Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hole Pattern As Datum
Hole Pattern As Datum
Uploaded by
Henrique Marques0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
504 views2 pagesHole Pattern as Datum
Original Title
Hole Pattern as Datum
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHole Pattern as Datum
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
504 views2 pagesHole Pattern As Datum
Hole Pattern As Datum
Uploaded by
Henrique MarquesHole Pattern as Datum
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 2
Design Tip
‘When a pattern of parallel
cylinders (e.g. hole pattern)
are used as a primary datum
feature, a position control is
used to control the spacing of
the cylinders within the
patter, When a pattern of
parallel cylinders is used as a
secondary or tertiary datum
feature, a position contro!
should be used to control the
spacing of the cylinders
within the pattern and the
orientation ofthe pattern to
the higher ranking darurns
wt
Author's Comment
In this ype of dimensioning,
the hole pater isnot defined
relative tothe outside edges
ofthe part. The hole pattern is
the origin of measurement.
‘The outside surfaces of the
partare dimensioned from the
hole pattern. Often the
outside surfaces are described
with basic dimensions, and
profile controls are used to
felate the outside surfaces to
the hole pattern
14-14
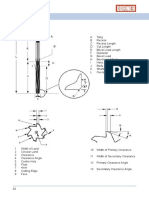
6. Pattern of Parailel Cylinders as a Datum
Feature
Using a pattem of parallel cylinders (e.g, diametrical features of size, likea
pattern of dowel pins or a pattern of holes) as a datum feature is a familiar
practice in industry. The patter of parallel cylinders is designated as a datum
feature by applying a datum identification symbol to the size dimension of the
pattern of cylinders. An example of specifying a pattem of cylinders as a
datum feature is shown in Figure 14-12.
‘When a pattem of paratiel cylinders (a hole pattern) is used as a datum fea-
ture, any feature control frames that reference the datum feature must include
under which material condition (MMC or LMC) the datum feature simulator
isto be constructed. The method for indicating the material condition isby
specifying an MMC or LMC modifier in the datum portion of the feature
control frame.
i
|
14-12 Pattem of Parallel Cylinders asa Darum Feature
‘When to Use Pattern of Parallel Cylinders (e.g. Hole Pattern) as a
Datum Feature
There are two common applications where a pattern of parallel cylinders is
used asa datum feature:
+ When the partis located by the pattern of cylinders in its assembly
+ When describing a functional relationship between a part feature and
aa datum axis created from the pattem of cylinders
In Figure 14-13, the pattern of parallel cylinders (hole pattem) locates the
part in its assembly. When a hole pattern locates the part and is used as a
datum feature, itis usually referenced as a secondary datum feature. When a
hole pattem is used as a secondary datum feature, itrestricts the part move-
‘ment in three directions. It serves as both a secondary and tertiary datum
feature; therefore, no tertiary datum feature is used.
____.: es
‘The Datum Reference Frame
Itisimportant to be able to visualize the datum feature simulator, datum axis,
datum planes, and datum reference frame for inspecting a geometric toler-
ance, When a pattem of parallel cylinders is used as a secondary datum fea-
ture, the patter is most often referenced at MMC. The datum feature simula-
torisa pattem of virtual condition gage pins. A datum axis exists at the center
ofeach virtual condition gage pin. Since the gage pins are considered to be
theoretically perfect, measurements can be taken from any one ofthese datum
axes, Figure 14-13 shows the datum plane and datum axes for the datums
referenced in the position control in Figure 14-12.
Degrees of Freedom Constrained
A part in space has six degrees of freedom. When inspecting a geometric
tolerance, some or all of the degrees of freedom must be constrained. Some
‘geometric tolerances only require three degrees of freedom to be restrained,
‘while other geometric tolerances require all six degrees of freedom to be re-
strained. The number of degrees of freedom that are constrained when in-
specting a geometric tolerance depends upon three factors: the type of datum
feature, the number of datums referenced, and the sequence of the datum
references, Whenever a geometric tolerance references a planar surface as
the primary datum feature and a pattern of parallel cylinders.as a secondary
datum feature, all six degrees of freedom are constrained,
Daten tate
‘oan pane A ‘minor
‘ning TOP contol ape tothe 1025105 aan Figure 1042
eget reason conan
Neveminlng bo Xane ve |
ovement lrg he Vans ve
evenan arg he Zax ve
Roan aint Xa ve
Reon acne Ve ve
Roan sande Zee ves
14-13 Degrees of Freedom Constrained
ao
Author's Comment
‘When # hole patter is used
asa datum featue, itis almost
always referenced at MMC or
LMC. If ahole pater that is
‘used as @ datum feature is
referenced at RFS, itis
extremely dificult (or impos-
sible) to create a repeatable
darumaxis
ne i?
a.
be present, the partis
considered. constrained.
‘Author's Comment
Datum axis B could be shown
passing through any one of
the holes.
14.15
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Countersunk Screws DIN 74-1 PDFDocument2 pagesCountersunk Screws DIN 74-1 PDFHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Iso 1660 PDFDocument8 pagesIso 1660 PDFHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Dowel Pin Tolerances PDFDocument4 pagesDowel Pin Tolerances PDFHenrique Marques100% (1)
- Unidal PDFDocument1 pageUnidal PDFHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- PEM - Threaded Inserts For Plastics PDFDocument20 pagesPEM - Threaded Inserts For Plastics PDFHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Nook Jack Catalog PDFDocument109 pagesNook Jack Catalog PDFHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Amsbeck MT - Fliehkraftbremsen - EngDocument12 pagesAmsbeck MT - Fliehkraftbremsen - EngHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Keyway DIN 6885 - Parallel Metric Keys and Keyway DimensionsDocument2 pagesKeyway DIN 6885 - Parallel Metric Keys and Keyway DimensionsHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Retaining Compound Design Guide: Securing Cylindrical AssembliesDocument20 pagesRetaining Compound Design Guide: Securing Cylindrical AssembliesHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Clearance Holes PDFDocument2 pagesClearance Holes PDFHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Metric Over - Under Dowel Pin ReamersDocument2 pagesMetric Over - Under Dowel Pin ReamersHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Reamer 2013Document8 pagesReamer 2013Henrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Iso 1660 PDFDocument8 pagesIso 1660 PDFHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- General Tolerances - DIN - ISO - 2768 PDFDocument2 pagesGeneral Tolerances - DIN - ISO - 2768 PDFHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Manual Thread Cutting - Course - Technique For Manual Working of Materials. Trainees' Handbook of Lessons - 7 PDFDocument7 pagesManual Thread Cutting - Course - Technique For Manual Working of Materials. Trainees' Handbook of Lessons - 7 PDFHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Dormer Reamer TolerancesDocument12 pagesDormer Reamer TolerancesHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Dormer Reamer Tolerances PDFDocument12 pagesDormer Reamer Tolerances PDFHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Manual Thread Cutting - Course - Technique For Manual Working of Materials. Trainees' Handbook of Lessons - 7Document7 pagesManual Thread Cutting - Course - Technique For Manual Working of Materials. Trainees' Handbook of Lessons - 7Henrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Pedagogy of The Concept of Load at A Distance in F.E.A. Codes (Basic Case Studies)Document20 pagesPedagogy of The Concept of Load at A Distance in F.E.A. Codes (Basic Case Studies)Henrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Electric Tug Solutions: WorldwideDocument5 pagesElectric Tug Solutions: WorldwideHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Latch Circuit: NOR Gate BistableDocument2 pagesLatch Circuit: NOR Gate BistableHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- CMA 77 100 Clock Antenna A4 1Document3 pagesCMA 77 100 Clock Antenna A4 1Henrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Fractional Inches To MM - BWDocument2 pagesFractional Inches To MM - BWHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet