Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 viewsGeneral Biology: System Consists of The
General Biology: System Consists of The
Uploaded by
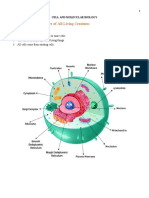
Philipp MendozaThe document summarizes key aspects of cells. It defines cells as the basic units of life and describes their main components. Specifically, it outlines the parts of eukaryotic cells including organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts and cell membrane. It also summarizes the parts of prokaryotic cells found in bacteria. Finally, it differentiates between animal and plant cells, noting that animal cells lack cell walls and chloroplasts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Cell Injury Mcqs ExplainedDocument5 pagesCell Injury Mcqs ExplainedDocAxi Maximo Jr Axibal90% (10)
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind MapPramod Jaiswal81% (21)
- Anatomy and Physiology LectrueDocument76 pagesAnatomy and Physiology LectrueButch Dumdum73% (15)
- Embryology Exam - I PDFDocument8 pagesEmbryology Exam - I PDFuprince100100% (1)
- Unit 1 - 3Document32 pagesUnit 1 - 3Sunita SharmaNo ratings yet
- 660a7ab160d0bf0018eb0ea0 - ## - Cell The Unit of Life Short NotesDocument2 pages660a7ab160d0bf0018eb0ea0 - ## - Cell The Unit of Life Short Notespradhananita848No ratings yet
- BIOL107 - Different Cell TypesDocument4 pagesBIOL107 - Different Cell TypesJahsuah OrillanedaNo ratings yet
- Biology 1: Cell Theory Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument4 pagesBiology 1: Cell Theory Cell Structure and FunctionsEmilio Villafria IVNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument10 pagesThe Cell Structure and TaxonomyKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- HDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesDocument43 pagesHDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesMariam Qais100% (1)
- General Biology 1 "CELL": Postulates of The Cell TheoryDocument9 pagesGeneral Biology 1 "CELL": Postulates of The Cell TheoryLaika LaiNo ratings yet
- CellDocument22 pagesCellrapidalerthubNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Prelim HandoutsDocument7 pagesGen Bio 1 Prelim HandoutsWinter ShiruzuNo ratings yet
- VIII Biology HO 3Document4 pagesVIII Biology HO 3aditiroy201208No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Cell: Cell-Is The Simplest Unit of Matter That Is AliveDocument5 pagesChapter 1: The Cell: Cell-Is The Simplest Unit of Matter That Is AliveScarlet VillamorNo ratings yet
- Spgbio NotesDocument22 pagesSpgbio NotesKaycee HeokkaidoNo ratings yet
- Cells To TissuesDocument4 pagesCells To TissuesJanelle Grace OrdanizaNo ratings yet
- Premidterms NotesDocument4 pagesPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Sem 1 NotesDocument12 pagesGen Bio Sem 1 NotesFrances Chynna KhoNo ratings yet
- Farmasi 1Document50 pagesFarmasi 1Suci Umniyah RamadaniNo ratings yet
- Cell Te Unit of Life Revision NotesDocument8 pagesCell Te Unit of Life Revision NotesHarismita AlagurajNo ratings yet
- Acp1 ActDocument6 pagesAcp1 ActAldrin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Biology & Chemistry (Reviewer)Document14 pagesBiology & Chemistry (Reviewer)Jaja Jr. Evasco EmbarqueNo ratings yet
- CellDocument6 pagesCellHONEYLYN CASINGNo ratings yet
- What Are Cell OrganellesDocument19 pagesWhat Are Cell OrganellesMaraon CharitaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellsjodeoiraluis josonNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument5 pagesCellsKdrama SweetieNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument18 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsAleia Trixie100% (1)
- تخدير المحاضرة الاولىDocument7 pagesتخدير المحاضرة الاولىXcv FfgNo ratings yet
- CellDocument23 pagesCellridabatool151214No ratings yet
- Earth Life Science Module 5Document15 pagesEarth Life Science Module 5Rosalyn Pagatpatan BarolaNo ratings yet
- Sel PDFDocument32 pagesSel PDFJeje DengiNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function3Document15 pagesCell Structure and Function3marklexter.b.bardelosaNo ratings yet
- K G K SCH YnplbWFuQGVtdWZzZC5vcmc Study Guide For Cells TestDocument8 pagesK G K SCH YnplbWFuQGVtdWZzZC5vcmc Study Guide For Cells TestRachael SinghNo ratings yet
- RSL Cell TheoryDocument48 pagesRSL Cell TheoryReynald Legarda Jr.No ratings yet
- Animal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalDocument6 pagesAnimal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalJohnson Macayan FernándezNo ratings yet
- Bio 221 Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesBio 221 Lecture NotesMuhammad LawalNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell by Pitogo, ChereyDocument28 pagesAnimal Cell by Pitogo, ChereyPixie DurstNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument18 pagesCell and Molecular BiologyHizzei Caballero100% (1)
- Submitted By: Hanana Zahid-1875 Maheen Fatima Hashmi-1865 Maha Ali-1997 Eman Arshad-1955Document9 pagesSubmitted By: Hanana Zahid-1875 Maheen Fatima Hashmi-1865 Maha Ali-1997 Eman Arshad-1955mahnoor.bsir1927No ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerJes NapiñasNo ratings yet
- Cell: The Building Blocks of Life: Awaluddin, M.KesDocument39 pagesCell: The Building Blocks of Life: Awaluddin, M.KesNovanda D. PahleviNo ratings yet
- Iit-Jam: Biotechnology (BT)Document55 pagesIit-Jam: Biotechnology (BT)sonamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Cell Structure and OrganellesDocument48 pagesChapter 1 - Cell Structure and OrganellesNatalie GraceNo ratings yet
- General Biology Cells1Document6 pagesGeneral Biology Cells1Kristine CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer MidtermDocument11 pagesScience Reviewer MidtermGenna CuencaNo ratings yet
- Cell Classix Session3 Made by Purnima Sharma 1Document7 pagesCell Classix Session3 Made by Purnima Sharma 1jeetjyoti787No ratings yet
- Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument53 pagesCell and Cell OrganellesShiffa SaheedNo ratings yet
- Human CellDocument12 pagesHuman CellCrystal GarciaNo ratings yet
- Bio Cells ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio Cells ReviewerKimberly LuistroNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Basic Cell BiologyDocument116 pagesUnit-I Basic Cell Biologyvishav sharmaNo ratings yet
- Bio1 Lesson 1 NotesDocument7 pagesBio1 Lesson 1 Notesykanemoto81No ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument2 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Lifevivek_theeasywaysNo ratings yet
- Cell 2Document22 pagesCell 2Graziela Sagun RepuyoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument58 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsKurt DimacaliNo ratings yet
- 4.06__Eukaryotic_Cells_-_Characteristics_of_Eukaryotic_CellsDocument2 pages4.06__Eukaryotic_Cells_-_Characteristics_of_Eukaryotic_CellsMae ann CumpletoNo ratings yet
- L.3 - The CellDocument3 pagesL.3 - The CellJari JariNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument8 pagesCELLRajendra Chikkamath100% (1)
- Chapter #1 Aishka NotesDocument5 pagesChapter #1 Aishka Notessales zfNo ratings yet
- Act 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5Document21 pagesAct 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5YEO, REGGIE ALBERT A.No ratings yet
- 1st Summative Exam - General BiologyDocument12 pages1st Summative Exam - General BiologyAgatha AquinoNo ratings yet
- Bio 101 General BiologyDocument7 pagesBio 101 General BiologyMohammed kashimNo ratings yet
- First Aid and ParamedicsDocument4 pagesFirst Aid and ParamedicsshubhmNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood CountDocument2 pagesComplete Blood CountZerrudo, Glen DaleNo ratings yet
- Your Cookbook For Gaining Keratinized Tissue: Geistlich Mucograft in Open HealingDocument4 pagesYour Cookbook For Gaining Keratinized Tissue: Geistlich Mucograft in Open HealingErdeli StefaniaNo ratings yet
- Sinelnikov Vol IIIDocument395 pagesSinelnikov Vol IIIFlorescu Diana NicoletaNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of The Passage-WilliamsDocument66 pagesAbnormalities of The Passage-Williamsapi-19641337100% (1)
- Materi PIR - Dr. Imam Subadi, SP - KFR-K Cellular Adaption in Exercise Movement and Exercise in Pain ManagementDocument29 pagesMateri PIR - Dr. Imam Subadi, SP - KFR-K Cellular Adaption in Exercise Movement and Exercise in Pain ManagementGhea Putri HendrianiNo ratings yet
- Sisay Berane 083 PancytopeniaDocument23 pagesSisay Berane 083 PancytopeniaRas Siko SafoNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument29 pagesHuman Digestive SystemRagini Dubey100% (1)
- Life Sciences p1 Nov 2019 Memo North WestDocument10 pagesLife Sciences p1 Nov 2019 Memo North Westmasegomvubu27No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Pain Types and Viscerogenic Pain PatternsDocument50 pagesChapter 3 Pain Types and Viscerogenic Pain PatternsCHANGEZ KHAN SARDAR100% (2)
- Topic 7: Respiration, Muscles and The Internal Environment Chapter 7B: Muscles, Movement and The HeartDocument4 pagesTopic 7: Respiration, Muscles and The Internal Environment Chapter 7B: Muscles, Movement and The HeartsalmaNo ratings yet
- Die Oog The Eye: Sss en Sintuie Cns and SensesDocument18 pagesDie Oog The Eye: Sss en Sintuie Cns and SensesYOLANDI BESTERNo ratings yet
- Fdar Immediate Newborn CareDocument2 pagesFdar Immediate Newborn CareMike Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- POP June 10,2021 1Document48 pagesPOP June 10,2021 1Kerod AbebeNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesMuscular SystemTyrone LeeNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Biology Chapter 6 Term 1 ST 1Document27 pagesCirculatory System: Biology Chapter 6 Term 1 ST 1Pranati SharmaNo ratings yet
- Why Each Item/material S Was Used To Represent The Organelle Cell Membrane CLAY I Used ClayDocument8 pagesWhy Each Item/material S Was Used To Represent The Organelle Cell Membrane CLAY I Used ClayJemuel Bucud LagartoNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition Gerard J Tortora Bryan H Derrickson DownloadDocument57 pagesTest Bank For Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition Gerard J Tortora Bryan H Derrickson Downloadbradleypetersonbqnsyzaegm100% (26)
- Physiology of Blood SystemsDocument12 pagesPhysiology of Blood SystemsjimmyNo ratings yet
- Pe 1 Task 4Document9 pagesPe 1 Task 4Rex Lander BlanzaNo ratings yet
- Longitudinal Section of The HeartDocument2 pagesLongitudinal Section of The HeartkayannaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chapter 11 AnswersDocument7 pagesUnit 2 Chapter 11 AnswersLeeanaNo ratings yet
- Malaysia Statistics, GLOBOCAN 2018.Document2 pagesMalaysia Statistics, GLOBOCAN 2018.CatherineYeohNo ratings yet
- Cell - Formative Assessment - MT 6315 2021Document1 pageCell - Formative Assessment - MT 6315 2021REGINE COELI LANSANGANNo ratings yet
- HISTOLO Lecture 3 - Histology of The Integumentary SystemDocument14 pagesHISTOLO Lecture 3 - Histology of The Integumentary SystemResty De Guzman SoteloNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Cord Coiling: Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocument4 pagesUmbilical Cord Coiling: Case Report and Review of LiteratureHesti hasanNo ratings yet
General Biology: System Consists of The
General Biology: System Consists of The
Uploaded by
Philipp Mendoza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views3 pagesThe document summarizes key aspects of cells. It defines cells as the basic units of life and describes their main components. Specifically, it outlines the parts of eukaryotic cells including organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts and cell membrane. It also summarizes the parts of prokaryotic cells found in bacteria. Finally, it differentiates between animal and plant cells, noting that animal cells lack cell walls and chloroplasts.
Original Description:
GenBio
Original Title
General Biology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes key aspects of cells. It defines cells as the basic units of life and describes their main components. Specifically, it outlines the parts of eukaryotic cells including organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts and cell membrane. It also summarizes the parts of prokaryotic cells found in bacteria. Finally, it differentiates between animal and plant cells, noting that animal cells lack cell walls and chloroplasts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views3 pagesGeneral Biology: System Consists of The
General Biology: System Consists of The
Uploaded by
Philipp MendozaThe document summarizes key aspects of cells. It defines cells as the basic units of life and describes their main components. Specifically, it outlines the parts of eukaryotic cells including organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts and cell membrane. It also summarizes the parts of prokaryotic cells found in bacteria. Finally, it differentiates between animal and plant cells, noting that animal cells lack cell walls and chloroplasts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
GENERAL BIOLOGY cell into sections, with each specializing
1. What is a cell? in different functions. Each function is
- Cells are the basic building vital to the cell’s life.
blocks of all living things. The
human body is composed of The plasma membrane is made
trillions of cells. They provide of phospholipids and protein and
structure for the body, take in serves as the selective boundary
nutrients from food, convert of the cell.
those nutrients into energy, The nucleus is surrounded by a
and carry out specialized nuclear envelope with nuclear
functions. Cells also contain pores. The nucleus stores and
the body’s hereditary material protects the DNA of the cell.
and can make copies of
themselves. The endomembrane
2. What is cell theory? system consists of the
endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi
The Cell Theory states: apparatus, and vesicles. It makes
lipids, membrane proteins, and
All living organisms are exported proteins and then
composed of cells. They may be “addresses” them and ships them
unicellular or multicellular. where they need to go.
The cell is the basic unit of life. Mitochondria are surrounded by
Cells arise from pre-existing cells. two membranes and have their
(They are not derived own DNA and ribosomes. They
from spontaneous generation.) transfer energy from food
molecules to ATP.
The modern version of the Cell Theory
includes the ideas that: Chloroplasts are surrounded by
two membranes, contain
Energy flow occurs within cells. thylakoids, and have their own
Heredity information (DNA) is DNA and protein. They transform
passed on from cell to cell. energy from the sun and CO2
All cells have the same basic from atmosphere into food
chemical composition. molecules (sugars).
The cytoskeleton is a network of
In addition to the cell theory, the gene
proteins: actin microfilaments,
theory, evolution, homeostasis, and
microtubules, and intermediate
the laws of thermodynamics form the
filaments. Cytoskeletal proteins
basic principles that are the foundation
support the structure of the cell,
for the study of life.
help with cell division, and control
cellular movements.
3. Parts of a eukaryotic
All eukaryotic cells have organelles, a
nucleus, and many internal membranes.
These components divide the eukaryotic
cell that attach to other bacterial
cells. Shorter pili called fimbriae
help bacteria attach to surfaces.
Flagella - Flagella are long, whip-
like protrusion that aids in cellular
locomotion.
Ribosomes - Ribosomes are cell
structures responsible
for protein production.
Plasmids - Plasmids
are gene carrying, circular DNA
structures that are not involved in
reproduction.
Nucleiod Region - Area of the
cytoplasm that contains the single
- bacterial DNA molecule.
4. Parts of prokaryotic cell
Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms
that are the earliest and most primitive
forms of life on earth.
Capsule - Found in some
bacterial cells, this additional
outer covering protects the cell
when it is engulfed by other
organisms, assists in retaining
moisture, and helps the cell
adhere to surfaces and nutrients.
Cell Wall - The cell wall is an
outer covering that protects the
4. Differentiate Animal cell from a
bacterial cell and gives it shape.
plant cell.
Cytoplasm - Cytoplasm is a gel-
- An animal cell is a type of
like substance composed mainly
eukaryotic cell with a
of water that also contains
membrane-bound nucleus
enzymes, salts, cell components,
and organelles. The other
and various organic molecules.
types of eukaryotic cells are
Cell Membrane or Plasma
the plant cells with a cell wall,
Membrane - The cell
chloroplasts, and a large
membrane surrounds the cell's
vacuole. But, animal cells
cytoplasm and regulates the flow
have neither of the above-
of substances in and out of the
mentioned organelles.
cell.
However, both animal and
Pili (Pilus singular)- Hair-like
plant cells share other cellular
structures on the surface of the
structures such as cell
membrane, cytoplasm,
nucleus, mitochondria,
lysosomes, Golgi, ribosomes,
and ER.
-
The animal cell can form
multicellular organisms in the
kingdom Animalia such as
worms, insects, amphibians,
reptiles, mammals, etc.
depending on the genetic
information in the genome.
Human cells are the various types of
cells that collectively make up the
human body. Around 210 functionally
different types of cells are present in
humans. Some of their functions are
secretion, storage, etc.
Both human cells and animal cells are
diploid, except the gametes, which are
haploid. The human genome is
approximately 3 billion base pairs in size.
It contains around 25,000 protein-coding
genes.
SOURCES:
http://pediaa.com/difference-between-
animal-cell-and-human-
cell/#Animal%20Cell%20vs%20Human
%20Cell%20-
%20Comparison%20of%20Key%20Diffe
rences
You might also like
- Cell Injury Mcqs ExplainedDocument5 pagesCell Injury Mcqs ExplainedDocAxi Maximo Jr Axibal90% (10)
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind MapPramod Jaiswal81% (21)
- Anatomy and Physiology LectrueDocument76 pagesAnatomy and Physiology LectrueButch Dumdum73% (15)
- Embryology Exam - I PDFDocument8 pagesEmbryology Exam - I PDFuprince100100% (1)
- Unit 1 - 3Document32 pagesUnit 1 - 3Sunita SharmaNo ratings yet
- 660a7ab160d0bf0018eb0ea0 - ## - Cell The Unit of Life Short NotesDocument2 pages660a7ab160d0bf0018eb0ea0 - ## - Cell The Unit of Life Short Notespradhananita848No ratings yet
- BIOL107 - Different Cell TypesDocument4 pagesBIOL107 - Different Cell TypesJahsuah OrillanedaNo ratings yet
- Biology 1: Cell Theory Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument4 pagesBiology 1: Cell Theory Cell Structure and FunctionsEmilio Villafria IVNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument10 pagesThe Cell Structure and TaxonomyKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- HDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesDocument43 pagesHDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesMariam Qais100% (1)
- General Biology 1 "CELL": Postulates of The Cell TheoryDocument9 pagesGeneral Biology 1 "CELL": Postulates of The Cell TheoryLaika LaiNo ratings yet
- CellDocument22 pagesCellrapidalerthubNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Prelim HandoutsDocument7 pagesGen Bio 1 Prelim HandoutsWinter ShiruzuNo ratings yet
- VIII Biology HO 3Document4 pagesVIII Biology HO 3aditiroy201208No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Cell: Cell-Is The Simplest Unit of Matter That Is AliveDocument5 pagesChapter 1: The Cell: Cell-Is The Simplest Unit of Matter That Is AliveScarlet VillamorNo ratings yet
- Spgbio NotesDocument22 pagesSpgbio NotesKaycee HeokkaidoNo ratings yet
- Cells To TissuesDocument4 pagesCells To TissuesJanelle Grace OrdanizaNo ratings yet
- Premidterms NotesDocument4 pagesPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Sem 1 NotesDocument12 pagesGen Bio Sem 1 NotesFrances Chynna KhoNo ratings yet
- Farmasi 1Document50 pagesFarmasi 1Suci Umniyah RamadaniNo ratings yet
- Cell Te Unit of Life Revision NotesDocument8 pagesCell Te Unit of Life Revision NotesHarismita AlagurajNo ratings yet
- Acp1 ActDocument6 pagesAcp1 ActAldrin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Biology & Chemistry (Reviewer)Document14 pagesBiology & Chemistry (Reviewer)Jaja Jr. Evasco EmbarqueNo ratings yet
- CellDocument6 pagesCellHONEYLYN CASINGNo ratings yet
- What Are Cell OrganellesDocument19 pagesWhat Are Cell OrganellesMaraon CharitaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellsjodeoiraluis josonNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument5 pagesCellsKdrama SweetieNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument18 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsAleia Trixie100% (1)
- تخدير المحاضرة الاولىDocument7 pagesتخدير المحاضرة الاولىXcv FfgNo ratings yet
- CellDocument23 pagesCellridabatool151214No ratings yet
- Earth Life Science Module 5Document15 pagesEarth Life Science Module 5Rosalyn Pagatpatan BarolaNo ratings yet
- Sel PDFDocument32 pagesSel PDFJeje DengiNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function3Document15 pagesCell Structure and Function3marklexter.b.bardelosaNo ratings yet
- K G K SCH YnplbWFuQGVtdWZzZC5vcmc Study Guide For Cells TestDocument8 pagesK G K SCH YnplbWFuQGVtdWZzZC5vcmc Study Guide For Cells TestRachael SinghNo ratings yet
- RSL Cell TheoryDocument48 pagesRSL Cell TheoryReynald Legarda Jr.No ratings yet
- Animal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalDocument6 pagesAnimal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalJohnson Macayan FernándezNo ratings yet
- Bio 221 Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesBio 221 Lecture NotesMuhammad LawalNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell by Pitogo, ChereyDocument28 pagesAnimal Cell by Pitogo, ChereyPixie DurstNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument18 pagesCell and Molecular BiologyHizzei Caballero100% (1)
- Submitted By: Hanana Zahid-1875 Maheen Fatima Hashmi-1865 Maha Ali-1997 Eman Arshad-1955Document9 pagesSubmitted By: Hanana Zahid-1875 Maheen Fatima Hashmi-1865 Maha Ali-1997 Eman Arshad-1955mahnoor.bsir1927No ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerJes NapiñasNo ratings yet
- Cell: The Building Blocks of Life: Awaluddin, M.KesDocument39 pagesCell: The Building Blocks of Life: Awaluddin, M.KesNovanda D. PahleviNo ratings yet
- Iit-Jam: Biotechnology (BT)Document55 pagesIit-Jam: Biotechnology (BT)sonamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Cell Structure and OrganellesDocument48 pagesChapter 1 - Cell Structure and OrganellesNatalie GraceNo ratings yet
- General Biology Cells1Document6 pagesGeneral Biology Cells1Kristine CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer MidtermDocument11 pagesScience Reviewer MidtermGenna CuencaNo ratings yet
- Cell Classix Session3 Made by Purnima Sharma 1Document7 pagesCell Classix Session3 Made by Purnima Sharma 1jeetjyoti787No ratings yet
- Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument53 pagesCell and Cell OrganellesShiffa SaheedNo ratings yet
- Human CellDocument12 pagesHuman CellCrystal GarciaNo ratings yet
- Bio Cells ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio Cells ReviewerKimberly LuistroNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Basic Cell BiologyDocument116 pagesUnit-I Basic Cell Biologyvishav sharmaNo ratings yet
- Bio1 Lesson 1 NotesDocument7 pagesBio1 Lesson 1 Notesykanemoto81No ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument2 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Lifevivek_theeasywaysNo ratings yet
- Cell 2Document22 pagesCell 2Graziela Sagun RepuyoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument58 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsKurt DimacaliNo ratings yet
- 4.06__Eukaryotic_Cells_-_Characteristics_of_Eukaryotic_CellsDocument2 pages4.06__Eukaryotic_Cells_-_Characteristics_of_Eukaryotic_CellsMae ann CumpletoNo ratings yet
- L.3 - The CellDocument3 pagesL.3 - The CellJari JariNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument8 pagesCELLRajendra Chikkamath100% (1)
- Chapter #1 Aishka NotesDocument5 pagesChapter #1 Aishka Notessales zfNo ratings yet
- Act 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5Document21 pagesAct 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5YEO, REGGIE ALBERT A.No ratings yet
- 1st Summative Exam - General BiologyDocument12 pages1st Summative Exam - General BiologyAgatha AquinoNo ratings yet
- Bio 101 General BiologyDocument7 pagesBio 101 General BiologyMohammed kashimNo ratings yet
- First Aid and ParamedicsDocument4 pagesFirst Aid and ParamedicsshubhmNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood CountDocument2 pagesComplete Blood CountZerrudo, Glen DaleNo ratings yet
- Your Cookbook For Gaining Keratinized Tissue: Geistlich Mucograft in Open HealingDocument4 pagesYour Cookbook For Gaining Keratinized Tissue: Geistlich Mucograft in Open HealingErdeli StefaniaNo ratings yet
- Sinelnikov Vol IIIDocument395 pagesSinelnikov Vol IIIFlorescu Diana NicoletaNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of The Passage-WilliamsDocument66 pagesAbnormalities of The Passage-Williamsapi-19641337100% (1)
- Materi PIR - Dr. Imam Subadi, SP - KFR-K Cellular Adaption in Exercise Movement and Exercise in Pain ManagementDocument29 pagesMateri PIR - Dr. Imam Subadi, SP - KFR-K Cellular Adaption in Exercise Movement and Exercise in Pain ManagementGhea Putri HendrianiNo ratings yet
- Sisay Berane 083 PancytopeniaDocument23 pagesSisay Berane 083 PancytopeniaRas Siko SafoNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument29 pagesHuman Digestive SystemRagini Dubey100% (1)
- Life Sciences p1 Nov 2019 Memo North WestDocument10 pagesLife Sciences p1 Nov 2019 Memo North Westmasegomvubu27No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Pain Types and Viscerogenic Pain PatternsDocument50 pagesChapter 3 Pain Types and Viscerogenic Pain PatternsCHANGEZ KHAN SARDAR100% (2)
- Topic 7: Respiration, Muscles and The Internal Environment Chapter 7B: Muscles, Movement and The HeartDocument4 pagesTopic 7: Respiration, Muscles and The Internal Environment Chapter 7B: Muscles, Movement and The HeartsalmaNo ratings yet
- Die Oog The Eye: Sss en Sintuie Cns and SensesDocument18 pagesDie Oog The Eye: Sss en Sintuie Cns and SensesYOLANDI BESTERNo ratings yet
- Fdar Immediate Newborn CareDocument2 pagesFdar Immediate Newborn CareMike Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- POP June 10,2021 1Document48 pagesPOP June 10,2021 1Kerod AbebeNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesMuscular SystemTyrone LeeNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Biology Chapter 6 Term 1 ST 1Document27 pagesCirculatory System: Biology Chapter 6 Term 1 ST 1Pranati SharmaNo ratings yet
- Why Each Item/material S Was Used To Represent The Organelle Cell Membrane CLAY I Used ClayDocument8 pagesWhy Each Item/material S Was Used To Represent The Organelle Cell Membrane CLAY I Used ClayJemuel Bucud LagartoNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition Gerard J Tortora Bryan H Derrickson DownloadDocument57 pagesTest Bank For Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition Gerard J Tortora Bryan H Derrickson Downloadbradleypetersonbqnsyzaegm100% (26)
- Physiology of Blood SystemsDocument12 pagesPhysiology of Blood SystemsjimmyNo ratings yet
- Pe 1 Task 4Document9 pagesPe 1 Task 4Rex Lander BlanzaNo ratings yet
- Longitudinal Section of The HeartDocument2 pagesLongitudinal Section of The HeartkayannaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chapter 11 AnswersDocument7 pagesUnit 2 Chapter 11 AnswersLeeanaNo ratings yet
- Malaysia Statistics, GLOBOCAN 2018.Document2 pagesMalaysia Statistics, GLOBOCAN 2018.CatherineYeohNo ratings yet
- Cell - Formative Assessment - MT 6315 2021Document1 pageCell - Formative Assessment - MT 6315 2021REGINE COELI LANSANGANNo ratings yet
- HISTOLO Lecture 3 - Histology of The Integumentary SystemDocument14 pagesHISTOLO Lecture 3 - Histology of The Integumentary SystemResty De Guzman SoteloNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Cord Coiling: Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocument4 pagesUmbilical Cord Coiling: Case Report and Review of LiteratureHesti hasanNo ratings yet