Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Matter
Matter
Uploaded by
dyanenfalhadapCopyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMatter is a substance that has inertia and occupies physical space.
According
to modern physics, matter consists of various types of particles, each with
mass and size.
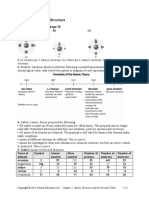
The most familiar examples of material particles are the electron,
the proton and the neutron. Combinations of these particles form atoms.
There are more than 100 different kinds of atoms, each kind constituting a
unique chemical element. A combination of atoms forms a molecule. Atoms
and/or molecules can join together to form a compound.
Matter can exist in several states, also called phases. The three most
common states are known as solid, liquid and gas. A single element or
compound of matter might exist in more than one of the three states,
depending on the temperature and pressure. Less familiar states of matter
include plasma, foam and Bose-Einstein condensate. These states occur
under special conditions.
Different kinds of matter can combine to form substances that may not
resemble any of the original ingredients. For example, hydrogen (a gaseous
element) and oxygen (another gaseous element) combine to form water (a
liquid compound at room temperature). The process of such combination is
called a chemical reaction. A chemical reaction involves interactions between
the electrons of the atoms, but does not affect the nuclei of the atoms.
In some situations, matter is converted into energy by atomic reactions, also
known as nuclear reactions. This type of reaction is fundamentally different
from the chemical reaction because it involves changes in the nuclei of atoms.
The most common example of an atomic reaction is the hydrogen fusion that
occurs inside the sun. The immense pressure inside the sun, and inside other
stars, forces atoms of hydrogen together to form atoms of helium. In this
process, some of the mass is converted to energy according to the formula
E = mc 2
where E is the energy in joules, m is the mass in kilograms, and c is the speed
of light, which is approximately 2.99792 x 10 8 meters per second in
a vacuum.
In recent years, scientists have confirmed the existence of a substance
called antimatter. The electron has an antiparticle twin called a positron, with
equal mass but opposite electric charge. Similarly, the proton has an
antimatter twin called an antiproton, and the neutron has an antimatter twin
called an antineutron. If a particle of matter encounters its antiparticle, both
are converted entirely to energy according to the above formula, where m is
the combined mass of the particle and the antiparticle. Small amounts of
antimatter have been isolated in laboratory conditions, but no one has yet
succeeded in creating a controlled a matter/antimatter reaction, or even an
uncontrolled reaction of significant size.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5835)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (350)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Essential University Physics Test Bank by Wolfson 3rd Edition Ch38Document27 pagesEssential University Physics Test Bank by Wolfson 3rd Edition Ch38ifghelpdeskNo ratings yet
- Subtle Energy and The Cosmos - Part 1 Yury KronnDocument10 pagesSubtle Energy and The Cosmos - Part 1 Yury KronnTyl3rNo ratings yet
- 1 Grading Infection ControlDocument8 pages1 Grading Infection ControldyanenfalhadapNo ratings yet
- Balloon Lung ExperimentDocument4 pagesBalloon Lung ExperimentdyanenfalhadapNo ratings yet
- Mopg-Nstp CWTS 1 2014-2015 2ND Sem (2-9-15)Document8 pagesMopg-Nstp CWTS 1 2014-2015 2ND Sem (2-9-15)dyanenfalhadapNo ratings yet
- Baking DocumentationDocument25 pagesBaking Documentationdyanenfalhadap100% (1)
- DT 13 05 2018Document29 pagesDT 13 05 2018TIRTH JOSHINo ratings yet
- Chemistry 101-WI50 Lecture 2Document31 pagesChemistry 101-WI50 Lecture 2JohnfedoNo ratings yet
- 1B - Atom Structure, BondingDocument99 pages1B - Atom Structure, BondingRaymond Chan100% (1)
- Regent Physics by Abhishek JaguessarDocument343 pagesRegent Physics by Abhishek Jaguessarreedoye21No ratings yet
- CH 3+4+5+6+7 PDFDocument149 pagesCH 3+4+5+6+7 PDFzuhair faddahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On An AtomDocument6 pagesLesson Plan On An AtomAnonymous ZsTY4mkysTNo ratings yet
- Biology The Unity and Diversity of Life 13th Edition by Starr Taggart and Evers ISBN Test BankDocument20 pagesBiology The Unity and Diversity of Life 13th Edition by Starr Taggart and Evers ISBN Test Bankrichard100% (35)
- Natoural Resource Management For Sustainable Development in The CaribberanDocument503 pagesNatoural Resource Management For Sustainable Development in The CaribberanAugusto OlguinNo ratings yet
- The Kingdom of The Gods - Geoffrey HodsonDocument263 pagesThe Kingdom of The Gods - Geoffrey Hodsonary100% (9)
- Nuclear Models Liquid Drop Model of The Nucleus: Bethe-Weizacker Semi-Empirical Mass Formula (SEMF)Document4 pagesNuclear Models Liquid Drop Model of The Nucleus: Bethe-Weizacker Semi-Empirical Mass Formula (SEMF)Ainebyoona ChriscentNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Directions-Atom Building ManipulativesDocument5 pagesTeacher's Directions-Atom Building ManipulativesAlejandra DíazFlores RNo ratings yet
- Physics of Nuclear Fusion: Reactions: IsotopesDocument4 pagesPhysics of Nuclear Fusion: Reactions: IsotopesMuhammad AnoshNo ratings yet
- Radiochemistry and RadiometryDocument20 pagesRadiochemistry and RadiometryAmanuel Maru100% (2)
- Nuclear Engineering NotesDocument36 pagesNuclear Engineering NotesMatthew CurmiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Fundamentals Particles QsDocument10 pagesAtomic Structure Fundamentals Particles QsJesulayomi BolajiNo ratings yet
- Elements As Mathematical StructureDocument34 pagesElements As Mathematical StructureIan BeardsleyNo ratings yet
- Review of Atomic Theory of Matter LectureDocument29 pagesReview of Atomic Theory of Matter LectureDerbew GahawNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Properties and Structure of Matter Powerpoint AllDocument60 pagesGrade 5 Properties and Structure of Matter Powerpoint Allapi-25442847475% (4)
- Several Problems of The Polish Physics Olympiad: Waldemar GorzkowskiDocument4 pagesSeveral Problems of The Polish Physics Olympiad: Waldemar GorzkowskiVikram SaurabhNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature and StudiesDocument23 pagesReview of Related Literature and StudiesVeejay Soriano CuevasNo ratings yet
- Section 1.2: Atomic StructureDocument3 pagesSection 1.2: Atomic StructuregzboyzoneNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics MCQDocument5 pagesElectrostatics MCQMohan Raj100% (1)
- Principles of Electronic Materials and Devices 4Th Edition Safa O Kasap Download PDF ChapterDocument51 pagesPrinciples of Electronic Materials and Devices 4Th Edition Safa O Kasap Download PDF Chapteraubrey.williams716100% (10)
- Atomic Structure FDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure FAshwin BalajiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure-522 PDFDocument72 pagesAtomic Structure-522 PDFAbhi KNo ratings yet
- Physics Annual Plan 2022-2023 Grade 11.xlsx - 11Document21 pagesPhysics Annual Plan 2022-2023 Grade 11.xlsx - 11Yoga PratamaNo ratings yet
- Updated Physics 5054 Faqs IgcseDocument72 pagesUpdated Physics 5054 Faqs IgcseHoud PirzadaNo ratings yet
- 086/IX/SA2/29/B1: Class - IX IX ScienceDocument12 pages086/IX/SA2/29/B1: Class - IX IX SciencebhartiyaanujNo ratings yet