Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab 1: Schmitt Trigger: + 15V For V - 15V For V
Lab 1: Schmitt Trigger: + 15V For V - 15V For V
Uploaded by
HaSanTaRiqOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 1: Schmitt Trigger: + 15V For V - 15V For V
Lab 1: Schmitt Trigger: + 15V For V - 15V For V
Uploaded by
HaSanTaRiqCopyright:
Available Formats
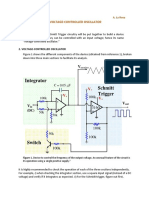
Lab 1: Schmitt Trigger
U.C. Davis Physics 116B (Rev. 05)
I NTRODUCTION
Vbb = 15V
Like the Wien bridge oscillator in 116A, the
Schmitt trigger is an application of positive
feedback. This circuit is a voltage comparator
with hysteresis. A voltage comparator will give R +15V
2
as its output one of two voltages: 2 _
Vin 7
6 Vout
�+15V for V in > V th 3 +
Vout =� 4
�-15V for V in < V th
-15V
where Vth is a threshold voltage. A voltage
comparator with hysteresis will have a different
Vth for rising input voltages than for falling R3
input voltages. R1
In this lab, we will build a Schmitt trigger
using the 741 op amp, our analog circuit
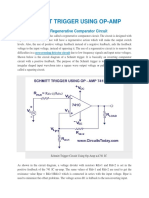
workhorse. We will measure Vth and verify the Fig 1: Schmitt trigger circuit.
circuit's operation as a voltage comparator.
1. SCHMITT T RIGGER For each set of resistor values, apply a sine
wave or a triangle wave to the input and sketch
The Schmitt trigger circuit is shown in figure the output. For your lab report, sketch these
1. Build this circuit at least twice, each time waveforms, showing the input voltages where
with a different set of resistors. Some the output switches and compare these to the
recommended values are 10kΩ, 10kΩ, 100kΩ; or Vth 's you measured with the voltmeter.
10kΩ, 10kΩ, 1MΩ; or 10kΩ, 22kΩ, 100kΩ.
Use the variable voltage supply for Vin and 2. SIMULATED N OISY S O U R C E
measure it with the voltmeter. Measure Vout
To see how a Schmitt trigger might be useful,
with the oscilloscope and note how fast the
we will construct a source with some fake noise
output switches from +15V to −15V . For each
introduced into it. Figure 2 shows how to do
set of resistors, record Vth for both positive and
this using two function generators and a second
negative transitions. See how close they are to op amp, used as a summing amplifier. Build
the predicted values: this circuit and use it as the input to your
R1 || R2 || R3 R | |R || R Schmitt trigger. Regard the 1 kHz sign wave as
Vth = Vbb + 1 2 3 Vout (1) the "signal" and the 10 kHz sine wave as the
R2 R3
"noise". For your lab report, sketch the input
For your lab report, report these measured and and output waveforms, being careful to show
predicted voltages and draw them on a Vout vs Vin each time the input crosses a Vth and what the
curve showing the hysteresis loop. (Make a output does in response. Try to determine
separate drawing for each set of R's.) approximately how much hysteresis is required to
filter out a given amount of noise.
large amplitude R
1 kHz sine wave R
(the signal)
_
Vout to Schmitt trigger
small amplitude +
R
10 kHz sine wave
(the noise)
Fig 2: Simulated noisy source.
22
You might also like
- Philips 32pfl5404 Chassis Tpm3.1e La (ET)Document84 pagesPhilips 32pfl5404 Chassis Tpm3.1e La (ET)varimasNo ratings yet
- Schmitt TriggerDocument5 pagesSchmitt TriggerPrajay Prasanth PNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier (Oscillator) : Pattanan Amatanon EE1A3Document6 pagesOperational Amplifier (Oscillator) : Pattanan Amatanon EE1A3pamatanonNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Cluster 4Document67 pagesUNIT 3 Cluster 4SandyNo ratings yet
- Schmitt Trigger, Multivibrator Circuits Lab ReportDocument11 pagesSchmitt Trigger, Multivibrator Circuits Lab ReportPriya S0% (1)
- Expt No: 08: Roll No: 8091 Name: Aditya SinghDocument8 pagesExpt No: 08: Roll No: 8091 Name: Aditya SinghAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Circuits and Electronics Chapter 3 and NotesDocument49 pagesCircuits and Electronics Chapter 3 and NotesDr. S. DasNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 05Document4 pagesExperiment No 05noushadNo ratings yet
- Schmitt Trigger Using Op AmpDocument4 pagesSchmitt Trigger Using Op Ampاحمد زغارىNo ratings yet
- Basic Opamp ApplicationsDocument5 pagesBasic Opamp ApplicationsNorbertNo ratings yet
- Schmitt TriggerDocument19 pagesSchmitt Triggerkirpaldoad100% (1)
- Lab 4: Introduction To Operational Amplifiers: ObjectiveDocument10 pagesLab 4: Introduction To Operational Amplifiers: Objectivepaul omondi ochiengNo ratings yet
- EX - NO:03 Comparator Circuits DateDocument7 pagesEX - NO:03 Comparator Circuits DateVijayakumar KNo ratings yet
- Analog Sample Interview QuestionsDocument30 pagesAnalog Sample Interview QuestionsSampoornaGonellaNo ratings yet
- Integratedelectronics (Unit 2) SCHMITT TRIGGER - OPAMPDocument2 pagesIntegratedelectronics (Unit 2) SCHMITT TRIGGER - OPAMPYogeshwaranNo ratings yet
- ppt5 - Operational Amplifiers - ApplicationsDocument45 pagesppt5 - Operational Amplifiers - ApplicationsMichael Angelo BerjaNo ratings yet
- Bistable Mono StableDocument30 pagesBistable Mono StableTurkish GatxyNo ratings yet
- DC Circuits: Review: - Current: The Rate of Flow of Electric Charge Past A Point in A CircuitDocument15 pagesDC Circuits: Review: - Current: The Rate of Flow of Electric Charge Past A Point in A Circuitdeskaug1No ratings yet
- Lab Report 4 - The Voltage Comparator and The Bi-Stable Circuit (Schmitt Trigger)Document4 pagesLab Report 4 - The Voltage Comparator and The Bi-Stable Circuit (Schmitt Trigger)Yasmim de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Schmitt TriggerDocument4 pagesSchmitt TriggerManojkumarNo ratings yet
- OPAMP NonlinearAppDocument45 pagesOPAMP NonlinearAppkajari chattopadhyayNo ratings yet
- 5.AC Phase Control Using SCRDocument8 pages5.AC Phase Control Using SCRabcdefgNo ratings yet
- Utkarsh Physics Ac Project 2.0OOODocument20 pagesUtkarsh Physics Ac Project 2.0OOOT VpNo ratings yet
- Oscillators 3Document8 pagesOscillators 3LJ TuliaoNo ratings yet
- I, V, C MeasurementsDocument12 pagesI, V, C MeasurementsArpandip boruahNo ratings yet
- DC BridgesDocument35 pagesDC BridgesSeanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 ComparatorDocument21 pagesLecture 6 ComparatorVinaasha BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Zero Crossing Detector and Window DetectorDocument7 pagesZero Crossing Detector and Window DetectorTimoth Dev50% (2)
- dc1192 1267351Document4 pagesdc1192 1267351Michael TriviñoNo ratings yet
- An Ideal Amplifier in A NonDocument8 pagesAn Ideal Amplifier in A NonLouys HongNo ratings yet
- Military Institute of Science & TechnologyDocument3 pagesMilitary Institute of Science & Technologyahmed rifatNo ratings yet
- Opamp ApplicationDocument38 pagesOpamp ApplicationS.m. FerdousNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 DDocument31 pagesUnit 2 DShaleva SinghNo ratings yet
- Utkarsh Physics Ac Project 2.0Document21 pagesUtkarsh Physics Ac Project 2.0T VpNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 06Document5 pagesExperiment No 06noushadNo ratings yet
- Edc Lab ManualsDocument76 pagesEdc Lab Manualsnaveenparthi100% (1)
- UNIT 3-Cluster - 4Document67 pagesUNIT 3-Cluster - 4Anvesh MagantiNo ratings yet
- BEEE Lab Manual CSVTUDocument44 pagesBEEE Lab Manual CSVTUMulty TalantedNo ratings yet
- CHAP3.Arus Bolak BalikDocument35 pagesCHAP3.Arus Bolak BalikOmi Luthfia RahmanNo ratings yet
- 13 AC Thevenin & Norton Transforms (1) - TaggedDocument32 pages13 AC Thevenin & Norton Transforms (1) - TaggedDaniel BallNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument32 pagesTransistorCedric Montiano100% (1)
- Laboratory Report Cover SheetDocument15 pagesLaboratory Report Cover SheetPreet PatelNo ratings yet
- ch4,5 MTV, 555 TUDocument16 pagesch4,5 MTV, 555 TUHayel ZayedNo ratings yet
- AIA10-Non-linear and Real Op-Amp CircuitsDocument37 pagesAIA10-Non-linear and Real Op-Amp CircuitsABDELRAHMAN REDA MAAMOUN ELSAID SEYAM A19EM0638No ratings yet
- Lica NotesDocument20 pagesLica NotesDHANYASRI BOLLANo ratings yet
- Lic Combined SlidesDocument288 pagesLic Combined SlidesMadhuNo ratings yet
- OpAmp F10Document32 pagesOpAmp F10Suguna PriyaNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument8 pagesLab ReportMuhammad Faizan TariqNo ratings yet
- Transistors Instructions: Read Hayes and Horowitz, Class 4, and Then Do The Exercises From Lab 4Document4 pagesTransistors Instructions: Read Hayes and Horowitz, Class 4, and Then Do The Exercises From Lab 4wizbizphdNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 04Document4 pagesExperiment No 04noushadNo ratings yet
- Schmitt TriggerDocument3 pagesSchmitt TriggerSakthi PonnusamiNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 BECE206L TH VL2023240102288 2023-10-26 Reference-Material-IDocument15 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 BECE206L TH VL2023240102288 2023-10-26 Reference-Material-Impkvarun69No ratings yet
- Part 1: Schmitt Trigger: TheoryDocument4 pagesPart 1: Schmitt Trigger: TheoryPrathyusha YedlaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Eletronics ProblemsDocument16 pagesElectrical Engineering Eletronics ProblemsarthurNo ratings yet
- HSST Electronics Part3 Op Amp Based MultivibratorsDocument16 pagesHSST Electronics Part3 Op Amp Based MultivibratorsAliNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifiers: The Ideal Op-Amp in Negative FeedbackDocument4 pagesOperational Amplifiers: The Ideal Op-Amp in Negative FeedbackABCD ENo ratings yet
- 2018 Lab 5B Voltage-Controlled - OscillatorDocument4 pages2018 Lab 5B Voltage-Controlled - OscillatorPatrick SibandaNo ratings yet
- Op Amp For ClassDocument27 pagesOp Amp For ClassRojan PradhanNo ratings yet
- OC and SC Test On Single Phase TransformerDocument5 pagesOC and SC Test On Single Phase TransformerhavejsnjNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Batch-05 WPS101 2 PDFDocument3 pagesBatch-05 WPS101 2 PDFHaSanTaRiqNo ratings yet
- Lab2 EquipmentIntroDocument5 pagesLab2 EquipmentIntroHaSanTaRiqNo ratings yet
- Lab2 EquipmentIntroDocument5 pagesLab2 EquipmentIntroHaSanTaRiqNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 MosfetsDocument4 pagesLab 4 MosfetsHaSanTaRiqNo ratings yet
- Physics HomeworkDocument6 pagesPhysics HomeworkHaSanTaRiqNo ratings yet
- Answer 1:: Propagation Speeds Faster Than C Would Induce A Stronger Field and Ever-IncreasingDocument1 pageAnswer 1:: Propagation Speeds Faster Than C Would Induce A Stronger Field and Ever-IncreasingHaSanTaRiqNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Controlled Fire Fighting Robot: DescriptionDocument1 pageBluetooth Controlled Fire Fighting Robot: DescriptionHaSanTaRiqNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Controlled Fire Fighting Robot Using Atmel 89C51 Micro-ControllerDocument15 pagesBluetooth Controlled Fire Fighting Robot Using Atmel 89C51 Micro-ControllerHaSanTaRiq100% (1)
- SoC Mod2 NotesDocument64 pagesSoC Mod2 NotesHeaven varghese C S C SNo ratings yet
- Presentation ANTENNA YC2YIZDocument37 pagesPresentation ANTENNA YC2YIZMuhammad Rayhan SyahNo ratings yet
- A mfc8000Document2 pagesA mfc8000GokerAkgunNo ratings yet
- Eww 1982 02Document132 pagesEww 1982 02Johnny1q0% (1)
- 3 - Discrete Event SimulationDocument33 pages3 - Discrete Event SimulationhebaNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Challenges of A Type-3 PLLDocument14 pagesAdvantages and Challenges of A Type-3 PLLAnonymous 2SiUWw2DKNo ratings yet
- Power Protection ComputerDocument5 pagesPower Protection ComputerEng IbontokoNo ratings yet
- Carel Energy Meter PDFDocument1 pageCarel Energy Meter PDFElşən Yusifoğlu ƏsgərovNo ratings yet
- Solution:: KVA IpDocument3 pagesSolution:: KVA IpNoor Mohammed100% (1)
- IEC 61000-4-2 (ESD) 20kV (Air), 12kV (Contact) IEC 61000-4-4 (EFT) 40A (5/50ns) IEC 61000-4-5 (Lightning) 7A (8/20 S) Cable Discharge Event (CDE)Document6 pagesIEC 61000-4-2 (ESD) 20kV (Air), 12kV (Contact) IEC 61000-4-4 (EFT) 40A (5/50ns) IEC 61000-4-5 (Lightning) 7A (8/20 S) Cable Discharge Event (CDE)cafosokNo ratings yet
- Function Generator: 0.002Hz To 2MhzDocument34 pagesFunction Generator: 0.002Hz To 2MhzsebastinNo ratings yet
- Communication System TC-307: Lecture 10, Week 4 Course Instructor: Nida NasirDocument86 pagesCommunication System TC-307: Lecture 10, Week 4 Course Instructor: Nida NasirAhmad IrfanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Latch and Flip-FlopDocument43 pagesLecture 10 Latch and Flip-FlopNagaNo ratings yet
- K3ZM20P Timers - MultifunctionDocument3 pagesK3ZM20P Timers - MultifunctioncarlosNo ratings yet
- Rg214 Rgflex Coax Braided Cable: Product Data Sheet RG214-50JFDocument1 pageRg214 Rgflex Coax Braided Cable: Product Data Sheet RG214-50JFFaqir Khan JadoonNo ratings yet
- AL6200 - ProductSpecifications D031089239 Rev BDocument2 pagesAL6200 - ProductSpecifications D031089239 Rev BVirgil PeiulescuNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument31 pagesChapter Threeelias ferhanNo ratings yet
- Brief 52202 57112 10820169518KNV.14000880 Part1 PDFDocument10 pagesBrief 52202 57112 10820169518KNV.14000880 Part1 PDFadarshNo ratings yet
- The Advantages of Latch-Based Design Under Process VariationDocument6 pagesThe Advantages of Latch-Based Design Under Process VariationPriyank PanchalNo ratings yet
- How To Use?: UFCD 5123 - English in The Professional ContextDocument21 pagesHow To Use?: UFCD 5123 - English in The Professional ContextAugusto CamposNo ratings yet
- 03 - Analog and Digital TriggeringDocument12 pages03 - Analog and Digital TriggeringAlejandro Soto AltamiranoNo ratings yet
- Siemens-7SJ62-dir OcDocument4 pagesSiemens-7SJ62-dir OcAbo Abdullah MohamedNo ratings yet
- SOC Testing Methodology and Practice: To Cite This VersionDocument3 pagesSOC Testing Methodology and Practice: To Cite This Versionamit malaghanNo ratings yet
- Imp Computer McqsDocument2 pagesImp Computer McqsM. WaqasNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD ReportDocument6 pagesAutoCAD Reportbiatris pNo ratings yet
- $R2YULPHDocument154 pages$R2YULPHJose Luis Ccanchi InfantesNo ratings yet
- Adp 3110Document12 pagesAdp 3110ricardoNo ratings yet
- MPLAB User Guide 51519cDocument360 pagesMPLAB User Guide 51519cMgc Elektronik100% (1)
- INVENTEC KRUG (KRUG 14,15 - UMA) WS BUILD 6050A2296601 REV X01 - Dell Latitude E5420 PDFDocument106 pagesINVENTEC KRUG (KRUG 14,15 - UMA) WS BUILD 6050A2296601 REV X01 - Dell Latitude E5420 PDFBala MuruganNo ratings yet