Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plate Tectonics
Plate Tectonics
Uploaded by
api-4358316440 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views10 pagesThis document discusses different types of plate boundaries and rock formations. It describes three types of convergent boundaries where oceanic plates collide with oceanic plates, continental plates collide with continental plates, or one plate is oceanic and one is continental. It also discusses divergent boundaries where new crust forms at mid-ocean ridges or new continental crust forms. Additionally, it explains transform boundaries where plates slide past one another, and describes the three ways sedimentary rock forms and how metamorphic and igneous rocks are created through heat, pressure and cooling of magma.
Original Description:
Original Title
plate tectonics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses different types of plate boundaries and rock formations. It describes three types of convergent boundaries where oceanic plates collide with oceanic plates, continental plates collide with continental plates, or one plate is oceanic and one is continental. It also discusses divergent boundaries where new crust forms at mid-ocean ridges or new continental crust forms. Additionally, it explains transform boundaries where plates slide past one another, and describes the three ways sedimentary rock forms and how metamorphic and igneous rocks are created through heat, pressure and cooling of magma.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views10 pagesPlate Tectonics
Plate Tectonics
Uploaded by
api-435831644This document discusses different types of plate boundaries and rock formations. It describes three types of convergent boundaries where oceanic plates collide with oceanic plates, continental plates collide with continental plates, or one plate is oceanic and one is continental. It also discusses divergent boundaries where new crust forms at mid-ocean ridges or new continental crust forms. Additionally, it explains transform boundaries where plates slide past one another, and describes the three ways sedimentary rock forms and how metamorphic and igneous rocks are created through heat, pressure and cooling of magma.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 10
Plate Tectonics
By: Diana Hernandez
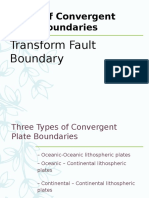
Convergent Boundary O-O
● When continental and oceanic
plates collide, the thinner and the
more dense oceanic plate is
overridden by disallowing the
thicker and less dense continental
plate.
Convergent Boundary O-C
● When two plates come towards each
other they create a convergent plate
boundary. The plates can meet where
they have oceanic crust or both have
continental crust, or they can meet
where one has oceanic and one has
continental.
Convergent Boundary C-C
● Convergent Plate Boundary -
Oceanic and Continental Plates.
When continental and oceanic
plates collide, the thinner and more
dense oceanic plate is overridden
by the thicker and less dense
continental plate.
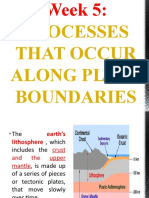
Divergent Continental
● Magma then oozes up from the
mantle to fill in the space
between the plates, forming a
raised ridge called a mid-ocean
ridge.
Divergent Ocean
● When continental and oceanic
plates collide, the thinner and more
dense oceanic plate is overridden
by the thicker and less dense
continental plate
Transform
● Transform Plate Boundaries are locations
where two plates slide past one another.
● Most transform faults are found in the
ocean basin and connect offsets in the
mid-ocean ridges.
Sedimentary
● Sedimentary rock can be created in
three different ways:
1. By the deposition of weathered
remains of other rocks.
2. By gathering and combining
sediments together.
3. By precipitation from solutions
Metamorphic
● It is formed by pre-existing rock.
● The original rock is exposed to
high heat and pressure, which
causes physical and chemical
changes to the rock.
● Examples of Metamorphic rock:
marble, slate.
Igneous
● They are created at the Earth’s
surface as a part of melting rocks in
the mantle and the crust.
● They are formed when magma is
cooled down on the Earth’s surface.
You might also like
- Richard P. Hilton-Dinosaurs and Other Mesozoic Reptiles of California (2003)Document347 pagesRichard P. Hilton-Dinosaurs and Other Mesozoic Reptiles of California (2003)Rodrigo TinocoNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson 4Document3 pagesScience Lesson 4purlfect8No ratings yet
- 3 Plate-TechtonicsDocument33 pages3 Plate-TechtonicsSakshi BhalewadikarNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic TheoryDocument88 pagesPlate Tectonic TheorySHWETA NATARAJANNo ratings yet
- Types of Plate Boundaries ConvergentDocument2 pagesTypes of Plate Boundaries ConvergentGeorcelle CarcillarNo ratings yet
- Purple and Green Animated Abstract Pattern Group Project Education PresentationDocument19 pagesPurple and Green Animated Abstract Pattern Group Project Education PresentationAnne Louise M. FilamorNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The EarthDocument4 pagesThe Structure of The EarthKishanNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics 1.1Document59 pagesPlate Tectonics 1.1sophiamarie.frias.xNo ratings yet
- PROCESSES THAT OCCUR ALONG PLATE BOUNDARIES - Week 5 and 6Document10 pagesPROCESSES THAT OCCUR ALONG PLATE BOUNDARIES - Week 5 and 6Menard Licuanan Rosales100% (1)
- Plate TectonicsDocument5 pagesPlate TectonicsZara AhmedNo ratings yet
- Inbound 2082121661556986964Document2 pagesInbound 2082121661556986964Jezell Ann Marie YuNo ratings yet
- Sci10 Plate TectonicsDocument44 pagesSci10 Plate TectonicsStill into youNo ratings yet
- Convergent Plate BoundariesDocument6 pagesConvergent Plate Boundariesjosh basteNo ratings yet
- The Earth's Structure and Plate TectonicsDocument17 pagesThe Earth's Structure and Plate TectonicsrocknismsNo ratings yet
- GEO1111 Lecture 4Document7 pagesGEO1111 Lecture 4uottawabiostudent12No ratings yet
- The Four LayersDocument12 pagesThe Four LayersNanette A. Marañon-SansanoNo ratings yet
- Plate BoundariesDocument55 pagesPlate BoundariesnoliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Plate BoundariesDocument46 pagesLesson 2 Plate BoundariesGian Andrei BenaguaNo ratings yet
- Earthsci Midterm 1 ReviewDocument6 pagesEarthsci Midterm 1 ReviewyadNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics - Chapter 1Document12 pagesPlate Tectonics - Chapter 1ellahbrackenNo ratings yet
- Sci LT #1 Term 2 G10 ReviewDocument8 pagesSci LT #1 Term 2 G10 Reviewmy3gr8kidoosNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics TheoryDocument8 pagesPlate Tectonics TheoryWendelyn Sumpo100% (1)
- Plate Boundaries PowerpointDocument25 pagesPlate Boundaries PowerpointRanz Panganiban100% (2)
- Reviewer Ni MadukusoDocument2 pagesReviewer Ni MadukusoAndrei Maddox PilotNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument2 pagesPlate TectonicsMarthaNo ratings yet
- Geography Unit 1Document12 pagesGeography Unit 1palaniappan aradhana AISSNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Continental & Oceanic Plates: by Doug Bennett Updated April 05, 2018Document4 pagesDifference Between Continental & Oceanic Plates: by Doug Bennett Updated April 05, 2018Gellian Mae Capondag CabalidaNo ratings yet
- Lithosphere VDocument2 pagesLithosphere VFarah NabihaNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review in ScienceDocument2 pagesPointers To Review in SciencePj JavierNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Group 3Document17 pagesEarth Science Group 3reignchan640No ratings yet
- (MR Sae) - SC - Causes of Earthquakes & Volcanic Eruptions-1Document11 pages(MR Sae) - SC - Causes of Earthquakes & Volcanic Eruptions-1saefurohmanNo ratings yet
- 04 - S24 - Plate TectonicsDocument57 pages04 - S24 - Plate Tectonicshldp2001No ratings yet
- Science Reviewer q1Document7 pagesScience Reviewer q1CypherNo ratings yet
- Geomophology PDFDocument20 pagesGeomophology PDFJoel T MbulanjeNo ratings yet
- Geo RevisionDocument4 pagesGeo RevisionFarfi UddinNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument43 pagesPlatesMerrie Anne BagsicNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift HypothesisDocument4 pagesContinental Drift HypothesisRaymart Dave MirandoNo ratings yet
- EARTHQUAKEDocument4 pagesEARTHQUAKEkennsindayenNo ratings yet
- Module 2 ScienceDocument2 pagesModule 2 ScienceSunoo KimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesLesson 2 Plate Tectonicsrobyngaylebautista2No ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument52 pagesEarth Sciencejazminelesliebunalade.bascNo ratings yet
- Science Test Study Sheet: General Facts About Earth'sDocument5 pagesScience Test Study Sheet: General Facts About Earth'sapi-281100019No ratings yet
- What Is PLATE Tectonics?Document51 pagesWhat Is PLATE Tectonics?Jane Idk100% (1)
- Notes Leaving Certificate Physical GeographyDocument39 pagesNotes Leaving Certificate Physical GeographySurbhi Singhal 0313No ratings yet
- Tectonic Plates and Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesTectonic Plates and Plate BoundariesManuel LisondraNo ratings yet
- Earth Science NotesDocument2 pagesEarth Science NotesCamilleNo ratings yet
- Tectonics PlatesDocument12 pagesTectonics PlatesChidhuro OwenNo ratings yet
- Geology-Notes 1PDocument43 pagesGeology-Notes 1Praul.rodriguezNo ratings yet
- As Notes On Rocks and Weathering 2020Document49 pagesAs Notes On Rocks and Weathering 2020Joyce Ama WilliamsNo ratings yet
- GRADE 10 Plate-BoundariesDocument23 pagesGRADE 10 Plate-BoundariesGilbert Monterde BaflorNo ratings yet
- (M2 POWERPOINT) Distribution and Plate BoundariesDocument15 pages(M2 POWERPOINT) Distribution and Plate BoundariesintodoieblissNo ratings yet
- Endogenic Processes: Continental Drift TDocument6 pagesEndogenic Processes: Continental Drift TmichelleNo ratings yet
- Three Main Types of Plate BounderiesDocument2 pagesThree Main Types of Plate BounderiesNyrrah PolvorosaNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics NotesDocument41 pagesPlate Tectonics NotesWilfred MuiaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Notes - Tectonics - Edexcel Geography A-LevelDocument24 pagesDetailed Notes - Tectonics - Edexcel Geography A-LevelAckeliah HemmingsNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: by Nishant DexterDocument20 pagesPlate Tectonics: by Nishant Dextersarrah asgarNo ratings yet
- Tectonic ImpactsDocument13 pagesTectonic ImpactsAria Grace100% (1)
- Geo Study GuideDocument4 pagesGeo Study Guidetarique.w.morgan5No ratings yet
- 1 Plate TectonicsDocument11 pages1 Plate TectonicsAyman M SNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: Divergent BoundaryDocument6 pagesPlate Tectonics: Divergent BoundaryLara Angela TiuNo ratings yet
- NAP Bhutan 2023 - WaterDocument39 pagesNAP Bhutan 2023 - WaterKaran GuptaNo ratings yet
- Textbook Ebook Deepwater Drilling Well Planning Design Engineering Operations and Technology Application Peter Aird All Chapter PDFDocument43 pagesTextbook Ebook Deepwater Drilling Well Planning Design Engineering Operations and Technology Application Peter Aird All Chapter PDFtammy.hirkaler365100% (8)
- References For Well Logging and Formation Evaluation.: - Harald Bolt, Wireline Depth Determination, Rev 3.3, Apr 2012Document4 pagesReferences For Well Logging and Formation Evaluation.: - Harald Bolt, Wireline Depth Determination, Rev 3.3, Apr 2012Ahmed FoudaNo ratings yet
- EarthDocument2 pagesEarthReambillo FamilyNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Studies ContentsDocument2 pagesBangladesh Studies ContentsTanzir MollikNo ratings yet
- Poke WildsDocument109 pagesPoke WildsKokotNo ratings yet
- Soil Water Dynamics, 2013Document15 pagesSoil Water Dynamics, 2013André FerrazNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Applied Mineralogy Springer Textbooks in Earth Sciences Geography and Environment First Edition Jens GötzeDocument70 pagesIntroduction To Applied Mineralogy Springer Textbooks in Earth Sciences Geography and Environment First Edition Jens Götzecalvin.griffin735100% (13)
- Laporan Akhir Paleontologi EkskursiDocument11 pagesLaporan Akhir Paleontologi EkskursiAdrianNo ratings yet
- Module 2 FinalDocument112 pagesModule 2 Finalaparna baburajNo ratings yet
- Guwahati: Places To VisitDocument5 pagesGuwahati: Places To Visitdrishti kuthariNo ratings yet
- EarthAndLifeScience (SHS) Q2 Mod21 EvolvingConceptOfLifeBasedOnEmergingPiecesOfEvidence V1Document24 pagesEarthAndLifeScience (SHS) Q2 Mod21 EvolvingConceptOfLifeBasedOnEmergingPiecesOfEvidence V1Emer Perez100% (12)
- Surviyung Chapter One Topo, MappingDocument62 pagesSurviyung Chapter One Topo, MappingNura GuyoNo ratings yet
- Knife Drop Creative Recipes Anyone Can Cook 2nd Edition Nick Digiovanni PDF Full ChapterDocument24 pagesKnife Drop Creative Recipes Anyone Can Cook 2nd Edition Nick Digiovanni PDF Full Chaptershielashegh89100% (15)
- Roads and Paths PDFDocument5 pagesRoads and Paths PDFsneha sara vargheseNo ratings yet
- LAS On DEFORMATION OF THE CRUSTDocument4 pagesLAS On DEFORMATION OF THE CRUSTRam KuizonNo ratings yet
- Cha 2014Document10 pagesCha 2014nhan nguyenNo ratings yet
- AusDocument143 pagesAusAnonymous 5siTEdNo ratings yet
- Imacnmnc Approved Mineral Symbols PDFDocument30 pagesImacnmnc Approved Mineral Symbols PDFmilton74No ratings yet
- Identificación de Sulfuros Complejos de Plata (Sulfosales) Contenidos en Un Concentrado de PB, Del Distrito Minero de Zimapán HidalgoDocument5 pagesIdentificación de Sulfuros Complejos de Plata (Sulfosales) Contenidos en Un Concentrado de PB, Del Distrito Minero de Zimapán HidalgoPauloValdiviesoNo ratings yet
- Form One Agriculture Notes 2022Document29 pagesForm One Agriculture Notes 2022Innocent MarungamiseNo ratings yet
- East of The Rocky MountainsDocument343 pagesEast of The Rocky MountainsscaryowlNo ratings yet
- KS4 Skills Book 4 Marks PDFDocument12 pagesKS4 Skills Book 4 Marks PDFsaffNo ratings yet
- Jacobs StaffDocument2 pagesJacobs StaffHisbullah 015No ratings yet
- Bieniawski'S RMR System: Geomechanical RocksDocument3 pagesBieniawski'S RMR System: Geomechanical Rockssubhajit majiNo ratings yet
- Science5 Q4 Mod1 How Rocks Turn To Soil v4Document21 pagesScience5 Q4 Mod1 How Rocks Turn To Soil v4Aiza Conchada0% (1)
- International Journal of Mining Science and Technology: Lu Jun, Van Dyke Mark, Su Daniel W.H., Hasenfus GregDocument7 pagesInternational Journal of Mining Science and Technology: Lu Jun, Van Dyke Mark, Su Daniel W.H., Hasenfus Gregpradhith kattaNo ratings yet
- Mining Plan Format (A & B Category Mines)Document10 pagesMining Plan Format (A & B Category Mines)Vedansh Thakur VedanshNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Remedial Test in Science 10Document2 pagesFirst Quarter Remedial Test in Science 10ERMA D. VASAYANo ratings yet