Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Demand and Supply Equilibrium
Demand and Supply Equilibrium
Uploaded by
AKASH KULSHRESTHAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Demand and Supply Equilibrium
Demand and Supply Equilibrium
Uploaded by
AKASH KULSHRESTHACopyright:
Available Formats
Demand and Supply Equilibrium
The demand curve shifts rightward when cookie
demand increases
When a market is in equilibrium, the price of a good or service tends to stay
the same. Equilibrium is the price at which the quantity demanded by
consumers is equal to the quantity that's supplied by suppliers. When either
demand or supply changes, however, the equilibrium price and quantity will
also change. That's what we're talking about in this lesson - changes in the
market equilibrium.
Let's look at some examples of changes in demand and supply, including an
illustration of what happens when both demand and supply increase or
decrease simultaneously. Before we begin, here's a helpful list of all the
possible changes to equilibrium that you'll encounter in macroeconomics:
Overview of Changes in Equilibrium Prices
Shifts in the Demand
Curve
(when supply is
unchanged)
means an increase in causes equilibrium to
to the right
demand increase
means a decrease in causes equilibrium to
to the left
demand decrease
Shifts in the Supply
Curve
(when demand is
unchanged)
means an increase in causes equilibrium to
to the right
supply decrease
means a decrease in causes equilibrium to
to the left
supply increase
As you can see, an increase in demand causes the equilibrium price to rise.
On the other hand, a decrease in demand causes the equilibrium price to fall.
An increase in supply causes the equilibrium price to fall, while a decrease in
supply causes the equilibrium price to rise.
Well, as it turns out, I'm thinking about chocolate chip cookies right now. For
some reason, talking about macroeconomics really increases my demand for
cookies. Ever since they removed the Cookie Monster from public television's
'Sesame Street,' I've noticed a remarkable decrease in the supply of cookies
in my house; however, my demand for cookies has only gone up and up and up!
So, let's look at an example of equilibrium in the cookie market and see what
happens when things change.
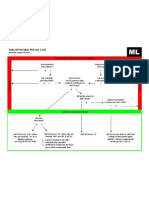
Let's say the equilibrium price for a chocolate chip cookie is $3. Here's an
example of the supply and demand curves, with an equilibrium price of $3,
which is at the intersection of the supply and demand curves. At a price of $3,
consumers will demand and suppliers will supply 5,000 cookies per year. Wow,
that sounds great, doesn't it? What happens when something causes a shift in
demand? Well, I'm glad you asked!
A drop in cookie demand causes the demand curve
to shift to the left
When household incomes increase by 30% this year (hey, this could happen!),
that means that the demand for cookies goes up. If the demand for cookies
increases, then this causes a shift of the demand curve to the right. As you
can see, a new equilibrium is created after the shift. The new equilibrium
price is higher than the old one because demand increased. At the new
equilibrium, the price for a cookie is now $5, and the quantity demanded,
which is the same as the quantity supplied, is 7,500 cookies at this higher
level of price.
Okay, so now, let's say that instead of increasing, household incomes
decrease this year by 30%. When they do, the demand for cookies is definitely
going to go down. A decrease in the demand for cookies will cause the
demand curve to shift to the left, and, assuming no change in anything else,
the equilibrium price will go down. The new equilibrium price is going to be
$2. At this price, only 2,500 cookies will get sold in this market instead of
5,000.
So far, we've talked about what happens to the demand for cookies. Let's look
at the supply side now.
There are various things that could lead to a shift in supply, but let's say that
a weird blue tornado flies through the city of Chiphaven, in West Cookieland.
(It's a beautiful place. I've been there - you should go there. It's a great place
for vacation - the kids would love it.) Unfortunately, half of all the cookie
factories are located here in Chiphaven, and the tornado picks up all the
cookie factories in the air (in addition to tens of thousands of cookies, if you
can imagine that) and destroys them. Thankfully, Studio 65, the nearby disco,
is perfectly intact!
So, what's the effect of this event? This natural disaster is going to lead to a
decrease in the supply of cookies. A decrease in the supply of cookies causes
the equilibrium price to rise. The new equilibrium price is $5 a cookie, and the
associated quantity has gone down to 2,500 cookies.
You might also like
- A level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Curso B31.12Document18 pagesCurso B31.12rafaelespino1100% (3)
- No Change in Demand and Increase in Supply: Hypothetical ExampleDocument7 pagesNo Change in Demand and Increase in Supply: Hypothetical Exampleishita sabooNo ratings yet
- Chapter (Eng. Eco) 003Document16 pagesChapter (Eng. Eco) 003dsbsabirkhanNo ratings yet
- Demand Curve: The Chart Below Shows That The Curve Is A Downward SlopeDocument7 pagesDemand Curve: The Chart Below Shows That The Curve Is A Downward SlopePrince Waqas AliNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economics & Management: Week 2 Prepared By: Miss. Fatima M. SaleemDocument81 pagesEngineering Economics & Management: Week 2 Prepared By: Miss. Fatima M. SaleemJehangir VakilNo ratings yet
- CLSP 8 NotesDocument12 pagesCLSP 8 NotesatharvanpandeyNo ratings yet
- Eco Section 2 5 To 13Document14 pagesEco Section 2 5 To 13Jiya YadukulNo ratings yet
- Demand & Supply 1Document8 pagesDemand & Supply 1AzharNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document15 pagesAssignment 3allisonbrown0999No ratings yet
- 2.1-2.9 How Market WorksDocument11 pages2.1-2.9 How Market Worksgrayce limNo ratings yet
- ECO2011 Basic Microeconomics - Lecture 6Document21 pagesECO2011 Basic Microeconomics - Lecture 61194390705No ratings yet
- Equilibrium Reflects The Perfect Balance of Supply and DemandDocument8 pagesEquilibrium Reflects The Perfect Balance of Supply and DemandGözde GürlerNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Transcript (English)Document72 pagesWeek 2 Transcript (English)Adik TanNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply ModelDocument24 pagesDemand and Supply ModelШугыла Есимхан100% (1)
- Factors Affecting Shift of Demand: When The Demand Curve ShiftsDocument7 pagesFactors Affecting Shift of Demand: When The Demand Curve ShiftsKirthi RkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document13 pagesChapter 3Bader F QasemNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document 4Document13 pagesUntitled Document 4sorayukiforger13No ratings yet
- 09-20-2009 12 54 35PMDocument1 page09-20-2009 12 54 35PManyashataledmundNo ratings yet
- Shifts in The Demand CurveDocument8 pagesShifts in The Demand CurveWill ColacitoNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 Supply & Demand - MicroeconomicsDocument48 pagesChap 4 Supply & Demand - MicroeconomicsZubaer RiadNo ratings yet
- Demand and SupplyDocument35 pagesDemand and SupplysiribandlaNo ratings yet
- Market ForcesDocument30 pagesMarket ForcesamorrisNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument13 pagesUntitledInzamam Ul Haq HashmiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics2Document39 pagesPrinciples of Economics2reda gadNo ratings yet
- Eco Unit 2Document17 pagesEco Unit 2aSQUARE test seriesNo ratings yet
- Economics Basics - Supply and Demand - InvestopediaDocument5 pagesEconomics Basics - Supply and Demand - Investopediaddeww100% (1)
- Demand and SupplyDocument8 pagesDemand and SupplyAbdul Qadir KhanNo ratings yet
- Law of Supply and Demand: Quantity SuppliedDocument3 pagesLaw of Supply and Demand: Quantity SuppliedmNo ratings yet
- Demand & SupplyDocument6 pagesDemand & SupplySoham GuhaNo ratings yet
- Micro EconomicsDocument57 pagesMicro Economicsali hansiNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply Law of DiminishingDocument6 pagesDemand and Supply Law of DiminishinggralenekovaNo ratings yet
- 3 Demand ForecastingDocument8 pages3 Demand ForecastingShanmukh GollapudiNo ratings yet
- Economics ReviewerDocument15 pagesEconomics ReviewerPatriciaNo ratings yet
- Market Supply and Demand, and Elasticity ConceptDocument58 pagesMarket Supply and Demand, and Elasticity ConceptAsahi My loveNo ratings yet
- Economics BasicsDocument17 pagesEconomics BasicsmdsalmanarNo ratings yet
- Suply Demand CurvesDocument7 pagesSuply Demand CurvesonkaliyaNo ratings yet
- Google Market Equilibrium ExamplesDocument11 pagesGoogle Market Equilibrium ExamplesAllicamet SumayaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Demand and SupplyDocument36 pagesUnit 4 - Demand and SupplyUtaa Divine KahuureNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument28 pagesEconomicstangabobo4545No ratings yet
- Economics Basics-Demand & SupplyDocument8 pagesEconomics Basics-Demand & SupplyNahiyan Islam ApuNo ratings yet
- Economics Assignment 1Document3 pagesEconomics Assignment 1GbengaNo ratings yet
- Supply and Demand and Market EquilibriumDocument10 pagesSupply and Demand and Market EquilibriumMerliza JusayanNo ratings yet
- DemandDocument37 pagesDemandRavi VarmaNo ratings yet
- Economics Basics: Supply and DemandDocument8 pagesEconomics Basics: Supply and Demandrizqi febriyantiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Price DeterminationDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Price DeterminationNeelabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Law of Supply and DemandDocument2 pagesUnderstanding The Law of Supply and DemandTommyYapNo ratings yet
- ECN1101 - Micro Economics: Ms. Farida's ClassDocument25 pagesECN1101 - Micro Economics: Ms. Farida's ClassFarida ViraniNo ratings yet
- Changes in Supply VDocument4 pagesChanges in Supply Vnodicoh572No ratings yet
- Macroeconomics-Compiled TopicsDocument12 pagesMacroeconomics-Compiled Topicskrystel basaNo ratings yet
- Practice 2Document24 pagesPractice 2Софи БреславецNo ratings yet
- zFIB8 30YhADocument21 pageszFIB8 30YhABuntyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 To 10Document16 pagesChapter 3 To 10Hsu Lae NandarNo ratings yet
- ECO2011 Basic Microeconomics - Lecture 5Document34 pagesECO2011 Basic Microeconomics - Lecture 51194390705No ratings yet
- Chapter Two - Theory of Demand, Supply and ElasticityDocument25 pagesChapter Two - Theory of Demand, Supply and ElasticityAnupomNo ratings yet
- Economics Basic3 Supply DemandDocument6 pagesEconomics Basic3 Supply Demandwaluyo2010No ratings yet
- Topic 8 SlideshowDocument11 pagesTopic 8 SlideshowNicole MuroiwaNo ratings yet
- Basic Analysis of Demand and Supply 1Document6 pagesBasic Analysis of Demand and Supply 1Jasmine GarciaNo ratings yet
- HEALTH ECONOMICS Supply & Demand, Market EquilibriumDocument10 pagesHEALTH ECONOMICS Supply & Demand, Market EquilibriumPao C Espi100% (1)
- Price Changes: Short Notes For Economics MuskanDocument4 pagesPrice Changes: Short Notes For Economics MuskanMuskan RahimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-Demand and SupplyDocument15 pagesLecture 3-Demand and SupplyGideon MukuiNo ratings yet
- Isoquant, Isocost Line, Expansion Path, Ridge Lines, Returns To ScaleDocument27 pagesIsoquant, Isocost Line, Expansion Path, Ridge Lines, Returns To ScaleAKASH KULSHRESTHA100% (2)
- Course Structure Micro EconomicsDocument8 pagesCourse Structure Micro EconomicsAKASH KULSHRESTHANo ratings yet
- Consumers Equlibrium With IC AnalysisDocument3 pagesConsumers Equlibrium With IC AnalysisAKASH KULSHRESTHANo ratings yet
- Akash Internship ReportDocument55 pagesAkash Internship ReportAKASH KULSHRESTHANo ratings yet
- Akash Internship ReportDocument54 pagesAkash Internship ReportAKASH KULSHRESTHANo ratings yet
- Ouestionnaire: Part - ADocument3 pagesOuestionnaire: Part - AAKASH KULSHRESTHANo ratings yet
- NIFTY 50 Tips For The WeekDocument52 pagesNIFTY 50 Tips For The WeekDasher_No_1No ratings yet
- PPP Canada Definition PDFDocument2 pagesPPP Canada Definition PDFPrateekNo ratings yet
- Czech Business and Trade 2/2010Document60 pagesCzech Business and Trade 2/2010zamorskaNo ratings yet
- Parle-G PLCDocument6 pagesParle-G PLCShruti KumariNo ratings yet
- Goodwill Accounting - See's CandyDocument2 pagesGoodwill Accounting - See's CandyNishant SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- 1553944252387Document15 pages1553944252387Gokul Singh BishtNo ratings yet
- IFM Chapter 11 AnswersDocument6 pagesIFM Chapter 11 AnswersPatty CherotschiltschNo ratings yet
- Individual Tax ReturnDocument6 pagesIndividual Tax Returnaklank_218105No ratings yet
- Sony Vaio Integrated Marketing CommunicationDocument26 pagesSony Vaio Integrated Marketing CommunicationMadhuri Singh0% (1)
- Materi Sosialisasi Kode Etik 2021Document85 pagesMateri Sosialisasi Kode Etik 2021Rii GIIRII100% (1)
- Directory ListingDocument62 pagesDirectory ListingMy Way To GameNo ratings yet
- Bs CHP - 2 WorksheetDocument2 pagesBs CHP - 2 WorksheetAryan AgrawalNo ratings yet
- New Players New GameDocument82 pagesNew Players New Gamepraetorians2009No ratings yet
- NCDMB HSE Presentation MUREV3Document7 pagesNCDMB HSE Presentation MUREV3seyi.alegreNo ratings yet
- Quality (Assignment)Document3 pagesQuality (Assignment)satoukookieNo ratings yet
- Quality Policy Metro Cash Carry - en PDFDocument2 pagesQuality Policy Metro Cash Carry - en PDFSrikanth GuruNo ratings yet
- Bank Financial Statements: Format of Bank Balance SheetDocument10 pagesBank Financial Statements: Format of Bank Balance SheetMannavan ThiruNo ratings yet
- 2222 Management SystemDocument5 pages2222 Management SystemUnokhogie EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- 12 Uncertainty in Future EventsDocument54 pages12 Uncertainty in Future EventsRolandianurNo ratings yet
- Folder - Career & Job FairDocument8 pagesFolder - Career & Job FairakashniranjaneNo ratings yet
- Makati City Ordinance 002-09Document3 pagesMakati City Ordinance 002-09alexjalecoNo ratings yet
- Bir Comparison SLSPDocument5 pagesBir Comparison SLSPchris cardino100% (1)
- Activity No. 2 - Tutorial No 2 PDFDocument6 pagesActivity No. 2 - Tutorial No 2 PDFAnthony MachadoNo ratings yet
- JETMOLD CatalogDocument16 pagesJETMOLD CatalogTy WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Iffco-Tokio General Insurance Co - LTD: Regd. Office: IFFCO Sadan C1 Distt. Centre, Saket, New Delhi - 110017Document3 pagesIffco-Tokio General Insurance Co - LTD: Regd. Office: IFFCO Sadan C1 Distt. Centre, Saket, New Delhi - 110017ams20110% (1)
- takehome-UAS - UM122 - ENGLISH FOR ACADEMIC PURPOSES - FINAL EXAM (2022-2023)Document15 pagestakehome-UAS - UM122 - ENGLISH FOR ACADEMIC PURPOSES - FINAL EXAM (2022-2023)Gema AhmadaNo ratings yet
- Unud 134 930996879 Daftar PustakaDocument9 pagesUnud 134 930996879 Daftar PustakaM Syamsul MaarifNo ratings yet
- News SummaryDocument21 pagesNews Summaryapi-290371470No ratings yet
- Flowchart For UCC 2-207Document1 pageFlowchart For UCC 2-207Matthew LeaperNo ratings yet