Professional Documents
Culture Documents
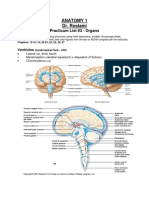
Bio 102 Lab Exam 4
Bio 102 Lab Exam 4
Uploaded by
Joaquin A. TorresCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- KLM Anatomy Mcqs AnsweredDocument33 pagesKLM Anatomy Mcqs AnsweredJohanna Haludilu100% (3)
- Torso GuideDocument373 pagesTorso GuideMonica PatracutaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of LabourDocument4 pagesMechanism of LabourAnnapurna DangetiNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing NotesDocument7 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing NotesVillanueva, Jony Miaca O.No ratings yet
- 1487 Female Genital Organs 58eb5017c09a5Document20 pages1487 Female Genital Organs 58eb5017c09a5rodriguezruajavierNo ratings yet
- Organ Systems of The ToadDocument26 pagesOrgan Systems of The ToadDianne AcobaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Male Rep. SysDocument89 pagesAnatomy of Male Rep. Syszodo_izyanNo ratings yet
- Digestive. Apolonio and BacayDocument18 pagesDigestive. Apolonio and BacayKariza AbuNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument34 pagesGross Anatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemDitas ChuNo ratings yet
- 07 - Uterus, Uterine Tubes, OvariesDocument52 pages07 - Uterus, Uterine Tubes, Ovariesck4realNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument16 pagesBrainRej CosainNo ratings yet
- Anatomy PracticalDocument11 pagesAnatomy PracticalHossein VakiliNo ratings yet
- Contents of PelvisDocument38 pagesContents of Pelvisdr_asalehNo ratings yet
- Anatomi PelvisDocument44 pagesAnatomi Pelvisari naNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive Organs 2018Document80 pagesMale Reproductive Organs 2018yasrul izad100% (1)
- Gross Anatomy and Histolgy of UrinarysystemDocument81 pagesGross Anatomy and Histolgy of UrinarysystemIncredible DivineNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument94 pagesHuman ReproductionDivya AgarawalNo ratings yet
- Perineum and Reproductive SystemDocument36 pagesPerineum and Reproductive SystemHesbon MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy For DocmmiesDocument41 pagesAnatomy For DocmmiesMartinez_DONo ratings yet
- BIOL 2023 CH1 Introduction To Anatomical TermsDocument19 pagesBIOL 2023 CH1 Introduction To Anatomical Termsyazst.julienNo ratings yet
- Abdomen Engl PDFDocument51 pagesAbdomen Engl PDFShuler0071No ratings yet
- MATERNAL and Child NSG NotesDocument46 pagesMATERNAL and Child NSG NotesjnetNo ratings yet
- Peritonem A ND Peritonealcavity PDFDocument62 pagesPeritonem A ND Peritonealcavity PDFKarem MaaliNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument37 pagesUntitledMin Nyo SinNo ratings yet
- Female Genital System - Internal Structures (CU-PA-2020)Document63 pagesFemale Genital System - Internal Structures (CU-PA-2020)karenadjei44No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Abdomen: Samara University Biomedical Sciences DepartmentDocument142 pagesAnatomy of The Abdomen: Samara University Biomedical Sciences Departmentfentaw melkieNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Reproduksi Pria: DR. Ahmad Zulfan Hendri, Sp. UDocument14 pagesAnatomi Reproduksi Pria: DR. Ahmad Zulfan Hendri, Sp. UocepNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System: Presented by Parmar Zenith F.Y.M.sc (N) GineraDocument59 pagesFemale Reproductive System: Presented by Parmar Zenith F.Y.M.sc (N) Ginerazenith parmarNo ratings yet
- 01 - 20131119 Skull IDocument56 pages01 - 20131119 Skull INancyLiao100% (2)
- Must KnowDocument2 pagesMust KnowLiana JeonNo ratings yet
- 06 Perineum GenitaliaDocument24 pages06 Perineum GenitaliaRoger ViloNo ratings yet
- WK 7Document48 pagesWK 7Lana AmerieNo ratings yet
- 1 Anatomi Organ PanggulDocument45 pages1 Anatomi Organ PanggulHutomo Budi Hasnian SyahNo ratings yet
- Nephrologi: - PWM Olly Indrajani - 18-3-2015Document128 pagesNephrologi: - PWM Olly Indrajani - 18-3-2015NandatholoeNo ratings yet
- Aparatul Genital MasculDocument22 pagesAparatul Genital MasculvalisianoNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Gi - Dr. AhmadDocument77 pagesAnatomi Gi - Dr. AhmadBarfat AkbarNo ratings yet
- Systema UrinariusDocument25 pagesSystema UrinariusHAMDANINo ratings yet
- Maternal AnatomyDocument60 pagesMaternal AnatomyRaraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Throat DR Oscar PresentasiDocument53 pagesAnatomy of The Throat DR Oscar Presentasiharyo wiryantoNo ratings yet
- Azmath - Anat of PharynxDocument36 pagesAzmath - Anat of Pharynxjeswanthyelavarthi2No ratings yet
- Digetive System: Anatomy of The Digestive SystemDocument17 pagesDigetive System: Anatomy of The Digestive SystemCarmela Martínez YustaNo ratings yet
- AP2 Lab11 Anatomy of Digestion SP21Document16 pagesAP2 Lab11 Anatomy of Digestion SP21chasek76icloud.comNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female Genital TractDocument30 pagesAnatomy of Female Genital TractHerman FiraNo ratings yet
- Peritoneum, Bladder and Male Pelvic StructuresDocument34 pagesPeritoneum, Bladder and Male Pelvic StructuresKoddyNo ratings yet
- Frogbodypartsandfunctions Leopard FrogDocument30 pagesFrogbodypartsandfunctions Leopard FrogElijah PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Department of Anatomy Hasanuddin University: Dr. Hasan NyambeDocument57 pagesDepartment of Anatomy Hasanuddin University: Dr. Hasan NyambeMaksi YantoNo ratings yet
- Male Repro 2019Document79 pagesMale Repro 2019yasrulNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument37 pagesUrinary SystemNOELIE IBACARRANo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument109 pagesAnimal KingdomvvNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female Genital TractDocument37 pagesAnatomy of Female Genital TractSemon YohannesNo ratings yet
- Throat AnatomyDocument70 pagesThroat AnatomyMegan ShanzuNo ratings yet
- OB NSGDocument28 pagesOB NSGEna RodasNo ratings yet
- Maternal Anatomy: Julao, Fritz Adrian C. Kho, Nicole Alexandra P. Lagmay, Paul Angelo ADocument115 pagesMaternal Anatomy: Julao, Fritz Adrian C. Kho, Nicole Alexandra P. Lagmay, Paul Angelo ANicole Alexandra KhoNo ratings yet
- Egg Membranes Placenta '10Document42 pagesEgg Membranes Placenta '10Biolife solutionsNo ratings yet
- Urogenital System of The VertebratesDocument51 pagesUrogenital System of The VertebratesFaye Nadine Cabural100% (1)
- Anatomy of Urinary Bladder and UrethraDocument41 pagesAnatomy of Urinary Bladder and UrethraHemanta PunNo ratings yet
- Revisit of Male & Female Genital Tracts Semester VIIDocument50 pagesRevisit of Male & Female Genital Tracts Semester VIIDr. AyshaNo ratings yet
- 1.female Reproductive SystemDocument52 pages1.female Reproductive SystemKhairul HananNo ratings yet
- Systema Lymphaticum: Lymphatic SystemDocument38 pagesSystema Lymphaticum: Lymphatic SystemGeorge GeorgeNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- Lymphatics and Lymph Circulation: Physiology and PathologyFrom EverandLymphatics and Lymph Circulation: Physiology and PathologyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- DDLT RetrievalDocument33 pagesDDLT RetrievalPriya RanjanNo ratings yet
- The AortaDocument52 pagesThe Aortaviorel79No ratings yet
- Spleen Ultrasound: Dlshsi-Cmrt-000-Basics of Mri-NjegatchalianDocument16 pagesSpleen Ultrasound: Dlshsi-Cmrt-000-Basics of Mri-NjegatchalianJohn Andre RamosNo ratings yet
- Rauma Epar: Soetamto Wibowo Bagian Bedah FK UNAIR / RSUD DR Soetomo SurabayaDocument37 pagesRauma Epar: Soetamto Wibowo Bagian Bedah FK UNAIR / RSUD DR Soetomo SurabayaMuhammad FirdausNo ratings yet
- Kütük Cubuk Uyum StandartlariDocument2 pagesKütük Cubuk Uyum StandartlariÖZGÜRNo ratings yet
- 19 20Document42 pages19 20Bharath ChandranNo ratings yet
- Structures of The ForegutDocument13 pagesStructures of The ForegutJatan KothariNo ratings yet
- SternumDocument43 pagesSternumAnika MarshiaNo ratings yet
- SPLANCHONOLOGYDocument5 pagesSPLANCHONOLOGYFadil FadillahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy MCQ - Abdomen - 2Document15 pagesAnatomy MCQ - Abdomen - 2ahsan gujjarNo ratings yet
- Student Guide To The Frog DissectionDocument3 pagesStudent Guide To The Frog Dissectionapi-233187566No ratings yet
- Floyd17 TB Ch12Document5 pagesFloyd17 TB Ch12sdjuknicNo ratings yet
- Scrotum Anatomy and Scanning TechniqueDocument7 pagesScrotum Anatomy and Scanning TechniqueAnonymous wyF4yQZwZNo ratings yet
- MCQ SpineDocument2 pagesMCQ Spineanggita tri yurisworo100% (9)
- Veterinary Necropsy Report Checklist and Guidelines: Section I - Administrative Data Part A - Contributor'S DataDocument12 pagesVeterinary Necropsy Report Checklist and Guidelines: Section I - Administrative Data Part A - Contributor'S DataFilippo Pile PastoreNo ratings yet
- Bio Mechanics of Spinal ColumnDocument59 pagesBio Mechanics of Spinal ColumnOnwaree Ing100% (4)
- Anatomy of PancreasDocument43 pagesAnatomy of PancreasShiv SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Mesentery: Structure, Function, and Role in DiseaseDocument11 pagesThe Mesentery: Structure, Function, and Role in DiseaseIsaacQueirozNo ratings yet
- 1st Slides Body CavityDocument25 pages1st Slides Body Cavityfaizi gNo ratings yet
- Inguinal Region 1617Document23 pagesInguinal Region 1617Gx NavinNo ratings yet
- Topographic Anatomy of Abdominal OrgansDocument18 pagesTopographic Anatomy of Abdominal OrgansHasnain IdreesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Thorax Mbbs CXRDocument55 pagesAnatomy of Thorax Mbbs CXRMehtab AhmadNo ratings yet
- Workbook For Radiographic Image Analysis 4th Edition Martensen Test BankDocument9 pagesWorkbook For Radiographic Image Analysis 4th Edition Martensen Test Bankedselladonna6c2d76100% (31)
- Biomechanics of SpineDocument40 pagesBiomechanics of SpineSreeraj S R100% (1)
- Anatomy OSPEDocument61 pagesAnatomy OSPEMusfiqur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Appendices (SNOMED)Document194 pagesAppendices (SNOMED)tz75d4jcskNo ratings yet
- How To Read Chest Abdomen CT Scan X-RayDocument86 pagesHow To Read Chest Abdomen CT Scan X-RaymuhammadfyNo ratings yet
Bio 102 Lab Exam 4
Bio 102 Lab Exam 4
Uploaded by
Joaquin A. TorresOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio 102 Lab Exam 4
Bio 102 Lab Exam 4
Uploaded by
Joaquin A. TorresCopyright:
Available Formats
BIO 102 - PART 4
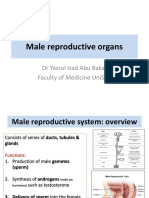
UROGENITAL SYSTEM
- Male Reproductive System
- The kidneys and their ducts • Scrotum - temperature regulation
• Kidneys (metanephroi)
• Testes (oval white body)
- Hilus (concavity)
• Spermatic cord (ventral, anterior to testes)
- Renal sinus (cavity within the hilus)
• Inguinal canal
- Penal pelvis (expanded beginning of ureter)
• External and internal inguinal rings
- Renal papilla (with openings of collecting • Ductus deferens (vas deferens) (*rabbit?)
tubules, projecting into the pelvis)
- Along the dorsal surface of the testes
- Cortex - with renal corpuscules
• Prostate gland - enlargement at the junction of
- Medulla - collecting tubules
deferent ducts and urethra
- Renal pyramid (12 in human, collecting tubules + • Urogenital canal = urethra + Deferent ducts
renal papilla)
• Bulbourethral glands (Cowper’s glands) - swellings
• Urinary bladder
on the urogenital canal, 1 inch posterior to prostate
• Covered by the peritoneum
• Penis - terminal inch of urogenital canal, strong
- Apex or vertex (free, anterior)
attachment to the pelvic region
- Fundus (posterior)
- Glans - pointed projection
• Urethra
- Crura - cavernous bodies diverge atnetior end of
• Rectovesical pouch - males; between bladder and penis
rectum
- Shaft
• Vesicouterine pouch - females; between bladder - Corpora cavernosa - 2 cylindrical bodies
and uterus
• Cavernous urethra (urogenital canal in penis, dorsal
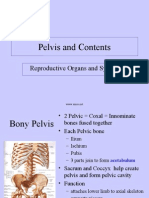
- Female Reproductive System side, depression between the 2 CC)
• Ovaries
• Vaginal sac (portion of peritoneal cavity in the
• Graafian follicles* - clear vesicles > contains ovum
scrotum, housing tetes) - cavity
• Corpora lutea* (only in pregnant)
• Tunica vaginalis - lining of previous, covering layer
• Mullerian or oviducts
of testes
- Uterine or Fallopian tube (lateral to ovary)
• Tunica albuginea
• Ostium (opening of the fallopian tube)
• Mesorchium (mesentery of the testes, continuous
- Fimbriae - fringed border
with: )
• Horn of the uterus (where young develop)
• Gubernaculum (attaches posterior end of testes to
• Broad ligament
the posterior scrotal wall,)
- Mesosalpinx (mesentery of fallopian tube)
- Homologous to the round ligament
- Mesovarium (suspends ovary)
• Epididymis
- Mesometrium (strong fold supporting the horns - Head (most anterior)
of the uterus
- Body (dorsal surface)
• Round ligament - horn of uterus > body wall
- Tail (most posterior)
• Body of the uterus (bipartite type)
• Where the gubernaculum is attached
• Vagina
- Notes
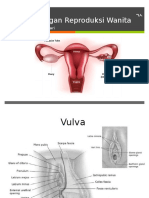
• External genitalia
• Testes in peritoneum - monotremes, marsupials,
• Clitoris* (homologous to male penis)
elephants, sirenea
• Urogenital canal (vagina + urethra)
• Descend in breeding season - mole, rodents, bats
• Anal glands
• Ovaries also move caudad in development
• cervix*
BIO 102 - PART 4
COELOM, DIGESTIVE & RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
• Thyroid gland
- The oral cavity and pharynx (p. 287) • Isthmus of the thyroid gland*
• Salivary glands -
- Pleural and pericardial cavities
- Parotid gland
• Pleural sac (parietal/visceral pleura)
- Submaxillary gland
• Mediastinal septum
- Sublingual gland
• Mediastinum
- Molar gland
• Diaphragm (with central tendon)
- Infraorbital glands*
• Lungs (anterior, middle, posterior)
• The oral cavity
- Right posterior (medial and lateral lobules)
- Lips
- Radix or root of the lung
- Cheeks
- Pulmonary ligament
- Vestibule
• Caval fold
- Har palate
• Postcaval vein
- Soft palate
• Parietal pericardium
- Nasopalatine ducts
• Visceral pericardium
- Tongue (with papillae)
• Thymus
• Filiform (anterior)
• Dorsal aorta
• Fungiform
• esophagus
• Vallate (4-6, v-shaped)
- Peritoneal cavity and its contents
- Frenulum (holding tongue)
• Abdominal or peritoneal cavity
- Flattened papillae (sides of previous)
- Peritoneum
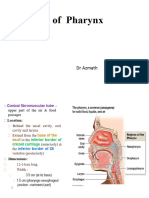
• The pharynx
- Parietal peritoneum
- Isthmus of the fauces
- Visceral peritoneum (serosa)
- Tonsillar fossa
- Dorsal mesentery
- Palatine tonsil
- Ventral mesentery
- Glossopalatine arch
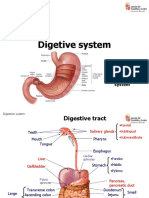
• Stomach
- Pharyngopalatine arch
- cardia, cardiac end of the stomach
- Nasopharynx
- Lesser and greater curvatures
- Posterior nares or choanae*
- Fundus
- Auditory or eustachian tubes
- Body of the stomach
- Esophagus
- Pylorus
- Epiglottis
• Mesogaster
- Hyoid apparatus, larynx, trachea, esophagus • Greater omentum
• Body of the hyoid
• Lesser peritoneal sac
• Anterior horn or cornua
• Lesser omentum (gastro-hepato-duodenal ligament)
• Posterior horn or cornua
• Spleen
• larynx
- Gastrosplenic ligament
- glottis
• Liver (left, right, caudate lobes)
- hyroid cartilage
• Gastrohepatic ligament
- cricoid cartilage
• Hepatoduodenal ligament
- arytenoids
• Gall bladder
- true vocal cords
• Cystic duct
- false vocal cords
• Bile duct
BIO 102 - PART 4
• Common bile duct
• Chorion - outer
• Hepatic portal vein
- Outermost, in contact with the egg shell or
• Foramen epiploicum
uterus
• Falciform ligament
- Ectoderm facing the embryo and outer
• Coronary ligament
mesoderm
• Intestine
• Amnion - inner
- Duodenum
- Sac enclosing the embryo
• Mesoduodenum
- reverse: outer ectoderm and inner mesoderm
• Duodenal ligament
- yolk sac and allantois
- Jejunum
• between the amnion and chorion on the ventral side
- ileum
• Lined by entoderm then vascular layer of mesoderm
• Pancreas
- allantois, amnion, chorion - only in reptiles, birds,
- Pancreatic ducts
mammals (amniotes)
- Ampulla of vater
• Birds and reptiles: allantois expands and outer wall
• Large intestine
fuses with the chorion to form the chorioallantoic
- Caecum
membrane - for diffusion of gases
- ascending, transverse, descending mesocolon
PLACENTA
• Urinary bladder
- Composed both embryonic and maternal tissues
• Comes from the allantoic stalk
- Reptiles and marsupials - yolk sac is the embryonic
- Medial and lateral ligaments
membrane involved (yolk sac placenta)
• Rectum
- Mammals above marsupials - chorioallantoic
• Lymph glands
membrane is involved - allantoic or true placenta
• Lymph nodules/peyer’s patches
• Villi - vascular projections of CA membrane
• Stomach rugae
- Diffuse placentation* (ungulates, whales, some
• Pyloric valve
primates)
• Small intesting villi
- Cotyledonary* (ruminants) - separate bunches
• Ileocolic valve
- Zonary (carnivores, elephants, Hyrax) - ring
EMBRYONIC MEMBRANES
- Discoid (insectivores, bats, rodents, primates)
- Yolk sac
- Non-deciduate* - no uterine tissue ejected at birth
• Saclike expansion of the ventral wall of the intestine
- Deciduate - uterine part of placenta is also shed
• Narrow yolks stalk near the body
• Filled with yolk utilized as food by the embryo
• In marsupials - large and vascular, functions as the
placenta constituting the yolk sac type of placenta
• Blood vessels: vitelline vessels
• In any group of vertebrates
- Allantois
• Evagination from the floor of the cloaca
• Embryonic urinary bladder
• Allantoic stalk forms adult bladder in amniotes
• Allantoic vessels
- Amnion and chorion
• Formed from somatopleure
BIO 102 - PART 4
ELASMOBRANCHS
• Gill pouches
- The body wall and pleuroperitoneal cavity
• External gill slits
• Pleuroperitoneal cavity
• Branchial bar
• Parietal peritoneum
• Interbranchial septum
- The viscera of the pleuroperitoneal cavity
• Demibranch
• Liver - left, right, median lobes
• Holobranch
• Gall bladder
• Afferent and efferent blood vessels
• Esophagus-stomach
• Gill lamellae
- Esophagus with papillae
- Urogenital system
- Stomach with rugae
• Female
• Pylorus
- Ovaries
• Spleen
- Mesovarium
• Intestine (duodenum)
- Kidneys
• Bile duct
- Chromaffine bodies*
• Pancreas
- Oviducts
• Valvular intestine
- Mesotubaria
• Rectal or digitiform gland
- Ostium
• Cloaca
- Shell or nidamental gland
• Anus
- Uterus
• Abdominal pores
- Cloaca
- The mesenteries
- Urinary papilla
• Dorsal
- Mesonephric or wolffian duct
- Mesogaster
• Male
- Gastrosplenic ligament
- Testes
- Mesentery
- Mesorchium
- Mesorectum
- Wolffian duct
- Mesovarium
- Efferent ductules
- Mesorchium
- Epididymis
- Mesotubarium
- Ductus deferens
• Ventral
- Leydig’s gland
- Gastro-hepato-duodenal ligament
- Seminal vesicle
- Hepatoduodenal ligament
- Sperm sac
- Suspensory ligament
- Cloaca
- Coronary ligament
• urodaeum
- The pericardial cavity
• coprodaeum
• Parietal pericardium
• Urogenital sinus
• Visceral pericardium
• Urogenital papilla
• Sinus venosus
• Transverse septum
- The oral and pharyngeal cavities and the respiratory
system
• Buccal or oral cavity primary tongue
• Pharynx - with spiracle and 5 elongated gill slits
You might also like
- KLM Anatomy Mcqs AnsweredDocument33 pagesKLM Anatomy Mcqs AnsweredJohanna Haludilu100% (3)
- Torso GuideDocument373 pagesTorso GuideMonica PatracutaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of LabourDocument4 pagesMechanism of LabourAnnapurna DangetiNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing NotesDocument7 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing NotesVillanueva, Jony Miaca O.No ratings yet
- 1487 Female Genital Organs 58eb5017c09a5Document20 pages1487 Female Genital Organs 58eb5017c09a5rodriguezruajavierNo ratings yet
- Organ Systems of The ToadDocument26 pagesOrgan Systems of The ToadDianne AcobaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Male Rep. SysDocument89 pagesAnatomy of Male Rep. Syszodo_izyanNo ratings yet
- Digestive. Apolonio and BacayDocument18 pagesDigestive. Apolonio and BacayKariza AbuNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument34 pagesGross Anatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemDitas ChuNo ratings yet
- 07 - Uterus, Uterine Tubes, OvariesDocument52 pages07 - Uterus, Uterine Tubes, Ovariesck4realNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument16 pagesBrainRej CosainNo ratings yet
- Anatomy PracticalDocument11 pagesAnatomy PracticalHossein VakiliNo ratings yet
- Contents of PelvisDocument38 pagesContents of Pelvisdr_asalehNo ratings yet
- Anatomi PelvisDocument44 pagesAnatomi Pelvisari naNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive Organs 2018Document80 pagesMale Reproductive Organs 2018yasrul izad100% (1)
- Gross Anatomy and Histolgy of UrinarysystemDocument81 pagesGross Anatomy and Histolgy of UrinarysystemIncredible DivineNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument94 pagesHuman ReproductionDivya AgarawalNo ratings yet
- Perineum and Reproductive SystemDocument36 pagesPerineum and Reproductive SystemHesbon MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy For DocmmiesDocument41 pagesAnatomy For DocmmiesMartinez_DONo ratings yet
- BIOL 2023 CH1 Introduction To Anatomical TermsDocument19 pagesBIOL 2023 CH1 Introduction To Anatomical Termsyazst.julienNo ratings yet
- Abdomen Engl PDFDocument51 pagesAbdomen Engl PDFShuler0071No ratings yet
- MATERNAL and Child NSG NotesDocument46 pagesMATERNAL and Child NSG NotesjnetNo ratings yet
- Peritonem A ND Peritonealcavity PDFDocument62 pagesPeritonem A ND Peritonealcavity PDFKarem MaaliNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument37 pagesUntitledMin Nyo SinNo ratings yet
- Female Genital System - Internal Structures (CU-PA-2020)Document63 pagesFemale Genital System - Internal Structures (CU-PA-2020)karenadjei44No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Abdomen: Samara University Biomedical Sciences DepartmentDocument142 pagesAnatomy of The Abdomen: Samara University Biomedical Sciences Departmentfentaw melkieNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Reproduksi Pria: DR. Ahmad Zulfan Hendri, Sp. UDocument14 pagesAnatomi Reproduksi Pria: DR. Ahmad Zulfan Hendri, Sp. UocepNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System: Presented by Parmar Zenith F.Y.M.sc (N) GineraDocument59 pagesFemale Reproductive System: Presented by Parmar Zenith F.Y.M.sc (N) Ginerazenith parmarNo ratings yet
- 01 - 20131119 Skull IDocument56 pages01 - 20131119 Skull INancyLiao100% (2)
- Must KnowDocument2 pagesMust KnowLiana JeonNo ratings yet
- 06 Perineum GenitaliaDocument24 pages06 Perineum GenitaliaRoger ViloNo ratings yet
- WK 7Document48 pagesWK 7Lana AmerieNo ratings yet
- 1 Anatomi Organ PanggulDocument45 pages1 Anatomi Organ PanggulHutomo Budi Hasnian SyahNo ratings yet
- Nephrologi: - PWM Olly Indrajani - 18-3-2015Document128 pagesNephrologi: - PWM Olly Indrajani - 18-3-2015NandatholoeNo ratings yet
- Aparatul Genital MasculDocument22 pagesAparatul Genital MasculvalisianoNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Gi - Dr. AhmadDocument77 pagesAnatomi Gi - Dr. AhmadBarfat AkbarNo ratings yet
- Systema UrinariusDocument25 pagesSystema UrinariusHAMDANINo ratings yet
- Maternal AnatomyDocument60 pagesMaternal AnatomyRaraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Throat DR Oscar PresentasiDocument53 pagesAnatomy of The Throat DR Oscar Presentasiharyo wiryantoNo ratings yet
- Azmath - Anat of PharynxDocument36 pagesAzmath - Anat of Pharynxjeswanthyelavarthi2No ratings yet
- Digetive System: Anatomy of The Digestive SystemDocument17 pagesDigetive System: Anatomy of The Digestive SystemCarmela Martínez YustaNo ratings yet
- AP2 Lab11 Anatomy of Digestion SP21Document16 pagesAP2 Lab11 Anatomy of Digestion SP21chasek76icloud.comNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female Genital TractDocument30 pagesAnatomy of Female Genital TractHerman FiraNo ratings yet
- Peritoneum, Bladder and Male Pelvic StructuresDocument34 pagesPeritoneum, Bladder and Male Pelvic StructuresKoddyNo ratings yet
- Frogbodypartsandfunctions Leopard FrogDocument30 pagesFrogbodypartsandfunctions Leopard FrogElijah PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Department of Anatomy Hasanuddin University: Dr. Hasan NyambeDocument57 pagesDepartment of Anatomy Hasanuddin University: Dr. Hasan NyambeMaksi YantoNo ratings yet
- Male Repro 2019Document79 pagesMale Repro 2019yasrulNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument37 pagesUrinary SystemNOELIE IBACARRANo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument109 pagesAnimal KingdomvvNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female Genital TractDocument37 pagesAnatomy of Female Genital TractSemon YohannesNo ratings yet
- Throat AnatomyDocument70 pagesThroat AnatomyMegan ShanzuNo ratings yet
- OB NSGDocument28 pagesOB NSGEna RodasNo ratings yet
- Maternal Anatomy: Julao, Fritz Adrian C. Kho, Nicole Alexandra P. Lagmay, Paul Angelo ADocument115 pagesMaternal Anatomy: Julao, Fritz Adrian C. Kho, Nicole Alexandra P. Lagmay, Paul Angelo ANicole Alexandra KhoNo ratings yet
- Egg Membranes Placenta '10Document42 pagesEgg Membranes Placenta '10Biolife solutionsNo ratings yet
- Urogenital System of The VertebratesDocument51 pagesUrogenital System of The VertebratesFaye Nadine Cabural100% (1)
- Anatomy of Urinary Bladder and UrethraDocument41 pagesAnatomy of Urinary Bladder and UrethraHemanta PunNo ratings yet
- Revisit of Male & Female Genital Tracts Semester VIIDocument50 pagesRevisit of Male & Female Genital Tracts Semester VIIDr. AyshaNo ratings yet
- 1.female Reproductive SystemDocument52 pages1.female Reproductive SystemKhairul HananNo ratings yet
- Systema Lymphaticum: Lymphatic SystemDocument38 pagesSystema Lymphaticum: Lymphatic SystemGeorge GeorgeNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- Lymphatics and Lymph Circulation: Physiology and PathologyFrom EverandLymphatics and Lymph Circulation: Physiology and PathologyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- DDLT RetrievalDocument33 pagesDDLT RetrievalPriya RanjanNo ratings yet
- The AortaDocument52 pagesThe Aortaviorel79No ratings yet
- Spleen Ultrasound: Dlshsi-Cmrt-000-Basics of Mri-NjegatchalianDocument16 pagesSpleen Ultrasound: Dlshsi-Cmrt-000-Basics of Mri-NjegatchalianJohn Andre RamosNo ratings yet
- Rauma Epar: Soetamto Wibowo Bagian Bedah FK UNAIR / RSUD DR Soetomo SurabayaDocument37 pagesRauma Epar: Soetamto Wibowo Bagian Bedah FK UNAIR / RSUD DR Soetomo SurabayaMuhammad FirdausNo ratings yet
- Kütük Cubuk Uyum StandartlariDocument2 pagesKütük Cubuk Uyum StandartlariÖZGÜRNo ratings yet
- 19 20Document42 pages19 20Bharath ChandranNo ratings yet
- Structures of The ForegutDocument13 pagesStructures of The ForegutJatan KothariNo ratings yet
- SternumDocument43 pagesSternumAnika MarshiaNo ratings yet
- SPLANCHONOLOGYDocument5 pagesSPLANCHONOLOGYFadil FadillahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy MCQ - Abdomen - 2Document15 pagesAnatomy MCQ - Abdomen - 2ahsan gujjarNo ratings yet
- Student Guide To The Frog DissectionDocument3 pagesStudent Guide To The Frog Dissectionapi-233187566No ratings yet
- Floyd17 TB Ch12Document5 pagesFloyd17 TB Ch12sdjuknicNo ratings yet
- Scrotum Anatomy and Scanning TechniqueDocument7 pagesScrotum Anatomy and Scanning TechniqueAnonymous wyF4yQZwZNo ratings yet
- MCQ SpineDocument2 pagesMCQ Spineanggita tri yurisworo100% (9)
- Veterinary Necropsy Report Checklist and Guidelines: Section I - Administrative Data Part A - Contributor'S DataDocument12 pagesVeterinary Necropsy Report Checklist and Guidelines: Section I - Administrative Data Part A - Contributor'S DataFilippo Pile PastoreNo ratings yet
- Bio Mechanics of Spinal ColumnDocument59 pagesBio Mechanics of Spinal ColumnOnwaree Ing100% (4)
- Anatomy of PancreasDocument43 pagesAnatomy of PancreasShiv SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Mesentery: Structure, Function, and Role in DiseaseDocument11 pagesThe Mesentery: Structure, Function, and Role in DiseaseIsaacQueirozNo ratings yet
- 1st Slides Body CavityDocument25 pages1st Slides Body Cavityfaizi gNo ratings yet
- Inguinal Region 1617Document23 pagesInguinal Region 1617Gx NavinNo ratings yet
- Topographic Anatomy of Abdominal OrgansDocument18 pagesTopographic Anatomy of Abdominal OrgansHasnain IdreesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Thorax Mbbs CXRDocument55 pagesAnatomy of Thorax Mbbs CXRMehtab AhmadNo ratings yet
- Workbook For Radiographic Image Analysis 4th Edition Martensen Test BankDocument9 pagesWorkbook For Radiographic Image Analysis 4th Edition Martensen Test Bankedselladonna6c2d76100% (31)
- Biomechanics of SpineDocument40 pagesBiomechanics of SpineSreeraj S R100% (1)
- Anatomy OSPEDocument61 pagesAnatomy OSPEMusfiqur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Appendices (SNOMED)Document194 pagesAppendices (SNOMED)tz75d4jcskNo ratings yet
- How To Read Chest Abdomen CT Scan X-RayDocument86 pagesHow To Read Chest Abdomen CT Scan X-RaymuhammadfyNo ratings yet