagesMental AltitudeAman OjhaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Nutrition: Colin R. Paterson, David AyoubDocument6 pagesClinical Nutrition: Colin R. Paterson, David AyoubruthchristinawibowoNo ratings yet
- SopDocument9 pagesSopPuri Purnama SariNo ratings yet
- Controlled Level and Variability of Systolic Blood Pressure On TheDocument7 pagesControlled Level and Variability of Systolic Blood Pressure On TheJeanette LuevanosNo ratings yet
- Axial Piston Closed Circuit Pumps: Series 42Document76 pagesAxial Piston Closed Circuit Pumps: Series 42Евгений ГубаревNo ratings yet
- Housing (Front) - Remove: Disassembly and AssemblyDocument4 pagesHousing (Front) - Remove: Disassembly and AssemblyMbahdiro KolenxNo ratings yet
- Practice 1-M12Document6 pagesPractice 1-M12Châu Nguyễn NgọcNo ratings yet
- Eaton Emergency Lighting Self Contained Safety Micropoint 2 Recessed Datasheet enDocument2 pagesEaton Emergency Lighting Self Contained Safety Micropoint 2 Recessed Datasheet enOjog Ciprian AlinNo ratings yet
- 14 Oct - SDRM - Prof. Nirmalya BDocument2 pages14 Oct - SDRM - Prof. Nirmalya BShivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- USFS Mission - Tanzania - May 2009 - Water Resources in Tabora and Rukwa - For FRAMEDocument57 pagesUSFS Mission - Tanzania - May 2009 - Water Resources in Tabora and Rukwa - For FRAMERahul K Awade0% (1)
- NMDs OrientationDocument31 pagesNMDs OrientationRasheedAladdinNGuiomalaNo ratings yet
- 2 PBDocument8 pages2 PBc76991350No ratings yet
- Sony ST-SA3ESDocument64 pagesSony ST-SA3ESNanoUrraNo ratings yet
- Ict G7 G8 LCP1Document3 pagesIct G7 G8 LCP1Jhobhel Christopher GalivoNo ratings yet
- Mounting Hardware and Accessories Wilcoxon Sensing Technologies 2020Document9 pagesMounting Hardware and Accessories Wilcoxon Sensing Technologies 2020Fabian MolinengoNo ratings yet
- Process of HospitalizationDocument24 pagesProcess of HospitalizationFara Zaman100% (3)
- Dish Id RosisDocument28 pagesDish Id RosisDM internaNo ratings yet
- Immuno NotesDocument9 pagesImmuno NotesMoe HussainNo ratings yet
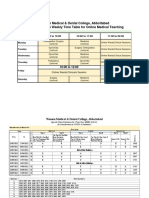
- Final Year MBBS Timetable (Online Classes) 2020-21Document2 pagesFinal Year MBBS Timetable (Online Classes) 2020-21em khanNo ratings yet
- Absorption ChillersDocument49 pagesAbsorption ChillersNallasivam Be A BizzaroNo ratings yet
- Strato2000 Service Manual - Rev3 PDFDocument325 pagesStrato2000 Service Manual - Rev3 PDFMaximus Decimus MeridiusNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument60 pagesProject ReportPrashant Bankar33% (6)
- Unloading Arm DatasheetDocument2 pagesUnloading Arm DatasheetbecpavanNo ratings yet
- Platts Nucleonics Week 19 July2012Document15 pagesPlatts Nucleonics Week 19 July2012Jovi Savitri Eka PutriNo ratings yet
- Toolbox Health and Safety SignsDocument2 pagesToolbox Health and Safety SignsAlexandru GabrielNo ratings yet
- 2021-2023 FO X RFR Tracker - KC NCDDP AFDocument147 pages2021-2023 FO X RFR Tracker - KC NCDDP AFJestoni Gonzales TortolaNo ratings yet
- Data Spare PartDocument8 pagesData Spare Partagung setiawanNo ratings yet