Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Secured Transactions: Freezer
Secured Transactions: Freezer
Uploaded by
El Sayed Abdelgawwad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThis document discusses secured transactions and key concepts related to attachment and perfection of security interests. It provides examples of how security interests can attach to: (1) after-acquired property like new office furniture or automobile inventory; and (2) true consignments where the consignor retains title to goods. It also notes some restrictions and exceptions, like how security interests in consumer goods are treated differently than commercial goods. Field warehousing is discussed as a method of perfecting a security interest by maintaining control over inventory on the debtor's premises.
Original Description:
67ghfds0
Original Title
Scan 0004
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses secured transactions and key concepts related to attachment and perfection of security interests. It provides examples of how security interests can attach to: (1) after-acquired property like new office furniture or automobile inventory; and (2) true consignments where the consignor retains title to goods. It also notes some restrictions and exceptions, like how security interests in consumer goods are treated differently than commercial goods. Field warehousing is discussed as a method of perfecting a security interest by maintaining control over inventory on the debtor's premises.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as rtf, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesSecured Transactions: Freezer
Secured Transactions: Freezer
Uploaded by
El Sayed AbdelgawwadThis document discusses secured transactions and key concepts related to attachment and perfection of security interests. It provides examples of how security interests can attach to: (1) after-acquired property like new office furniture or automobile inventory; and (2) true consignments where the consignor retains title to goods. It also notes some restrictions and exceptions, like how security interests in consumer goods are treated differently than commercial goods. Field warehousing is discussed as a method of perfecting a security interest by maintaining control over inventory on the debtor's premises.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as rtf, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
p
224 MODULE 26 SECURED TRANSACTIONS
EXAMPLE: An appliance dealer sells a freezer to lackfor family use. Assume attachment has
occurred. lack then sells it to Cindy who is aware of the security interest that the dealer still has in
the freezer. Even if Cindy is buying this for household use, she takes subject to the security interest.
(2) Sale of promissory notes
(3) Assignment of health care insurance to health care provider
(4) Temporary automatic perfection for twenty days for instruments, certificated securities, nego-
tiable documents, and proceeds of sale of perfected security interest
D. Other Issues under Secured Transactions
as well
1. as all office furniture subsequently acquired. The security interest in the new furniture cannot attach until the debtor
acquires rights in the other office furniture.
Af
ter a. Typically used for inventory and accounts receivable when debtor also has rights to sell inventory
and collect accounts (e.g., a floating lien)
-
ac (1) Sometimes used for equipment
qu EXAMPLE: A, an automobile dealer, to obtain a loan, grants a bank a security interest covering "all automobiles
-now possessed and hereafter acquired." As the dealer obtains rights in the new inventory of automobiles, the
ire security intere.st attaches as to those newly acquired automobiles.
d b. Certain restrictions exist if debtor buys consumer goods
pr 2. Computer software embedded in goods is treated as part of those goods and not as software
op 3. Field warehousing is used to perfect security interest (analogous to possession or control)
a. Debtor keeps inventory on his/her premises under control of third party such as bonded ware-
ert
houseman or secured party's employee ,
y b. Secured party keeps control over inventory such as use of separate room or fenced-off portion
an with sign showing secured party's control
4. Co~signments
d
a. . Consignment of security interest
fut
(1) If it is a "true consignment," consignee is simply a sales agent who does not own the goods
ur but sells them for consignor
e
(a) "True consignment" exists when
go
1] Consignor retains title to goods
od 2] Consignee has no obligation to buy goods
s 3] Consignor has right to all proceeds (pays consignee commission)
EXAMPLE: Manufacturer (consignor) gives possession of goods to a marketing representative
ar (consignee) to sell those goods on commission.
e
(b) To perfect hislher interest, a consignor must
co
1] File a financing statement under secured transactions law and give notice to the con-
ve signee's creditors who have perfected security interests in the same type of goods
re
a] Notice must contain description of the goods to .bedelivered and be given before
d the consignee receives possession of goods
w EXAMPLE: P delivers goods to A on consignment. The consignment is a "true consignment"
in that P has title to the goods and pays A a commission for selling the goods. Any goods that
he are unsold are returned by A to P. A does not pay for any unsold goods. Creditors of A can
assert claims against the goods that A possesses unless P has given notice to the creditors. The
n general way to accomplish this is by filing under the secured transactions law.
pa
(2) If it is not a true consignment because it is actually a sale from creditor to debtor in which
rti debtor then owns the goods, look for a security agreement
es
(a) Attachment and perfection occur as in typical secured transaction
ag
re
e
to
thi
s
EXAMPLE
An
agreement
states that
the collateral
consists of
all of
debtor's
furniture
now located
in his office
You might also like
- Law On SalesDocument61 pagesLaw On SalesCarlota Nicolas Villaroman100% (3)
- Atm Hack To Get Much More Money Than You Withdraw and DL Link2Document2 pagesAtm Hack To Get Much More Money Than You Withdraw and DL Link2steven80% (5)
- Secured Transactions OutlineDocument27 pagesSecured Transactions OutlineJ M100% (1)
- Cape Law: Texts and Cases - Contract Law, Tort Law, and Real PropertyFrom EverandCape Law: Texts and Cases - Contract Law, Tort Law, and Real PropertyNo ratings yet
- World English 3 Split BDocument127 pagesWorld English 3 Split Bmaria de los angeles lopez100% (1)
- Secured Trans (Good Explanations)Document42 pagesSecured Trans (Good Explanations)JasonGershensonNo ratings yet
- Contract of BailmentDocument12 pagesContract of BailmentAyush GaurNo ratings yet
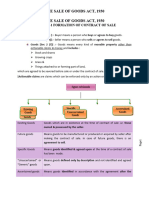
- Sale of Goods ActDocument33 pagesSale of Goods Actfiza100% (2)
- Warehouse Receipts Law Short VersionDocument8 pagesWarehouse Receipts Law Short VersionMaverick PascualNo ratings yet
- Secured Transactions_TERM SHEETDocument10 pagesSecured Transactions_TERM SHEETmebernstNo ratings yet
- Random Info - UCCDocument11 pagesRandom Info - UCCTina KayNo ratings yet
- Secured Transactions OutlineDocument20 pagesSecured Transactions Outlineprentice brown100% (4)
- Sale of Goods Act, 1930: Question Bank Unit:1Document10 pagesSale of Goods Act, 1930: Question Bank Unit:1gargee thakareNo ratings yet
- 6 12 MarksDocument3 pages6 12 MarksOk KucheNo ratings yet
- Business Law UNIT 3Document16 pagesBusiness Law UNIT 3sonwaniswatantraNo ratings yet
- Secured Transactions Outline - HorowitzDocument10 pagesSecured Transactions Outline - Horowitza thaynNo ratings yet
- Warehouse Receipts Law Reviewer IIDocument9 pagesWarehouse Receipts Law Reviewer IIUi Bin DMNo ratings yet
- Asset Privatization Trust v. T.J. Enterprises.Document5 pagesAsset Privatization Trust v. T.J. Enterprises.Jude Raphael S. FanilaNo ratings yet
- Business Law 138 142Document5 pagesBusiness Law 138 142humaira fatimaNo ratings yet
- Warehouse Receipts Law NotesDocument7 pagesWarehouse Receipts Law NotesRia De AndaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Secured Transactions Outline 2Document17 pages2016 Secured Transactions Outline 2jackojidemasiadoNo ratings yet
- WR Review CastroDocument7 pagesWR Review CastrocathydavaoNo ratings yet
- 1 PRELIM SalesDocument21 pages1 PRELIM SalesLilac heartNo ratings yet
- Credit Notes 09-30Document6 pagesCredit Notes 09-30Ria De AndaNo ratings yet
- Law On Sales NotesDocument10 pagesLaw On Sales NotesEdrielle DaquioagNo ratings yet
- Sec. Trans.-Essay-ChecklistDocument4 pagesSec. Trans.-Essay-ChecklistNicole Marie Torres100% (1)
- Ownership of and To Deliver A Determinate Thing, While The Other Party (Buyer or Vendee)Document6 pagesOwnership of and To Deliver A Determinate Thing, While The Other Party (Buyer or Vendee)Rosemarie A. EnorNo ratings yet
- Warehouse Receipt Law 3Document10 pagesWarehouse Receipt Law 3Ej CalaorNo ratings yet
- The Sales of Goods Act (1930)Document44 pagesThe Sales of Goods Act (1930)swatishetNo ratings yet
- SALES PrintDocument22 pagesSALES PrintJoyce Fe Egsaen MagannonNo ratings yet
- 1 Warehouse Receipt Law RevDocument10 pages1 Warehouse Receipt Law RevJaphet C. VillaruelNo ratings yet
- Law On SalesDocument35 pagesLaw On SalesHAKUNA MATATANo ratings yet
- Unit - Ii LESSON-18 Law of Sale of GoodsDocument7 pagesUnit - Ii LESSON-18 Law of Sale of Goodshumaira fatimaNo ratings yet
- Business Law-Unit 3Document42 pagesBusiness Law-Unit 3Erick KadohNo ratings yet
- 05 MSM-1 The Sale of Goods Act 1930Document8 pages05 MSM-1 The Sale of Goods Act 1930Harleen KohliNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Sales of Goods ActDocument42 pagesModule 2 Sales of Goods ActAshish SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- The Law On Sales, Agency and Credit Transactions Sales Summary ReportDocument4 pagesThe Law On Sales, Agency and Credit Transactions Sales Summary ReportchiwaNo ratings yet
- Handout - BAILMENTDocument7 pagesHandout - BAILMENTaanyaNo ratings yet
- Sale of Goods ActDocument26 pagesSale of Goods Actashmit.5217No ratings yet
- Summary NIL ReportsDocument23 pagesSummary NIL ReportsVedia Genon IINo ratings yet
- Sales of Goods Act, 1930Document7 pagesSales of Goods Act, 1930Aqsa BalouchNo ratings yet
- Warehouse ReceiptDocument7 pagesWarehouse ReceiptMara VinluanNo ratings yet
- Sale of Goods Act NotesDocument45 pagesSale of Goods Act NotesAnkit JindalNo ratings yet
- TRUST RECEIPTS LAW NOTES by SAPDocument5 pagesTRUST RECEIPTS LAW NOTES by SAPStephany PolinarNo ratings yet
- Indian Sale of Goods Act, 1932 Introduction, Sale and Agreement To SellDocument4 pagesIndian Sale of Goods Act, 1932 Introduction, Sale and Agreement To Sellravurirajkumar2005No ratings yet
- Law On Sale My LectureDocument35 pagesLaw On Sale My LectureMicah ErguizaNo ratings yet
- Ijoart: Managed Inventory With Special Reference of Cost StructureDocument5 pagesIjoart: Managed Inventory With Special Reference of Cost StructureAngelica PostreNo ratings yet
- Trust Receipts: Definition/Concept of A Trust Receipt TransactionDocument5 pagesTrust Receipts: Definition/Concept of A Trust Receipt TransactionPortia WynonaNo ratings yet
- Sale of Goods Act, 1930Document73 pagesSale of Goods Act, 1930Achyuth BjNo ratings yet
- RFBT 3 (OBLIGATIONS of The VENDOR) Topic 2Document4 pagesRFBT 3 (OBLIGATIONS of The VENDOR) Topic 2MollyNo ratings yet
- Security: Credit TransactionsDocument43 pagesSecurity: Credit TransactionsMary Ann IsananNo ratings yet
- Commercial LawDocument18 pagesCommercial LawIan BinoyaNo ratings yet
- NEON2Document8 pagesNEON2Aira TantoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Consummation of SaleDocument9 pagesChapter 6 - Consummation of SaleClarissa Malig-onNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 The Law On Sales Obligations of The VendorDocument32 pagesLecture 2 The Law On Sales Obligations of The VendorMillicent AlmueteNo ratings yet
- Indemnity & Guaranty, Contract of Bailment and Contract of AgencyDocument10 pagesIndemnity & Guaranty, Contract of Bailment and Contract of Agencyahmad rezaNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Law On Sales AADLDocument14 pagesWeek 4 Law On Sales AADLCasper VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Sales WarrantyDocument5 pagesSales WarrantyJC LaygoNo ratings yet
- Module 22 Federal Securities Acts and Antitrust LawDocument2 pagesModule 22 Federal Securities Acts and Antitrust LawEl Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- P L N L U N N T MP: Sarbanes-Ox Eyactof2 2Document2 pagesP L N L U N N T MP: Sarbanes-Ox Eyactof2 2El Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Agency: I. Formation of The Agency RelationshipDocument7 pagesAgency: I. Formation of The Agency RelationshipEl Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Federal Securities Acts and Antitrust LawDocument3 pagesFederal Securities Acts and Antitrust LawEl Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- C Ayton Act of 1914: Module 22 Fe E A SE UDocument2 pagesC Ayton Act of 1914: Module 22 Fe E A SE UEl Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Module 22 Federal Securities Acts and Antitrust LawDocument2 pagesModule 22 Federal Securities Acts and Antitrust LawEl Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Scan 0014Document2 pagesScan 0014El Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Scan 0015Document2 pagesScan 0015El Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- M Dule 22 Federal Securities Acts and Antitrust LawDocument2 pagesM Dule 22 Federal Securities Acts and Antitrust LawEl Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Federal Securities Acts and Antitrust Law: C o C eDocument2 pagesFederal Securities Acts and Antitrust Law: C o C eEl Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Contracts: D Still Owes CTDocument2 pagesContracts: D Still Owes CTEl Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Scan 0021Document2 pagesScan 0021El Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Scan 0002Document2 pagesScan 0002El Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Scan 0014Document2 pagesScan 0014El Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Scan 0020Document2 pagesScan 0020El Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- S S S T I E: ContractsDocument2 pagesS S S T I E: ContractsEl Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Scan 0003Document2 pagesScan 0003El Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Scan 0014Document2 pagesScan 0014El Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Ill LLQ J: ContractsDocument2 pagesIll LLQ J: ContractsEl Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Cont A: R CTSDocument2 pagesCont A: R CTSEl Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Cont Acts: G A A yDocument1 pageCont Acts: G A A yEl Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- J .T/DTD: Tjrrji?"Document1 pageJ .T/DTD: Tjrrji?"El Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Contracts: Over IDocument2 pagesContracts: Over IEl Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Scan 0002Document2 pagesScan 0002El Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Scan 0007Document2 pagesScan 0007El Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Module 26 Secured Transactions:: S G S C R eDocument2 pagesModule 26 Secured Transactions:: S G S C R eEl Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Module 26 Secured Transactions:: o C, G eDocument2 pagesModule 26 Secured Transactions:: o C, G eEl Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Scan 0007Document1 pageScan 0007El Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Fi V Y, A (A A y I R S (B) A R S Si: Secured TransactionsDocument2 pagesFi V Y, A (A A y I R S (B) A R S Si: Secured TransactionsEl Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Priorities: Secu Ed TransactionsDocument2 pagesPriorities: Secu Ed TransactionsEl Sayed AbdelgawwadNo ratings yet
- Siwarex Calibration ProcedureDocument14 pagesSiwarex Calibration ProcedureHector HerreraNo ratings yet
- Citizens Charter Feb-2022Document23 pagesCitizens Charter Feb-2022SUNILABHI_APNo ratings yet
- Complaint Handling Model Policy WordDocument13 pagesComplaint Handling Model Policy WordnattyNo ratings yet
- Norma ISO - 27005 - 2022 - OCRDocument70 pagesNorma ISO - 27005 - 2022 - OCRPablo PS100% (3)
- 23-06689 - BPSU-CAT Confirmation SlipDocument1 page23-06689 - BPSU-CAT Confirmation SlipMark AtienzaNo ratings yet
- 1.31 - Intro To Ethical Hacking - Security ControlsDocument34 pages1.31 - Intro To Ethical Hacking - Security ControlsGiang LeNo ratings yet
- Aws VPC User Guide - Vpc-UgDocument328 pagesAws VPC User Guide - Vpc-UgjaisinglaNo ratings yet
- Access Control Unit User'S Guide: Netaxs-123Document152 pagesAccess Control Unit User'S Guide: Netaxs-123JMAC SupplyNo ratings yet
- Blackwater Mill Residential Home - CQC ReportDocument21 pagesBlackwater Mill Residential Home - CQC ReportOnTheWightNewsNo ratings yet
- CommBiz 102395709 0 260323 Authority 02 473 2692749819441Document3 pagesCommBiz 102395709 0 260323 Authority 02 473 2692749819441bigman walthoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 FingerprintsDocument6 pagesAssignment 2 Fingerprintsapi-242667307No ratings yet
- Accomplishment-Report GF010A UpdatedDocument2 pagesAccomplishment-Report GF010A Updatedmary ann mamarilNo ratings yet
- HahaDocument3 pagesHahaAbdul Haneef100% (1)
- Asiignment 2advanced Opertaing Systems ICT3631 Student NumberDocument6 pagesAsiignment 2advanced Opertaing Systems ICT3631 Student NumberCalvin MulaudziNo ratings yet
- Tax Audit ManualDocument314 pagesTax Audit ManualVigneshVigneshNo ratings yet
- International Morse Code: What Is Cryptography?Document3 pagesInternational Morse Code: What Is Cryptography?Mariana Vasquez CruzNo ratings yet
- Guru Granth Sahib Darpan by Prof Sahib SinghDocument6,288 pagesGuru Granth Sahib Darpan by Prof Sahib SinghKawaldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Presentación Tésis A Walking City For The 21st Century - ArchDailyDocument4 pagesPresentación Tésis A Walking City For The 21st Century - ArchDailyFranco Martín LópezNo ratings yet
- PG Success Story Woodside Energy PDFDocument3 pagesPG Success Story Woodside Energy PDFLaammeem NoonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Ethical, Social, and Political Issues in E-CommerceDocument17 pagesChapter 8: Ethical, Social, and Political Issues in E-CommerceMaria Antoinette Portillo FelixNo ratings yet
- CDA TemplateDocument2 pagesCDA TemplateLaudArchNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Cryptography and The Public Key Infrastructure - Attempt Review2Document4 pagesQuiz - Cryptography and The Public Key Infrastructure - Attempt Review2busola TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Backup Process For McAfee DevicesDocument11 pagesBackup Process For McAfee DevicesabbuasherNo ratings yet
- UAS Bahasa Inggris FILKOMDocument8 pagesUAS Bahasa Inggris FILKOMSyarif HidayatNo ratings yet
- PMBL Ur6Document1 pagePMBL Ur6Mr. AnonymousNo ratings yet
- LO1 Plan For Installation of Telecommunications Network EquipmentDocument28 pagesLO1 Plan For Installation of Telecommunications Network EquipmentAnonymous AguLF9963HNo ratings yet
- Attendance Sheet (For Examination Centre)Document2 pagesAttendance Sheet (For Examination Centre)Joanna HernandezNo ratings yet
- ES10IS2 English For Intel v2.0Document68 pagesES10IS2 English For Intel v2.0Walter CisnerosNo ratings yet