Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6th Sem SDDII
6th Sem SDDII
Uploaded by
Anonymous hJZatOU2t2Copyright:
You might also like
- Boiler Magnetite Exfoliation Report June 2005Document23 pagesBoiler Magnetite Exfoliation Report June 2005lacoste11111100% (1)
- Final Webpage DesignDocument9 pagesFinal Webpage DesignAnonymous OGVOs4VBNo ratings yet
- Indian ConstitutionDocument5 pagesIndian Constitutionyexov33854No ratings yet
- Python ProgrammingDocument10 pagesPython Programmingyexov33854No ratings yet
- Elements of Aeronautical EngineeringDocument6 pagesElements of Aeronautical Engineeringyexov33854No ratings yet
- 16. Diploma in Civil Engineering (Rural Engineering) Sem-IDocument82 pages16. Diploma in Civil Engineering (Rural Engineering) Sem-Igovindbgs06No ratings yet
- SEM IV 21 Electronics EngineeringDocument30 pagesSEM IV 21 Electronics EngineeringyogeshNo ratings yet
- Fluids Mechanics & MachineryDocument6 pagesFluids Mechanics & Machineryyexov33854No ratings yet
- Abet Format Syllabus - GCV463 - Specifications & BOQ - 201710Document3 pagesAbet Format Syllabus - GCV463 - Specifications & BOQ - 201710Oec EngNo ratings yet
- Basic Simulation LabDocument3 pagesBasic Simulation LabGautam KumarNo ratings yet
- 5th Sem & 6th Sem Syllabus KukDocument31 pages5th Sem & 6th Sem Syllabus KukvivekNo ratings yet
- VTH Sem - Computer Science EngineeringDocument18 pagesVTH Sem - Computer Science EngineeringPriyanshi YadavNo ratings yet
- Cse Btech III Yr V Sem Scheme Syllabus July 2022Document26 pagesCse Btech III Yr V Sem Scheme Syllabus July 2022Ved Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- I Sem: Scheme of Teaching and Examination of B. Architecture (Cbcs Scheme-2018)Document9 pagesI Sem: Scheme of Teaching and Examination of B. Architecture (Cbcs Scheme-2018)Pooja vijayNo ratings yet
- Bca F.Y.Document33 pagesBca F.Y.backtogNo ratings yet
- Holy Spirit University of Kaslik: Course SyllabusDocument3 pagesHoly Spirit University of Kaslik: Course SyllabusElie OtayekNo ratings yet
- State Board of Technical Education, Bihar: V Semester Diploma in Civil Engineering / Civil (Rural) EngineeringDocument22 pagesState Board of Technical Education, Bihar: V Semester Diploma in Civil Engineering / Civil (Rural) EngineeringPranjal PandeyNo ratings yet
- 4th Sem 15 Civil Engineering PDFDocument12 pages4th Sem 15 Civil Engineering PDFdhiraj kumarNo ratings yet
- SEM IV 15 Civil EngineeringDocument20 pagesSEM IV 15 Civil EngineeringArman RajNo ratings yet
- W.e.f.-July-2010 Academic Session-2010-11 1Document27 pagesW.e.f.-July-2010 Academic Session-2010-11 1Devil KingNo ratings yet
- F.Y.B.Sc Electronics Syllabus NEP 2020Document39 pagesF.Y.B.Sc Electronics Syllabus NEP 2020Dipak ValviNo ratings yet
- SEM III BR Computer Science and EngineeringDocument21 pagesSEM III BR Computer Science and EngineeringyogeshNo ratings yet
- 1 HR 1 HR Tutorial 2 HR Practical 1 CreditDocument7 pages1 HR 1 HR Tutorial 2 HR Practical 1 CreditHitesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- VTU B.arch Syllabus 2018 SchemeDocument33 pagesVTU B.arch Syllabus 2018 SchemeKruthiNo ratings yet
- Barchchsyll1 5Document33 pagesBarchchsyll1 5AnirudhMagniNo ratings yet
- HMT - Course FileDocument16 pagesHMT - Course FileajitsssNo ratings yet
- DVTP LAB Manual R21 ITDocument44 pagesDVTP LAB Manual R21 ITanyoneNo ratings yet
- Ce 6Document1 pageCe 6btirt btirtNo ratings yet
- SEM-VI-15-Civil-Engineering SajjanDocument110 pagesSEM-VI-15-Civil-Engineering Sajjanthenomore poetryNo ratings yet
- CSE VIII Semester Scheme Syllabus 2Document21 pagesCSE VIII Semester Scheme Syllabus 2garima khasdeoNo ratings yet
- Abet Format Syllabus - GCV405 - Reinforced Concrete II - Rev 20180827Document3 pagesAbet Format Syllabus - GCV405 - Reinforced Concrete II - Rev 20180827Oec EngNo ratings yet
- B.tech CSE Syllabus 2020-24-09-Apr-20 VNDocument191 pagesB.tech CSE Syllabus 2020-24-09-Apr-20 VNsatyam sharmaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - CBGS I and II Semester SET A 6july17Document26 pagesMicrosoft Word - CBGS I and II Semester SET A 6july17tejpratapNo ratings yet
- 2018-19 F.E. To B.E. Mechanical Engineering StructureDocument11 pages2018-19 F.E. To B.E. Mechanical Engineering Structurenavneetkpatil8409No ratings yet
- Course Contents/Syllabus:: L T P/S SW/F W Total Credit UnitsDocument6 pagesCourse Contents/Syllabus:: L T P/S SW/F W Total Credit UnitsSDMNo ratings yet
- Estimation, Costing and SpecificationsDocument4 pagesEstimation, Costing and SpecificationsPronceNo ratings yet
- Ce 7Document1 pageCe 7btirt btirtNo ratings yet
- PattonDocument2 pagesPattonATHISH 02No ratings yet
- Revised B.com. Program SyllabusDocument31 pagesRevised B.com. Program Syllabussayakkarmakarslg1No ratings yet
- Cse Btech IV Yr Vii Sem Scheme Syllabus July 2022Document25 pagesCse Btech IV Yr Vii Sem Scheme Syllabus July 2022Ved Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Proposed B.tech First Year Scheme 2024 - 28Document3 pagesProposed B.tech First Year Scheme 2024 - 28sachinsaurav89No ratings yet
- Teaching Scheme of M. Tech Artificial IntelligenceDocument4 pagesTeaching Scheme of M. Tech Artificial IntelligenceJahanvi SharmaNo ratings yet
- SEM V 15 Civil EngineeringDocument45 pagesSEM V 15 Civil EngineeringAman KumarNo ratings yet
- B. Tech Computer Science and Buisness Systems SchemeDocument6 pagesB. Tech Computer Science and Buisness Systems SchemeAkshayNo ratings yet
- CSE IYearAutonomoussyllabusDocument52 pagesCSE IYearAutonomoussyllabusRazha GarrixNo ratings yet
- 4th Semester Electronics Engg.Document24 pages4th Semester Electronics Engg.PRAKASH GOSWAMINo ratings yet
- 4th 5th 6th Semester Electronics Engg. Merged PDFDocument60 pages4th 5th 6th Semester Electronics Engg. Merged PDFShubham kumarNo ratings yet
- 4 - 09-14-2021 - 14-46-32 - B.Tech CSE 4th YearDocument53 pages4 - 09-14-2021 - 14-46-32 - B.Tech CSE 4th YearGOURAB PANDITNo ratings yet
- New SyllabusDocument3 pagesNew SyllabusAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Ce 5Document1 pageCe 5btirt btirtNo ratings yet
- 78th PDFDocument35 pages78th PDFsushantNo ratings yet
- BE CSE AI&DS 19-5-2022 Scheme and SyllabusDocument69 pagesBE CSE AI&DS 19-5-2022 Scheme and SyllabusMOFANo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering Scheme of Instruction & Examination and Syllabi B.E. I and II Semesters (Group-A) of Four Year Degree Programme in B.E.Document25 pagesFaculty of Engineering Scheme of Instruction & Examination and Syllabi B.E. I and II Semesters (Group-A) of Four Year Degree Programme in B.E.Ramavath sunil naikNo ratings yet
- Co - WCS 5013Document5 pagesCo - WCS 5013Sani Oghang PekanNo ratings yet
- Table of Specifications: Midterm ExaminationDocument2 pagesTable of Specifications: Midterm ExaminationShela RamosNo ratings yet
- Syllubs SEM-IV-15-Civil-EngineeringDocument23 pagesSyllubs SEM-IV-15-Civil-EngineeringrandhirNo ratings yet
- Fea RDocument21 pagesFea RajithjkingsNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-06-18 at 4.35.56 PMDocument13 pagesScreenshot 2023-06-18 at 4.35.56 PMNikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Subhajit Bed PDFDocument2 pagesSubhajit Bed PDFSubhajit BakshiNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Teaching and Examination For Vi Semester Diploma in Civil EngineeringDocument32 pagesScheme of Teaching and Examination For Vi Semester Diploma in Civil EngineeringYashwant BadoleNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam-Testing Concept-PERT/CPM/Gantt Chart/FPA/EVA/Timebox (Chapter-3)From EverandCISA Exam-Testing Concept-PERT/CPM/Gantt Chart/FPA/EVA/Timebox (Chapter-3)Rating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (3)
- Bill of Materials - Cost and ESTIMATESDocument38 pagesBill of Materials - Cost and ESTIMATESmnmusorNo ratings yet
- Jeffadd Additives: Performance ProductsDocument2 pagesJeffadd Additives: Performance ProductsPhuong The NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chemi Presentation 2Document25 pagesChemi Presentation 2teddyNo ratings yet
- Sample - Objective Ques Engg MaterialDocument1 pageSample - Objective Ques Engg MaterialAnunay MilindNo ratings yet
- Ingevity Capa CoatingsDocument4 pagesIngevity Capa CoatingsKanagarajan VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Rdlo / Rdlo V: Axially Split Volute Casing PumpDocument24 pagesRdlo / Rdlo V: Axially Split Volute Casing PumpfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Influence of Nano - Sized Powder Content On Physical Properties of Waste Acid Refractory BrickDocument19 pagesInfluence of Nano - Sized Powder Content On Physical Properties of Waste Acid Refractory BrickamnajamNo ratings yet
- Romans and Architecture PDFDocument86 pagesRomans and Architecture PDFDevika Hemalatha DeviNo ratings yet
- Chapter-10 Case StudiesDocument4 pagesChapter-10 Case Studiessafeer ahmadNo ratings yet
- SOP For Cleaning and Sterilization of Glass Ware Used in Microbiology Lab.Document3 pagesSOP For Cleaning and Sterilization of Glass Ware Used in Microbiology Lab.Bejoy Karim100% (1)
- Wrought Alloys: Near Equivalent Designations: Table - 1Document3 pagesWrought Alloys: Near Equivalent Designations: Table - 1Chidanand KoppaNo ratings yet
- Batc NFMDocument75 pagesBatc NFMMaria BotelhoNo ratings yet
- Centricast CL 1520 Piping System Spec SheetDocument2 pagesCentricast CL 1520 Piping System Spec SheetOlmer Romero MendezNo ratings yet
- B P ® G EP: Lack Earl ReaseDocument3 pagesB P ® G EP: Lack Earl ReaseWeslei BritoNo ratings yet
- The Ancient Metallurgy in AzerbaijanDocument12 pagesThe Ancient Metallurgy in AzerbaijanAlireza EsfandiarNo ratings yet
- Combustion and Flame Class 8Document4 pagesCombustion and Flame Class 8Vinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Caillebotis AMICODocument112 pagesCaillebotis AMICOMathieu NormandeauNo ratings yet
- Flame Retardant PolymerDocument13 pagesFlame Retardant Polymerpolypolyy100% (1)
- Liquefied Gas Tanker Familiarisation CourseDocument266 pagesLiquefied Gas Tanker Familiarisation CourseGeorge Ponpyka100% (7)
- 6,123 (&,QGXVWULDO/XEULFDQWV: SINOPEC Industrial LubricantDocument12 pages6,123 (&,QGXVWULDO/XEULFDQWV: SINOPEC Industrial LubricantSalman Ahmed PrinceNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes Ch08 The Dblock F-Block ElementsDocument4 pages12 Chemistry Notes Ch08 The Dblock F-Block ElementsABHISHEKNo ratings yet
- Material List Grounding Untuk PO Rev.1Document2 pagesMaterial List Grounding Untuk PO Rev.1BANGGANo ratings yet
- New Procedures For Materials 2020Document700 pagesNew Procedures For Materials 2020Mengalvio GraçaNo ratings yet
- GR 11 Chemistry Exam ReviewerDocument7 pagesGR 11 Chemistry Exam ReviewerrdncdNo ratings yet
- PFDDocument8 pagesPFDSanthoz JaganNo ratings yet
- Clent List Delhi NCRDocument11 pagesClent List Delhi NCRabhimanyu.xplastNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 The S-Block ElementsDocument18 pagesChapter 10 The S-Block ElementsYash PlayNo ratings yet
- Tech. Specs. For Metal Doors, Windows, Ventlators Louvers Etc.Document8 pagesTech. Specs. For Metal Doors, Windows, Ventlators Louvers Etc.SaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- How Many KG of Cement Is Needed For A Meter Cube of Concrete - QuoraDocument5 pagesHow Many KG of Cement Is Needed For A Meter Cube of Concrete - QuoraPd ProxyNo ratings yet
6th Sem SDDII
6th Sem SDDII
Uploaded by
Anonymous hJZatOU2t2Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
6th Sem SDDII
6th Sem SDDII
Uploaded by
Anonymous hJZatOU2t2Copyright:
Diploma in Civil Engg.
Semester IV
VII. Course Curriculum Detailing (Semester- VI)
CSVTU, Bhilai- NITTTR, Bhopal Page 1
Diploma in Civil Engg. Semester IV
A) Course Code :
B) Course Title : Structural Design and Drafting II
C) Pre- requisite Course Code and Title :
D) Rationale :
E) Course Outcomes :
. CO-1 Design riveted and welded joints as per code IS: 800: 2007.
CO-2 Design of tension members as per code IS: 800: 2007.
CO- 3 Design of compression members, columns and column’s bases as per code IS: 800: 2007.
CO- 4 Design of steel beams as per code IS: 800: 2007.
CO-5 Analyze continuous beam, roof trusses and design roof trusses as per code IS: 800: 2007.
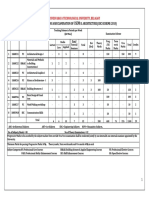
F) Scheme of Studies:
Board of Scheme of Studies
Study (Hours/Week)
Course
Course Title CI LI SW Total Study Total
Code
+ Hours Credits(C)
SL (CI+LI+SW+SL) (CI+
LI+SW+SL)
Civil Structural Design 5 1 1 7 7
Engineering and Drafting II
Legend: CI: Classroom Instruction (Includes different instructional strategies i.e. Lecture (L) and Tutorial (T) and
others) , LI : Laboratory Instruction (Includes Practical performances in laboratory workshop, field or other
locations using different instructional strategies ) SW: Sessional Work (includes assignment, seminar, mini
project etc.), SL: Self Learning, C:Credits
Note: SW & SL has to be planned and performed under the continuous guidance and feedback of teacher to ensure
outcome of Learning.
G) Scheme of Assessment:
Scheme of Assessment (Marks)
Total Marks (PA+ ESA+ATT)
Progressive Assessment (PA) End Semester
Assessment (ESA)
Laboratory Assessment
Classro Laboratory Assessment
Classroom Assessment
Sessional work (SW)
(CA+LA+SW+ATT)
Course Course
Attendance (ATT)
om (LA)
Board Code Title Assessm
Total ESA
of Study
Total PA
(CA+LA)
ent
(CA)
(LA)
(CA)
Total (LA)
Performanc
Class
Viva -
Voce
e
Test
PRA PD
(CT)
A
CSVTU, Bhilai- NITTTR, Bhopal Page 2
Diploma in Civil Engg. Semester IV
Civil Structura 20 25 20 05 50 20 10 100 70 30 100 200
Enginee l Design
ring and
Drafting
II
Legend : PRA : Process Assessment, PDA : Product Assessment
Note: Separate passing is must for Progressive and End Semester Assessment.
H) Course-Curriculum Detailing:
This course curriculum detailing depicts learning outcomes at course level and session level and their
attainment by the students through Classroom Instruction (CI), Laboratory Instruction (LI), Sessional Work
(SW) and Self Learning (SL). Students are expected to demonstrate the attainment of Session Outcomes
(SOs) and finally Course Outcomes (COs) upon the completion of course.
Convert unit of the given physical quantity from one unit system to other.
CO-1 Design riveted and welded joints as per code IS: 800: 2007.
(Approx. Hrs: CI+LI = 19)
Session Outcomes Laboratory Instruction Class room Instruction (CI) Self Learning
(SOs) (LI) (SL)
Unit-1.0
1.0 Design of Rivetted and
Welded Joints
1.1.Introduction to IS: 800 –
2007
1.1.1 Structural steel and
properties of structural steel
1.1.2 Limit state design
1.1.3 Limit state of strength
1.1.4 Limit state of
serviceability.
1.1.5 Action (loads)
1.1.6 Design strength
1.1.7 Partial safety factor for
materials
1.1.8 Loads, Load combination
and partial safety factors for
loads.
1.1.9 Maximum effective
slenderness ratio
1.2 Riveted Connections
Types of Rivet, Permissible
stresses in rivets, types of
riveted joints, specifications
as per IS 800-2002,
Failure of riveted joint,
strength and efficiency of
CSVTU, Bhilai- NITTTR, Bhopal Page 3
Diploma in Civil Engg. Semester IV
Session Outcomes Laboratory Instruction Class room Instruction (CI) Self Learning
(SOs) (LI) riveted joint, Design of (SL)
Riveted Connection only
axially loaded number (No
staggered rivetting)
1.3
SW-1 Suggested Sessional Work (SW):
a. Assignments:
1. Explain advantages and disadvantages of concrete.
2. Identify the major Bouge’s compounds of cement? Discuss their roll in hydration of cement.
3. Differentiate between (a) Setting and hardening of cement (b) Quick setting and rapid hardening
cement.
4. Explain consistency, initial and final setting time of cement.
5. How the aggregate classified according size, shape and texture.
6. Explain grading of aggregate and its significance? Describe the process of sieve analysis for
determination of fineness modulus of an aggregate.
7. Discuss bulking of sand. If the sand is measured by volume and no allowance is made for bulking
of sand, what will be its effect on concrete?
b. Mini Project
1. Find the compressive strength of concrete block using different aggregates.
2. Find the compressive strength of concrete block using different types of cement.
3. Find the compressive strength of concrete block using binding materials and different aggregates.
CO-2 Design of tension members as per code IS: 800: 2007.
(Approx. Hrs: CI+LI = 16 )
Session Outcomes Laboratory Instruction Class room Instruction (CI) Self Learning (SL)
(SOs) (LI)
LE2.1 Test for workability ( Unit-2 Fresh concrete SL 2.1 Identify
SO2.1 Describes basic slump test): 2.1 Fresh concrete and its effect of poor
terminology related to (a)To verify the effect of properties - water cement workability during
fresh concrete. water, fine aggregate/coarse ratio, Workability, hardness, construction.
aggregate ratio and Segregation and bleeding
SO2.2 Explain and aggregate/Cement ratio SL 2.2 Identify ill
2.2 Factors affecting
recommend workability on slump workability effect of
of concrete for different (b) To test cube 2.1.3 Methods of segregation,
civil engineering works. strength of concrete with var measurement of workability bleeding, harshness
ying water cement ratio Slump Test & Compaction on structure.
SO 2.3 Explain Factor Test Vee Bee SL 2.3 Explain
concrete LE2.2 Compaction factor consistometer, flow table test
effect of improper
manufacturing test for workability 2.1.4 Recommended slumps
(IS: 1199) curing in
process. for placement in various
conditions as per IS:456- construction
SO 2.4 identify SL 2.4 Iidentify
admixture for 2000/SP-23
2.1.5 Relation between new admixtures
different concrete
workability and strength of used in construction
works. concrete
CSVTU, Bhilai- NITTTR, Bhopal Page 4
Diploma in Civil Engg. Semester IV
Session Outcomes Laboratory Instruction Class room Instruction (CI) Self Learning (SL)
(SOs) (LI) 2.2 Batching of materials, now a days.
Methods of mixing of
concrete – Hand & Machine
Mixing, mixing time ,
Transportation and Placing
of concrete.
2.3 Ready mixed concrete
,proportioning ready mixed
concrete, production of ready
mixed concrete
2.4 Methods of compaction
of concrete and its suitability
, Factors affecting
compaction
2.5 Finishing of concrete
2.6 Curing and its
importance , its methods and
suitability ,Effect of curing
on development of strength
of concrete
2.7 Admixtures and its
benefits , Types of
Admixtures - Accelerator
and Retarder Plasticizer and
Super Plasticizer and Air
entraining admixture ,
Utility of Admixtures
SW-2 Suggested Sessional Work (SW) :
a. Assignments:
1. List the limiting values of water cement ratios and cement content according to IS 456-2000
for some important situations?
2. Compare different methods to measure workability of concrete and recommend values for
placement in various conditions.
3. Explain the effect of vibration on the strength of concrete? Explain the different types of
vibrators.
4. Differentiate between volume batching and weigh batching in concrete mix procedure.
5. Explain methods of transportation of concrete.
6. Explain the ready mixed concrete with its classification.
7. Define curing of concrete and list methods of curing.
b. Mini Project:
I. Plot the effect of W/C ratio on Compressive Strength of Concrete using different admixtures.
II. Compare compressive strength of concrete using different admixtures.
c. Other Activities (Specify):
PPT on Prepare concrete for different civil engineering works as per IS specification.
CO- 3 Design of compression members, columns and column’s bases as per code IS: 800: 2007.
(Approx. Hrs: CI+LI = 16 )
Session Outcomes Laboratory Instruction (LI) Class room Instruction Self Learning
CSVTU, Bhilai- NITTTR, Bhopal Page 5
Diploma in Civil Engg. Semester IV
(SOs) (CI) (SL)
SO 3.1 Describes LE3.1. Conduct Split Hardened Concrete SL 3.1 Explain
basic terminologies Cylinder Test 3.1 Hardened Concrete and Creep of
related to hardened its Properties Concrete & its
concrete. LE 3.2. Determine the 3.2 Compressive Strength effect , factors
SO 3.2 Explain and compressive strength of ,Tensile Strength, Bond affecting Creep
concrete cubes. Strength, Flexure Strength SL 3.2 State
perform various tests
Durability, impermeability Importance of
related to hardened LE 3.3 conduct 3.3 Factors affecting NDT.
concrete. Non destructive test on concre Compressive Strength SL 3.3
te (a) Rebound hammer test 3.4 IS Test Procedure to summarizes
SO 3.3 find Compressive & different types
Identify use of LE 3.4 determine flexural Tensile Strength of of special
special concrete for strength of concrete beam Concrete, Acceptance concrete.
different construction Criteria , Mean Strength &
works. Standard Deviation
3.5 Durability of Concrete
& factors affecting it
3.6 Economy of Concrete
& factors affecting it
3.7 Methods of Non
Destructive Test of
Concrete Rebound
Hammer Test, Ultrasonic
Pulse Velocity Test
3.9 Introduction to Special
concrete: Light weight
concrete, Mass concrete,
Fibre reinforced concrete,
Polymer concrete, High
density concrete, No fines
concrete, Ferro cement,
Shortcrete
SW-3 Suggested Sessional Work (SW) :
a. Assignments:
1. Enumerate the fundamental factors influencing the compressive strength of concrete.
2. How are the compressive and flexural strength of concrete determined?
3. Discuss the various aspect of durability of concrete. What measures are suggested by IS 456-2000 to
ensure durable structures.
4. What is non destructive test of hardened concrete? Describe ultrasonic pulse velocity test.
5. Discuss the properties of structural lightweight concrete and its applications.
6. Define is shotcrete? Explain the procedure of shotcreting a surface.
7. Explain fibre reinforced concrete and its advantages.
8. Explain ferrocement.
9. Enlist polymer concrete composites.
CO- 4 Design of steel beams as per code IS: 800: 2007.
(Approx. Hrs: CI+LI = 16)
Session Outcomes Laboratory Instruction Class room Instruction (CI) Self Learning
CSVTU, Bhilai- NITTTR, Bhopal Page 6
Diploma in Civil Engg. Semester IV
(SOs) (LI) (SL)
SO4.1 Explain the LE 4.1 Perform Concrete Concrete Mix design
need of quality Mix Design by weight 4.1 Factors causing variation in SL4.1
control. batching as per I. S. quality of concrete, Distinguish the
SO4.2 Interpret Method. 4.2 Field Control , Advantages volumetric
concrete mix design. of Quality control. analysis and
SO4.3 Perform 4.3 Statistical Quality control. analytical (by
Concrete Mix Design 4.4.1 Concrete Mix Design and weight) analysis.
as per I. S. Method its importance.
4.4.2 Nominal Mix and Design SL 4.2 Compare
Mix. the mix design
4.4.3 Factors affecting concrete using different
mix design. quality of
4.4.4 Different methods of Mix aggregates.
Design and its suitability.
4.5 I.S. method to design a
Concrete Mix As per IS 10262-
2009.
4.6 Example of Mix design as
per I.S. method
4.7 safety precautions observed
SW-4 Suggested Sessional Work (SW):
a. Assignments:
1. Briefly explain the factors causing variation in the quality of concrete. What parameters are used in
measuring this variability?
2. Identify the advantages of quality control?
3. Enlist the factors governing the design of concrete mix.
4. Describe the procedure for concrete mix proportioning using IS 10262-2009 with the help of its flow
chart.
5. Define trial mixes and how do they help in achieving the objectives of mix design?
b. Mini Project
1. Mix design for given set of data.
CO- 5 CO-5 Analyze continuous beam, roof trusses and design of roof trusses as per code IS: 800:
2007.
(Approx. Hrs: CI+LI = 16 )
Session Outcomes Laboratory Instruction Class room Instruction (CI) Self Learning
(SOs) (LI) (SL)
CSVTU, Bhilai- NITTTR, Bhopal Page 7
Diploma in Civil Engg. Semester IV
Session Outcomes Laboratory Instruction Class room Instruction (CI) Self Learning
(SOs)
SO5.1 Identifies the (LI) Defects and Repair of (SL)
cause for concrete
deterioration/defects of 5.1 Deterioration of concrete, 5.1 Latest
concrete and its Types of deteriorations and its research and
prevention. effects, Prevention of concrete development in
SO5.2 Identifies the deterioration the field of
cause for corrosion in 5.2 Corrosion of concrete
reinforcement and its reinforcement, Effect of technology
prevention. corrosion of reinforcement in 5.2 Journals
concrete and remedial available in the
SO5.3 Explains Types, measures
causes and remedies of library, its
5.3 Types, causes and publishers,
concrete cracks before remedies of concrete cracks
hardening and after Editors and place
before hardening and after of publications.
hardening. hardening 5.3 The various
SO5.4 Summarize 5.4 Evaluation of cracks, authorities in the
materials to use for methods of evaluation of field of concrete
repair cracks. cracks technology and
SO5.5 Apply different 5.5 Prevention of cracks , their field of
methods to repair cracks Materials for repair of cracks specialization.
in concrete. ,Methods used for repair of
cracked Concrete
5.6 Repair and strengthening
of column, repair of concrete
floor slab system, overlays and
surface treatments, underwater
repairs.
5.7 Strengthening of damaged
structures, section
enlargement, Strengthening of
beams and slabs.
Legend: CI: Classroom Instruction (Includes different instructional strategies i.e. Lecture (L) and Tutorial (T) and
others), LI : Laboratory Instruction (Includes Practical performances in Laboratory, Workshop, field or other
locations using different instructional strategies) SL: Self Learning
SW-5 Suggested Sessional Work (SW) :
a. Assignments:
1. Enumerate types of deteriorations, its effects and Prevention.
2. Explain effect of corrosion and its remedial measures.
3. Explain briefly the purpose and procedure for the damage assessment in concrete element.
4. Write short notes on materials and methods used for repair of cracks in Concrete.
5. Explain briefly the strengthening of deficient structures.
b. Mini Project:
Prepare a report on cracks in the college building and its causes.
c. Other Activities (Specify):
1. Describe common types of repairs of cracks.
.
Note: Performance under Laboratory and Sessional work may appear in more than one COs/SOs.
CSVTU, Bhilai- NITTTR, Bhopal Page 8
Diploma in Civil Engg. Semester IV
CSVTU, Bhilai- NITTTR, Bhopal Page 9
Diploma in Civil Engg. Semester IV
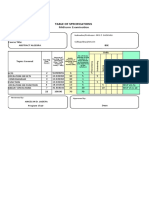
I) Suggested Specification Table (For ESA of Classroom Instruction CI+SW+SL):
Unit Unit Marks Distribution Total
Num Title R U A Marks
ber
I Introduction to Concrete 4 6 4 14
II Fresh concrete 4 6 4 14
III Hardened Concrete 4 6 4 14
IV Concrete Mix design 4 6 4 14
V Defects and Repair of concrete 4 6 4 14
Total 20 30 20 70
Legend: R: Remember, U: Understand, A: Apply and above
J) Suggested Specification Table (For ESA of Laboratory Instruction*):
Assessment of
Laboratory Work
Laborator
(Marks)
y
Short Laboratory Experiment Title
Instructio
Performance Viva-
n Number
PRA PDA Voce
LE 1.1 Determines fine silt in aggregate by field method. 25 20 05
LE 1.2 Determine flakiness index and elongation index of
coarse aggregate (IS 2386Part I)
LE 1.3 Determine specific gravity and water absorption of
aggregate (IS2386part III for aggregates of
size 40 mm to 10 mm)
LE 1.4 Determine
the compressive strength of Portland cement (IS269)
LE 1.6 Perform Field test of cement
LE 1.5 Determine of bulk density
and voids of aggregates ((IS2386part III)
LE 1.6 Determine particle size distribution of fine, coarse and
all in aggregate by sieve
analysis (grading of aggregate)
LE 1.7 7Determine Fineness modulus of fine and coarse
aggregate by sieve analysis.
Determine particle size distribution of fine, coarse and
LE 1.8 all in aggregate by sieve
CSVTU, Bhilai - NITTTR, Bhopal Page 10
Diploma in Civil Engg. Semester IV
analysis (grading of aggregate)
LE2.1 Test for workability (slump test): (a)To verify the
effect of water, fine aggregate/coarse aggregate ratio
and aggregate/Cement ratio on slump (b) To test cube
strength of concrete with varying water cement ratio
LE2.2 Compaction factor test for workability (IS: 1199)
LE3.1. Conduct Split Cylinder Test
LE 3.2. Determine the compressive strength of concrete cubes.
LE 3.3 conduct Non destructive test on concrete (a) Rebound
hammer test (b) Ultrasonic pulse velocity test
LE 3.4 Determine flexural strength of concrete beam
LE 4.1 Perform Concrete Mix Design by weight batching as
per I. S. Method.
* Assessment rubric, process and product check list with rating scale need to be prepared by the course
wise teachers for each experiment for conduction and assessment of laboratory experiments /practicals
Legend : PRA: Process Assessment, PDA : Product Assessment
Note : Only one experiment has to performed at the end semester examination of 30 Marks as
per assessment scheme
CSVTU, Bhilai - NITTTR, Bhopal Page 11
Diploma in Civil Engg. Semester IV
K) Suggested Instructional/Implementation Strategies:
1. Improved Lecture
2. Tutorial
3. Case Method
4. Industrial visits
5. Industrial Training
6. Field Trips
7. Demonstration
8. ICT Based Teaching Learning (Video Demonstration, CBT, Blog, Face book, Mobile)
9. Brainstorming
10. Others
L) Suggested Learning Resources:
(a) Books :
S. Title Author Publisher Edition & Year
No.
1 Concrete Technology M. S. Shetty S. Chand
2 Concrete Technology M. L. Gambhir Tata Mcgraw 5th , 2013
Hill Education
Private Limited
3 Concrete Technology S. S. Bhavikatti I. K. 2015
International
Publishing
House
(b) Open source software and website address :
1. nptel.ac.in
2. swayam portal
M) List of Major Laboratory Equipment and Tools:
S. Name of Equipment Broad Relevant
No. Specifications Experiment
Number
1 Flakiness and As per IS CODE 2386Part I LE 1.2
Elongation gauge
2 Weighing Machine 50 kg, 10 kg, 1 kg LE 1.2,, LE 1.3,
LE 1.4, LE 1.7,
LE 1.8,LE 4.1
3 Sieve set IS standard sieve sets 80 mm, 40 mm, 20 LE 1.7, LE 1.8,
mm, 10 mm, 4.75 mm, 30 cm dia sieve LE 4.1
with lid and pan
4 Sieve Shaker motorised LE 1.7 , LE 1.8
6 Automatic electric Automatic electric Oven LE 1.3
Oven
7 Compression testing 2000 KN Compression testing machine, 9 LE 1.4, LE 3.2
machine with mould nos 7.06 X 7.06 X 7.06 cm3 mould, 9 nos
CSVTU, Bhilai - NITTTR, Bhopal Page 12
Diploma in Civil Engg. Semester IV
and complete set 15 X 15 X 15 T cm3 mould ,temping Rod,
spatula
8 Vibrating table Electrically operated LE 3.2
9 Sieve set for FA IS standard sieve sets 4.75 mm, 2.36 mm, LE 1.7, LE 1.8,
1.18 mm, 600 microns, 300 microns,150 LE 4.1
microns, 90 microns , 75 microns, 20 cm
dia sieve with lid and pan
9 Slump cone apparatus Slump cone apparatus set as per IS code LE 2.1
10 Compaction factor Compaction factor apparatus complete set LE 2.2
test IS: 1199 as per code IS: 1199
12 Split cylinder test 10 cm X 30 cm cylinder LE 3.1
apparatus for tensile
strength of concrete
13 Rebound IS I 3311 LE 3.3
hammer apparatus
14 UTM 20 Ton capacity, LE 3.2 ,LE 3.4
N) Mapping of POs & PSOs with COs:
Programme Outcomes Programme
Course (POs) Specific
Outcomes Outcomes
(COs) (PSOs)
Titles
Basic Discipline Experiments Engineerin The Environment Ethics Individual & Communication Life Long
knowledge knowledge & Practice g Tools Engineer & & PO-7 Team work PO-9 learning PSO-1 PSO-2
PO-1 PO-2 PO-3 PO-4 Society Sustainabilit PO-8 PO-10
PO-5 y
PO-6
CO 1 - 3 3 2 - 1 - 1 - 2 3 3
Identify the
need of
concrete
and
importance
of each
ingredient.
CO 2 - 3 3 2 - 1 - 1 - 2 3 3
Prepare
concrete
for
different
civil
engineering
works as
per IS
specificatio
n.
CO- 3 - 3 3 2 - 1 - 1 - 2 3 3
CSVTU, Bhilai - NITTTR, Bhopal Page 13
Diploma in Civil Engg. Semester IV
Identify
desired
properties in
hardened
concrete and
Use of
special
concrete.
CO- 4 - 3 3 2 - 1 - 1 - 2 3 3
Prepare
concrete mix
design as
per IS
method.
CO- 5 Apply - 3 3 2 - 1 - 1 - 2 3 3
prevention
and repair
techniques
on concrete
cracks.
CSVTU, Bhilai - NITTTR, Bhopal Page 14
Diploma in Civil Engg. Semester IV
O) Course Curriculum Map:
POs & PSOs COs No. & Title SOs No. Laboratory Classroom Instruction Self Learning
No. Instruction (CI) (SL)
(LI)
PO- CO - 1 Identify the need of SO1.1 LE1.1 Unit 1 Introduction to the SL 1.1
2,3,4,6,8,10 concrete and importance of SO1.2 LE1.2 Concrete SL 1.2
PSO-1,2 each ingredient. SO1.3 LE1.3
SO 1.4 LE 1.4
SO 1.5 LE 1.5
LE 1.6
LE 1.7
LE 1.8
PO- CO - 2 Prepare concrete for SO.2.1 LE. 2.1 Unit 2 Fresh concrete SL 2.1
2,3,4,6,8,10 different civil engineering SO.2.2 LE. 2.2 SL 2.2
PSO-1,2 works as per IS specification SO2.3 SL 2.3
SO 2.4 SL 2.4
PO- CO- 3 Identify desired SO.3.1 LE3.1 Unit 3 Hardened concrete SL 3.1
2,3,4,6,8,10 properties in hardened concrete SO3.2 LE 3.2 SL 3.2
PSO-1,2 and Use of special concrete. SO3.3 LE3.3 SL 3.3
LE3.4
PO- CO- 4 Prepare SO4.1 LE4.1 Unit 4 Concrete Mix SL 4.1
2,3,4,6,8,10 concrete mix design as per IS SO4.2 design SL 4.2
PSO-1,2 method. SO4.3
PO- CO- 5 Apply prevention and SO5.1 Unit 5 Defects and repair SL 5.1
2,3,4,6,8,10 repair techniques on concrete SO5.2 techniques on concrete SL 5.2
PSO-1,2 cracks. SO5.3 cracks. SL 5.3
SO 5.4
SO 5.5
CSVTU, Bhilai - NITTTR, Bhopal Page 15
Diploma in Civil Engg. Semester IV
Legend: CI: Classroom Instruction (Includes different instructional strategies i.e. Lecture (L) and Tutorial (T) and others) , LI : Laboratory Instruction
(Includes Practical performances in Laboratory, Workshop, field or other locations using different instructional strategies) SL: Self Learning
CSVTU, Bhilai - NITTTR, Bhopal Page 16
You might also like
- Boiler Magnetite Exfoliation Report June 2005Document23 pagesBoiler Magnetite Exfoliation Report June 2005lacoste11111100% (1)
- Final Webpage DesignDocument9 pagesFinal Webpage DesignAnonymous OGVOs4VBNo ratings yet
- Indian ConstitutionDocument5 pagesIndian Constitutionyexov33854No ratings yet
- Python ProgrammingDocument10 pagesPython Programmingyexov33854No ratings yet
- Elements of Aeronautical EngineeringDocument6 pagesElements of Aeronautical Engineeringyexov33854No ratings yet
- 16. Diploma in Civil Engineering (Rural Engineering) Sem-IDocument82 pages16. Diploma in Civil Engineering (Rural Engineering) Sem-Igovindbgs06No ratings yet
- SEM IV 21 Electronics EngineeringDocument30 pagesSEM IV 21 Electronics EngineeringyogeshNo ratings yet
- Fluids Mechanics & MachineryDocument6 pagesFluids Mechanics & Machineryyexov33854No ratings yet
- Abet Format Syllabus - GCV463 - Specifications & BOQ - 201710Document3 pagesAbet Format Syllabus - GCV463 - Specifications & BOQ - 201710Oec EngNo ratings yet
- Basic Simulation LabDocument3 pagesBasic Simulation LabGautam KumarNo ratings yet
- 5th Sem & 6th Sem Syllabus KukDocument31 pages5th Sem & 6th Sem Syllabus KukvivekNo ratings yet
- VTH Sem - Computer Science EngineeringDocument18 pagesVTH Sem - Computer Science EngineeringPriyanshi YadavNo ratings yet
- Cse Btech III Yr V Sem Scheme Syllabus July 2022Document26 pagesCse Btech III Yr V Sem Scheme Syllabus July 2022Ved Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- I Sem: Scheme of Teaching and Examination of B. Architecture (Cbcs Scheme-2018)Document9 pagesI Sem: Scheme of Teaching and Examination of B. Architecture (Cbcs Scheme-2018)Pooja vijayNo ratings yet
- Bca F.Y.Document33 pagesBca F.Y.backtogNo ratings yet
- Holy Spirit University of Kaslik: Course SyllabusDocument3 pagesHoly Spirit University of Kaslik: Course SyllabusElie OtayekNo ratings yet
- State Board of Technical Education, Bihar: V Semester Diploma in Civil Engineering / Civil (Rural) EngineeringDocument22 pagesState Board of Technical Education, Bihar: V Semester Diploma in Civil Engineering / Civil (Rural) EngineeringPranjal PandeyNo ratings yet
- 4th Sem 15 Civil Engineering PDFDocument12 pages4th Sem 15 Civil Engineering PDFdhiraj kumarNo ratings yet
- SEM IV 15 Civil EngineeringDocument20 pagesSEM IV 15 Civil EngineeringArman RajNo ratings yet
- W.e.f.-July-2010 Academic Session-2010-11 1Document27 pagesW.e.f.-July-2010 Academic Session-2010-11 1Devil KingNo ratings yet
- F.Y.B.Sc Electronics Syllabus NEP 2020Document39 pagesF.Y.B.Sc Electronics Syllabus NEP 2020Dipak ValviNo ratings yet
- SEM III BR Computer Science and EngineeringDocument21 pagesSEM III BR Computer Science and EngineeringyogeshNo ratings yet
- 1 HR 1 HR Tutorial 2 HR Practical 1 CreditDocument7 pages1 HR 1 HR Tutorial 2 HR Practical 1 CreditHitesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- VTU B.arch Syllabus 2018 SchemeDocument33 pagesVTU B.arch Syllabus 2018 SchemeKruthiNo ratings yet
- Barchchsyll1 5Document33 pagesBarchchsyll1 5AnirudhMagniNo ratings yet
- HMT - Course FileDocument16 pagesHMT - Course FileajitsssNo ratings yet
- DVTP LAB Manual R21 ITDocument44 pagesDVTP LAB Manual R21 ITanyoneNo ratings yet
- Ce 6Document1 pageCe 6btirt btirtNo ratings yet
- SEM-VI-15-Civil-Engineering SajjanDocument110 pagesSEM-VI-15-Civil-Engineering Sajjanthenomore poetryNo ratings yet
- CSE VIII Semester Scheme Syllabus 2Document21 pagesCSE VIII Semester Scheme Syllabus 2garima khasdeoNo ratings yet
- Abet Format Syllabus - GCV405 - Reinforced Concrete II - Rev 20180827Document3 pagesAbet Format Syllabus - GCV405 - Reinforced Concrete II - Rev 20180827Oec EngNo ratings yet
- B.tech CSE Syllabus 2020-24-09-Apr-20 VNDocument191 pagesB.tech CSE Syllabus 2020-24-09-Apr-20 VNsatyam sharmaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - CBGS I and II Semester SET A 6july17Document26 pagesMicrosoft Word - CBGS I and II Semester SET A 6july17tejpratapNo ratings yet
- 2018-19 F.E. To B.E. Mechanical Engineering StructureDocument11 pages2018-19 F.E. To B.E. Mechanical Engineering Structurenavneetkpatil8409No ratings yet
- Course Contents/Syllabus:: L T P/S SW/F W Total Credit UnitsDocument6 pagesCourse Contents/Syllabus:: L T P/S SW/F W Total Credit UnitsSDMNo ratings yet
- Estimation, Costing and SpecificationsDocument4 pagesEstimation, Costing and SpecificationsPronceNo ratings yet
- Ce 7Document1 pageCe 7btirt btirtNo ratings yet
- PattonDocument2 pagesPattonATHISH 02No ratings yet
- Revised B.com. Program SyllabusDocument31 pagesRevised B.com. Program Syllabussayakkarmakarslg1No ratings yet
- Cse Btech IV Yr Vii Sem Scheme Syllabus July 2022Document25 pagesCse Btech IV Yr Vii Sem Scheme Syllabus July 2022Ved Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Proposed B.tech First Year Scheme 2024 - 28Document3 pagesProposed B.tech First Year Scheme 2024 - 28sachinsaurav89No ratings yet
- Teaching Scheme of M. Tech Artificial IntelligenceDocument4 pagesTeaching Scheme of M. Tech Artificial IntelligenceJahanvi SharmaNo ratings yet
- SEM V 15 Civil EngineeringDocument45 pagesSEM V 15 Civil EngineeringAman KumarNo ratings yet
- B. Tech Computer Science and Buisness Systems SchemeDocument6 pagesB. Tech Computer Science and Buisness Systems SchemeAkshayNo ratings yet
- CSE IYearAutonomoussyllabusDocument52 pagesCSE IYearAutonomoussyllabusRazha GarrixNo ratings yet
- 4th Semester Electronics Engg.Document24 pages4th Semester Electronics Engg.PRAKASH GOSWAMINo ratings yet
- 4th 5th 6th Semester Electronics Engg. Merged PDFDocument60 pages4th 5th 6th Semester Electronics Engg. Merged PDFShubham kumarNo ratings yet
- 4 - 09-14-2021 - 14-46-32 - B.Tech CSE 4th YearDocument53 pages4 - 09-14-2021 - 14-46-32 - B.Tech CSE 4th YearGOURAB PANDITNo ratings yet
- New SyllabusDocument3 pagesNew SyllabusAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Ce 5Document1 pageCe 5btirt btirtNo ratings yet
- 78th PDFDocument35 pages78th PDFsushantNo ratings yet
- BE CSE AI&DS 19-5-2022 Scheme and SyllabusDocument69 pagesBE CSE AI&DS 19-5-2022 Scheme and SyllabusMOFANo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering Scheme of Instruction & Examination and Syllabi B.E. I and II Semesters (Group-A) of Four Year Degree Programme in B.E.Document25 pagesFaculty of Engineering Scheme of Instruction & Examination and Syllabi B.E. I and II Semesters (Group-A) of Four Year Degree Programme in B.E.Ramavath sunil naikNo ratings yet
- Co - WCS 5013Document5 pagesCo - WCS 5013Sani Oghang PekanNo ratings yet
- Table of Specifications: Midterm ExaminationDocument2 pagesTable of Specifications: Midterm ExaminationShela RamosNo ratings yet
- Syllubs SEM-IV-15-Civil-EngineeringDocument23 pagesSyllubs SEM-IV-15-Civil-EngineeringrandhirNo ratings yet
- Fea RDocument21 pagesFea RajithjkingsNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-06-18 at 4.35.56 PMDocument13 pagesScreenshot 2023-06-18 at 4.35.56 PMNikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Subhajit Bed PDFDocument2 pagesSubhajit Bed PDFSubhajit BakshiNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Teaching and Examination For Vi Semester Diploma in Civil EngineeringDocument32 pagesScheme of Teaching and Examination For Vi Semester Diploma in Civil EngineeringYashwant BadoleNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam-Testing Concept-PERT/CPM/Gantt Chart/FPA/EVA/Timebox (Chapter-3)From EverandCISA Exam-Testing Concept-PERT/CPM/Gantt Chart/FPA/EVA/Timebox (Chapter-3)Rating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (3)
- Bill of Materials - Cost and ESTIMATESDocument38 pagesBill of Materials - Cost and ESTIMATESmnmusorNo ratings yet
- Jeffadd Additives: Performance ProductsDocument2 pagesJeffadd Additives: Performance ProductsPhuong The NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chemi Presentation 2Document25 pagesChemi Presentation 2teddyNo ratings yet
- Sample - Objective Ques Engg MaterialDocument1 pageSample - Objective Ques Engg MaterialAnunay MilindNo ratings yet
- Ingevity Capa CoatingsDocument4 pagesIngevity Capa CoatingsKanagarajan VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Rdlo / Rdlo V: Axially Split Volute Casing PumpDocument24 pagesRdlo / Rdlo V: Axially Split Volute Casing PumpfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Influence of Nano - Sized Powder Content On Physical Properties of Waste Acid Refractory BrickDocument19 pagesInfluence of Nano - Sized Powder Content On Physical Properties of Waste Acid Refractory BrickamnajamNo ratings yet
- Romans and Architecture PDFDocument86 pagesRomans and Architecture PDFDevika Hemalatha DeviNo ratings yet
- Chapter-10 Case StudiesDocument4 pagesChapter-10 Case Studiessafeer ahmadNo ratings yet
- SOP For Cleaning and Sterilization of Glass Ware Used in Microbiology Lab.Document3 pagesSOP For Cleaning and Sterilization of Glass Ware Used in Microbiology Lab.Bejoy Karim100% (1)
- Wrought Alloys: Near Equivalent Designations: Table - 1Document3 pagesWrought Alloys: Near Equivalent Designations: Table - 1Chidanand KoppaNo ratings yet
- Batc NFMDocument75 pagesBatc NFMMaria BotelhoNo ratings yet
- Centricast CL 1520 Piping System Spec SheetDocument2 pagesCentricast CL 1520 Piping System Spec SheetOlmer Romero MendezNo ratings yet
- B P ® G EP: Lack Earl ReaseDocument3 pagesB P ® G EP: Lack Earl ReaseWeslei BritoNo ratings yet
- The Ancient Metallurgy in AzerbaijanDocument12 pagesThe Ancient Metallurgy in AzerbaijanAlireza EsfandiarNo ratings yet
- Combustion and Flame Class 8Document4 pagesCombustion and Flame Class 8Vinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Caillebotis AMICODocument112 pagesCaillebotis AMICOMathieu NormandeauNo ratings yet
- Flame Retardant PolymerDocument13 pagesFlame Retardant Polymerpolypolyy100% (1)
- Liquefied Gas Tanker Familiarisation CourseDocument266 pagesLiquefied Gas Tanker Familiarisation CourseGeorge Ponpyka100% (7)
- 6,123 (&,QGXVWULDO/XEULFDQWV: SINOPEC Industrial LubricantDocument12 pages6,123 (&,QGXVWULDO/XEULFDQWV: SINOPEC Industrial LubricantSalman Ahmed PrinceNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes Ch08 The Dblock F-Block ElementsDocument4 pages12 Chemistry Notes Ch08 The Dblock F-Block ElementsABHISHEKNo ratings yet
- Material List Grounding Untuk PO Rev.1Document2 pagesMaterial List Grounding Untuk PO Rev.1BANGGANo ratings yet
- New Procedures For Materials 2020Document700 pagesNew Procedures For Materials 2020Mengalvio GraçaNo ratings yet
- GR 11 Chemistry Exam ReviewerDocument7 pagesGR 11 Chemistry Exam ReviewerrdncdNo ratings yet
- PFDDocument8 pagesPFDSanthoz JaganNo ratings yet
- Clent List Delhi NCRDocument11 pagesClent List Delhi NCRabhimanyu.xplastNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 The S-Block ElementsDocument18 pagesChapter 10 The S-Block ElementsYash PlayNo ratings yet
- Tech. Specs. For Metal Doors, Windows, Ventlators Louvers Etc.Document8 pagesTech. Specs. For Metal Doors, Windows, Ventlators Louvers Etc.SaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- How Many KG of Cement Is Needed For A Meter Cube of Concrete - QuoraDocument5 pagesHow Many KG of Cement Is Needed For A Meter Cube of Concrete - QuoraPd ProxyNo ratings yet