Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
64 viewsA Carbapenem
A Carbapenem
Uploaded by
Jaz MnCarbapenems are broad-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotics used intravenously or intramuscularly. Monobactams like aztreonam have a narrower spectrum mainly against gram-negative bacteria. Beta-lactamase inhibitors like clavulanic acid, sulbactam, and tazobactam protect beta-lactam antibiotics from bacterial beta-lactamases. They work by irreversibly binding to and inactivating the beta-lactamases. When combined with beta-lactam antibiotics, they increase their antibacterial activity by 4 to 32 fold. Common side effects of carbapenems include gastrointestinal issues. Beta-lact
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Advanced Endodontics PDFDocument375 pagesAdvanced Endodontics PDFMihalache Catalin90% (10)
- Physician Patient RelationshipDocument25 pagesPhysician Patient RelationshipUser 010897020197100% (1)
- 1618008-The Risk and Protective Factors of Pornography AddictionDocument30 pages1618008-The Risk and Protective Factors of Pornography AddictionJaz MnNo ratings yet
- Common Cold and InfluenzaDocument5 pagesCommon Cold and InfluenzaJaz MnNo ratings yet
- List of Antibiotic Classes: Aminopenicillin Antipseudomonal PENICILLIN (Known As)Document2 pagesList of Antibiotic Classes: Aminopenicillin Antipseudomonal PENICILLIN (Known As)Jaz MnNo ratings yet
- Skin and Skin Structure Infection Skin and Skin Structure InfectionDocument2 pagesSkin and Skin Structure Infection Skin and Skin Structure InfectionJaz MnNo ratings yet
- The Role of Complement Proteins in B-Cell Activation C3d ("Second Signals") 1. Antigen Receptor-Mediated Signal Transduction in B-LymphocytesDocument5 pagesThe Role of Complement Proteins in B-Cell Activation C3d ("Second Signals") 1. Antigen Receptor-Mediated Signal Transduction in B-LymphocytesJaz MnNo ratings yet
- Sunburn (Suntan) & Insect Bites and StingsDocument5 pagesSunburn (Suntan) & Insect Bites and StingsJaz MnNo ratings yet
- Injury or Trauma Include:: Muscle Cramp Sprain Strain Rheumatoid Arthritis Osteoarthritis Bursitis TendinitisDocument5 pagesInjury or Trauma Include:: Muscle Cramp Sprain Strain Rheumatoid Arthritis Osteoarthritis Bursitis TendinitisJaz MnNo ratings yet
- General Mechanism of Action1Document2 pagesGeneral Mechanism of Action1Jaz MnNo ratings yet
- Function of Pituitary HormonesDocument1 pageFunction of Pituitary HormonesJaz MnNo ratings yet
- Mba 1 in PDFDocument41 pagesMba 1 in PDFtheshoeslover1No ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of Test Bank For Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing 9th by Townsend All ChapterDocument41 pagesFull Download PDF of Test Bank For Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing 9th by Townsend All Chaptersetderofis100% (2)
- OPT EP Kimber Student Insurance BrochureDocument20 pagesOPT EP Kimber Student Insurance BrochureKanakamedala Sai Rithvik ee18b051No ratings yet
- Radiation Safety SOP: Scope/PurposeDocument4 pagesRadiation Safety SOP: Scope/Purposezen AlkaffNo ratings yet
- LeiningerDocument36 pagesLeiningerAshley EmperadorNo ratings yet
- Stature - Raxter Et Al 2007Document2 pagesStature - Raxter Et Al 2007Litzley Shannen SanchezNo ratings yet
- Personal Finance 11th Edition Kapoor Test BankDocument25 pagesPersonal Finance 11th Edition Kapoor Test BankJackEstesiobz100% (61)
- Safer at Home Order Final 7.29.20 PDFDocument11 pagesSafer at Home Order Final 7.29.20 PDFMary HodginNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Esoteric HealingDocument4 pagesAn Overview of Esoteric HealingLeoni Hodgson100% (1)
- Biomechanics of Open Bite TreatmentDocument40 pagesBiomechanics of Open Bite TreatmentMaitreye PriyadarshiniNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Case Study Design Considerations For An Orthopedic Hip ImplantDocument8 pagesModule 7 Case Study Design Considerations For An Orthopedic Hip ImplantrihabNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Survival Kit Checklist PDFDocument59 pagesThe Ultimate Survival Kit Checklist PDFKen Lecter100% (1)
- Comparison of Endoscopic Cartilage Myringoplasty in Dry and Wet Ears With Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument6 pagesComparison of Endoscopic Cartilage Myringoplasty in Dry and Wet Ears With Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediafatinfatharaniNo ratings yet
- Rigel 333 Instruction ManualDocument37 pagesRigel 333 Instruction ManualTerraTerro Welleh WellehNo ratings yet
- Mandatory Public Disclosure 1Document4 pagesMandatory Public Disclosure 1Manikanta SatishNo ratings yet
- Endodontic DiagnosisDocument7 pagesEndodontic Diagnosisاحمد عبد الحسن حمود عليNo ratings yet
- Dr. Wasim PathanDocument3 pagesDr. Wasim PathanwasimNo ratings yet
- Cinematic Environs - Desert WastesDocument28 pagesCinematic Environs - Desert WastesPhilmore Pockets100% (1)
- To Study The Efficacy of Nirgundipatra Swaras Taila Karnapurana in The Management of Pootikarna With Special Reference To Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument6 pagesTo Study The Efficacy of Nirgundipatra Swaras Taila Karnapurana in The Management of Pootikarna With Special Reference To Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- COPARDocument21 pagesCOPAREdra VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Slam Dunk Proof: Iran Threatens Missile Attack On US Bio-Weapon Labs, Intel Drop (Updating)Document6 pagesSlam Dunk Proof: Iran Threatens Missile Attack On US Bio-Weapon Labs, Intel Drop (Updating)philo-sophosNo ratings yet
- Gendering LanguageDocument53 pagesGendering LanguagePRINCESS KAYE ANGEL MAMALONo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Medical DeviceDocument14 pagesRisk Assessment Medical DeviceBudi SusantoNo ratings yet
- OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY CollectionDocument12 pagesOBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY CollectionAhmad Syahmi YZNo ratings yet
- NIOSH Hazardous DrugsDocument22 pagesNIOSH Hazardous DrugsjimstasonNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Guide To Critiquing Research Part 2Document7 pagesStep by Step Guide To Critiquing Research Part 2michael ndlovuNo ratings yet
- For Peer Review: Theory and Language of Climate Change CommunicationDocument18 pagesFor Peer Review: Theory and Language of Climate Change CommunicationUsman AliNo ratings yet
- Assessment of KidneysDocument1 pageAssessment of KidneysWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
A Carbapenem
A Carbapenem
Uploaded by
Jaz Mn0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
64 views4 pagesCarbapenems are broad-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotics used intravenously or intramuscularly. Monobactams like aztreonam have a narrower spectrum mainly against gram-negative bacteria. Beta-lactamase inhibitors like clavulanic acid, sulbactam, and tazobactam protect beta-lactam antibiotics from bacterial beta-lactamases. They work by irreversibly binding to and inactivating the beta-lactamases. When combined with beta-lactam antibiotics, they increase their antibacterial activity by 4 to 32 fold. Common side effects of carbapenems include gastrointestinal issues. Beta-lact
Original Description:
A Carbapenem
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCarbapenems are broad-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotics used intravenously or intramuscularly. Monobactams like aztreonam have a narrower spectrum mainly against gram-negative bacteria. Beta-lactamase inhibitors like clavulanic acid, sulbactam, and tazobactam protect beta-lactam antibiotics from bacterial beta-lactamases. They work by irreversibly binding to and inactivating the beta-lactamases. When combined with beta-lactam antibiotics, they increase their antibacterial activity by 4 to 32 fold. Common side effects of carbapenems include gastrointestinal issues. Beta-lact
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
64 views4 pagesA Carbapenem
A Carbapenem
Uploaded by
Jaz MnCarbapenems are broad-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotics used intravenously or intramuscularly. Monobactams like aztreonam have a narrower spectrum mainly against gram-negative bacteria. Beta-lactamase inhibitors like clavulanic acid, sulbactam, and tazobactam protect beta-lactam antibiotics from bacterial beta-lactamases. They work by irreversibly binding to and inactivating the beta-lactamases. When combined with beta-lactam antibiotics, they increase their antibacterial activity by 4 to 32 fold. Common side effects of carbapenems include gastrointestinal issues. Beta-lact
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
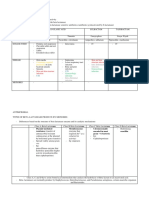
CARBAPENEM/MONOPENEM/BETA-LACTAMASE INHIBITORS
Carbapenam MONOPENEM BETA LACTAMASE INHIBITOR
Example :
EXAMPLES 1. IMIPENEM Disrupt bacterial
cell wall 1. CLAVULANIC ACID
resist hydrolysis of MOST beta synthesis – same 2. SULBACTAM
lactamases but not mettalo-beta like other beta- 3. TAZOBACTAM (IV WITH
lactamase lactam. piperacillin)
imipenem undergoes cleavage by Unique: BETA- Have beta-lactam ring but do
DEHYDROPTIDASE (found in the LACTAM IS not have significant
brush boarder of the proximal renal NOT FUSED antibacterial activity
tubule). Combine imipenem and WITH OTHER Bind and inactivate beta-
cilastatin prevent the parent drug from RING. lactamase (protecting
being inactive toxic metabolite. Lead to antibiotics that normally
nephrotoxic. 1. AZTREONAM substrate for these enzyme)
(IV or IM) Formulated in combination
(do not need co-administered cilastatin) with beta-lactamase sensitive
2. MEROPENEM antibiotics.
3. DORIPENEM
4. ERTAPENEM (IV &IM)
Synthetic beta-lactam antibiotic based
on thienamycin (from Streptomyces
cattleya)
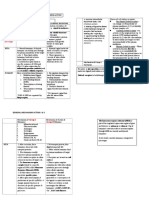
SPECTRUM Imipenem, meropenem and Lack / narrow
doripenem (have empirical therapy antimicrobial
because active against beta (thus, empirical
lactamase producing (broad therapy) activity
spectrum): against Gram
+ve and
1. Gram +ve COCCI: anaerobes
o staphyloc. Aureus* Antimicrobial
o staphy. Epidermidis mainly against
o staph. Faecalis Enterobacteriace
o strepto. Group A,B,C ae including P.
o strep. Pneumonia aeruginosa
Resistant against
*staphyl. are resistance to most of beta-
METHICILLIN lactamases
EXCEPT
2. Gram +ve BACILLI EXTENDED-
o Listeria monocytogenes SPECTRUM
beta-lactamases
3. Gram -ve COCCI: Relatively
o Neisseria meningitidis nontoxic
o N. gonorrhoeae Has low
immunogenic
4. Gram -ve RODS: potential and
o Acinobacter sp. little cross-
o Citrobacter sp. reactivity
o E. coli Can be used
o Gardnella vaginalis in pt with
o H. influenza penicillin
o Klebsiella sp. hypersensiti
o P. aeruginosa vity
o Salmonella sp
o Serratia sp
5. Anaerobes
o Clostridium sp.
o Propionibacterium
o Peptostrepto/ peptococcus
o Bacteroides sp.
o Fusobacterium sp
6. Others
o Actinomyces
o Spirochetes
o Chlamydia
ERTAPENEM lack coverage for:
P. aeruginosa
Enterococcus
Acinetobacter
RESISTANC Resistance to carbapenem Azobactam is Bacteria resistance to beta lactamase
E 1. Reduced permeability of the outer resistance to most inhibitor:
membrane of Gram-negative beta-lactamase 1. Due to genetic mutation:
bacteria (due to diminished except extended Clavulanic acid cause
production of porins) causing spectrum beta mutation in
reduced bacterial uptake lactamase chromosomally encoded
2. Reduced affinity of the target class C B-lactamases
penicillin binding proteins (PBP) Depression of inducible
3. Increased expression of efflux chromosomally encoded
pump components (bacteria has B-lactamase
the ability to pump out Overproduction of
carbapenem out of the cell wall WILD type class A
4. Production of antibiotic-destroying penicillinase (TEM 1
enzymes (carbapenemases, and TEM 2) that cause
METALLO-Β-LACTAMASES- low sensitivity to b-
class b). lactam inhibitor
PHARMAC Carbapenems and monobactams are IRREVERSIBLE binding with
OKINETICS NOT ABSORBED after oral most β-lactamases.
/ administration. Combine with β-lactams
PHARMAC Use IV or IM (ertapenem) antibiotics increase the
ODYNAMI Imipenem/cilastatin and meropenem antibacterial activity
C administered IV and PENETRATES approximately 4- to 32-fold.
WELL into most body fluids and Increase the inoculum size
tissues including cerebrospinal fluid, decrease the effectiveness of the
achieving concentrations matching combination.
or exceeding those required to β-lactamases inhibitors can
inhibit most susceptible bacteria. paradoxically induce increased
Plasma protein binding is production of β-lactamases
approximately 2%. There is one from the bacteria they
metabolite which is encountered.
microbiologically inactive. The relative ability of the β-
The elimination half-life is lactamases inhibitor to induce β-
approximately 1 hour. lactamases production is in the
following order: clavulanic acid
> sulbactam > tazobactam.
ADR/ Side 1. Nausea/ vomiting/ diarrhea (GIT 1. Due to given by Absorption
Effect disturbance) – 1 mark injection it cause Clavulanic acid absorbed with
2. Eosinophilia phlebitis oral bioavailability of 89 –
3. Neutropenia 2. Skin rash 97%.
3. Test for liver Sulbactam is not well absorbed
High imipenem / cilastatin lead to abnormality but use of prodrug in
seizure 4. Can accumulate combination with ampicillin
in patient that increase it bioavailability.
has renal failure Tazobactom is not absorbed by
the oral route.
HOWEVER, THIS Distribution
DRUG SAFE FOR Clavulanic acid is 20% bound
* Carbapenem differs from penicillin THOSE WHO to serum protein and distributed
where the sulphur atom in the ALLERGIC AGAIN into liver, kidneys, lymph node,
thiazolidine ring is replaced with carbon. PENICILLIN AND bile, peritoneal fluid, CSF,
Monobactam unique one ring only CEPHALOSPORIN bone and synovial fluid.
(sbb low Sulbactam is 38% bound to
immunogenic serum protein and penetrates
potential as it has into fluids and tissues
little cross reaction (intraperitoneal fluid, sputum,
with antibodies CSF in inflamed meninges,
induced by other beta intestinal mucosa and
lactam. myometrium)
Serum binding of tazobactam is
20 – 26% and penetrates
bronchial secretion, fat, muscle,
lung, appendix, skin prostate
and gallbladder.
Metabolism/Excretion
Clavulanic acid undergoes
some hepatic metabolism to
give two major metabolites that
eliminated by renal and do not
have antibacterial or β-
lactamases inhibitors activity.
Approximately 40 – 75% of
clavulanic acid excreted
unchanged in urine.
Sulbactam does not undergo
metabolism. Excreted by renal
unchanged and clearance of
sulbactam is greatly decreased
in patients with renal
impairment.
Tazobactam is primarily
excreted in urine and no-nrenal
clearance via biliary excretion
and hepatic metabolism.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Advanced Endodontics PDFDocument375 pagesAdvanced Endodontics PDFMihalache Catalin90% (10)
- Physician Patient RelationshipDocument25 pagesPhysician Patient RelationshipUser 010897020197100% (1)
- 1618008-The Risk and Protective Factors of Pornography AddictionDocument30 pages1618008-The Risk and Protective Factors of Pornography AddictionJaz MnNo ratings yet
- Common Cold and InfluenzaDocument5 pagesCommon Cold and InfluenzaJaz MnNo ratings yet
- List of Antibiotic Classes: Aminopenicillin Antipseudomonal PENICILLIN (Known As)Document2 pagesList of Antibiotic Classes: Aminopenicillin Antipseudomonal PENICILLIN (Known As)Jaz MnNo ratings yet
- Skin and Skin Structure Infection Skin and Skin Structure InfectionDocument2 pagesSkin and Skin Structure Infection Skin and Skin Structure InfectionJaz MnNo ratings yet
- The Role of Complement Proteins in B-Cell Activation C3d ("Second Signals") 1. Antigen Receptor-Mediated Signal Transduction in B-LymphocytesDocument5 pagesThe Role of Complement Proteins in B-Cell Activation C3d ("Second Signals") 1. Antigen Receptor-Mediated Signal Transduction in B-LymphocytesJaz MnNo ratings yet
- Sunburn (Suntan) & Insect Bites and StingsDocument5 pagesSunburn (Suntan) & Insect Bites and StingsJaz MnNo ratings yet
- Injury or Trauma Include:: Muscle Cramp Sprain Strain Rheumatoid Arthritis Osteoarthritis Bursitis TendinitisDocument5 pagesInjury or Trauma Include:: Muscle Cramp Sprain Strain Rheumatoid Arthritis Osteoarthritis Bursitis TendinitisJaz MnNo ratings yet
- General Mechanism of Action1Document2 pagesGeneral Mechanism of Action1Jaz MnNo ratings yet
- Function of Pituitary HormonesDocument1 pageFunction of Pituitary HormonesJaz MnNo ratings yet
- Mba 1 in PDFDocument41 pagesMba 1 in PDFtheshoeslover1No ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of Test Bank For Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing 9th by Townsend All ChapterDocument41 pagesFull Download PDF of Test Bank For Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing 9th by Townsend All Chaptersetderofis100% (2)
- OPT EP Kimber Student Insurance BrochureDocument20 pagesOPT EP Kimber Student Insurance BrochureKanakamedala Sai Rithvik ee18b051No ratings yet
- Radiation Safety SOP: Scope/PurposeDocument4 pagesRadiation Safety SOP: Scope/Purposezen AlkaffNo ratings yet
- LeiningerDocument36 pagesLeiningerAshley EmperadorNo ratings yet
- Stature - Raxter Et Al 2007Document2 pagesStature - Raxter Et Al 2007Litzley Shannen SanchezNo ratings yet
- Personal Finance 11th Edition Kapoor Test BankDocument25 pagesPersonal Finance 11th Edition Kapoor Test BankJackEstesiobz100% (61)
- Safer at Home Order Final 7.29.20 PDFDocument11 pagesSafer at Home Order Final 7.29.20 PDFMary HodginNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Esoteric HealingDocument4 pagesAn Overview of Esoteric HealingLeoni Hodgson100% (1)
- Biomechanics of Open Bite TreatmentDocument40 pagesBiomechanics of Open Bite TreatmentMaitreye PriyadarshiniNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Case Study Design Considerations For An Orthopedic Hip ImplantDocument8 pagesModule 7 Case Study Design Considerations For An Orthopedic Hip ImplantrihabNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Survival Kit Checklist PDFDocument59 pagesThe Ultimate Survival Kit Checklist PDFKen Lecter100% (1)
- Comparison of Endoscopic Cartilage Myringoplasty in Dry and Wet Ears With Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument6 pagesComparison of Endoscopic Cartilage Myringoplasty in Dry and Wet Ears With Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediafatinfatharaniNo ratings yet
- Rigel 333 Instruction ManualDocument37 pagesRigel 333 Instruction ManualTerraTerro Welleh WellehNo ratings yet
- Mandatory Public Disclosure 1Document4 pagesMandatory Public Disclosure 1Manikanta SatishNo ratings yet
- Endodontic DiagnosisDocument7 pagesEndodontic Diagnosisاحمد عبد الحسن حمود عليNo ratings yet
- Dr. Wasim PathanDocument3 pagesDr. Wasim PathanwasimNo ratings yet
- Cinematic Environs - Desert WastesDocument28 pagesCinematic Environs - Desert WastesPhilmore Pockets100% (1)
- To Study The Efficacy of Nirgundipatra Swaras Taila Karnapurana in The Management of Pootikarna With Special Reference To Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument6 pagesTo Study The Efficacy of Nirgundipatra Swaras Taila Karnapurana in The Management of Pootikarna With Special Reference To Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- COPARDocument21 pagesCOPAREdra VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Slam Dunk Proof: Iran Threatens Missile Attack On US Bio-Weapon Labs, Intel Drop (Updating)Document6 pagesSlam Dunk Proof: Iran Threatens Missile Attack On US Bio-Weapon Labs, Intel Drop (Updating)philo-sophosNo ratings yet
- Gendering LanguageDocument53 pagesGendering LanguagePRINCESS KAYE ANGEL MAMALONo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Medical DeviceDocument14 pagesRisk Assessment Medical DeviceBudi SusantoNo ratings yet
- OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY CollectionDocument12 pagesOBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY CollectionAhmad Syahmi YZNo ratings yet
- NIOSH Hazardous DrugsDocument22 pagesNIOSH Hazardous DrugsjimstasonNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Guide To Critiquing Research Part 2Document7 pagesStep by Step Guide To Critiquing Research Part 2michael ndlovuNo ratings yet
- For Peer Review: Theory and Language of Climate Change CommunicationDocument18 pagesFor Peer Review: Theory and Language of Climate Change CommunicationUsman AliNo ratings yet
- Assessment of KidneysDocument1 pageAssessment of KidneysWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet