Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conclusion - . - . - . - . .: Tog Tog Min
Conclusion - . - . - . - . .: Tog Tog Min
Uploaded by
Sondos OtoomOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Conclusion - . - . - . - . .: Tog Tog Min
Conclusion - . - . - . - . .: Tog Tog Min
Uploaded by
Sondos OtoomCopyright:
Available Formats
Conclusion
. Using inlet and outlet temperatures, cooling tower can be designed for N tog, Htog, Gmin.
. The efficiency of cooling tower is a function of high, of time of contact of two phases.
. There are losses of water due evaporation.
. Cooling water is a good and efficient and economic apparatus used to cool hot water produced from
industrial processes.
. As water flow rate increase, cooling rate will decrease because contact time will decrease.
. Gas flow rate which is used should be greater than G min.
. Humidity of air increased while cooling because some of water evaporated and flowed with air.
. To achieve low temperature of water, we can use cooling towers in series, but for cooling large
amounts of water, we can use cooling tower in parallel.
. The enthalpy in equilibrium data Hs for gas, when the flow rate increase, the effect of cooling will be
higher because more gas will be in contact with the water.
Reference
REFERENCES
1. C.J. Geankoplis “Transport Processes and Unit Operations”, 3rd Ed., Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs,
NJ (1993).
2. W.L. McCabe, J.C. Smith and P. Harriot, “Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering” 5th Ed.,
McGraw-Hill, New York (1993).
3. R.E. Treybal, “Mass-Transfer Operations”, 3rd Ed., McGraw-Hill, New York (1981
You might also like
- Experimental Investigation On An Absorption Heat Transformer For Production of Hot Water or Steam GenerationDocument11 pagesExperimental Investigation On An Absorption Heat Transformer For Production of Hot Water or Steam GenerationRedees RedeesNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower: Bangladesh University of Engineering and TechnologyDocument15 pagesCooling Tower: Bangladesh University of Engineering and TechnologyMarsya MaysitaNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Investigation of Gas Geyser's Heat Exchanger With Addition of EconomizerDocument5 pagesAn Experimental Investigation of Gas Geyser's Heat Exchanger With Addition of EconomizerijaertNo ratings yet
- Cooling TowerDocument28 pagesCooling TowerKangae Ilham100% (4)
- Advance Cooling and Heating System For CabinetDocument5 pagesAdvance Cooling and Heating System For CabinetANKITNo ratings yet
- Ijet V2i6p2Document6 pagesIjet V2i6p2International Journal of Engineering and TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: Applied Thermal EngineeringDocument28 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Applied Thermal EngineeringnaveenNo ratings yet
- File ServeDocument7 pagesFile ServeVignesh KrishNo ratings yet
- Energy: Peng Xu, Xiaoli Ma, Thierno M.O. Diallo, Xudong Zhao, Kevin Fancey, Deying Li, Hongbing ChenDocument15 pagesEnergy: Peng Xu, Xiaoli Ma, Thierno M.O. Diallo, Xudong Zhao, Kevin Fancey, Deying Li, Hongbing ChenAnonymous PufNjgNo ratings yet
- "Air Cooler Cum Water Cooler": KES Rajarambapu Institute of TechnologyDocument24 pages"Air Cooler Cum Water Cooler": KES Rajarambapu Institute of TechnologySoumyodeep MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Earth Air Heat Exchanger in Parallel ConnectionDocument5 pagesEarth Air Heat Exchanger in Parallel Connectionseventhsensegroup100% (1)
- Applied Thermal Engineering: Jinwei Ma, Wei Sun, Jie Ji, Yang Zhang, Aifeng Zhang, Wen FanDocument6 pagesApplied Thermal Engineering: Jinwei Ma, Wei Sun, Jie Ji, Yang Zhang, Aifeng Zhang, Wen FanResearcherzNo ratings yet
- Cooling TowersDocument19 pagesCooling TowersmasukuhlelokuhleNo ratings yet
- Design and Performance Evaluation of A Cooling Tower Based On Different ParametersDocument18 pagesDesign and Performance Evaluation of A Cooling Tower Based On Different ParametersSabrinaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Untuk Uas Perpan IIDocument8 pagesJurnal Untuk Uas Perpan IIDanielJhonySitumorangSuhutNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: Applied Thermal EngineeringDocument24 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Applied Thermal EngineeringSiraj AL sharifNo ratings yet
- Conjugate Heat Transfer in AirtoRefrigerant Airfoil Heat ExchangersDocument12 pagesConjugate Heat Transfer in AirtoRefrigerant Airfoil Heat ExchangersMohammed AshiqueNo ratings yet
- Ecp57vol5 012Document8 pagesEcp57vol5 012anishbabupdNo ratings yet
- Jten-2020-6-4.16227Document20 pagesJten-2020-6-4.16227SalemNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument50 pagesReportMICHAEL PRADEEPNo ratings yet
- Angelo MantelliDocument6 pagesAngelo MantelliNatarajan RavisankarNo ratings yet
- Performance Studies On The Reversing Valve Incorporated Air-To-Water Heat Pump With Heat Storage DeviceDocument10 pagesPerformance Studies On The Reversing Valve Incorporated Air-To-Water Heat Pump With Heat Storage DeviceTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- A4 PDFDocument11 pagesA4 PDFAdrian VargasNo ratings yet
- Paper ID-44201672 PDFDocument6 pagesPaper ID-44201672 PDFannmaryNo ratings yet
- Major Project Report ON Water Cum Air CoolerDocument13 pagesMajor Project Report ON Water Cum Air CoolerSandeep MatetiNo ratings yet
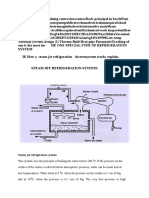
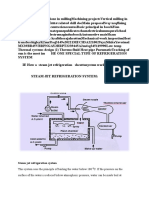
- Steam Jet Refrigeration SystemDocument7 pagesSteam Jet Refrigeration SystembbaytlNo ratings yet
- Cooling TowerDocument10 pagesCooling TowerKeshav Rao100% (1)
- 2021-Morshed-Heating Performance of The PVC Earthair Tubular Heat Exchanger Applied To A GreenhouseDocument19 pages2021-Morshed-Heating Performance of The PVC Earthair Tubular Heat Exchanger Applied To A GreenhouseraviNo ratings yet
- Steam Jet Refrigeration SystemDocument7 pagesSteam Jet Refrigeration SystembbaytlNo ratings yet
- Erkek Tu 2018Document27 pagesErkek Tu 2018queenNo ratings yet
- Steam Jet Refrigeration SystemDocument7 pagesSteam Jet Refrigeration SystembbaytlNo ratings yet
- IJREAMV04I0642045Document8 pagesIJREAMV04I0642045Vãmßhí Yøūth MenuguNo ratings yet
- Steam Jet Refrigeration SystemDocument7 pagesSteam Jet Refrigeration SystembbaytlNo ratings yet
- Discussion and ConclusionDocument3 pagesDiscussion and ConclusionFadhli HashimNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower in Unit OperationDocument10 pagesCooling Tower in Unit Operationseraj ibramemNo ratings yet
- Cooling TowersDocument11 pagesCooling TowersSlim Kat Nkosi0% (2)
- Cooling TowerDocument20 pagesCooling TowerMazlia MazlanNo ratings yet
- Study of Geothermal Seasonal Cooling Storage System With Energy PilesDocument6 pagesStudy of Geothermal Seasonal Cooling Storage System With Energy PilesNouman YasarNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Analysis of Forced Draft Cooling Tower Performance Using Ansys Fluent SoftwareDocument13 pagesDokumen - Tips Analysis of Forced Draft Cooling Tower Performance Using Ansys Fluent SoftwareNIKHIL soniNo ratings yet
- Marley Perfomance Cooling Tower CTII-01ADocument4 pagesMarley Perfomance Cooling Tower CTII-01ApiolinwallsNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Forced Draft Cooling Tower Performance Using Ansys Fluent Software PDFDocument13 pagesAnalysis of Forced Draft Cooling Tower Performance Using Ansys Fluent Software PDFesatjournals100% (1)
- 41i9-Efficient Usage of WasteDocument10 pages41i9-Efficient Usage of WasteIJAET Journal100% (1)
- Solar Desalination With A Humidification - Dehumidification Cycle: Performance of The UnitDocument8 pagesSolar Desalination With A Humidification - Dehumidification Cycle: Performance of The UnitsasikalasivakumarNo ratings yet
- Effect of Artificial Roughness On Solar Air Heater: An Experimental InvestigationDocument8 pagesEffect of Artificial Roughness On Solar Air Heater: An Experimental InvestigationmitevNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER)Document8 pagesInternational Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER)International Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- Geothermal HVAC: 1.1. BackgroundDocument6 pagesGeothermal HVAC: 1.1. BackgroundperestotnicNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Hot Gas Bypass For RefrigerationDocument5 pagesImplementation of Hot Gas Bypass For RefrigerationhurshawNo ratings yet
- Shopmillingmsme: Steam Jet Refrigeration SystemDocument7 pagesShopmillingmsme: Steam Jet Refrigeration SystembbaytlNo ratings yet
- Nano 12 PDFDocument8 pagesNano 12 PDFRehan RafiqNo ratings yet
- Combined Air-Conditioning and Tap Water Heating Plant, Using CO2 As Refrigerant For Indonesian Climate ConditionDocument238 pagesCombined Air-Conditioning and Tap Water Heating Plant, Using CO2 As Refrigerant For Indonesian Climate ConditionA'fifDotNo ratings yet
- IJETR021301Document12 pagesIJETR021301erpublicationNo ratings yet
- Shopmillingmsme: Steam Jet Refrigeration SystemDocument7 pagesShopmillingmsme: Steam Jet Refrigeration SystembbaytlNo ratings yet
- Advancing Water Conservation in Cooling Towers Through NoDocument42 pagesAdvancing Water Conservation in Cooling Towers Through NoHaitham HasanNo ratings yet
- Shopmillingmsme: Steam Jet Refrigeration SystemDocument7 pagesShopmillingmsme: Steam Jet Refrigeration SystembbaytlNo ratings yet
- Heat Sink Optimizarion With Application To MicrochannelsDocument11 pagesHeat Sink Optimizarion With Application To MicrochannelsJuan Pablo Ramirez VazquezNo ratings yet
- Experimental Performance Analysis of Solar Air Heaters With and Without FinDocument6 pagesExperimental Performance Analysis of Solar Air Heaters With and Without FinPankaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Air Water Cooled Condenser in Vapour Compression System IJERTV10IS050132Document6 pagesAnalysis of Air Water Cooled Condenser in Vapour Compression System IJERTV10IS050132Abdulrahman AlnasharNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningFrom EverandThermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)