Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thiessen Method Example
Thiessen Method Example
Uploaded by
G-Joy FajilanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thiessen Method Example
Thiessen Method Example
Uploaded by
G-Joy FajilanCopyright:
Available Formats
Thiessen Method Example
Q. In the following figure a hypothetical basin and precipittaion depths measured by gages in this basin are given.
Calculate the areal average precipitation using Average Method and Thiessen Method.
Average Method
∑ 𝑃 𝑃𝐴 + 𝑃𝐵 + 𝑃𝐶 + 𝑃𝐷 20 + 8 + 14 + 12
𝑃𝑎𝑣𝑒 = = = = 14 𝑚𝑚
𝑁𝑝 4 4
Thiessen Method
First connect all of the measurement points, crosses in the figure are measurement points and they have been
connected with dashed lines. Second, perpendicularly bisect each of the “connecting” lines and extend the
bisecting lines until the either intersect the watershed boundary or another bisecting line.
∑ 𝑃𝐴 𝑃𝐴 𝐴𝐴 + 𝑃𝐵 𝐴𝐵 + 𝑃𝐶 𝐴𝐶 + 𝑃𝐷 𝐴𝐷 + 𝑃𝐸 𝐴𝐸 + 𝑃𝐹 𝐴𝐹
𝑃𝑎𝑣𝑒 = =
∑𝐴 𝐴𝐴 + 𝐴𝐵 + 𝐴𝐶 + 𝐴𝐷 + 𝐴𝐸 + 𝐴𝐹
(20𝑚𝑚)(0,5𝑘𝑚)(0,15𝑘𝑚) + (8𝑚𝑚)(0,5𝑘𝑚)(0,2𝑘𝑚) + (14𝑚𝑚)(0,7𝑘𝑚)(0,15𝑘𝑚)
𝑃𝑎𝑣𝑒 = +⋯
(0,5𝑘𝑚)(0,15𝑘𝑚) + (0,5𝑘𝑚)(0,2𝑘𝑚) + (0,7𝑘𝑚)(0,15𝑘𝑚)
(12𝑚𝑚)(0,7𝑘𝑚)(0,2𝑘𝑚) + (16𝑚𝑚)(0,5𝑘𝑚)(0,05𝑘𝑚) + (10𝑚𝑚)(0,7𝑘𝑚)(0,05𝑘𝑚)
… = 12,91 𝑚𝑚
(0,7𝑘𝑚)(0,2𝑘𝑚) + (0,5𝑘𝑚)(0,05𝑘𝑚) + (0,7𝑘𝑚)(0,05𝑘𝑚)
You might also like
- Hydraulics ProblemsDocument88 pagesHydraulics ProblemsG-Joy Fajilan100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document16 pagesChapter 1noman iqbal (nomylogy)No ratings yet
- Section 5: Finite Volume Methods For The Navier Stokes EquationsDocument27 pagesSection 5: Finite Volume Methods For The Navier Stokes EquationsUmutcanNo ratings yet
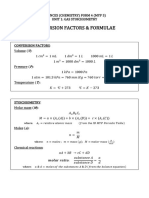
- CONVERSION FACTORS & FORMULAE - U1 Gas StoichiometryDocument2 pagesCONVERSION FACTORS & FORMULAE - U1 Gas StoichiometrykarlaNo ratings yet
- F CN (A, B), That F (n+1) Exists On (A, B), and x0 (A, B) - For Every XDocument4 pagesF CN (A, B), That F (n+1) Exists On (A, B), and x0 (A, B) - For Every XAYESHA SHAZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document30 pagesChapter 4noman iqbal (nomylogy)No ratings yet
- Reynolds Transport Theorem 09-28-2016Document29 pagesReynolds Transport Theorem 09-28-2016Anonymous K48TgviNo ratings yet
- Tutoria Quimica 2Document7 pagesTutoria Quimica 2Isabella MuñozNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures 1 Chapter 5.0 PDFDocument8 pagesTheory of Structures 1 Chapter 5.0 PDFEfraim PablacioNo ratings yet
- Line Integral - L6Document14 pagesLine Integral - L6Prakritish GhoshNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Instrumentation Lab: Experiment 1Document44 pagesMeasurement and Instrumentation Lab: Experiment 1Pranay DumbhareNo ratings yet
- STAT 408 Part 11Document3 pagesSTAT 408 Part 11rionsabitNo ratings yet
- Clase 7 - Mat. II - Funciones Reales de Var. Vect. 3Document11 pagesClase 7 - Mat. II - Funciones Reales de Var. Vect. 3cleber fidel carhuaypiñaNo ratings yet
- Camilla Pilati, Lab Report, Stading WavesDocument4 pagesCamilla Pilati, Lab Report, Stading WavescampilatiNo ratings yet
- Separation of VariablesDocument13 pagesSeparation of VariablesxingmingNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Cross Product and Equation of LineDocument7 pagesLec 3 Cross Product and Equation of LineMahad ElahiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Errors and ApproximationsDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Errors and ApproximationsjihasydxNo ratings yet
- Gr11 Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesGr11 Physics Formula SheetAndrew NguyenNo ratings yet
- Simple Linear RegressionclassroomDocument37 pagesSimple Linear RegressionclassroomNishikata ManipolNo ratings yet
- 0 C4 04Document39 pages0 C4 04Cartoon WorldNo ratings yet
- Bisection MethodDocument20 pagesBisection MethodMalibu BarbieNo ratings yet
- Discrete Uniform DistributionDocument7 pagesDiscrete Uniform DistributionRani GarginalNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Resueltos en InstructoríaDocument12 pagesEjercicios Resueltos en InstructoríaKristina RivasNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer-DESKTOP-TMOCD0EDocument20 pagesMass Transfer-DESKTOP-TMOCD0EAshna WaseemNo ratings yet
- MEC503 Lecture2Document8 pagesMEC503 Lecture2مصطفى عبدالله عبدالرحمن اغاNo ratings yet
- Simusoidal Circuits and RLC CircuitsDocument20 pagesSimusoidal Circuits and RLC CircuitsIbrahim GhunaimNo ratings yet
- L6 - Line IntegralDocument14 pagesL6 - Line IntegralChiku RohitNo ratings yet
- Phys 4410 HW 10 Done at CuDocument14 pagesPhys 4410 HW 10 Done at CuChristian Alic KelleyNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies Lecture 4Document5 pagesDynamics of Rigid Bodies Lecture 4Jaya Mae MañagoNo ratings yet
- Project 1 - ReportDocument19 pagesProject 1 - ReportGenius BoyNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 9 WK30 Answers 2023-24Document7 pagesProblem Set 9 WK30 Answers 2023-24Soham AherNo ratings yet
- Definition of Definite IntegralDocument20 pagesDefinition of Definite IntegralMichael LorrenzNo ratings yet
- GT 3 SolutionsDocument11 pagesGT 3 Solutionssri sai surajNo ratings yet
- ECON7310 Project1Document8 pagesECON7310 Project1Xuanyu HUNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 - Maxwell DistributionDocument8 pagesLecture 02 - Maxwell DistributionKowser mahmudNo ratings yet
- MT1 Phys 3023 - SP23 - Model AnswersDocument7 pagesMT1 Phys 3023 - SP23 - Model AnswersabdullahelnahhasNo ratings yet
- Summary (ES) أ. احمد الزريعيDocument7 pagesSummary (ES) أ. احمد الزريعيLilian AlkordyNo ratings yet
- Temario - T71 - Diseño y Cálculo de Estructuras Metálicas I - CEDocument125 pagesTemario - T71 - Diseño y Cálculo de Estructuras Metálicas I - CEKaren JimenezNo ratings yet
- Harold's Precalculus Rectangular - Polar - Parametric "Cheat Sheet"Document7 pagesHarold's Precalculus Rectangular - Polar - Parametric "Cheat Sheet"HarshNo ratings yet
- Z Observed At 0, Δt, 2Δt, ... , Nδt (=T) Denoted As Z (0), Z (Δt), Z (2Δt), ... , Z (T)Document10 pagesZ Observed At 0, Δt, 2Δt, ... , Nδt (=T) Denoted As Z (0), Z (Δt), Z (2Δt), ... , Z (T)Wang包了儿No ratings yet
- Integration-3 - TDocument16 pagesIntegration-3 - TEverything What U WantNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Concepts In: Numerical AnalysisDocument21 pagesPreliminary Concepts In: Numerical AnalysisLingos HeavensbeeNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous Linear Differential Equation With Constant CoefficientsDocument1 pageHomogeneous Linear Differential Equation With Constant CoefficientstumambingaleahNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis Formula Paper - Updated 2017Document4 pagesData Analysis Formula Paper - Updated 2017Rand GhaddarNo ratings yet
- Elecromagnetic Fields and Waves IDocument50 pagesElecromagnetic Fields and Waves Iasiwecollins19No ratings yet
- 100 - Sukrith DNS - IJtteDocument5 pages100 - Sukrith DNS - IJttesreekumaNo ratings yet
- ISOM2500 Regression Practice SolutionsDocument3 pagesISOM2500 Regression Practice Solutions3456123No ratings yet
- 003 02 KNN - Distances W3L1Document10 pages003 02 KNN - Distances W3L1DOESSKKUNo ratings yet
- SHERIFF 445Document32 pagesSHERIFF 445petermmtuNo ratings yet
- Phys 242: Tutorial Questions Set Ii 2021Document6 pagesPhys 242: Tutorial Questions Set Ii 2021anthony kingsleyNo ratings yet
- Phys 242: Tutorial Questions Set Ii 2021Document6 pagesPhys 242: Tutorial Questions Set Ii 2021anthony kingsleyNo ratings yet
- SumsDocument41 pagesSumsshoyeb haqueNo ratings yet
- Prueba Diagnostica 3secDocument29 pagesPrueba Diagnostica 3secAlis ReyesNo ratings yet
- MayliDocument29 pagesMayliisra alba albNo ratings yet
- Fisg39 Clase 22022021Document5 pagesFisg39 Clase 22022021JoelNo ratings yet
- Practica 2 TMMDocument2 pagesPractica 2 TMMdiban49680No ratings yet
- HaDocument15 pagesHaNicole Easther GabilangosoNo ratings yet
- Correction de L'examen Mécanique Quantique 2 Session Normale 2022Document12 pagesCorrection de L'examen Mécanique Quantique 2 Session Normale 2022jojhuuwnnteNo ratings yet
- 14 Numerical Differentiation 2Document26 pages14 Numerical Differentiation 2محمد خطباNo ratings yet
- Excercise3 S CurveDocument22 pagesExcercise3 S CurveG-Joy FajilanNo ratings yet
- Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: GjoyDocument2 pagesGjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: Gjoy: JP: GjoyG-Joy FajilanNo ratings yet
- Longitudinal FactorDocument5 pagesLongitudinal FactorG-Joy FajilanNo ratings yet
- Appendix F - Volume PDFDocument11 pagesAppendix F - Volume PDFG-Joy FajilanNo ratings yet