Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Paramecium Color
Paramecium Color
Uploaded by
api-444439435Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Kingdom Protista NotesDocument3 pagesKingdom Protista Noteshafizhusain0% (1)
- Gigamon Solution Overview PDFDocument46 pagesGigamon Solution Overview PDFVan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Econ231W MWD ExampleDocument7 pagesEcon231W MWD ExampleMangapul Parmonangan DamanikNo ratings yet
- 2017-18 T.Y.B.Sc. Chemistry PDFDocument47 pages2017-18 T.Y.B.Sc. Chemistry PDFAkshay Khambare0% (1)
- Amateur RadioDocument28 pagesAmateur RadioJaneNo ratings yet
- Phaeophyta: Stypopodium TurbinariaDocument13 pagesPhaeophyta: Stypopodium TurbinariabetriaceNo ratings yet
- PoriferaDocument25 pagesPoriferaAmelia MeiriskaNo ratings yet
- Lower InvertebratesDocument19 pagesLower Invertebratesjaneomego90No ratings yet
- Paramecium: Classification, Structure, Function and CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesParamecium: Classification, Structure, Function and CharacteristicsGail EmbudoNo ratings yet
- Unicellular (Single-Celled) Protists - Eukaryotic Protozoan: EuglenaDocument3 pagesUnicellular (Single-Celled) Protists - Eukaryotic Protozoan: EuglenaEGSRHEtjykudli.u;No ratings yet
- ParameciumDocument25 pagesParameciumAde AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Introductiontoplantbiology022 ArDocument51 pagesIntroductiontoplantbiology022 ArHayatNo ratings yet
- Triploblastic AcelomatesDocument61 pagesTriploblastic AcelomatesfatimaNo ratings yet
- Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument5 pagesPhylum Platyhelmintheskaran kundiNo ratings yet
- Animal Diversity SummaryDocument24 pagesAnimal Diversity SummaryAna Melissa BarsalloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument8 pagesAnatomy of Flowering PlantssukhmansharmaaaNo ratings yet
- Protistas Lab and ExerciseDocument17 pagesProtistas Lab and Exerciseparaguai440% (1)
- Phylum CtenophoraDocument8 pagesPhylum CtenophoraMuhammad JanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: ProtistaDocument8 pagesChapter 4: ProtistaNawal Che IsmailNo ratings yet
- Vertebrates and Invertebrate Phylum.: Prepared By: Arifa AsadDocument18 pagesVertebrates and Invertebrate Phylum.: Prepared By: Arifa Asadarifaasad100% (1)
- Protist PacketDocument7 pagesProtist PacketAyesha MartiniNo ratings yet
- Acoelomate Bilateral AnimalsDocument31 pagesAcoelomate Bilateral AnimalsHirendra GurnaniNo ratings yet
- Diversity of AnimalsDocument83 pagesDiversity of Animalsu22811495No ratings yet
- Act. 1 - Animal-Like Protists - Instruction SheetDocument4 pagesAct. 1 - Animal-Like Protists - Instruction SheetMickeyNo ratings yet
- Study of ParameciumDocument22 pagesStudy of ParameciumDon DasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8. Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument5 pagesLesson 8. Phylum PlatyhelminthesAndreaaAAaa TagleNo ratings yet
- Flatworms 1Document63 pagesFlatworms 1Budi AfriyansyahNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Cell BioDocument7 pagesExperiment 1 Cell BioWinserng 永森No ratings yet
- Description MicroscopeDocument4 pagesDescription MicroscopeRanma SaotomeNo ratings yet
- Hemichordates: Is Divided Into 3 PartsDocument8 pagesHemichordates: Is Divided Into 3 Partstaimoor shahzadNo ratings yet
- ProstistaDocument43 pagesProstistaNovelynLozano-EdrosoNo ratings yet
- Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum MolluscaDocument44 pagesPhylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum MolluscaAngel FebiolaNo ratings yet
- PP13 Diversity of AnimalsDocument83 pagesPP13 Diversity of AnimalsmatodziNo ratings yet
- The Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument24 pagesThe Phylum PlatyhelminthesFlora NeriNo ratings yet
- Filum Platyhelmintes I. DefinitionDocument38 pagesFilum Platyhelmintes I. DefinitionNsc Rhyrin 'syafa' LestariniNo ratings yet
- Protozoa: Characteristics, Reproduction and ClassificationDocument13 pagesProtozoa: Characteristics, Reproduction and ClassificationAristeo EbioNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 PlatyhelminthesDocument17 pagesExercise 4 PlatyhelminthesAlicia Marie ElizaldeNo ratings yet
- Phylum PoriferaDocument18 pagesPhylum Poriferagonoles81No ratings yet
- Culture of Marine PolychaeteDocument7 pagesCulture of Marine PolychaeteyaumilakbarNo ratings yet
- CiliophoraDocument4 pagesCiliophoraSungdeok MinNo ratings yet
- Lab 09 Protists and FungiDocument13 pagesLab 09 Protists and Fungi13ucciNo ratings yet
- Protists: Protista The Very FirstDocument5 pagesProtists: Protista The Very FirstclaricejennNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document3 pagesLab 5alyssa cambaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Protista: Submitted ToDocument57 pagesKingdom Protista: Submitted ToAlleli AspiliNo ratings yet
- Brown AlgaeDocument19 pagesBrown AlgaelaluwimaNo ratings yet
- Nervous and Sensory Functions, Excretion and Osmoregulation Reproduction, Development and MetamorphosisDocument20 pagesNervous and Sensory Functions, Excretion and Osmoregulation Reproduction, Development and MetamorphosisAROOJ ASLAMNo ratings yet
- Sharnbasveshwar Residential Composite P.U. College, KalaburagiDocument8 pagesSharnbasveshwar Residential Composite P.U. College, KalaburagiShreenithiNo ratings yet
- 124 Lec Protozoan DiversityDocument9 pages124 Lec Protozoan Diversityinder604cheemaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 LabDocument6 pagesChapter 4 LabGeorges SarkisNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Biological Classfication NotesDocument5 pagesCH 2 Biological Classfication NotesJiya GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Diversity in Living Organisms NOTESDocument15 pagesDiversity in Living Organisms NOTEStejas mittalNo ratings yet
- Protista LaboratoryDocument22 pagesProtista LaboratoryRicardo RicoNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument54 pagesBiological ClassificationAyesha MahboobNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 Feb 19 Trematode-1Document29 pagesLecture 16 Feb 19 Trematode-1Rajkumar MandalNo ratings yet
- PlatyhelminthesDocument3 pagesPlatyhelminthesZunaira NoreenNo ratings yet
- 3.ecosystem Diversity: Ecosystem Is A Dynamic Complex of Living Being and Non-Living Environment WhichDocument10 pages3.ecosystem Diversity: Ecosystem Is A Dynamic Complex of Living Being and Non-Living Environment Whichkiran PoudelNo ratings yet
- ProtistDocument5 pagesProtistGerald Agacid BangeroNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University IslamabadDocument16 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University IslamabadAbdullah NagraNo ratings yet
- Amphibian 2022&23ADocument9 pagesAmphibian 2022&23AqueendaxxyNo ratings yet
- Porifera - Overview - Zoology Optional Notes For UPSC PDF DownloadDocument8 pagesPorifera - Overview - Zoology Optional Notes For UPSC PDF Downloadads112425No ratings yet
- Introduction To Kingdom ProtistaDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Kingdom ProtistaJersson JuarioNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Protista (Protist)Document45 pagesKingdom Protista (Protist)Miluska Valverde CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Article 1-3 A Review 2Document11 pagesArticle 1-3 A Review 2api-444439435No ratings yet
- Articles 4-7 2Document12 pagesArticles 4-7 2api-444439435No ratings yet
- Declaration Intro Teacher - 2Document12 pagesDeclaration Intro Teacher - 2api-444439435No ratings yet
- EconDocument16 pagesEconapi-444439435No ratings yet
- Reconstruction Amendments 2019Document12 pagesReconstruction Amendments 2019api-444439435No ratings yet
- Math 4 Mid-Term Review 1Document11 pagesMath 4 Mid-Term Review 1api-444439435No ratings yet
- Classroom Observation WorksheetDocument4 pagesClassroom Observation Worksheetapi-444439435No ratings yet
- Payed: FG Glat GlaDocument1 pagePayed: FG Glat Glaapi-444439435No ratings yet
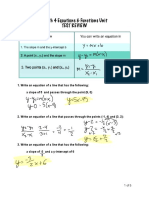
- Math 4 Equations & Functions Unit Test ReviewDocument5 pagesMath 4 Equations & Functions Unit Test Reviewapi-444439435No ratings yet
- Ax2Tbxtc: Xt8Xxt2Document3 pagesAx2Tbxtc: Xt8Xxt2api-444439435No ratings yet
- Seetvl: Try - IeDocument4 pagesSeetvl: Try - Ieapi-444439435No ratings yet
- Q.1 HW Math 4: Graph The Following Quadratic Equations. Give The Coordinates of The VertexDocument1 pageQ.1 HW Math 4: Graph The Following Quadratic Equations. Give The Coordinates of The Vertexapi-444439435No ratings yet
- Trig Review WsDocument4 pagesTrig Review Wsapi-444439435No ratings yet
- Sin 55 ADocument1 pageSin 55 Aapi-444439435No ratings yet
- Chain Hoist Brochure - HlTachiDocument17 pagesChain Hoist Brochure - HlTachisravan thumojuNo ratings yet
- Bohler Welding Thermalpower - ENGDocument24 pagesBohler Welding Thermalpower - ENGghostinshellNo ratings yet
- Comparative Aerodynamic Analysis of A Missile With 8 Fin TailDocument8 pagesComparative Aerodynamic Analysis of A Missile With 8 Fin Tailtolomeo05No ratings yet
- A7.5 Blood VesselsDocument5 pagesA7.5 Blood VesselsshannonNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice: Name: Gerald Pratama S. Class: XI-MIPA-2Document6 pagesPassive Voice: Name: Gerald Pratama S. Class: XI-MIPA-2Gerald SimbolonNo ratings yet
- Higher Unit 5a Topic TestDocument24 pagesHigher Unit 5a Topic TestLouis SharrockNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Frames (Seismic Loading)Document45 pagesAnalysis of Frames (Seismic Loading)Jef Junio AlvarezNo ratings yet
- HP Software and Driver Downloads For HP Printers, Laptops, Desktops and More - HP® Customer SupportDocument3 pagesHP Software and Driver Downloads For HP Printers, Laptops, Desktops and More - HP® Customer SupportRamy ElhelwNo ratings yet
- Manual Central TelefonicaDocument159 pagesManual Central TelefonicaMarilyn FreitesNo ratings yet
- GALVI Engineering - Installation and Maintenance Manual Shoe Brakes NV HYDDocument41 pagesGALVI Engineering - Installation and Maintenance Manual Shoe Brakes NV HYDArvind Yeram100% (1)
- NP Hard and NP CompleteDocument15 pagesNP Hard and NP CompleteveningstonNo ratings yet
- ATV16 Manual Programacion en PDFDocument36 pagesATV16 Manual Programacion en PDFCarlos MataNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction: Prestressing of ConcreteDocument5 pagesChapter 1: Introduction: Prestressing of ConcreteSamih S. BarzaniNo ratings yet
- List of Formula - Managerial StatisticsDocument6 pagesList of Formula - Managerial Statisticsmahendra pratap singhNo ratings yet
- K8422 of No.820 SQN FAA 1940: Fairey Swordfish MK 1Document3 pagesK8422 of No.820 SQN FAA 1940: Fairey Swordfish MK 1Lorenzo Martinez Valenzuela100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Basic Heat TransferDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Basic Heat TransferGabo MarquezNo ratings yet
- NFC Technology: Assessment Effective of Security Towards Protecting NFC Devices & ServicesDocument5 pagesNFC Technology: Assessment Effective of Security Towards Protecting NFC Devices & Servicesfifa playNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Plate No. 3Document1 pageHydraulics Plate No. 3VincentNo ratings yet
- The Biology and Genetics of Curly HairDocument8 pagesThe Biology and Genetics of Curly HairIsabela MartinsNo ratings yet
- 17th EOM Letter N AgendaDocument63 pages17th EOM Letter N AgendaSiddharth MohantyNo ratings yet
- Measurement, Instrumentation and Control ME2400 Assignment 2Document13 pagesMeasurement, Instrumentation and Control ME2400 Assignment 2Chinmay TambatNo ratings yet
- Texto 1: The Digital AgeDocument6 pagesTexto 1: The Digital AgeMaria Cristina LourenconiNo ratings yet
- Protocolo Comunicacion EnvoyDocument12 pagesProtocolo Comunicacion Envoyfmaestre76No ratings yet
- L9 Logistical Regression Models UpdatedDocument10 pagesL9 Logistical Regression Models UpdatedMahmudul hasanNo ratings yet
- Sciadv Abd0957Document17 pagesSciadv Abd0957Shivaprakash Jagalur MuttNo ratings yet
- Earth Science 2Document2 pagesEarth Science 2Sean CaloyloyNo ratings yet
- Sel Relay Trip CurveDocument8 pagesSel Relay Trip CurveAhmed Magdy100% (1)
Paramecium Color
Paramecium Color
Uploaded by
api-444439435Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Paramecium Color
Paramecium Color
Uploaded by
api-444439435Copyright:
Available Formats
Name Biology II
Protists — Ciliate Anatomy
Paramecia
The Genus Paramecium is commonly found throughout the world, in fresh and marine
water containing bacteria and decaying organic matter Paramecium is a small unicellular
organism. It is elongated and ranges in size from 120 to 300 microns. The outside of the cell
is covered with a tough pellicle. Label the pellicle. The posterior half is slightly wider than the
anterior half and is bluntly pointed, while the anterior end is rounded. On its underside there
is a large and long groove running about half the length of its body. The outer surface of the
organism is covered with many hundreds of minute hair-like projections called cilia. Label the
cilia. This large ciliate protozoan that lives in stagnant freshwater has an oral groove on one
side that leads inward to the gullet and eventually the mouth. Color and label the oral groove
light pink and the gullet red. Paramecia have two nuclei --- a larger macronucleus and a
smaller micronucleus. The macronucleus, which is relatively large and located near the
center of the organism, controls most of the metabolic functions of the cell. Color and label
the macronucleus light blue. The micronucleus, which lies partly within a depression on the
oral side of the macronucleus, is involved primarily in reproductive and hereditary functions.
Color and label the micronucleus dark blue.
Because paramecia live in water, they require an organelle to pump out excess water
so they do not lyse (burst). These organelles are the contractile vacuoles, usually one at
each end, each surrounded by several radiating canals which collect water from the
surrounding cytoplasm. Color and label BOTH contractile vacuoles purple. The contractile
vacuoles serve a critical function of osmoregulation, as water tends to accumulate inside the
cytoplasm due to osmotic pressure. These structures are absent in marine Paramecium.
Food vacuoles, which are round in shape, contain enzymes to digest the other smaller
protozoans that the paramecium feeds on. Label and color the food vacuoles yellow. These
vacuoles can be seen at the mouth where the food is loaded into them for digestion.
Undigested food leaves through the anal pore. Color and label the anal pore brown. At the
base of the cilia are defensive structures called trichocysts. These structures can discharge
their contents as long threads. Label the trichocysts.
Questions:
1. What is the funnel like depression on the pellicle called?
Oral groove
2. How do paramecia regulate their water content?
Contractile vacuoles
3. Paramecia are heterotrophs. Explain this statement.
They eat other organisms
4. How do paramecia move?
Cilia
5. What is the function of the macronucleus?
It controls most of the cells
6. What is the function of the micronucleus?
It controls reproduction and the passing of genes
7. What do paramecia use for defense?
Trichocysts
8. Where can you find paramecia?
Fresh water
9. What do paramecia eat?
Other small protozoans
10. Where does digestion occur in a paramecium?
Food vacuoles
Paramecium
You might also like
- Kingdom Protista NotesDocument3 pagesKingdom Protista Noteshafizhusain0% (1)
- Gigamon Solution Overview PDFDocument46 pagesGigamon Solution Overview PDFVan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Econ231W MWD ExampleDocument7 pagesEcon231W MWD ExampleMangapul Parmonangan DamanikNo ratings yet
- 2017-18 T.Y.B.Sc. Chemistry PDFDocument47 pages2017-18 T.Y.B.Sc. Chemistry PDFAkshay Khambare0% (1)
- Amateur RadioDocument28 pagesAmateur RadioJaneNo ratings yet
- Phaeophyta: Stypopodium TurbinariaDocument13 pagesPhaeophyta: Stypopodium TurbinariabetriaceNo ratings yet
- PoriferaDocument25 pagesPoriferaAmelia MeiriskaNo ratings yet
- Lower InvertebratesDocument19 pagesLower Invertebratesjaneomego90No ratings yet
- Paramecium: Classification, Structure, Function and CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesParamecium: Classification, Structure, Function and CharacteristicsGail EmbudoNo ratings yet
- Unicellular (Single-Celled) Protists - Eukaryotic Protozoan: EuglenaDocument3 pagesUnicellular (Single-Celled) Protists - Eukaryotic Protozoan: EuglenaEGSRHEtjykudli.u;No ratings yet
- ParameciumDocument25 pagesParameciumAde AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Introductiontoplantbiology022 ArDocument51 pagesIntroductiontoplantbiology022 ArHayatNo ratings yet
- Triploblastic AcelomatesDocument61 pagesTriploblastic AcelomatesfatimaNo ratings yet
- Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument5 pagesPhylum Platyhelmintheskaran kundiNo ratings yet
- Animal Diversity SummaryDocument24 pagesAnimal Diversity SummaryAna Melissa BarsalloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument8 pagesAnatomy of Flowering PlantssukhmansharmaaaNo ratings yet
- Protistas Lab and ExerciseDocument17 pagesProtistas Lab and Exerciseparaguai440% (1)
- Phylum CtenophoraDocument8 pagesPhylum CtenophoraMuhammad JanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: ProtistaDocument8 pagesChapter 4: ProtistaNawal Che IsmailNo ratings yet
- Vertebrates and Invertebrate Phylum.: Prepared By: Arifa AsadDocument18 pagesVertebrates and Invertebrate Phylum.: Prepared By: Arifa Asadarifaasad100% (1)
- Protist PacketDocument7 pagesProtist PacketAyesha MartiniNo ratings yet
- Acoelomate Bilateral AnimalsDocument31 pagesAcoelomate Bilateral AnimalsHirendra GurnaniNo ratings yet
- Diversity of AnimalsDocument83 pagesDiversity of Animalsu22811495No ratings yet
- Act. 1 - Animal-Like Protists - Instruction SheetDocument4 pagesAct. 1 - Animal-Like Protists - Instruction SheetMickeyNo ratings yet
- Study of ParameciumDocument22 pagesStudy of ParameciumDon DasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8. Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument5 pagesLesson 8. Phylum PlatyhelminthesAndreaaAAaa TagleNo ratings yet
- Flatworms 1Document63 pagesFlatworms 1Budi AfriyansyahNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Cell BioDocument7 pagesExperiment 1 Cell BioWinserng 永森No ratings yet
- Description MicroscopeDocument4 pagesDescription MicroscopeRanma SaotomeNo ratings yet
- Hemichordates: Is Divided Into 3 PartsDocument8 pagesHemichordates: Is Divided Into 3 Partstaimoor shahzadNo ratings yet
- ProstistaDocument43 pagesProstistaNovelynLozano-EdrosoNo ratings yet
- Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum MolluscaDocument44 pagesPhylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nematoda Phylum MolluscaAngel FebiolaNo ratings yet
- PP13 Diversity of AnimalsDocument83 pagesPP13 Diversity of AnimalsmatodziNo ratings yet
- The Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument24 pagesThe Phylum PlatyhelminthesFlora NeriNo ratings yet
- Filum Platyhelmintes I. DefinitionDocument38 pagesFilum Platyhelmintes I. DefinitionNsc Rhyrin 'syafa' LestariniNo ratings yet
- Protozoa: Characteristics, Reproduction and ClassificationDocument13 pagesProtozoa: Characteristics, Reproduction and ClassificationAristeo EbioNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 PlatyhelminthesDocument17 pagesExercise 4 PlatyhelminthesAlicia Marie ElizaldeNo ratings yet
- Phylum PoriferaDocument18 pagesPhylum Poriferagonoles81No ratings yet
- Culture of Marine PolychaeteDocument7 pagesCulture of Marine PolychaeteyaumilakbarNo ratings yet
- CiliophoraDocument4 pagesCiliophoraSungdeok MinNo ratings yet
- Lab 09 Protists and FungiDocument13 pagesLab 09 Protists and Fungi13ucciNo ratings yet
- Protists: Protista The Very FirstDocument5 pagesProtists: Protista The Very FirstclaricejennNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document3 pagesLab 5alyssa cambaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Protista: Submitted ToDocument57 pagesKingdom Protista: Submitted ToAlleli AspiliNo ratings yet
- Brown AlgaeDocument19 pagesBrown AlgaelaluwimaNo ratings yet
- Nervous and Sensory Functions, Excretion and Osmoregulation Reproduction, Development and MetamorphosisDocument20 pagesNervous and Sensory Functions, Excretion and Osmoregulation Reproduction, Development and MetamorphosisAROOJ ASLAMNo ratings yet
- Sharnbasveshwar Residential Composite P.U. College, KalaburagiDocument8 pagesSharnbasveshwar Residential Composite P.U. College, KalaburagiShreenithiNo ratings yet
- 124 Lec Protozoan DiversityDocument9 pages124 Lec Protozoan Diversityinder604cheemaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 LabDocument6 pagesChapter 4 LabGeorges SarkisNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Biological Classfication NotesDocument5 pagesCH 2 Biological Classfication NotesJiya GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Diversity in Living Organisms NOTESDocument15 pagesDiversity in Living Organisms NOTEStejas mittalNo ratings yet
- Protista LaboratoryDocument22 pagesProtista LaboratoryRicardo RicoNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument54 pagesBiological ClassificationAyesha MahboobNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 Feb 19 Trematode-1Document29 pagesLecture 16 Feb 19 Trematode-1Rajkumar MandalNo ratings yet
- PlatyhelminthesDocument3 pagesPlatyhelminthesZunaira NoreenNo ratings yet
- 3.ecosystem Diversity: Ecosystem Is A Dynamic Complex of Living Being and Non-Living Environment WhichDocument10 pages3.ecosystem Diversity: Ecosystem Is A Dynamic Complex of Living Being and Non-Living Environment Whichkiran PoudelNo ratings yet
- ProtistDocument5 pagesProtistGerald Agacid BangeroNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University IslamabadDocument16 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University IslamabadAbdullah NagraNo ratings yet
- Amphibian 2022&23ADocument9 pagesAmphibian 2022&23AqueendaxxyNo ratings yet
- Porifera - Overview - Zoology Optional Notes For UPSC PDF DownloadDocument8 pagesPorifera - Overview - Zoology Optional Notes For UPSC PDF Downloadads112425No ratings yet
- Introduction To Kingdom ProtistaDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Kingdom ProtistaJersson JuarioNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Protista (Protist)Document45 pagesKingdom Protista (Protist)Miluska Valverde CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Article 1-3 A Review 2Document11 pagesArticle 1-3 A Review 2api-444439435No ratings yet
- Articles 4-7 2Document12 pagesArticles 4-7 2api-444439435No ratings yet
- Declaration Intro Teacher - 2Document12 pagesDeclaration Intro Teacher - 2api-444439435No ratings yet
- EconDocument16 pagesEconapi-444439435No ratings yet
- Reconstruction Amendments 2019Document12 pagesReconstruction Amendments 2019api-444439435No ratings yet
- Math 4 Mid-Term Review 1Document11 pagesMath 4 Mid-Term Review 1api-444439435No ratings yet
- Classroom Observation WorksheetDocument4 pagesClassroom Observation Worksheetapi-444439435No ratings yet
- Payed: FG Glat GlaDocument1 pagePayed: FG Glat Glaapi-444439435No ratings yet
- Math 4 Equations & Functions Unit Test ReviewDocument5 pagesMath 4 Equations & Functions Unit Test Reviewapi-444439435No ratings yet
- Ax2Tbxtc: Xt8Xxt2Document3 pagesAx2Tbxtc: Xt8Xxt2api-444439435No ratings yet
- Seetvl: Try - IeDocument4 pagesSeetvl: Try - Ieapi-444439435No ratings yet
- Q.1 HW Math 4: Graph The Following Quadratic Equations. Give The Coordinates of The VertexDocument1 pageQ.1 HW Math 4: Graph The Following Quadratic Equations. Give The Coordinates of The Vertexapi-444439435No ratings yet
- Trig Review WsDocument4 pagesTrig Review Wsapi-444439435No ratings yet
- Sin 55 ADocument1 pageSin 55 Aapi-444439435No ratings yet
- Chain Hoist Brochure - HlTachiDocument17 pagesChain Hoist Brochure - HlTachisravan thumojuNo ratings yet
- Bohler Welding Thermalpower - ENGDocument24 pagesBohler Welding Thermalpower - ENGghostinshellNo ratings yet
- Comparative Aerodynamic Analysis of A Missile With 8 Fin TailDocument8 pagesComparative Aerodynamic Analysis of A Missile With 8 Fin Tailtolomeo05No ratings yet
- A7.5 Blood VesselsDocument5 pagesA7.5 Blood VesselsshannonNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice: Name: Gerald Pratama S. Class: XI-MIPA-2Document6 pagesPassive Voice: Name: Gerald Pratama S. Class: XI-MIPA-2Gerald SimbolonNo ratings yet
- Higher Unit 5a Topic TestDocument24 pagesHigher Unit 5a Topic TestLouis SharrockNo ratings yet
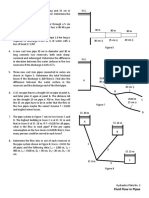
- Analysis of Frames (Seismic Loading)Document45 pagesAnalysis of Frames (Seismic Loading)Jef Junio AlvarezNo ratings yet
- HP Software and Driver Downloads For HP Printers, Laptops, Desktops and More - HP® Customer SupportDocument3 pagesHP Software and Driver Downloads For HP Printers, Laptops, Desktops and More - HP® Customer SupportRamy ElhelwNo ratings yet
- Manual Central TelefonicaDocument159 pagesManual Central TelefonicaMarilyn FreitesNo ratings yet
- GALVI Engineering - Installation and Maintenance Manual Shoe Brakes NV HYDDocument41 pagesGALVI Engineering - Installation and Maintenance Manual Shoe Brakes NV HYDArvind Yeram100% (1)
- NP Hard and NP CompleteDocument15 pagesNP Hard and NP CompleteveningstonNo ratings yet
- ATV16 Manual Programacion en PDFDocument36 pagesATV16 Manual Programacion en PDFCarlos MataNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction: Prestressing of ConcreteDocument5 pagesChapter 1: Introduction: Prestressing of ConcreteSamih S. BarzaniNo ratings yet
- List of Formula - Managerial StatisticsDocument6 pagesList of Formula - Managerial Statisticsmahendra pratap singhNo ratings yet
- K8422 of No.820 SQN FAA 1940: Fairey Swordfish MK 1Document3 pagesK8422 of No.820 SQN FAA 1940: Fairey Swordfish MK 1Lorenzo Martinez Valenzuela100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Basic Heat TransferDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Basic Heat TransferGabo MarquezNo ratings yet
- NFC Technology: Assessment Effective of Security Towards Protecting NFC Devices & ServicesDocument5 pagesNFC Technology: Assessment Effective of Security Towards Protecting NFC Devices & Servicesfifa playNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Plate No. 3Document1 pageHydraulics Plate No. 3VincentNo ratings yet
- The Biology and Genetics of Curly HairDocument8 pagesThe Biology and Genetics of Curly HairIsabela MartinsNo ratings yet
- 17th EOM Letter N AgendaDocument63 pages17th EOM Letter N AgendaSiddharth MohantyNo ratings yet
- Measurement, Instrumentation and Control ME2400 Assignment 2Document13 pagesMeasurement, Instrumentation and Control ME2400 Assignment 2Chinmay TambatNo ratings yet
- Texto 1: The Digital AgeDocument6 pagesTexto 1: The Digital AgeMaria Cristina LourenconiNo ratings yet
- Protocolo Comunicacion EnvoyDocument12 pagesProtocolo Comunicacion Envoyfmaestre76No ratings yet
- L9 Logistical Regression Models UpdatedDocument10 pagesL9 Logistical Regression Models UpdatedMahmudul hasanNo ratings yet
- Sciadv Abd0957Document17 pagesSciadv Abd0957Shivaprakash Jagalur MuttNo ratings yet
- Earth Science 2Document2 pagesEarth Science 2Sean CaloyloyNo ratings yet
- Sel Relay Trip CurveDocument8 pagesSel Relay Trip CurveAhmed Magdy100% (1)