Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
373 viewsImmunity First and Second Dose of Injection (With Graph)
Immunity First and Second Dose of Injection (With Graph)
Uploaded by
WONGThe document discusses two types of immunity: artificially active immunity from the hepatitis B vaccine, which requires multiple doses to induce a sufficient antibody level for protection; and artificially passive immunity from treatments like the rabies vaccine, which provides immediate short-term immunity from an antibody injection but requires additional doses if the infection persists due to declining antibody levels over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Biology Final Exam Grade 9Document2 pagesBiology Final Exam Grade 9Yesha Shah100% (1)
- f5 c8 Probability Distribution NewDocument7 pagesf5 c8 Probability Distribution NewYoga NathanNo ratings yet
- Vumbi Marking Guide of Biology A Level Carrefour Umurezi 2023-2024-1Document6 pagesVumbi Marking Guide of Biology A Level Carrefour Umurezi 2023-2024-1Theogene NTEGEREJIMANANo ratings yet
- Biology Summary NotesDocument5 pagesBiology Summary NotesNoraNo ratings yet
- Business Studies 2015 HSC ExamDocument18 pagesBusiness Studies 2015 HSC ExamMNo ratings yet
- HKCEE - Biology - 1999 - Paper I - A PDFDocument4 pagesHKCEE - Biology - 1999 - Paper I - A PDFChinlam210No ratings yet
- Flashcards - Topic 10 Diseases and Immunity - CIE Biology IGCSEDocument37 pagesFlashcards - Topic 10 Diseases and Immunity - CIE Biology IGCSEJane Lea100% (1)
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationVernonNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 November 1999Document5 pagesPaper 2 November 1999MSHNo ratings yet
- HSBDocument12 pagesHSBjemima MillsNo ratings yet
- Planning An Investigation Model Answers Five Complete PlansDocument16 pagesPlanning An Investigation Model Answers Five Complete PlansAhmad Kabil100% (1)
- Inheritance Worksheet 2: Fig. 1.1 Shows A Goat With White FurDocument4 pagesInheritance Worksheet 2: Fig. 1.1 Shows A Goat With White FurTarshihiNo ratings yet
- 0653 s03 Ms 1+2+3+5+6Document28 pages0653 s03 Ms 1+2+3+5+6Sofia M Vigo AguiarNo ratings yet
- 8-ICSE-X Biology 2020 PaperDocument16 pages8-ICSE-X Biology 2020 Paperaarnavgeneral1308No ratings yet
- Homeostasis..answer Key WorksheetDocument4 pagesHomeostasis..answer Key WorksheetUCL Sports100% (1)
- Tutorial 6 Transport in PlantsDocument7 pagesTutorial 6 Transport in PlantsyanasakaranNo ratings yet
- Section A 1. The Characteristics of Living Things, Cell Structure, Function and SpecializationDocument12 pagesSection A 1. The Characteristics of Living Things, Cell Structure, Function and SpecializationJerry100% (1)
- Alwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 10. Diseases and Immunity NotesDocument35 pagesAlwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 10. Diseases and Immunity NotesMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument6 pagesTransport in PlantsFred H HalderNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Homeostasis PDFDocument77 pages2.1 Homeostasis PDFtess_15No ratings yet
- Nutrition QuestionsDocument22 pagesNutrition Questionsnoddy60No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Integrated Science Week 2 Lesson 2Document5 pagesGrade 8 Integrated Science Week 2 Lesson 2Balram HaroldNo ratings yet
- Marking Schemes For Topic 1,2 Stafford PapersDocument57 pagesMarking Schemes For Topic 1,2 Stafford PapersSuha AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Alwadi International School Human Influences On Ecosystems Notes & WorksheetDocument55 pagesAlwadi International School Human Influences On Ecosystems Notes & WorksheetMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Biology Past PapersDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Biology Past PapersAdam mahabirNo ratings yet
- 19 - Organisms and Their EnvironmentDocument5 pages19 - Organisms and Their EnvironmentAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- Beetroot Core Practical Writing FrameDocument5 pagesBeetroot Core Practical Writing FrameJett0% (1)
- 12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFDocument51 pages12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFUmair Khan Marwat100% (1)
- Reproduction - ScoreDocument6 pagesReproduction - ScoreIslahNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants CIE IGCSE Biology 610 Classified Paster Paper 2Document21 pagesTransport in Plants CIE IGCSE Biology 610 Classified Paster Paper 2IGCSE Physics & ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 1 Edexcel Jan 96-June 05Document190 pagesBiology Unit 1 Edexcel Jan 96-June 05api-3729563100% (2)
- 04 - Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification FIBDocument5 pages04 - Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification FIBDianaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 NotesDocument23 pagesTopic 2 NotesVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans Grade 9Document49 pagesGas Exchange in Humans Grade 9harliv2.5chandhokNo ratings yet
- QS AnswersDocument8 pagesQS AnswersJorif100% (1)
- Characteristics of Living Things CellsDocument13 pagesCharacteristics of Living Things CellsFrances FlynnNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Perfect Score Answering Technique 2012Document12 pagesChemistry Perfect Score Answering Technique 2012钟㛃彤No ratings yet
- English 10 StandardsDocument65 pagesEnglish 10 Standardszaineddin SaadeddinNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Course ContentDocument2 pagesIGCSE Biology Course Contentjoedbmelvin0% (1)
- Pure Bio CH 17 Textbook Answers PDFDocument3 pagesPure Bio CH 17 Textbook Answers PDFashaNo ratings yet
- 0654 2013 IGCSE Coordinated Sciences Paper 2Document32 pages0654 2013 IGCSE Coordinated Sciences Paper 2jwinlynNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Membranes, Proteins, DNA and Gene Expression MSDocument13 pagesUNIT 1 Membranes, Proteins, DNA and Gene Expression MSpramodini JayalathNo ratings yet
- 9700 w14 QP 21Document16 pages9700 w14 QP 21rashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- % Chapter 2 Regulation of Body Temperature: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument32 pages% Chapter 2 Regulation of Body Temperature: Multiple-Choice QuestionsK C100% (1)
- IGCSE Answers Chapters 01 05Document7 pagesIGCSE Answers Chapters 01 05María Eugenia MolteniNo ratings yet
- Cells 2 FDocument10 pagesCells 2 FEANo ratings yet
- Coordination and Response IGCSE NotesDocument11 pagesCoordination and Response IGCSE NotesDrRemyaranjith Menon100% (1)
- Enzymes: Biology Matters G.C.E. 'O' Level (2 Edition) : Textbook AnswersDocument2 pagesEnzymes: Biology Matters G.C.E. 'O' Level (2 Edition) : Textbook AnswersJack KowmanNo ratings yet
- Gmo PDFDocument18 pagesGmo PDFIgorVutucNo ratings yet
- Excretion in Humans 2 QPDocument11 pagesExcretion in Humans 2 QPMikiko Fujiwara SamaNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Topic 18 Variation and Selection - CAIE Biology IGCSEDocument2 pagesDefinitions - Topic 18 Variation and Selection - CAIE Biology IGCSEG VeezNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Section 5 Lesson 1Document92 pagesIGCSE Biology Section 5 Lesson 1salmaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Coordination and Response WsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Coordination and Response WsAnand Kumar ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes For O LevelsDocument13 pagesBiology Notes For O Levelstahira mujahidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MicroorganismsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 MicroorganismsNIKHILPATNINo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology ImmunityDocument1 pageForm 5 Biology ImmunityWONGNo ratings yet
- Prof. Dr. Payman A.Hamaseed: VaccinationDocument19 pagesProf. Dr. Payman A.Hamaseed: Vaccinationasia groupNo ratings yet
- Concept Communicable DiseasesDocument477 pagesConcept Communicable DiseasesrimeoznekNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Nursing 2020Document421 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing 2020Kenneth Myro GarciaNo ratings yet
- Infection Control in Clinical SettingDocument35 pagesInfection Control in Clinical SettingRinku patelNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Biology Chapter 8 Dynamic EcosystemDocument6 pagesForm 4 Biology Chapter 8 Dynamic EcosystemWONGNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology ImmunityDocument1 pageForm 5 Biology ImmunityWONGNo ratings yet
- How Antibodies Work?: Brentha Tay Hui Yee Yap Xin RuDocument12 pagesHow Antibodies Work?: Brentha Tay Hui Yee Yap Xin RuWONGNo ratings yet
- Stages of MitosisDocument2 pagesStages of MitosisWONGNo ratings yet
Immunity First and Second Dose of Injection (With Graph)
Immunity First and Second Dose of Injection (With Graph)
Uploaded by
WONG0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
373 views1 pageThe document discusses two types of immunity: artificially active immunity from the hepatitis B vaccine, which requires multiple doses to induce a sufficient antibody level for protection; and artificially passive immunity from treatments like the rabies vaccine, which provides immediate short-term immunity from an antibody injection but requires additional doses if the infection persists due to declining antibody levels over time.
Original Description:
Artificially Active immunity and Artificially Passive Immunity
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses two types of immunity: artificially active immunity from the hepatitis B vaccine, which requires multiple doses to induce a sufficient antibody level for protection; and artificially passive immunity from treatments like the rabies vaccine, which provides immediate short-term immunity from an antibody injection but requires additional doses if the infection persists due to declining antibody levels over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
373 views1 pageImmunity First and Second Dose of Injection (With Graph)
Immunity First and Second Dose of Injection (With Graph)
Uploaded by
WONGThe document discusses two types of immunity: artificially active immunity from the hepatitis B vaccine, which requires multiple doses to induce a sufficient antibody level for protection; and artificially passive immunity from treatments like the rabies vaccine, which provides immediate short-term immunity from an antibody injection but requires additional doses if the infection persists due to declining antibody levels over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
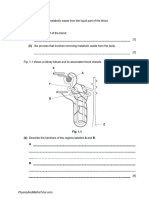
Artificially Active Immunity (Hepatitis B)
1. The first dose usually induces a low level of antibody concentration which is not
sufcient to protect the person against disease.
2. Second dose is needed to increase the production of antibody until it reaches the
immunity level
3. Vaccine is a preparation of weakened, dead pathogens. It stimulates the immune system
in the body to reach the level of immunity.
Artificially acquired Passive Immunity (e.g.: Rabies, Tetanus, Snake Bite, and Botulism)1
1. The first injection offers immediate immunity against the disease.
2. The concentration of antibodies in the blood after the first injection is sufficient to
provide immunity against the disease.
3. The quantity of antibody in blood last for only two weeks / does not last long.
4. A second dose is given when the person is still infected by the disease.
5. The concentration of antibodies in his blood has dropped below the immunity level
6. A second injection of serum is needed to raise the concentration of antibodies above
the immunity level needed to fight against the infection.
You might also like
- Biology Final Exam Grade 9Document2 pagesBiology Final Exam Grade 9Yesha Shah100% (1)
- f5 c8 Probability Distribution NewDocument7 pagesf5 c8 Probability Distribution NewYoga NathanNo ratings yet
- Vumbi Marking Guide of Biology A Level Carrefour Umurezi 2023-2024-1Document6 pagesVumbi Marking Guide of Biology A Level Carrefour Umurezi 2023-2024-1Theogene NTEGEREJIMANANo ratings yet
- Biology Summary NotesDocument5 pagesBiology Summary NotesNoraNo ratings yet
- Business Studies 2015 HSC ExamDocument18 pagesBusiness Studies 2015 HSC ExamMNo ratings yet
- HKCEE - Biology - 1999 - Paper I - A PDFDocument4 pagesHKCEE - Biology - 1999 - Paper I - A PDFChinlam210No ratings yet
- Flashcards - Topic 10 Diseases and Immunity - CIE Biology IGCSEDocument37 pagesFlashcards - Topic 10 Diseases and Immunity - CIE Biology IGCSEJane Lea100% (1)
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationVernonNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 November 1999Document5 pagesPaper 2 November 1999MSHNo ratings yet
- HSBDocument12 pagesHSBjemima MillsNo ratings yet
- Planning An Investigation Model Answers Five Complete PlansDocument16 pagesPlanning An Investigation Model Answers Five Complete PlansAhmad Kabil100% (1)
- Inheritance Worksheet 2: Fig. 1.1 Shows A Goat With White FurDocument4 pagesInheritance Worksheet 2: Fig. 1.1 Shows A Goat With White FurTarshihiNo ratings yet
- 0653 s03 Ms 1+2+3+5+6Document28 pages0653 s03 Ms 1+2+3+5+6Sofia M Vigo AguiarNo ratings yet
- 8-ICSE-X Biology 2020 PaperDocument16 pages8-ICSE-X Biology 2020 Paperaarnavgeneral1308No ratings yet
- Homeostasis..answer Key WorksheetDocument4 pagesHomeostasis..answer Key WorksheetUCL Sports100% (1)
- Tutorial 6 Transport in PlantsDocument7 pagesTutorial 6 Transport in PlantsyanasakaranNo ratings yet
- Section A 1. The Characteristics of Living Things, Cell Structure, Function and SpecializationDocument12 pagesSection A 1. The Characteristics of Living Things, Cell Structure, Function and SpecializationJerry100% (1)
- Alwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 10. Diseases and Immunity NotesDocument35 pagesAlwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 10. Diseases and Immunity NotesMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument6 pagesTransport in PlantsFred H HalderNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Homeostasis PDFDocument77 pages2.1 Homeostasis PDFtess_15No ratings yet
- Nutrition QuestionsDocument22 pagesNutrition Questionsnoddy60No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Integrated Science Week 2 Lesson 2Document5 pagesGrade 8 Integrated Science Week 2 Lesson 2Balram HaroldNo ratings yet
- Marking Schemes For Topic 1,2 Stafford PapersDocument57 pagesMarking Schemes For Topic 1,2 Stafford PapersSuha AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Alwadi International School Human Influences On Ecosystems Notes & WorksheetDocument55 pagesAlwadi International School Human Influences On Ecosystems Notes & WorksheetMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Biology Past PapersDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Biology Past PapersAdam mahabirNo ratings yet
- 19 - Organisms and Their EnvironmentDocument5 pages19 - Organisms and Their EnvironmentAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- Beetroot Core Practical Writing FrameDocument5 pagesBeetroot Core Practical Writing FrameJett0% (1)
- 12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFDocument51 pages12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFUmair Khan Marwat100% (1)
- Reproduction - ScoreDocument6 pagesReproduction - ScoreIslahNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants CIE IGCSE Biology 610 Classified Paster Paper 2Document21 pagesTransport in Plants CIE IGCSE Biology 610 Classified Paster Paper 2IGCSE Physics & ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 1 Edexcel Jan 96-June 05Document190 pagesBiology Unit 1 Edexcel Jan 96-June 05api-3729563100% (2)
- 04 - Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification FIBDocument5 pages04 - Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification FIBDianaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 NotesDocument23 pagesTopic 2 NotesVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans Grade 9Document49 pagesGas Exchange in Humans Grade 9harliv2.5chandhokNo ratings yet
- QS AnswersDocument8 pagesQS AnswersJorif100% (1)
- Characteristics of Living Things CellsDocument13 pagesCharacteristics of Living Things CellsFrances FlynnNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Perfect Score Answering Technique 2012Document12 pagesChemistry Perfect Score Answering Technique 2012钟㛃彤No ratings yet
- English 10 StandardsDocument65 pagesEnglish 10 Standardszaineddin SaadeddinNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Course ContentDocument2 pagesIGCSE Biology Course Contentjoedbmelvin0% (1)
- Pure Bio CH 17 Textbook Answers PDFDocument3 pagesPure Bio CH 17 Textbook Answers PDFashaNo ratings yet
- 0654 2013 IGCSE Coordinated Sciences Paper 2Document32 pages0654 2013 IGCSE Coordinated Sciences Paper 2jwinlynNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Membranes, Proteins, DNA and Gene Expression MSDocument13 pagesUNIT 1 Membranes, Proteins, DNA and Gene Expression MSpramodini JayalathNo ratings yet
- 9700 w14 QP 21Document16 pages9700 w14 QP 21rashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- % Chapter 2 Regulation of Body Temperature: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument32 pages% Chapter 2 Regulation of Body Temperature: Multiple-Choice QuestionsK C100% (1)
- IGCSE Answers Chapters 01 05Document7 pagesIGCSE Answers Chapters 01 05María Eugenia MolteniNo ratings yet
- Cells 2 FDocument10 pagesCells 2 FEANo ratings yet
- Coordination and Response IGCSE NotesDocument11 pagesCoordination and Response IGCSE NotesDrRemyaranjith Menon100% (1)
- Enzymes: Biology Matters G.C.E. 'O' Level (2 Edition) : Textbook AnswersDocument2 pagesEnzymes: Biology Matters G.C.E. 'O' Level (2 Edition) : Textbook AnswersJack KowmanNo ratings yet
- Gmo PDFDocument18 pagesGmo PDFIgorVutucNo ratings yet
- Excretion in Humans 2 QPDocument11 pagesExcretion in Humans 2 QPMikiko Fujiwara SamaNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Topic 18 Variation and Selection - CAIE Biology IGCSEDocument2 pagesDefinitions - Topic 18 Variation and Selection - CAIE Biology IGCSEG VeezNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Section 5 Lesson 1Document92 pagesIGCSE Biology Section 5 Lesson 1salmaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Coordination and Response WsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Coordination and Response WsAnand Kumar ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes For O LevelsDocument13 pagesBiology Notes For O Levelstahira mujahidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MicroorganismsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 MicroorganismsNIKHILPATNINo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology ImmunityDocument1 pageForm 5 Biology ImmunityWONGNo ratings yet
- Prof. Dr. Payman A.Hamaseed: VaccinationDocument19 pagesProf. Dr. Payman A.Hamaseed: Vaccinationasia groupNo ratings yet
- Concept Communicable DiseasesDocument477 pagesConcept Communicable DiseasesrimeoznekNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Nursing 2020Document421 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing 2020Kenneth Myro GarciaNo ratings yet
- Infection Control in Clinical SettingDocument35 pagesInfection Control in Clinical SettingRinku patelNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Biology Chapter 8 Dynamic EcosystemDocument6 pagesForm 4 Biology Chapter 8 Dynamic EcosystemWONGNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology ImmunityDocument1 pageForm 5 Biology ImmunityWONGNo ratings yet
- How Antibodies Work?: Brentha Tay Hui Yee Yap Xin RuDocument12 pagesHow Antibodies Work?: Brentha Tay Hui Yee Yap Xin RuWONGNo ratings yet
- Stages of MitosisDocument2 pagesStages of MitosisWONGNo ratings yet