Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bubble Research PDF
Bubble Research PDF
Uploaded by
Robin ParmarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies PDFDocument27 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies PDFEmmanuel Del Rosario82% (11)
- Target - Global Factory ListDocument220 pagesTarget - Global Factory ListMauricio Viola CastellaNo ratings yet
- A Structural Study On Bubble Deck Slab and Its Properties: Mir Shahed Ali, Dr. S. Amaresh BabuDocument6 pagesA Structural Study On Bubble Deck Slab and Its Properties: Mir Shahed Ali, Dr. S. Amaresh BabuGrace HerdiyantiNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Study On Bubble Deck Slab System With Elliptical BallsDocument7 pagesAn Experimental Study On Bubble Deck Slab System With Elliptical BallsrohithNo ratings yet
- Bubble Deck Slab DesignDocument9 pagesBubble Deck Slab Designnihar100% (1)
- Bubble Deck AbstractDocument4 pagesBubble Deck AbstractRajat Maheshwari0% (1)
- 192 Experimental Study On Voided Biaxial Slab and Its ApplicationDocument5 pages192 Experimental Study On Voided Biaxial Slab and Its Applicationbogdan.kukosNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Bubbled Beam: Shaikh Nadeem Ashraf Nawazoddin, Prof. Shete G.NDocument6 pagesExperimental Study On Bubbled Beam: Shaikh Nadeem Ashraf Nawazoddin, Prof. Shete G.NluckyNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Voided Biaxial Slab and Its ApplicationDocument5 pagesExperimental Study On Voided Biaxial Slab and Its ApplicationEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Etude Pales BambouDocument2 pagesEtude Pales BambouMatteoNo ratings yet
- Analytical and Experimental Investigation On Voided Slab: NtroductionDocument8 pagesAnalytical and Experimental Investigation On Voided Slab: NtroductionShinde vishalNo ratings yet
- Voided Slab: % Weight SavingsDocument3 pagesVoided Slab: % Weight SavingsHemanth GowdaNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Numerical Investigation On Structural Behaviour of Bubble Deck Slab With Conventional SlabDocument4 pagesExperimental and Numerical Investigation On Structural Behaviour of Bubble Deck Slab With Conventional SlabEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Fin Irjmets1639807704 PDFDocument6 pagesFin Irjmets1639807704 PDFAkhil RajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Experimental Studies On Comparison of Conventional Slab and Bubble Deck Slab Based On Strength and EconomyDocument14 pagesExperimental Studies On Comparison of Conventional Slab and Bubble Deck Slab Based On Strength and EconomyDESH KARTHIKNo ratings yet
- Bubble Deck TechDocument23 pagesBubble Deck TechFasi Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Expanded Polystyrene ConcreteDocument7 pagesExpanded Polystyrene ConcreteIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study of Floating Concrete: Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience June 2020Document10 pagesExperimental Study of Floating Concrete: Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience June 2020Haril BoranaNo ratings yet
- Bubble Deck Slab Seminar by Waseem Raja, Sec CDocument20 pagesBubble Deck Slab Seminar by Waseem Raja, Sec CWaseem Rj100% (1)
- Study of Flexural Behavior, Thermal Variation and Luminosity Test On Filler SlabsDocument6 pagesStudy of Flexural Behavior, Thermal Variation and Luminosity Test On Filler Slabsabhishek pNo ratings yet
- Study of Flexural Behavior, Thermal Variation and Luminosity Test On Filler Slabs PDFDocument6 pagesStudy of Flexural Behavior, Thermal Variation and Luminosity Test On Filler Slabs PDFabhishek pNo ratings yet
- Structural Behavior of Bubble Deck SlabDocument7 pagesStructural Behavior of Bubble Deck Slabgulilero_yo100% (1)
- F 11600476 C 219Document6 pagesF 11600476 C 219AbdelRahman AyoubiNo ratings yet
- Burbujas de ConcretoDocument10 pagesBurbujas de Concretoeduardofarfan30123265No ratings yet
- Sustainable Construction Using EPS Beads in Light Weight Blocks To Form Innovative Foam Concrete As A Green Building MaterialDocument10 pagesSustainable Construction Using EPS Beads in Light Weight Blocks To Form Innovative Foam Concrete As A Green Building Materialmahdi najafzadehNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Bubble Deck Beam Using HDPE BallsDocument8 pagesExperimental Study On Bubble Deck Beam Using HDPE BallsIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Bubble Deck Slab With Conventional R.C.C SlabDocument7 pagesComparative Study of Bubble Deck Slab With Conventional R.C.C SlabIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Structural Behavior of Bubble Deck SlabDocument6 pagesStructural Behavior of Bubble Deck SlabrohithNo ratings yet
- Comparitive Study of Voided Slab and Conventional Slab Using ANSYS Workbench 14.5Document25 pagesComparitive Study of Voided Slab and Conventional Slab Using ANSYS Workbench 14.5Shinde vishalNo ratings yet
- Investigation On Wall Panel Sandwiched With LightwDocument16 pagesInvestigation On Wall Panel Sandwiched With LightwAamin RashidNo ratings yet
- 55 Falih2020Document18 pages55 Falih2020eng. douaaNo ratings yet
- Structural Behaviorof High Strength Precast Reinforced Concrete Vierendeel TrussDocument13 pagesStructural Behaviorof High Strength Precast Reinforced Concrete Vierendeel Trussemad mohamedNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of High Strength Precast Reinforced Concrete Walls Used (Vierendeel Truss Form)Document12 pagesExperimental Investigation of High Strength Precast Reinforced Concrete Walls Used (Vierendeel Truss Form)emad mohamedNo ratings yet
- Concrete Lightweight EpsDocument4 pagesConcrete Lightweight EpsFelipe Bastos100% (1)
- To Study Comparison Between Conventional Slab and Bubble Deck SlabDocument7 pagesTo Study Comparison Between Conventional Slab and Bubble Deck SlabNoor KhreisatNo ratings yet
- PET Bottle House ArticleDocument6 pagesPET Bottle House ArticleSushantTiwari100% (3)
- Himasree 2017 IOP Conf. Ser. - Earth Environ. Sci. 80 012041Document9 pagesHimasree 2017 IOP Conf. Ser. - Earth Environ. Sci. 80 012041bocove2670No ratings yet
- EPS For Green BuildingDocument7 pagesEPS For Green BuildingNicole Campos CastroNo ratings yet
- Expanded Polystyrene ConcreteDocument24 pagesExpanded Polystyrene ConcreteAtul RaiNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Akshayapriyadharshini.V Santhoshkumar .K.SDocument24 pagesPresented By: Akshayapriyadharshini.V Santhoshkumar .K.SSanket MahadikNo ratings yet
- Voided SlabDocument35 pagesVoided SlabPallepatiShirishRaoNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Eco-BricksDocument7 pagesExperimental Study On Eco-BricksmelaligareNo ratings yet
- Voided Biaxial Slabs - State of Art: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental ScienceDocument10 pagesVoided Biaxial Slabs - State of Art: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental ScienceShinde vishalNo ratings yet
- Strength Behavior of Bamboo Reinforced CDocument9 pagesStrength Behavior of Bamboo Reinforced CBRYLLE KYLLE OIDEMNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report FinalDocument34 pagesSeminar Report FinalSanthosh PrabuNo ratings yet
- Articuloooo PDFDocument7 pagesArticuloooo PDFFiorela Tatiana Elera ZuritaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Mortar Produced With Recycled Clay Brick Aggregate and PET PDFDocument6 pagesProperties of Mortar Produced With Recycled Clay Brick Aggregate and PET PDFPatito Lisbhet Romero BuenoNo ratings yet
- Irjet V5i2116 PDFDocument6 pagesIrjet V5i2116 PDFCharles Kyle CerezoNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument7 pages1 PBTondiNo ratings yet
- Review On Bubble Deck Slabs Technology and Their ApplicationsDocument6 pagesReview On Bubble Deck Slabs Technology and Their ApplicationsNoor KhreisatNo ratings yet
- Seismic Analysis of 3d Sandwich Panel Wall Building With Varying Soil Strata in Different Zon IJERTV6IS060268 PDFDocument5 pagesSeismic Analysis of 3d Sandwich Panel Wall Building With Varying Soil Strata in Different Zon IJERTV6IS060268 PDFVirat DesaiNo ratings yet
- Bamboo Based Composites For Wind Turbine Blades: Previous PaperDocument2 pagesBamboo Based Composites For Wind Turbine Blades: Previous PapersreeramNo ratings yet
- Straw Bale ReportDocument54 pagesStraw Bale Reportshweta dhawale100% (1)
- Structural, Acoustic, and Aesthetic Performances of Double Layer Wall Made of Oyster Shell and Polymer As Green Material in Green ConstructionDocument8 pagesStructural, Acoustic, and Aesthetic Performances of Double Layer Wall Made of Oyster Shell and Polymer As Green Material in Green ConstructionGrace CalitongNo ratings yet
- Parametric Study On Polystyrene Sheet in Concrete: Gandhi Dhrumil & Unnati SoniDocument14 pagesParametric Study On Polystyrene Sheet in Concrete: Gandhi Dhrumil & Unnati SoniTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Study of Use of Polystyrene As A Partial Replacement For Fine Aggregate in ConcreteDocument3 pagesStudy of Use of Polystyrene As A Partial Replacement For Fine Aggregate in ConcreteInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 45 Ijmperdfeb201845Document8 pages45 Ijmperdfeb201845TJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Influence of Continuous Plastic Fibers Reinforcement Arrangement in Concrete StrengthenedDocument9 pagesInfluence of Continuous Plastic Fibers Reinforcement Arrangement in Concrete StrengthenedIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNo ratings yet
- Name: Suchitra Ramasamy Matrix Number: CF160003Document4 pagesName: Suchitra Ramasamy Matrix Number: CF160003ikhmal siddiqNo ratings yet
- Composite Structures: Dora FotiDocument9 pagesComposite Structures: Dora FotiYara MounaNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture Toughness: A Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture ToughnessFrom EverandA Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture Toughness: A Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture ToughnessNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Matrix Composites: Fiber Reinforced Ceramics and their ApplicationsFrom EverandCeramic Matrix Composites: Fiber Reinforced Ceramics and their ApplicationsWalter KrenkelNo ratings yet
- SJVNL Interview Preparation DocumentDocument8 pagesSJVNL Interview Preparation DocumentRobin ParmarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Robin ParmarNo ratings yet
- Apprentice NotificationDocument9 pagesApprentice NotificationRobin ParmarNo ratings yet
- Use GKP or Arihant Publication Book For GATE TutorDocument1 pageUse GKP or Arihant Publication Book For GATE TutorRobin ParmarNo ratings yet
- GATE 2014: General Instructions During Examination: Common Data Button That Appears On The ScreenDocument17 pagesGATE 2014: General Instructions During Examination: Common Data Button That Appears On The ScreenRobin ParmarNo ratings yet
- List of Machinery and Equipments Concrete LabDocument7 pagesList of Machinery and Equipments Concrete LabRobin ParmarNo ratings yet
- ENCE353 Superposition Handout2011Document6 pagesENCE353 Superposition Handout2011Robin ParmarNo ratings yet
- Himachal Pradesh Technical University Hamirpur: Odd SemesterDocument2 pagesHimachal Pradesh Technical University Hamirpur: Odd SemesterRobin ParmarNo ratings yet
- Cee 3369B Materials For Civil Engineering: A.M. Soliman, PHD, LecturerDocument64 pagesCee 3369B Materials For Civil Engineering: A.M. Soliman, PHD, LecturerKarla Isabel Salgado SánchezNo ratings yet
- TMS 302 Sound STD Commentary UpdateDocument15 pagesTMS 302 Sound STD Commentary UpdateHani Nemrawi100% (1)
- General Specification: Welding - MaterialsDocument14 pagesGeneral Specification: Welding - MaterialsGil-Alain EgnakouNo ratings yet
- Special Metals NIMONIC® Alloy 90: Categories: Material NotesDocument3 pagesSpecial Metals NIMONIC® Alloy 90: Categories: Material NotesDragomirescu AlinaNo ratings yet
- Commercial Silanes BrouchureDocument8 pagesCommercial Silanes Brouchuremaged_abdnaghoNo ratings yet
- Fracture Toughness - Part2 - 03Document15 pagesFracture Toughness - Part2 - 03karrarNo ratings yet
- Subhead-3 HT & LT Overhead Distribution LineDocument13 pagesSubhead-3 HT & LT Overhead Distribution Linesalman sahNo ratings yet
- Aty JetDocument4 pagesAty JetVikash YadavNo ratings yet
- A Review of Nucleation, Growth and Low Temperature Synthesis of Diamond Thin Films PDFDocument36 pagesA Review of Nucleation, Growth and Low Temperature Synthesis of Diamond Thin Films PDFZixian JiaNo ratings yet
- Floating Screed System: High Performance Flooring and Tiling ProductsDocument2 pagesFloating Screed System: High Performance Flooring and Tiling ProductsWaled Hantash100% (1)
- Filament WindingDocument28 pagesFilament WindingKalusu Raman100% (1)
- Standard Test Method For Tensile Strength of Concrete Surfaces and The Bond Strength or Tensile Strength of Concrete Repair and Overlay Materials by Direct TensionDocument5 pagesStandard Test Method For Tensile Strength of Concrete Surfaces and The Bond Strength or Tensile Strength of Concrete Repair and Overlay Materials by Direct TensionlikodblackbordNo ratings yet
- Injection Molding Resin Shrink and Vents PDFDocument1 pageInjection Molding Resin Shrink and Vents PDFEco TefuNo ratings yet
- Processing and Properties of Metal Matrix CompositesDocument17 pagesProcessing and Properties of Metal Matrix CompositesMallu IngalagiNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Waterproofing Stampable Overlay Decorative Concrete Overlay Stamp Mix Is A LatexDocument16 pagesDokumen - Tips Waterproofing Stampable Overlay Decorative Concrete Overlay Stamp Mix Is A Latexm_shahbaghiNo ratings yet
- Stock Reconciliation - 2017Document16 pagesStock Reconciliation - 2017NidDouNo ratings yet
- Aliplast Katalog enDocument140 pagesAliplast Katalog enJelena GraovčevićNo ratings yet
- EARTHING PresentationDocument15 pagesEARTHING PresentationsemajamesNo ratings yet
- Sika Waterbar: Flexible PVC WaterstopDocument4 pagesSika Waterbar: Flexible PVC WaterstopKwok MorrisNo ratings yet
- Isotropically Small Crystalline Lamellae Induced by High Biaxial-Stretching Rate As A Key Microstructure For Super-Tough Polylactide FilmDocument12 pagesIsotropically Small Crystalline Lamellae Induced by High Biaxial-Stretching Rate As A Key Microstructure For Super-Tough Polylactide FilmLong LeNo ratings yet
- MAT Gasite 28G Dl-DataDocument1 pageMAT Gasite 28G Dl-DataCarlos HernándezNo ratings yet
- Material Comparison For Sa240 TP304Document3 pagesMaterial Comparison For Sa240 TP304QC Taner 453No ratings yet
- ASTM D4048 - 19aDocument5 pagesASTM D4048 - 19amancjaNo ratings yet
- UOP Type 13X-APG Data SheetDocument1 pageUOP Type 13X-APG Data SheetAmir RahbariNo ratings yet
- Diamond Wrap UHT - CitadelDocument1 pageDiamond Wrap UHT - CitadelRiankwnNo ratings yet
- 4 - Non Woven Bonding SystemsDocument10 pages4 - Non Woven Bonding SystemsShumaila KhanNo ratings yet
- TDS Fixoflex H PDFDocument4 pagesTDS Fixoflex H PDFLulzim BeqirajNo ratings yet
- 3M Heat Shrink Tubing & Sleeving CatalogueDocument9 pages3M Heat Shrink Tubing & Sleeving CatalogueRenato AbalosNo ratings yet
Bubble Research PDF
Bubble Research PDF
Uploaded by
Robin ParmarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bubble Research PDF
Bubble Research PDF
Uploaded by
Robin ParmarCopyright:
Available Formats
Special Issue - 2018 International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)
ISSN: 2278-0181
ETCEA - 2K18 Conference Proceedings
Performance Analysis of Bubble Deck Slab Using
Elliptical Balls
Abhija Mohan Archana Sukumaran
PG Scholar, Sree Buddha College of Engineering, Assistant Professor, Sree Buddha College of Engineering,
Alapuzha Pathanamthitta cluster of APJ Abdul Kalam Alapuzha Pathanamthitta cluster of APJ Abdul Kalam
Technological University, Ayathil, Elavumthitta P.O, Technological University, Ayathil, Elavumthitta P.O,
Pathanamthitta-689625 Pathanamthitta-689625
Abstract: Concrete plays a major role in the Thus, it makes buildings consuming more materials such as
construction field. In building construction slab is one of concrete and steel reinforcement. Increase the self-weight
the largest and important structural member of the slab due to increase in thickness. So many studies
consuming concrete. Concrete slab use more concrete were conducted for to reduce the disadvantages caused by
than requirement, hence has to be optimized. So reduce self-weight of the concrete.
the concrete in center of the slab by using hollow
recycled plastic balls. High density polyethylene (HDPE) For past few decades, several attempts have been
hollow balls replace the ineffective concrete in the center made to create biaxial slabs with hollow cavities in order to
of the slab, thus decreasing the dead weight and reduce the self-weight. But there have a chance of stress
increasing the efficiency of the floor. Voids in the middle concentration in corner of hollow cavities. Stress
of a flat slab eliminate 35% of a slab’s self-weight concentration in hollow cavities leads to severe crack
removing constraints of high dead loads and short generation in slabs. Most attempts have consisted of laying
spans. Combination of recycled plastic bubbles permits blocks of a less heavy material like expanded polystyrene
50% longer spans between columns without any beams. between the bottom and top reinforcement, while other
This provides a wide range of cost and construction types including waffle slabs or grid slabs. These types, only
benefits. In this paper, Finite element analysis (FEA) waffle slabs can be regarded to have a certain use in the
was carried out by using ANSYS software to study the market. But the use will always be very limited due to
structural behavior of bubble deck slab with different reduced resistances towards shear, local punching and fire.
arrangements of elliptical balls.
Keywords: Bubble Deck Slab System; ANSYS; High
density polyethylene hollow balls
I. INTRODUCTION
The invention of a new type of hollow core slabs was a
breakthrough at the turn of 20th and 21st centuries. Bubble
deck slab technology is an innovatory method of virtually
eliminating all concrete from the middle of a floor slab,
thereby reducing dead weight and increasing the efficiency
of the floor by using recycled hollow plastic balls. Bubble
deck is the invention of Jorgen Bruenig in 1990’s, who
developed the first biaxial hollow core slab (now known as
bubble deck) in Denmark. The main obstacle with concrete
constructions in case of horizontal slabs is the high weight, Fig.1.1 Bubble deck slab
which limits the span. So the major developments of
reinforced concrete have focused on enhancing the span Though many materials have been selected for the study
reducing the weight or overcoming concrete's natural related to this, materials like polypropylene and
weakness in tension. In a general way, the slab was polyethylene were found ideal because of reduced weight
designed only to resist vertical load. However, as people and act as good crack arrester. Then materials like
are getting more interest of residential environment polypropylene and polyethylene were used for creation of
recently, noise and vibration of slab are getting more hollow plastic balls. These hollow plastic balls are
important, as the span is increased, the deflection of the introduced in the middle portion of the slab between top
slab is also increased. Therefore, the slab thickness should and bottom reinforcement, thereby reducing self-weight of
be increase. Increasing the slab thickness makes the slabs the slab. To avoid the disadvantages which were caused by
heavier, and will increased column and foundations size. increasing self-weight of the slabs, the bubble deck slab
technology was suggested.
Volume 6, Issue 06 Published by, www.ijert.org 1
Special Issue - 2018 International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)
ISSN: 2278-0181
ETCEA - 2K18 Conference Proceedings
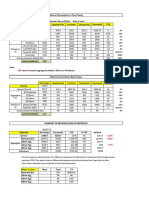
Behaviour of bubble deck slab is influenced by the ratio of TABLE I MATERIAL PROPERTIES
bubble diameter to slab thickness. The reinforcements are Young’s modulus = 25000MPa
placed as two meshes one at the bottom part and one at the Poisons ratio = 0.2
upper part that can be tided or welded. The distance Concrete
Compressive strength = 25 MPa
between the bars are kept corresponding to the dimensions
Density = 2400kg/m3
of the bubbles that are to be provided between the top and
bottom meshes. In this technology it locks ellipsoids Young’s modulus = 2×105 N/mm2
between the top and bottom reinforcement meshes, thereby Steel Poisons ratio = 0.3
creating a natural cell structure, acting like a solid slab. Tensile yield stress= 415 MPa
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) hollow spheres replace
Density = 7850 kg/m3
the ineffective concrete in the center of the slab, thus
decreasing the dead weight and increasing the efficiency of Young’s modulus =1030 MPa
HDPE
the floor. Poisson’s ratio = 0.4
Density = 970 kg/m3
II. OBJECTIVES
1. To validate ANSYS Soft ware.
2. To find out performance of bubble deck slab for different
arrangements of elliptical balls.
III. METHODOLOGY
This chapter describes the methodology of the thesis
work..The methodology includes study of bubble deck slab
and ANSYS software. The whole thesis work is divided
into the following sequential steps. The following
flowchart represents the methodology of the thesis work to
be completed.
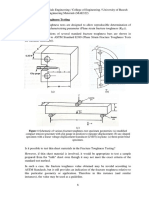
A. Modelling
In this project work, Bubble deck slab using spherical balls, Fig.4.2 Bubble deck slab with longitudinally shuffled elliptical balls
different arrangement of elliptical balls and using
combination of elliptical and spherical balls are modeled
using Finite Element Software ANSYS. M25 grade
concrete and high density polyethylene balls are used for
the study. Four Bubble deck slabs were modelled
Bubble deck slab using elliptical balls longitudinally
shuffled (type I)
Bubble deck slab using elliptical balls transversally
shuffled (type II)
Bubble deck slab using staggered arrangement of
elliptical balls(type III)
Fig.4.3 Bubble deck slab with transversely shuffled elliptical ball
B. Dimensional Details
Three dimensional bubble deck slab was modelled in D. Meshing and Loading
ANSYS with dimension of (1900x800x230) mm. The void
is of elliptical shape with dimension of (180x240) mm and The bubble deck slab is modeled using a tetrahedral
is made of High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) elliptical mesh which is a 4-node mesh. The loading is given by
balls. Reinforcing rebar at the top and bottom layers is point load with with fixed end support.
8mm dia and the concrete cover is 25mm. Reinforcement
provided for vertical support is having diameter of 12mm
C. Material Properties
Bubble deck mainly composed of three main materials
concrete, steel and HDPE balls. The material properties
are given below
Volume 6, Issue 06 Published by, www.ijert.org 2
Special Issue - 2018 International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)
ISSN: 2278-0181
ETCEA - 2K18 Conference Proceedings
IV. RESULTS AND DISSCUSSION
DEFORMATION
Fig.4.9 Deformation Diagram of Bubble deck slab with
longitudinally shuffled elliptical balls
Fig.4.9 Deformation Diagram of Bubble deck slab with transversely
shuffled elliptical balls
Fig.4.6 Meshing of bubble deck slab
E. Analysis of Bubble Deck Slab
Analysis was done using ANSYS software. Finite element
analysis will provide indepth knowledge about the behavior of
the member; it performed with proper boundary conditions and
material properties. There are different analyses performed in
this study.
Fig.4.9 Deformation Diagram of Bubble deck slab with staggered
arrangement of elliptical balls
Volume 6, Issue 06 Published by, www.ijert.org 3
Special Issue - 2018 International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)
ISSN: 2278-0181
ETCEA - 2K18 Conference Proceedings
TABLE II DEFORMATION
MODELS DEFORMATIONS LOAD(kN)
(mm)
Type I 20.914 220
Type II 21.39 216
Type III 21.4 212
IV.CONCLUSIONS
Bubble deck slab is analysed in ANSYS software and the
results where compared. Analysis was performed on the
bubble deck slab with elliptical balls of different
arrangements. Type I bubble deck slab has better load
carrying capacity as compare to type II and type III.
Deformation is comparatively less for type I bubble deck
slab than the other two types of bubble deck slab.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I am thankful to my guide, Asst. Professor, Archana
Sukumaran in Civil Engineering Department for her
constant encouragement and able guidance. Also I thank
my parents, friends etc. for their continuous support in
making this work complete
REFERENCES
[1] Amer M Ibrahim, Nazar K Ali and Wissam D Salman(2013),
“Flexural capacities of reinforced concrete two-way bubble
deck slabs of plastic spherical voids”, Diyala Journal of
Engineering Sciences Vol.06, Pp 9-20”
[2] Arati Shetkar and Nagesh Hanche(2015), “An experimental study
on bubble deck slab system with elliptical balls”, Proceeding of
NCRIET-2015 and Indian J.Sci, Vol.12(1):021027.
[3] Harishma K.R and Reshmi K.N (2015), “A study on bubble deck
slab”, International Journal of Advanced Research Trends in
Engineering and Technology(IJARTET),Vol.II, special issue X
[4] M.Surendar and M.Ranjitham (2016), “ Numerical and
experimental study on bubble deck slab” , IJESC
,DOI10.4010/2016 Vol 08, Pp 451 -566.
[5] NeerajTiwari and SanaZafar (2016), “ Structural behaviour of
bubble deck slabs and its application: An overview”, IJSRD -
International Journal for Scientific Research and Development,
Vol. 4, Issue 02, 2016 | ISSN (online): 2321-061
[6] P.PrabhuTeja, S.Anusha and C.H Mounika(2012), “Structural
behavior of bubble deck slab”, IEEE-International Conference
On Advances In Engineering, Science and Management
(ICAESM),Vol.20, pp.21-41.
[7] Reshma Mathew and Binu.P (2016), “Punching shear strength
development of bubble deck slab using GFRP stirrups”, IOSR
Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSRJMCE) e-
ISSN, 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, PP 01-06.
[8] Subramanian.K and Bhuvaneshwari.P (2015), “Finite element
analysis of voided slab with high density polypropylene void
formers”, International Journal ChemTech Reserch,Vol. 08,pp
746-753
[9] Saifee Bhagat and Dr.K.B.Parikh (2014), “ Comparative study of
voided flat plate slab and solid flat plate slab”, International
Journal Of Innovative Research and Development”,Vol.11,pp.78-
82
[10] Sonal R. Naik Dinesh Joshi (2017), “A Voided Slab and
Conventiona Flat Slab; A Comparative Study” IJSTE -
International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering |
Volume 4 | Issue 1 | Jul 2017 ISSN (online): 2349-784X
Volume 6, Issue 06 Published by, www.ijert.org 4
You might also like
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies PDFDocument27 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies PDFEmmanuel Del Rosario82% (11)
- Target - Global Factory ListDocument220 pagesTarget - Global Factory ListMauricio Viola CastellaNo ratings yet
- A Structural Study On Bubble Deck Slab and Its Properties: Mir Shahed Ali, Dr. S. Amaresh BabuDocument6 pagesA Structural Study On Bubble Deck Slab and Its Properties: Mir Shahed Ali, Dr. S. Amaresh BabuGrace HerdiyantiNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Study On Bubble Deck Slab System With Elliptical BallsDocument7 pagesAn Experimental Study On Bubble Deck Slab System With Elliptical BallsrohithNo ratings yet
- Bubble Deck Slab DesignDocument9 pagesBubble Deck Slab Designnihar100% (1)
- Bubble Deck AbstractDocument4 pagesBubble Deck AbstractRajat Maheshwari0% (1)
- 192 Experimental Study On Voided Biaxial Slab and Its ApplicationDocument5 pages192 Experimental Study On Voided Biaxial Slab and Its Applicationbogdan.kukosNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Bubbled Beam: Shaikh Nadeem Ashraf Nawazoddin, Prof. Shete G.NDocument6 pagesExperimental Study On Bubbled Beam: Shaikh Nadeem Ashraf Nawazoddin, Prof. Shete G.NluckyNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Voided Biaxial Slab and Its ApplicationDocument5 pagesExperimental Study On Voided Biaxial Slab and Its ApplicationEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Etude Pales BambouDocument2 pagesEtude Pales BambouMatteoNo ratings yet
- Analytical and Experimental Investigation On Voided Slab: NtroductionDocument8 pagesAnalytical and Experimental Investigation On Voided Slab: NtroductionShinde vishalNo ratings yet
- Voided Slab: % Weight SavingsDocument3 pagesVoided Slab: % Weight SavingsHemanth GowdaNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Numerical Investigation On Structural Behaviour of Bubble Deck Slab With Conventional SlabDocument4 pagesExperimental and Numerical Investigation On Structural Behaviour of Bubble Deck Slab With Conventional SlabEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Fin Irjmets1639807704 PDFDocument6 pagesFin Irjmets1639807704 PDFAkhil RajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Experimental Studies On Comparison of Conventional Slab and Bubble Deck Slab Based On Strength and EconomyDocument14 pagesExperimental Studies On Comparison of Conventional Slab and Bubble Deck Slab Based On Strength and EconomyDESH KARTHIKNo ratings yet
- Bubble Deck TechDocument23 pagesBubble Deck TechFasi Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Expanded Polystyrene ConcreteDocument7 pagesExpanded Polystyrene ConcreteIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study of Floating Concrete: Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience June 2020Document10 pagesExperimental Study of Floating Concrete: Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience June 2020Haril BoranaNo ratings yet
- Bubble Deck Slab Seminar by Waseem Raja, Sec CDocument20 pagesBubble Deck Slab Seminar by Waseem Raja, Sec CWaseem Rj100% (1)
- Study of Flexural Behavior, Thermal Variation and Luminosity Test On Filler SlabsDocument6 pagesStudy of Flexural Behavior, Thermal Variation and Luminosity Test On Filler Slabsabhishek pNo ratings yet
- Study of Flexural Behavior, Thermal Variation and Luminosity Test On Filler Slabs PDFDocument6 pagesStudy of Flexural Behavior, Thermal Variation and Luminosity Test On Filler Slabs PDFabhishek pNo ratings yet
- Structural Behavior of Bubble Deck SlabDocument7 pagesStructural Behavior of Bubble Deck Slabgulilero_yo100% (1)
- F 11600476 C 219Document6 pagesF 11600476 C 219AbdelRahman AyoubiNo ratings yet
- Burbujas de ConcretoDocument10 pagesBurbujas de Concretoeduardofarfan30123265No ratings yet
- Sustainable Construction Using EPS Beads in Light Weight Blocks To Form Innovative Foam Concrete As A Green Building MaterialDocument10 pagesSustainable Construction Using EPS Beads in Light Weight Blocks To Form Innovative Foam Concrete As A Green Building Materialmahdi najafzadehNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Bubble Deck Beam Using HDPE BallsDocument8 pagesExperimental Study On Bubble Deck Beam Using HDPE BallsIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Bubble Deck Slab With Conventional R.C.C SlabDocument7 pagesComparative Study of Bubble Deck Slab With Conventional R.C.C SlabIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Structural Behavior of Bubble Deck SlabDocument6 pagesStructural Behavior of Bubble Deck SlabrohithNo ratings yet
- Comparitive Study of Voided Slab and Conventional Slab Using ANSYS Workbench 14.5Document25 pagesComparitive Study of Voided Slab and Conventional Slab Using ANSYS Workbench 14.5Shinde vishalNo ratings yet
- Investigation On Wall Panel Sandwiched With LightwDocument16 pagesInvestigation On Wall Panel Sandwiched With LightwAamin RashidNo ratings yet
- 55 Falih2020Document18 pages55 Falih2020eng. douaaNo ratings yet
- Structural Behaviorof High Strength Precast Reinforced Concrete Vierendeel TrussDocument13 pagesStructural Behaviorof High Strength Precast Reinforced Concrete Vierendeel Trussemad mohamedNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of High Strength Precast Reinforced Concrete Walls Used (Vierendeel Truss Form)Document12 pagesExperimental Investigation of High Strength Precast Reinforced Concrete Walls Used (Vierendeel Truss Form)emad mohamedNo ratings yet
- Concrete Lightweight EpsDocument4 pagesConcrete Lightweight EpsFelipe Bastos100% (1)
- To Study Comparison Between Conventional Slab and Bubble Deck SlabDocument7 pagesTo Study Comparison Between Conventional Slab and Bubble Deck SlabNoor KhreisatNo ratings yet
- PET Bottle House ArticleDocument6 pagesPET Bottle House ArticleSushantTiwari100% (3)
- Himasree 2017 IOP Conf. Ser. - Earth Environ. Sci. 80 012041Document9 pagesHimasree 2017 IOP Conf. Ser. - Earth Environ. Sci. 80 012041bocove2670No ratings yet
- EPS For Green BuildingDocument7 pagesEPS For Green BuildingNicole Campos CastroNo ratings yet
- Expanded Polystyrene ConcreteDocument24 pagesExpanded Polystyrene ConcreteAtul RaiNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Akshayapriyadharshini.V Santhoshkumar .K.SDocument24 pagesPresented By: Akshayapriyadharshini.V Santhoshkumar .K.SSanket MahadikNo ratings yet
- Voided SlabDocument35 pagesVoided SlabPallepatiShirishRaoNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Eco-BricksDocument7 pagesExperimental Study On Eco-BricksmelaligareNo ratings yet
- Voided Biaxial Slabs - State of Art: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental ScienceDocument10 pagesVoided Biaxial Slabs - State of Art: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental ScienceShinde vishalNo ratings yet
- Strength Behavior of Bamboo Reinforced CDocument9 pagesStrength Behavior of Bamboo Reinforced CBRYLLE KYLLE OIDEMNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report FinalDocument34 pagesSeminar Report FinalSanthosh PrabuNo ratings yet
- Articuloooo PDFDocument7 pagesArticuloooo PDFFiorela Tatiana Elera ZuritaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Mortar Produced With Recycled Clay Brick Aggregate and PET PDFDocument6 pagesProperties of Mortar Produced With Recycled Clay Brick Aggregate and PET PDFPatito Lisbhet Romero BuenoNo ratings yet
- Irjet V5i2116 PDFDocument6 pagesIrjet V5i2116 PDFCharles Kyle CerezoNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument7 pages1 PBTondiNo ratings yet
- Review On Bubble Deck Slabs Technology and Their ApplicationsDocument6 pagesReview On Bubble Deck Slabs Technology and Their ApplicationsNoor KhreisatNo ratings yet
- Seismic Analysis of 3d Sandwich Panel Wall Building With Varying Soil Strata in Different Zon IJERTV6IS060268 PDFDocument5 pagesSeismic Analysis of 3d Sandwich Panel Wall Building With Varying Soil Strata in Different Zon IJERTV6IS060268 PDFVirat DesaiNo ratings yet
- Bamboo Based Composites For Wind Turbine Blades: Previous PaperDocument2 pagesBamboo Based Composites For Wind Turbine Blades: Previous PapersreeramNo ratings yet
- Straw Bale ReportDocument54 pagesStraw Bale Reportshweta dhawale100% (1)
- Structural, Acoustic, and Aesthetic Performances of Double Layer Wall Made of Oyster Shell and Polymer As Green Material in Green ConstructionDocument8 pagesStructural, Acoustic, and Aesthetic Performances of Double Layer Wall Made of Oyster Shell and Polymer As Green Material in Green ConstructionGrace CalitongNo ratings yet
- Parametric Study On Polystyrene Sheet in Concrete: Gandhi Dhrumil & Unnati SoniDocument14 pagesParametric Study On Polystyrene Sheet in Concrete: Gandhi Dhrumil & Unnati SoniTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Study of Use of Polystyrene As A Partial Replacement For Fine Aggregate in ConcreteDocument3 pagesStudy of Use of Polystyrene As A Partial Replacement For Fine Aggregate in ConcreteInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 45 Ijmperdfeb201845Document8 pages45 Ijmperdfeb201845TJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Influence of Continuous Plastic Fibers Reinforcement Arrangement in Concrete StrengthenedDocument9 pagesInfluence of Continuous Plastic Fibers Reinforcement Arrangement in Concrete StrengthenedIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNo ratings yet
- Name: Suchitra Ramasamy Matrix Number: CF160003Document4 pagesName: Suchitra Ramasamy Matrix Number: CF160003ikhmal siddiqNo ratings yet
- Composite Structures: Dora FotiDocument9 pagesComposite Structures: Dora FotiYara MounaNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture Toughness: A Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture ToughnessFrom EverandA Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture Toughness: A Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture ToughnessNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Matrix Composites: Fiber Reinforced Ceramics and their ApplicationsFrom EverandCeramic Matrix Composites: Fiber Reinforced Ceramics and their ApplicationsWalter KrenkelNo ratings yet
- SJVNL Interview Preparation DocumentDocument8 pagesSJVNL Interview Preparation DocumentRobin ParmarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Robin ParmarNo ratings yet
- Apprentice NotificationDocument9 pagesApprentice NotificationRobin ParmarNo ratings yet
- Use GKP or Arihant Publication Book For GATE TutorDocument1 pageUse GKP or Arihant Publication Book For GATE TutorRobin ParmarNo ratings yet
- GATE 2014: General Instructions During Examination: Common Data Button That Appears On The ScreenDocument17 pagesGATE 2014: General Instructions During Examination: Common Data Button That Appears On The ScreenRobin ParmarNo ratings yet
- List of Machinery and Equipments Concrete LabDocument7 pagesList of Machinery and Equipments Concrete LabRobin ParmarNo ratings yet
- ENCE353 Superposition Handout2011Document6 pagesENCE353 Superposition Handout2011Robin ParmarNo ratings yet
- Himachal Pradesh Technical University Hamirpur: Odd SemesterDocument2 pagesHimachal Pradesh Technical University Hamirpur: Odd SemesterRobin ParmarNo ratings yet
- Cee 3369B Materials For Civil Engineering: A.M. Soliman, PHD, LecturerDocument64 pagesCee 3369B Materials For Civil Engineering: A.M. Soliman, PHD, LecturerKarla Isabel Salgado SánchezNo ratings yet
- TMS 302 Sound STD Commentary UpdateDocument15 pagesTMS 302 Sound STD Commentary UpdateHani Nemrawi100% (1)
- General Specification: Welding - MaterialsDocument14 pagesGeneral Specification: Welding - MaterialsGil-Alain EgnakouNo ratings yet
- Special Metals NIMONIC® Alloy 90: Categories: Material NotesDocument3 pagesSpecial Metals NIMONIC® Alloy 90: Categories: Material NotesDragomirescu AlinaNo ratings yet
- Commercial Silanes BrouchureDocument8 pagesCommercial Silanes Brouchuremaged_abdnaghoNo ratings yet
- Fracture Toughness - Part2 - 03Document15 pagesFracture Toughness - Part2 - 03karrarNo ratings yet
- Subhead-3 HT & LT Overhead Distribution LineDocument13 pagesSubhead-3 HT & LT Overhead Distribution Linesalman sahNo ratings yet
- Aty JetDocument4 pagesAty JetVikash YadavNo ratings yet
- A Review of Nucleation, Growth and Low Temperature Synthesis of Diamond Thin Films PDFDocument36 pagesA Review of Nucleation, Growth and Low Temperature Synthesis of Diamond Thin Films PDFZixian JiaNo ratings yet
- Floating Screed System: High Performance Flooring and Tiling ProductsDocument2 pagesFloating Screed System: High Performance Flooring and Tiling ProductsWaled Hantash100% (1)
- Filament WindingDocument28 pagesFilament WindingKalusu Raman100% (1)
- Standard Test Method For Tensile Strength of Concrete Surfaces and The Bond Strength or Tensile Strength of Concrete Repair and Overlay Materials by Direct TensionDocument5 pagesStandard Test Method For Tensile Strength of Concrete Surfaces and The Bond Strength or Tensile Strength of Concrete Repair and Overlay Materials by Direct TensionlikodblackbordNo ratings yet
- Injection Molding Resin Shrink and Vents PDFDocument1 pageInjection Molding Resin Shrink and Vents PDFEco TefuNo ratings yet
- Processing and Properties of Metal Matrix CompositesDocument17 pagesProcessing and Properties of Metal Matrix CompositesMallu IngalagiNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Waterproofing Stampable Overlay Decorative Concrete Overlay Stamp Mix Is A LatexDocument16 pagesDokumen - Tips Waterproofing Stampable Overlay Decorative Concrete Overlay Stamp Mix Is A Latexm_shahbaghiNo ratings yet
- Stock Reconciliation - 2017Document16 pagesStock Reconciliation - 2017NidDouNo ratings yet
- Aliplast Katalog enDocument140 pagesAliplast Katalog enJelena GraovčevićNo ratings yet
- EARTHING PresentationDocument15 pagesEARTHING PresentationsemajamesNo ratings yet
- Sika Waterbar: Flexible PVC WaterstopDocument4 pagesSika Waterbar: Flexible PVC WaterstopKwok MorrisNo ratings yet
- Isotropically Small Crystalline Lamellae Induced by High Biaxial-Stretching Rate As A Key Microstructure For Super-Tough Polylactide FilmDocument12 pagesIsotropically Small Crystalline Lamellae Induced by High Biaxial-Stretching Rate As A Key Microstructure For Super-Tough Polylactide FilmLong LeNo ratings yet
- MAT Gasite 28G Dl-DataDocument1 pageMAT Gasite 28G Dl-DataCarlos HernándezNo ratings yet
- Material Comparison For Sa240 TP304Document3 pagesMaterial Comparison For Sa240 TP304QC Taner 453No ratings yet
- ASTM D4048 - 19aDocument5 pagesASTM D4048 - 19amancjaNo ratings yet
- UOP Type 13X-APG Data SheetDocument1 pageUOP Type 13X-APG Data SheetAmir RahbariNo ratings yet
- Diamond Wrap UHT - CitadelDocument1 pageDiamond Wrap UHT - CitadelRiankwnNo ratings yet
- 4 - Non Woven Bonding SystemsDocument10 pages4 - Non Woven Bonding SystemsShumaila KhanNo ratings yet
- TDS Fixoflex H PDFDocument4 pagesTDS Fixoflex H PDFLulzim BeqirajNo ratings yet
- 3M Heat Shrink Tubing & Sleeving CatalogueDocument9 pages3M Heat Shrink Tubing & Sleeving CatalogueRenato AbalosNo ratings yet