Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Digitalsignaturevmp
Digitalsignaturevmp
Uploaded by
Anumod Pattari0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views9 pagesDigital signatures provide authentication of electronic documents and messages in the same way physical signatures authenticate paper documents. They use public key cryptography where a private key is used to encrypt a digital signature and a corresponding public key is used to decrypt and verify the signature. This ensures the message was not altered and authenticates the sender. Some advantages of digital signatures are they are faster and more cost efficient than physical signatures, help prevent alteration of documents, and make it easy to share signed documents electronically. However, digital signatures also have limitations like needing secure private keys and being unable to provide non-repudiation on their own.
Original Description:
Original Title
digitalsignaturevmp.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDigital signatures provide authentication of electronic documents and messages in the same way physical signatures authenticate paper documents. They use public key cryptography where a private key is used to encrypt a digital signature and a corresponding public key is used to decrypt and verify the signature. This ensures the message was not altered and authenticates the sender. Some advantages of digital signatures are they are faster and more cost efficient than physical signatures, help prevent alteration of documents, and make it easy to share signed documents electronically. However, digital signatures also have limitations like needing secure private keys and being unable to provide non-repudiation on their own.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views9 pagesDigitalsignaturevmp
Digitalsignaturevmp
Uploaded by
Anumod PattariDigital signatures provide authentication of electronic documents and messages in the same way physical signatures authenticate paper documents. They use public key cryptography where a private key is used to encrypt a digital signature and a corresponding public key is used to decrypt and verify the signature. This ensures the message was not altered and authenticates the sender. Some advantages of digital signatures are they are faster and more cost efficient than physical signatures, help prevent alteration of documents, and make it easy to share signed documents electronically. However, digital signatures also have limitations like needing secure private keys and being unable to provide non-repudiation on their own.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 9
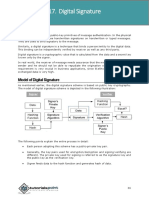
DIGITAL SIGNATURES
Digital signatures are used to authenticate the
identity of the sender. It is like signing a
message in electronic form. A digital signature
is a protocol that produces the same effect as
a real signature. It is a mark that only the
sender can make and other people can easily
recognize that it belongs to the sender.
PDF documents are used to share all kinds of
information, including that of a confidential
nature or with a legal value, like a contract. In
order to ensure that a document has not been
modified by someone other than its author,
and to verify that the author is who we expect
and not somebody else, digital signatures are
necessary.
Digital signatures are often used to implement
electronic signatures, which includes any
electronic data that carries the intent of a
signature, but not all electronic signatures use
digital signatures. Digital seals and signatures
are equivalent to handwritten signatures and
stamped seals.
Advantages of digital signatures v/s handwritten
signatures
The crucial difference of the handwritten
signature is that the electronic signature
Da(m) is intimately connected with the
message, whereas the handwritten signature
is added to the message and always looks the
same and that's why is easy to forge. As a
consequence no one can alter the signed
message Da(m) and trying to make it seem as
if the signature is by the real person. For, if
Da(m) is altered at all, then the application of
the public key Ea to the altered signed
message Da(m)" yields a clear text which will
appear totally random. Sending documents
digitally is faster and more cost-efficient.
Digital signing software is easy to use and
cost-effective.
E-documents dramatically reduce the risk of
being stolen, damaged, intercepted, lost,
destroyed, altered, or read by unwanted eyes.
One of the benefits of electronic signature
software is it’s designed to seamlessly
integrate with other applications, so you can
use it to sign different kinds of documents in
various formats.
Digital signatures make it easy to close a sale
on the spot, turn around contracts faster, and
finalize documents that require signatures
from multiple parties.
Disadvantage using digital signatures
Once an entire signature is published by the
signer, anyone can verify it. But moreover
once the signature has been verified,
(assuming that this is an originally signed
document with no copies after being signed)
no one else may verify the signature.
One obvious solution to this would be to
make copies of the signed document.
Another solution could turn the problem of
digital signature into an advantage. Using
digital signatures we can specify who will
verify the signature exclusively:
The private key must be kept in a secured
manner. Although digital signature provides
authenticity, it does not ensure secrecy of the
data.
To provide the secrecy, some other technique
such as encryption and decryption needs to
be used.
The process of generation and verification of
digital signature requires considerable
amount of time.
When the digital signature is not verified by
the public key, then the receiver simply marks
the message as invalid but he does not know
whether the message was corrupted or the
false private key was used.
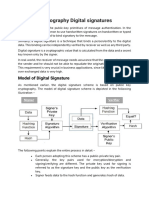
Digital signature creation
The creation of a Digital Signature is a
complex mathematical process. However as
the complexities of the process are computed
by the computer, applying a Digital Signature
is no more difficult that creating a
handwritten one.
Digital signatures are based on public key
cryptography, also known as asymmetric
cryptography. Using a public key algorithm,
such as RSA, one can generate two keys that
are mathematically linked: one private and
one public.
Digital signatures work because public key
cryptography depends on two mutually
authenticating cryptographic keys. The
individual who is creating the digital signature
uses their own private key to encrypt
signature-related data; the only way to
decrypt that data is with the signer's public
key. This is how digital signatures are
authenticated.
MAC (Message
Authentication Code
A message authentication code (MAC), or tag,
is a security code that is typed in by the user
of a computer to access accounts or portals.
This code is attached to the message or
request sent by the user. Message
authentication codes (MACs) attached to the
message must be recognized by the receiving
system in order to grant the user access.
Message authentication codes (MACs) are
commonly used in electronic funds transfers
(EFTs) to maintain information integrity. They
confirm that a message is authentic; that it
really does come, in other words, from the
stated sender, and hasn’t undergone any
changes en route. A verifier who also
possesses the key can use it to identify
changes to the content of the message in
question.
A message authentication code (MAC)
(sometimes also known as keyed hash)
protects against message forgery by anyone
who doesn't know the secret key (shared by
sender and receiver).
This means that the receiver can forge any
message – thus we have both integrity and
authentication (as long as the receiver doesn't
have a split personality), but not non-
repudiation.
Also an attacker could replay earlier messages
authenticated with the same key, so a
protocol should take measures against this .
(Also, in case of a two-sided conversation,
make sure that either both sides have
different keys, or by another way make sure
that messages from one side can't sent back
by an attacker to this side.)
Limitations of MAC
* Establishment of Shared Secret.
* Inability to Provide Non-Repudiation.
submitted by: Vishnu MP
PCS051824
You might also like
- ServiceNow Encryption OptionsDocument41 pagesServiceNow Encryption OptionsMarcusViníciusNo ratings yet
- Unlocking The Cloud Operating Model: Achieving The Fastest Path To Value in A Modern, Multi-Cloud DatacenterDocument25 pagesUnlocking The Cloud Operating Model: Achieving The Fastest Path To Value in A Modern, Multi-Cloud DatacenterPo DragonwarriorNo ratings yet
- Digitel SignatureDocument21 pagesDigitel Signatureapi-3746880No ratings yet
- Digital SignatureDocument13 pagesDigital SignatureradhikaNo ratings yet
- Digital Signature PRJCTDocument23 pagesDigital Signature PRJCTGANESH KANDNo ratings yet
- Digital Signature 2Document10 pagesDigital Signature 2vikasNo ratings yet
- Digital SignatureDocument18 pagesDigital Signaturesahil tiwariNo ratings yet
- Digital Signatures: Digital Signatures Are Used To "Sign" Messages To Validate The Source and Integrity of The ContentsDocument33 pagesDigital Signatures: Digital Signatures Are Used To "Sign" Messages To Validate The Source and Integrity of The ContentsSaad MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Digital SignatureDocument27 pagesDigital SignatureUday SankarNo ratings yet
- Digital Signatures: Model of Digital SignatureDocument4 pagesDigital Signatures: Model of Digital SignatureMansiNo ratings yet
- Digital Signature11Document5 pagesDigital Signature11Lukman HadiyatullohNo ratings yet
- Egerton University COMP 424: Computer SecurityDocument10 pagesEgerton University COMP 424: Computer SecuritySylas Okong'oNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report 2010 Digital SignatureDocument31 pagesSeminar Report 2010 Digital SignatureBibinMathew100% (1)
- Digital SignatureDocument3 pagesDigital SignatureNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Networks Internet E-Commerce Mobile Telephones Wireless Microphones Wireless Intercom Bluetooth Automatic Teller MachinesDocument6 pagesNetworks Internet E-Commerce Mobile Telephones Wireless Microphones Wireless Intercom Bluetooth Automatic Teller MachinessufiyanamujawarNo ratings yet
- Block Chain NotesDocument15 pagesBlock Chain Notesnaveen pareekNo ratings yet
- "Digital Signatures Under Information Technology Act 2000 ": Project ReportDocument15 pages"Digital Signatures Under Information Technology Act 2000 ": Project ReportkartikNo ratings yet
- Digital Signature ReportDocument15 pagesDigital Signature ReportSaša ĐorđevićNo ratings yet
- Seminar Digital SignatureDocument11 pagesSeminar Digital Signaturegarima_gaur27No ratings yet
- Digital SignatureDocument5 pagesDigital SignatureYugeshNo ratings yet
- DigitalSignature LecDocument26 pagesDigitalSignature LecInshal AyazNo ratings yet
- Digital SignatureDocument13 pagesDigital Signaturebpanigrahi306No ratings yet
- Cryptography Digital SignaturesDocument3 pagesCryptography Digital SignaturesAnasham TegegnNo ratings yet
- Digital Signature (Application of Image Processing)Document7 pagesDigital Signature (Application of Image Processing)giridharkumarabNo ratings yet
- Digital SignatureDocument21 pagesDigital SignatureAvneet KaurNo ratings yet
- Digital Signature: A Seminar Report OnDocument22 pagesDigital Signature: A Seminar Report Onthasneem khanum 596No ratings yet
- Digital SignatureDocument4 pagesDigital SignatureLAUNDANo ratings yet
- Digtal Signature 19mco014Document2 pagesDigtal Signature 19mco014emmanual cheeranNo ratings yet
- Digital SignatureDocument4 pagesDigital SignatureMuskan BhagiaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Digital SignatureDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Digital SignatureDhruv JainNo ratings yet
- Digital SignaturesDocument6 pagesDigital SignaturesVaishnavi/ven .PNo ratings yet
- Ecommerce Notes For BcomDocument115 pagesEcommerce Notes For BcomDrKrishna Priya ChakireddyNo ratings yet
- E&clDocument10 pagesE&clSBANo ratings yet
- Expt 10 Digital SignaturesDocument2 pagesExpt 10 Digital SignaturesaniketNo ratings yet
- Digital Signature Seminar ReportDocument20 pagesDigital Signature Seminar ReportMukesh Chetwani0% (1)
- Cyber Laws and Ethics, Digital Signature and E-RecordsDocument29 pagesCyber Laws and Ethics, Digital Signature and E-RecordsAnkush Kumar YedeNo ratings yet
- The Different Types of Threats On The Internet, Which Can Create DamageDocument11 pagesThe Different Types of Threats On The Internet, Which Can Create DamageHariharKaliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Digital SignatureDocument6 pagesChapter 5 - Digital SignatureChris MumeloNo ratings yet
- Topic1 Lesson1to9 IAaS1Document62 pagesTopic1 Lesson1to9 IAaS1Kervi Sanares BacuelNo ratings yet
- Assignment Cyber Law E.N 54Document6 pagesAssignment Cyber Law E.N 54Tajamul IslamNo ratings yet
- Ebook CryptographyDocument14 pagesEbook CryptographyhuvajiNo ratings yet
- Whitfield Diffie Martin Hellman: Key GenerationDocument3 pagesWhitfield Diffie Martin Hellman: Key GenerationSufiyan KhanNo ratings yet
- Nis 1Document13 pagesNis 1badg15594No ratings yet
- Digital SignatureDocument3 pagesDigital SignatureMohd Mubeen KhanNo ratings yet
- DS - Final ReportDocument23 pagesDS - Final ReportNamra SahebaNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional University: Cryptography in Digital SignatureDocument4 pagesLovely Professional University: Cryptography in Digital Signaturegoyal_No ratings yet
- Digital Signature and Electronic SignatureDocument4 pagesDigital Signature and Electronic SignatureMahimaNo ratings yet
- Sample ReportDocument12 pagesSample Report30 Yuvraj PatilNo ratings yet
- Digital SignatureDocument19 pagesDigital SignatureGaurav Kumar100% (1)
- Digital Signatures: Model of Digital SignatureDocument3 pagesDigital Signatures: Model of Digital SignatureParveen ThakurNo ratings yet
- Unit 4. Cryptography and Network Security: Introduction To CryptographyDocument11 pagesUnit 4. Cryptography and Network Security: Introduction To CryptographyVanam AkhilaNo ratings yet
- Law & Emerging Technologies: TH THDocument19 pagesLaw & Emerging Technologies: TH THAnuj Singh RaghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- Digital SignatureDocument23 pagesDigital SignatureRaje TwinkleNo ratings yet
- Basics of Digital Signatures and PKI SDocument4 pagesBasics of Digital Signatures and PKI SPramedicaPerdanaPutraNo ratings yet
- CSC ActivityDocument16 pagesCSC ActivityMrunali Porete CSE-11No ratings yet
- Cryptography Digital SignaturesDocument1 pageCryptography Digital Signatureschirag shahNo ratings yet
- Digital SignatureDocument4 pagesDigital Signaturesanamanand3300No ratings yet
- Digital SignatureDocument25 pagesDigital Signaturehardiks110yahoocomNo ratings yet
- This Article Is About Secure Cryptographic SignaturesDocument9 pagesThis Article Is About Secure Cryptographic SignaturesDeepika SharmaNo ratings yet
- 11.digitial SignaturesDocument34 pages11.digitial SignaturesRukhsana KousarNo ratings yet
- Securing Email Communication: How to Protect Your Correspondence from Wiretapping Using Free ToolsFrom EverandSecuring Email Communication: How to Protect Your Correspondence from Wiretapping Using Free ToolsNo ratings yet
- BlockChain Technology & Blueprint Ultimate Guide: Learn Everything You Need To Know For Beginners & ExperiencedFrom EverandBlockChain Technology & Blueprint Ultimate Guide: Learn Everything You Need To Know For Beginners & ExperiencedNo ratings yet
- Cisco Expressway Certificate Creation and Use Deployment Guide X8 8Document37 pagesCisco Expressway Certificate Creation and Use Deployment Guide X8 8Samuel Ogweng OkelloNo ratings yet
- IBM DS8000 Encryption For Data at Rest, Transparent Cloud Tiering and Endpoint Security (DS8000 Release 9.2)Document252 pagesIBM DS8000 Encryption For Data at Rest, Transparent Cloud Tiering and Endpoint Security (DS8000 Release 9.2)cmkgroupNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Storage Media Encryption: BRKSAN-2893Document35 pagesDesign and Implementation of Storage Media Encryption: BRKSAN-2893jeffgrantinctNo ratings yet
- CSA CCMv4.0 Final 031521Document222 pagesCSA CCMv4.0 Final 031521Elizabeth Mayta SalazarNo ratings yet
- Data Encryption Best Practices For Edge EnvironmentsDocument7 pagesData Encryption Best Practices For Edge Environmentspk bsdkNo ratings yet
- Understanding Public Key CryptographyDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Public Key CryptographyjeremyNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Public Key CryptographyDocument20 pages3.1 Public Key CryptographyTHIRU MURUGAN R 2k20BCA339No ratings yet
- Digital Signature ForuzanDocument47 pagesDigital Signature ForuzanSagar Lodhiya0% (1)
- CS707 FinalTerm Exam Paper Q ADocument9 pagesCS707 FinalTerm Exam Paper Q ASaeed SaeedNo ratings yet
- The Key-Distribution Problem A Public-Key SolutionDocument11 pagesThe Key-Distribution Problem A Public-Key SolutionASHOK KUMAR MNo ratings yet
- Time Complexity Analysis of Rsa and Ecc Based Security Algorithms in Cloud DataDocument8 pagesTime Complexity Analysis of Rsa and Ecc Based Security Algorithms in Cloud DataSia BoualemNo ratings yet
- Entrust and You New VersionDocument40 pagesEntrust and You New VersionAhmad ShahinNo ratings yet
- 9303 p12 Cons enDocument60 pages9303 p12 Cons enNtambo KabekeNo ratings yet
- Security in Wireless MANDocument12 pagesSecurity in Wireless MANAnanthavenkatesh GummidiNo ratings yet
- Developing Basic Cryptography Lab Modules With Open SSLDocument14 pagesDeveloping Basic Cryptography Lab Modules With Open SSLRASHMI H CNo ratings yet
- 032 CryptoHC7825IPVPNDocument2 pages032 CryptoHC7825IPVPNPFNo ratings yet
- xxxx xxxx 4215: ష / Enrolment No.: 0620/00118/22415Document1 pagexxxx xxxx 4215: ష / Enrolment No.: 0620/00118/22415Turning PointNo ratings yet
- Implementation Security Digital Signature Using Rivest Shamir Adleman RSA Algorithm As A Letter Validation and Distribution Validation SystemDocument7 pagesImplementation Security Digital Signature Using Rivest Shamir Adleman RSA Algorithm As A Letter Validation and Distribution Validation Systemraflihw CaksonoNo ratings yet
- Ponemon Global Encryption Trends Study Re EsDocument36 pagesPonemon Global Encryption Trends Study Re EsAngel KodituwakkuNo ratings yet
- Achieving PCI DSS Compliance With Thales Data Protection White PaperDocument21 pagesAchieving PCI DSS Compliance With Thales Data Protection White PaperMinh Quang Intercom VietnamNo ratings yet
- The Forrester Wave Public Cloud Platform Native Security Q2 2018Document14 pagesThe Forrester Wave Public Cloud Platform Native Security Q2 2018Shah NawazNo ratings yet
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKIDocument16 pagesPublic Key Infrastructure (PKIhamza iliyas100% (1)
- Digital SignatureDocument48 pagesDigital SignatureMoksha PatelNo ratings yet
- Pki and Digital Certification Infrastructure PDFDocument6 pagesPki and Digital Certification Infrastructure PDFmeunomeNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Encryption Features For VSP F Series and VSP G SeriesDocument12 pagesOverview of The Encryption Features For VSP F Series and VSP G SeriesHtc HtcNo ratings yet
- Iflix ConfigDocument2 pagesIflix Configjalak prawira100% (1)
- Network Security & Troubleshooting: Data Telecommunication & Network EngineeringDocument65 pagesNetwork Security & Troubleshooting: Data Telecommunication & Network EngineeringMarno03No ratings yet
- Design of A Secure Chat Application Based On AES CDocument7 pagesDesign of A Secure Chat Application Based On AES CÑitheeshwar WynžNo ratings yet