Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Qualitative & Quantitative Research
Qualitative & Quantitative Research
Uploaded by
Bryan AliCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Didactics of English Language TeachingDocument49 pagesDidactics of English Language TeachingAmel Amol100% (2)
- COSTAATT CoverpageDocument1 pageCOSTAATT CoverpageBryan AliNo ratings yet
- Final PPT Experimental ResearchDocument36 pagesFinal PPT Experimental ResearchYosephine Susie Saraswati100% (2)
- Richard Shoup and Thomas Etter - Can Causal Influence Propagate Backwards in Time? - A Simple Experiment in Markov Chains and CausalityDocument5 pagesRichard Shoup and Thomas Etter - Can Causal Influence Propagate Backwards in Time? - A Simple Experiment in Markov Chains and CausalityCanola_Olive100% (1)
- Rubric For Metacognitive Reading ReportsDocument1 pageRubric For Metacognitive Reading ReportsCyruz LapinasNo ratings yet
- Communication Studies Sample ResponsesDocument7 pagesCommunication Studies Sample ResponsesBryan AliNo ratings yet
- UnderGraduate Confirmation ReceiptDocument1 pageUnderGraduate Confirmation ReceiptBryan AliNo ratings yet
- Acceptance Letter PDFDocument2 pagesAcceptance Letter PDFBryan AliNo ratings yet
- Elections 01Document4 pagesElections 01Bryan AliNo ratings yet
- Elections 02Document4 pagesElections 02Bryan AliNo ratings yet
- Engineering:: Analysis InformationDocument2 pagesEngineering:: Analysis InformationBryan AliNo ratings yet
- COSTAATT CoverpageDocument1 pageCOSTAATT CoverpageBryan AliNo ratings yet
- At1 Reflective EssayDocument2 pagesAt1 Reflective EssayMylleNo ratings yet
- "Don't Stop When You're Tired, Stop When You're Done": Review Tips/GuideDocument3 pages"Don't Stop When You're Tired, Stop When You're Done": Review Tips/GuideJeremy JavierNo ratings yet
- Implications For Language TeacherDocument1 pageImplications For Language TeacherRaquel AlfaroNo ratings yet
- MooreDocument12 pagesMooreHiram Meléndez-JuarbeNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research MethodologyDocument20 pagesQualitative Research Methodologyitsme_theone4u100% (1)
- Nursing Research Methodology 5 PDFDocument12 pagesNursing Research Methodology 5 PDFCarlos Samuel QuimbenzeNo ratings yet
- Sample Notes of Sociology OptionalDocument111 pagesSample Notes of Sociology OptionalJainPalash100% (1)
- 6 - Sociology As A ScieneceDocument14 pages6 - Sociology As A ScieneceJiaNo ratings yet
- PRAC-RESEARCH 2 ReviewerDocument6 pagesPRAC-RESEARCH 2 ReviewerJocelyn RosalNo ratings yet
- European Scientific Journal Vol.8 No.6Document10 pagesEuropean Scientific Journal Vol.8 No.6Europe Scientific JournalNo ratings yet
- Case Formulation ToolDocument1 pageCase Formulation Tooljg261940No ratings yet
- The Philosophy of Francisco Suárez. (Aho, T.) PDFDocument4 pagesThe Philosophy of Francisco Suárez. (Aho, T.) PDFAdriel AkárioNo ratings yet
- Research Means To Carefully Analyze The Problems or To Do The Detailed Study of The Specific Problems, by Making Use of Special Scientific MethodsDocument4 pagesResearch Means To Carefully Analyze The Problems or To Do The Detailed Study of The Specific Problems, by Making Use of Special Scientific MethodsJules MarcoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.1 Lesson 5Document2 pagesChapter 3.1 Lesson 5Tim AngNo ratings yet
- Nature and Scope of EconometricsDocument2 pagesNature and Scope of EconometricsDebojyoti Ghosh86% (7)
- OUTLINE Qualitative Research Methods in EducationDocument5 pagesOUTLINE Qualitative Research Methods in EducationAakhan KhanNo ratings yet
- Kashaf 20Document3 pagesKashaf 20sohaNo ratings yet
- Materials Development IntroDocument13 pagesMaterials Development IntroMay Rona Marie ParanNo ratings yet
- ჯეკენდოფი PDFDocument185 pagesჯეკენდოფი PDFTazo ChaduneliNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: Agents and EnvironmentDocument27 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Agents and EnvironmentHashim Omar AbukarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Personal and Professional DevelopmentDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Personal and Professional Developmenttitan abcdNo ratings yet
- PR1 11-DescartesDocument8 pagesPR1 11-DescartesKeij AlolosanNo ratings yet
- CrimEd 603 ExplanationDocument40 pagesCrimEd 603 ExplanationJohnpatrick DejesusNo ratings yet
- Human Flourishing GROUP 1Document22 pagesHuman Flourishing GROUP 1Shane Roxccei CiasicoNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - The Scientific Method: DEFINE The SCIENTIFIC METHOD in Your Own Words? Maximum of 3 Sentences OnlyDocument2 pagesWeek 2 - The Scientific Method: DEFINE The SCIENTIFIC METHOD in Your Own Words? Maximum of 3 Sentences OnlyKirtch Stone T. JudillaNo ratings yet
- Metacognition: Thinking About One's ThinkingDocument5 pagesMetacognition: Thinking About One's ThinkingFelicen JunaNo ratings yet
Qualitative & Quantitative Research
Qualitative & Quantitative Research
Uploaded by
Bryan AliOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Qualitative & Quantitative Research
Qualitative & Quantitative Research
Uploaded by
Bryan AliCopyright:
Available Formats
Qualitative Research
Qualitative Research is mainly investigative research. It is used to gain an understanding of underlying
reasons, opinions, and motivations. Qualitative research presents non-quantitative type of analysis.
Qualitative research is collecting, analyzing and interpreting data by observing what people do and say.
It provides insights into the problem or helps to develop ideas or hypotheses for potential quantitative
research. Qualitative Research is also used to uncover trends in thought and opinions, and dive deeper
into the problem. Qualitative data collection methods vary using unstructured or semi-structured
techniques. Some common methods include focus groups (group discussions), individual interviews, and
participation/observations. The sample size is typically small, and respondents are selected to fulfil a
given quota.
Qualitative research refers to the meanings, definitions, characteristics, symbols, metaphors, and
description of things. Qualitative research is much more subjective and uses very different methods of
collecting information, mainly individual, in-depth interviews and focus groups.
The nature of this type of research is exploratory and open ended. Small number of people are
interviewed in depth and or a relatively small number of focus groups are conducted. Qualitative
research can be further classified in the following type.
I. Phenomenology:-a form of research in which the researcher attempts to understand how one or more
individuals experience a phenomenon. Eg:-we might interview 20 victims of bhopal tragedy.
II. Ethnography:- this type of research focuses on describing the culture of a group of people. A culture is
the shared attributes, values, norms, practices, language, and material things of a group of people. Eg:-
the researcher might decide to go and live with the tribal in Andaman island and study the culture and
the educational practices.
III. Case study:-is a form of qualitative research that is focused on providing a detailed account of one or
more cases. Eg:-we may study a classroom that was given a new curriculum for technology use.
IV. Grounded theory:- it is an inductive type of research, based or grounded in the observations of data
from which it was developed; it uses a variety of data sources, including quantitative data, review of
records, interviews, observation and surveys
V. Historical research: - it allows one to discuss past and present events in the context of the present
condition, and allows one to reflect and provide possible answers to current issues and problems. E.g:-
the lending pattern of business in the 19th century.
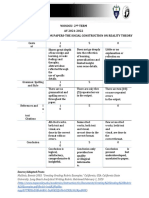
Qualitative Research Method Advantages Disadvantages
Phenomenology
Ethnography It can easily evolve and discover It can be difficult to choose a
new things. representative sample.
It helps people know more It takes a lot of time.
about other cultures. It depends on people’s
It helps businesses learn more openness and honesty.
about their target market.
Case study
Quantitative Research
This research is based on numeric figures or numbers. Quantitative research aim to measure the
quantity or amount and compares it with past records and tries to project for future period. In social
sciences, “quantitative research refers to the systematic empirical investigation of quantitative
properties and phenomena and their relationships”. The objective of quantitative research is to develop
and employ mathematical models, theories or hypothesis pertaining to phenomena.
The process of measurement is central to quantitative research because it provides fundamental
connection between empirical observation and mathematical expression of quantitative relationships.
Statistics is the most widely used branch of mathematics in quantitative research. Statistical methods
are used extensively with in fields such as economics and commerce.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Didactics of English Language TeachingDocument49 pagesDidactics of English Language TeachingAmel Amol100% (2)
- COSTAATT CoverpageDocument1 pageCOSTAATT CoverpageBryan AliNo ratings yet
- Final PPT Experimental ResearchDocument36 pagesFinal PPT Experimental ResearchYosephine Susie Saraswati100% (2)
- Richard Shoup and Thomas Etter - Can Causal Influence Propagate Backwards in Time? - A Simple Experiment in Markov Chains and CausalityDocument5 pagesRichard Shoup and Thomas Etter - Can Causal Influence Propagate Backwards in Time? - A Simple Experiment in Markov Chains and CausalityCanola_Olive100% (1)
- Rubric For Metacognitive Reading ReportsDocument1 pageRubric For Metacognitive Reading ReportsCyruz LapinasNo ratings yet
- Communication Studies Sample ResponsesDocument7 pagesCommunication Studies Sample ResponsesBryan AliNo ratings yet
- UnderGraduate Confirmation ReceiptDocument1 pageUnderGraduate Confirmation ReceiptBryan AliNo ratings yet
- Acceptance Letter PDFDocument2 pagesAcceptance Letter PDFBryan AliNo ratings yet
- Elections 01Document4 pagesElections 01Bryan AliNo ratings yet
- Elections 02Document4 pagesElections 02Bryan AliNo ratings yet
- Engineering:: Analysis InformationDocument2 pagesEngineering:: Analysis InformationBryan AliNo ratings yet
- COSTAATT CoverpageDocument1 pageCOSTAATT CoverpageBryan AliNo ratings yet
- At1 Reflective EssayDocument2 pagesAt1 Reflective EssayMylleNo ratings yet
- "Don't Stop When You're Tired, Stop When You're Done": Review Tips/GuideDocument3 pages"Don't Stop When You're Tired, Stop When You're Done": Review Tips/GuideJeremy JavierNo ratings yet
- Implications For Language TeacherDocument1 pageImplications For Language TeacherRaquel AlfaroNo ratings yet
- MooreDocument12 pagesMooreHiram Meléndez-JuarbeNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research MethodologyDocument20 pagesQualitative Research Methodologyitsme_theone4u100% (1)
- Nursing Research Methodology 5 PDFDocument12 pagesNursing Research Methodology 5 PDFCarlos Samuel QuimbenzeNo ratings yet
- Sample Notes of Sociology OptionalDocument111 pagesSample Notes of Sociology OptionalJainPalash100% (1)
- 6 - Sociology As A ScieneceDocument14 pages6 - Sociology As A ScieneceJiaNo ratings yet
- PRAC-RESEARCH 2 ReviewerDocument6 pagesPRAC-RESEARCH 2 ReviewerJocelyn RosalNo ratings yet
- European Scientific Journal Vol.8 No.6Document10 pagesEuropean Scientific Journal Vol.8 No.6Europe Scientific JournalNo ratings yet
- Case Formulation ToolDocument1 pageCase Formulation Tooljg261940No ratings yet
- The Philosophy of Francisco Suárez. (Aho, T.) PDFDocument4 pagesThe Philosophy of Francisco Suárez. (Aho, T.) PDFAdriel AkárioNo ratings yet
- Research Means To Carefully Analyze The Problems or To Do The Detailed Study of The Specific Problems, by Making Use of Special Scientific MethodsDocument4 pagesResearch Means To Carefully Analyze The Problems or To Do The Detailed Study of The Specific Problems, by Making Use of Special Scientific MethodsJules MarcoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.1 Lesson 5Document2 pagesChapter 3.1 Lesson 5Tim AngNo ratings yet
- Nature and Scope of EconometricsDocument2 pagesNature and Scope of EconometricsDebojyoti Ghosh86% (7)
- OUTLINE Qualitative Research Methods in EducationDocument5 pagesOUTLINE Qualitative Research Methods in EducationAakhan KhanNo ratings yet
- Kashaf 20Document3 pagesKashaf 20sohaNo ratings yet
- Materials Development IntroDocument13 pagesMaterials Development IntroMay Rona Marie ParanNo ratings yet
- ჯეკენდოფი PDFDocument185 pagesჯეკენდოფი PDFTazo ChaduneliNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: Agents and EnvironmentDocument27 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Agents and EnvironmentHashim Omar AbukarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Personal and Professional DevelopmentDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Personal and Professional Developmenttitan abcdNo ratings yet
- PR1 11-DescartesDocument8 pagesPR1 11-DescartesKeij AlolosanNo ratings yet
- CrimEd 603 ExplanationDocument40 pagesCrimEd 603 ExplanationJohnpatrick DejesusNo ratings yet
- Human Flourishing GROUP 1Document22 pagesHuman Flourishing GROUP 1Shane Roxccei CiasicoNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - The Scientific Method: DEFINE The SCIENTIFIC METHOD in Your Own Words? Maximum of 3 Sentences OnlyDocument2 pagesWeek 2 - The Scientific Method: DEFINE The SCIENTIFIC METHOD in Your Own Words? Maximum of 3 Sentences OnlyKirtch Stone T. JudillaNo ratings yet
- Metacognition: Thinking About One's ThinkingDocument5 pagesMetacognition: Thinking About One's ThinkingFelicen JunaNo ratings yet