Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geometric Representation of IFC Objects
Geometric Representation of IFC Objects
Uploaded by
scribdztOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geometric Representation of IFC Objects
Geometric Representation of IFC Objects
Uploaded by
scribdztCopyright:
Available Formats
10 | Autodesk Revit IFC manual
2.4.2 Geometric representation of IFC objects
There are three basic possibilities for geometrically representing a three-dimensional IFC object:
- extrusions
- solid body representation using a sweep, and
- representation using B-reps.
Extrusions
Are the most common and simple graphical method and are used for most of the cases when the shape
can be described by a simple profile.
Swept solids
As the name implies, an element is created with the swept solid
method using a sweep. In this case, a defined profile is led along a
path (direction vector) to generate the solid. This profile may change
due to rotation or distortion along the path. Revit uses this method
for describing rebar and other shapes which cannot be described
with extrusions.
B-rep
The method known as boundary representation (B-rep) can also be
described as a boundary surface model. The surfaces of a component
are represented using coordinates and together form the actual solid,
allowing even complex forms to be represented.
B-rep objects use complex calculations to represent individual
surfaces in detail, and thus use more data memory.
NURBS and other smooth surfaces
In the IFC4 schema, it is possible to generate B-rep objects as
advanced B-reps using NURBS (non-uniform rational B-splines)
surfaces. The memory space required is thus drastically reduced,
while the bodies are represented more accurately.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR REVIT USERS
You might also like
- Post Implementation ReviewDocument2 pagesPost Implementation Reviewscribdzt100% (1)
- Post Implementation Review TemplateDocument10 pagesPost Implementation Review TemplatescribdztNo ratings yet
- CalcIII Complete Assignments PDFDocument58 pagesCalcIII Complete Assignments PDFEko PrayetnoNo ratings yet
- 328fabd5daddb3ae693f7ff00b2dab0a_1c5a7eb974f8d7803fd15c52c72e499eDocument9 pages328fabd5daddb3ae693f7ff00b2dab0a_1c5a7eb974f8d7803fd15c52c72e499eSnigdha YadavNo ratings yet
- Lec03 Advanced Modeling - 2122Document31 pagesLec03 Advanced Modeling - 2122吳先生No ratings yet
- CADA Module 4Document18 pagesCADA Module 4Hi 123No ratings yet
- Study Portion 1 - 24.03.2023Document6 pagesStudy Portion 1 - 24.03.2023YUVA RAJA BNo ratings yet
- Unit II CAPD MF5012 ME MFGDocument47 pagesUnit II CAPD MF5012 ME MFGKarthikeyan KmbNo ratings yet
- Geometric Modeling: Geometrical Entities E.G. Circular, Rectangular, Straight. Elliptical Etc. Refers To GeometricalDocument9 pagesGeometric Modeling: Geometrical Entities E.G. Circular, Rectangular, Straight. Elliptical Etc. Refers To Geometricalstephen mwendwaNo ratings yet
- Half-Space (Geometry) : Boundary RepresentationDocument5 pagesHalf-Space (Geometry) : Boundary RepresentationSudeep Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Direct Manipulations of B-Spline and NURBS CurvesDocument12 pagesDirect Manipulations of B-Spline and NURBS Curvesmatous1No ratings yet
- Curve, Surface and SolidDocument62 pagesCurve, Surface and SolidwadlanNo ratings yet
- Cad Cam Unit-2 Uo1Document18 pagesCad Cam Unit-2 Uo1SRINIVAS UNIVERSITY RESEARCH SCHOLAR ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGYNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 (Detail)Document123 pagesUnit 2 (Detail)vishwajeet patilNo ratings yet
- CAD CAM Viva QuestionsDocument3 pagesCAD CAM Viva QuestionsAshok BhatiaNo ratings yet
- CAD CAM Viva QuestionsDocument3 pagesCAD CAM Viva QuestionsTheja Sree100% (3)
- Oblak Tocaka Krivulje I PloheDocument8 pagesOblak Tocaka Krivulje I PloheMercedes DieselNo ratings yet
- Short Answer QuestionsDocument8 pagesShort Answer QuestionsRajyalakshmi MNo ratings yet
- Curve and SurfacesDocument28 pagesCurve and SurfacesAnonymous u87aqFoNo ratings yet
- 3D Geometric Modelling Based On NURBSDocument11 pages3D Geometric Modelling Based On NURBSDodeptrai BkNo ratings yet
- Lec 39Document30 pagesLec 39RamanNo ratings yet
- Ronan Boulic and Olivier RenaultDocument18 pagesRonan Boulic and Olivier Renaultsnehal medheNo ratings yet
- B - Trees: A New Representation For Non-Slicing FloorplansDocument6 pagesB - Trees: A New Representation For Non-Slicing FloorplansRaffi SkNo ratings yet
- 8 Solid and Assembly ModelingDocument127 pages8 Solid and Assembly ModelingNaveen YadavNo ratings yet
- Subdivision Surface Modeling Technology: October 2017Document16 pagesSubdivision Surface Modeling Technology: October 2017Hung VuNo ratings yet
- Graphics Note 5-6Document27 pagesGraphics Note 5-6Technical DipeshNo ratings yet
- CADM Unit Geometric Modeling - SurfacesDocument31 pagesCADM Unit Geometric Modeling - SurfacesWilsonNo ratings yet
- Dhanalakshmi College of Engineering, ChennaiDocument21 pagesDhanalakshmi College of Engineering, ChennaiDeus KajejwaNo ratings yet
- Technical Talk On CAD: Kurian Antony M.E Cad/CamDocument28 pagesTechnical Talk On CAD: Kurian Antony M.E Cad/Camjust4kurianNo ratings yet
- VarioustypesofsurfacesDocument15 pagesVarioustypesofsurfacesVishnu SakaravarthyNo ratings yet
- 2006-1252: Concept Modeling With Nurbs, Polygon, and Subdivision SurfacesDocument7 pages2006-1252: Concept Modeling With Nurbs, Polygon, and Subdivision SurfacesmohammadNo ratings yet
- Various Types of Surfaces: Made By:-Nilesh Bhojani Guided By: - Prof. B.K. PatelDocument15 pagesVarious Types of Surfaces: Made By:-Nilesh Bhojani Guided By: - Prof. B.K. Patelnilesh bhojaniNo ratings yet
- A Polyhedron Representation For Computer Vision: by Bruce G. BaumgartDocument8 pagesA Polyhedron Representation For Computer Vision: by Bruce G. BaumgartfopweripwioeNo ratings yet
- GIS I CH 2 Data ModelDocument49 pagesGIS I CH 2 Data Modeleyoba2590No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Apr 27, 2021Document3 pagesAdobe Scan Apr 27, 2021Syko GamingNo ratings yet
- Image Deformation Using Moving Least SquaresDocument8 pagesImage Deformation Using Moving Least SquaresBui Minh TuanNo ratings yet
- 3D Modelling: DR Rajesh Panda Sto - Cad/Cam - CipetDocument52 pages3D Modelling: DR Rajesh Panda Sto - Cad/Cam - CipetRajesh PandaNo ratings yet
- Cad/cam NotesDocument21 pagesCad/cam NotesS A ABDUL SUKKURNo ratings yet
- ApproachDocument10 pagesApproachabcdNo ratings yet
- Surface Modeling: by M.Mariyappan.,M.E Ap/Mech Sgi-SetDocument18 pagesSurface Modeling: by M.Mariyappan.,M.E Ap/Mech Sgi-SetKamalakkannan RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Unit III Surface ModellingDocument24 pagesUnit III Surface ModellingSuhasNo ratings yet
- CO3 and CO4Document128 pagesCO3 and CO4koushiksai141No ratings yet
- Answers CGDocument8 pagesAnswers CGRohit sharmaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Solid ModellingDocument31 pagesPresentation On Solid ModellingdivyanshuNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4 3D Object Representations MethodsDocument2 pagesUNIT-4 3D Object Representations MethodsRajyalakshmi MNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Cadd Ii - 2023Document14 pagesLab Manual Cadd Ii - 2023Akhil RajNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2468502X23000311 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S2468502X23000311 MainAsry Kartika DwyNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Two Marks Question and Answer: Me6501 Computer Aided DesignDocument12 pagesUnit - I Two Marks Question and Answer: Me6501 Computer Aided DesignKamalakkannan RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Graphics - 2 MarksDocument8 pagesGraphics - 2 MarkssherlinbecseNo ratings yet
- Unit-3-Computer Aided DesignDocument21 pagesUnit-3-Computer Aided DesignMuthuvel M100% (5)
- CATIADocument5 pagesCATIAkiran2381100% (1)
- Unit 3Document34 pagesUnit 322 SAI SUSHMA SNo ratings yet
- Various Types of Surfaces: Made By:-Nilesh Bhojani Guided By: - Prof. B.K. PatelDocument15 pagesVarious Types of Surfaces: Made By:-Nilesh Bhojani Guided By: - Prof. B.K. Patelnilesh bhojaniNo ratings yet
- CS71 - Computer Graphics 2 MarksDocument23 pagesCS71 - Computer Graphics 2 MarkspeyartheriyathuNo ratings yet
- 3D CadDocument4 pages3D CadGowdhaman ElangovanNo ratings yet
- Interactive Design of Planar Curved Folding by Re EctionDocument5 pagesInteractive Design of Planar Curved Folding by Re EctionAkshay VasishtaNo ratings yet
- Cad Exp 3Document5 pagesCad Exp 3VedprakashNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I - GM PPT FinalDocument126 pagesUNIT-I - GM PPT Finalavishal ramNo ratings yet
- McENG 6218 Ch2Document129 pagesMcENG 6218 Ch2yemane gebremichalNo ratings yet
- Softimage User Guide - Geometric ObjectsDocument4 pagesSoftimage User Guide - Geometric ObjectsJeremy GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Binary Space Partitioning: Exploring Binary Space Partitioning: Foundations and Applications in Computer VisionFrom EverandBinary Space Partitioning: Exploring Binary Space Partitioning: Foundations and Applications in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Bounding Volume: Exploring Spatial Representation in Computer VisionFrom EverandBounding Volume: Exploring Spatial Representation in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Pyramid Image Processing: Exploring the Depths of Visual AnalysisFrom EverandPyramid Image Processing: Exploring the Depths of Visual AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Image Based Modeling and Rendering: Exploring Visual Realism: Techniques in Computer VisionFrom EverandImage Based Modeling and Rendering: Exploring Visual Realism: Techniques in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Misc Nest Manual 20Document1 pageMisc Nest Manual 20scribdztNo ratings yet
- Panel Systems: Joint LocationsDocument1 pagePanel Systems: Joint LocationsscribdztNo ratings yet
- Partnership Comes Full Circle: The West Australian Remarked in AnDocument1 pagePartnership Comes Full Circle: The West Australian Remarked in AnscribdztNo ratings yet
- Jeonju Paper Is Pioneering The Globalisation Footprint of The PaperDocument1 pageJeonju Paper Is Pioneering The Globalisation Footprint of The PaperscribdztNo ratings yet
- Saving Changes: Entity MenuDocument1 pageSaving Changes: Entity MenuscribdztNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Solidification Time 1Document1 pagePrediction of Solidification Time 1scribdztNo ratings yet
- Vic Tica Guidance NotesDocument39 pagesVic Tica Guidance NotesscribdztNo ratings yet
- Defining A Firm Folder For Images and Symbols - Tekla User AssistanceDocument1 pageDefining A Firm Folder For Images and Symbols - Tekla User AssistancescribdztNo ratings yet
- Calendar 2014 Portrait in ColourDocument1 pageCalendar 2014 Portrait in ColourscribdztNo ratings yet
- Perth Airport - 1944-1994Document20 pagesPerth Airport - 1944-1994scribdztNo ratings yet
- Tekla Structures AdministratorsUpgradeGuide181to190Document38 pagesTekla Structures AdministratorsUpgradeGuide181to190scribdztNo ratings yet
- SolidWorks Training Files2010Document2 pagesSolidWorks Training Files2010scribdztNo ratings yet
- Monthly Planner A5 A4Document2 pagesMonthly Planner A5 A4scribdztNo ratings yet
- Date Slider For Daily Routine: Inbox Do/delay/delegate/diminishDocument2 pagesDate Slider For Daily Routine: Inbox Do/delay/delegate/diminishscribdztNo ratings yet
- Proofs PDFDocument2 pagesProofs PDFdelante.calebjamesNo ratings yet
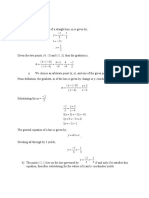
- Introduction To Partial Differential Equation - III. Numerical MethodsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Partial Differential Equation - III. Numerical Methodssoundarya raghuwanshiNo ratings yet
- Anushasan - Full Syllabus Test - SolDocument24 pagesAnushasan - Full Syllabus Test - SolnirmlaNo ratings yet
- Add Polynomials SEDocument5 pagesAdd Polynomials SEPagoejaNo ratings yet
- Question 1Document9 pagesQuestion 1mwidaniNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Chapter 2 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Test Paper 01Document5 pagesCBSE Class 12 Mathematics Chapter 2 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Test Paper 01chankit vashishtNo ratings yet
- Bascal ReviewerDocument3 pagesBascal Reviewerhatdog blueNo ratings yet
- Logarithmic FunctionsDocument57 pagesLogarithmic FunctionsKelvin Mark KaabayNo ratings yet
- Ubd Unit PlanDocument4 pagesUbd Unit PlanEllenNo ratings yet
- احمد الزهراني-شرح المنطق الرقمي بالعربيةDocument107 pagesاحمد الزهراني-شرح المنطق الرقمي بالعربيةرغوووودي رغووووديNo ratings yet
- Advanced Integration TechniquesDocument155 pagesAdvanced Integration Techniquesspsarathy100% (1)
- IGCSE (9-1) Maths New Topics: Perpendicular Lines: NameDocument13 pagesIGCSE (9-1) Maths New Topics: Perpendicular Lines: NameMark PrincelyNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade Enrichment Invest. Unit 9-Identifying FunctionsDocument27 pages8th Grade Enrichment Invest. Unit 9-Identifying FunctionsDenetera CobbNo ratings yet
- Yxcyxc XC Yxcyxc XC: James Stewart Lothar Redlin Saleem WatsonDocument2 pagesYxcyxc XC Yxcyxc XC: James Stewart Lothar Redlin Saleem Watsonjovica37No ratings yet
- Worksheet For Real NumbersDocument10 pagesWorksheet For Real NumbersComputer10 ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 Summative Test No. 1 Mga Layunin Code Bahagda N Bilang NG Aytem Kinalalagyan NG BilangDocument4 pagesQuarter 4 Summative Test No. 1 Mga Layunin Code Bahagda N Bilang NG Aytem Kinalalagyan NG BilangJanine Canlas100% (4)
- Mathematical Techniques For Control SystemDocument10 pagesMathematical Techniques For Control SystemDeepthiNo ratings yet
- Ho CH 5 Codes MarmolDocument2 pagesHo CH 5 Codes MarmolGina Marmol0% (1)
- Grade 7 Mathematics Curriculum GuideDocument2 pagesGrade 7 Mathematics Curriculum GuideGlenn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Secant Method (Sauer)Document6 pagesSecant Method (Sauer)Ismael LinsNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 2010 AnswersDocument24 pagesUnit 4 2010 AnswersalicenuoliNo ratings yet
- MCQ Cse PutDocument8 pagesMCQ Cse PutAnurag ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Week 10 - FACTORIAL, AND PERMUTATIONS AND COMBINATIONSDocument7 pagesWeek 10 - FACTORIAL, AND PERMUTATIONS AND COMBINATIONSEmmanuel GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Hint: Assume That The Events "Son Calls" and "Daughter Calls" Are Independent, and The JointDocument2 pagesHint: Assume That The Events "Son Calls" and "Daughter Calls" Are Independent, and The JointNguyễn TrọngNo ratings yet
- Math Lesson For Life: Always Be Careful With The SIGNS )Document5 pagesMath Lesson For Life: Always Be Careful With The SIGNS )JM Panganiban IINo ratings yet
- Polar Coordinate System - WikipediaDocument25 pagesPolar Coordinate System - WikipediaSatya Ranjan PadhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Number System and CodesDocument40 pagesChapter 2 Number System and Codessenawagari07fNo ratings yet
- ZombiesDocument12 pagesZombiesZerohedgeNo ratings yet