Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter Light-Reflection and Refraction
Chapter Light-Reflection and Refraction
Uploaded by
VIDYA M0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageThis document discusses key concepts of light reflection and refraction. It covers the basic properties of light including reflection, refraction, and dispersion. It defines different types of reflection and media that light can pass through. The key laws of reflection and refraction are defined, including Snell's law. Mirrors and lenses are examined, including image formation using ray diagrams and experimental verification. Formulas for mirrors and lenses are provided to calculate values like focal length and magnification.
Original Description:
light
Original Title
Chapter 10 Light
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses key concepts of light reflection and refraction. It covers the basic properties of light including reflection, refraction, and dispersion. It defines different types of reflection and media that light can pass through. The key laws of reflection and refraction are defined, including Snell's law. Mirrors and lenses are examined, including image formation using ray diagrams and experimental verification. Formulas for mirrors and lenses are provided to calculate values like focal length and magnification.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageChapter Light-Reflection and Refraction
Chapter Light-Reflection and Refraction
Uploaded by
VIDYA MThis document discusses key concepts of light reflection and refraction. It covers the basic properties of light including reflection, refraction, and dispersion. It defines different types of reflection and media that light can pass through. The key laws of reflection and refraction are defined, including Snell's law. Mirrors and lenses are examined, including image formation using ray diagrams and experimental verification. Formulas for mirrors and lenses are provided to calculate values like focal length and magnification.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
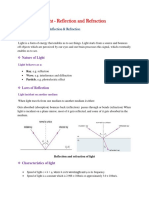
Chapter Light- reflection and refraction
Light is a form of energy. Properties of light are reflection, refraction, dispersion,
diffraction etc
Different media of light are transparent, translucent and opaque
Two types of reflection are Regular and diffused. Regular happen on a smooth surface, a
clear image is produced and diffused reflection happen on a rough surface, the image
formed is diffused.
Laws of reflection of light states that (i) angle of reflection is equal to angle of
incidence(ii) incident ray, reflected ray and the normal lie in the same plane.
Plane mirror forms a virtual and erect image of same size.
Spherical mirrors are of two types, concave and convex.
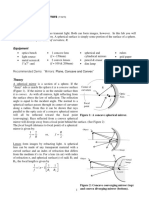
Study of Image formation by a concave mirror and convex mirror can be done by
drawing ray diagrams.
Study of Image formation of a concave mirror by doing experiment in the lab
Mirror formula to find out the focal length is 1/f = 1/u + 1/v where u is the object
distance and v is the image distance. Magnification= -v/u
Numerical based on mirror formula
The concept of refraction is the bending of light rays when it moves from one medium to
another with different refractive index.
Laws of refraction -Snell’s law states that the ratio of sin i with sin r is a constant known
as refractive index of the medium.
The Refraction through a glass slab is done by drawing the ray diagram.
Drawing and verifying in the lab
The terms associated with Lenses are optic centre, principal axis, focus and focal length
for both convex and concave.
Study of image formation by a convex lens and concavelens can be done by drawing ray
diagrams
Study of Image formation of a convex lens by experimental method in the lab.
Lens formula is 1/f = 1/v – 1/u and magnification= v/u and Numerical based on lens
formula
Power of a lens P= 1/f in metre or 100/f in cm. Power of combination of lenses can be
found out by P= P1 + P2 + P3 +….
You might also like
- Lesson Plans - LightDocument9 pagesLesson Plans - Lightjatinder kaur100% (6)
- Lecture Notes 7 - 203 OpticsDocument33 pagesLecture Notes 7 - 203 OpticsGramoz Cubreli100% (1)
- Physics 122Document107 pagesPhysics 122stephenalfa7No ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument44 pagesReflection and Refraction of LightArman Akram100% (1)
- LIGHT - Light i-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesLIGHT - Light i-WPS OfficeUtsav BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Padhle 10th - Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument37 pagesPadhle 10th - Light - Reflection & Refractionved bhaskerNo ratings yet
- Light Mirrors and LensesDocument28 pagesLight Mirrors and LensesJohn Malig100% (1)
- 2 Out 2 PDFDocument426 pages2 Out 2 PDFSwapnil MaladkarNo ratings yet
- WP4 Light WavesDocument16 pagesWP4 Light Waveswarona letangNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument31 pagesLight - Reflection & RefractionsagarNo ratings yet
- Light, Optics & ColourDocument38 pagesLight, Optics & ColourKrish ChopraNo ratings yet
- Support material, X, Chapter- LightDocument12 pagesSupport material, X, Chapter- Lightaestheticmax23No ratings yet
- Class 10 SCIENCE - PhysicsDocument59 pagesClass 10 SCIENCE - PhysicsRamya L NNo ratings yet
- LIGHTDocument14 pagesLIGHTTECH CORNERNo ratings yet
- Notes: Introduction To Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument10 pagesNotes: Introduction To Light - Reflection & RefractionShardul SumantNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument48 pagesChapter 9 - Light - Reflection and Refractionsekhsayan0102No ratings yet
- LensesDocument31 pagesLensesDejaunae LawsonNo ratings yet
- 3rd TERM PHYSICS SS2 SC-WPS Office NoteDocument17 pages3rd TERM PHYSICS SS2 SC-WPS Office Notekrankstephen20No ratings yet
- Physics Formula Class10Document38 pagesPhysics Formula Class10srizwan.1979No ratings yet
- Reflection RefractionDocument38 pagesReflection RefractionHandini Novita SariNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument19 pagesPhysics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsAsamNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and Refraction NotesDocument9 pagesLight - Reflection and Refraction NotesRaviraj Desai100% (2)
- Light - Reflection and Refraction: Laws of Re EctionDocument10 pagesLight - Reflection and Refraction: Laws of Re EctioncharanNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Ligtht: PTH Apparentde RealdepthDocument6 pagesRefraction of Ligtht: PTH Apparentde RealdepthmmolokimoremiNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and RefractionDocument20 pagesLight Reflection and RefractionShaurya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument56 pagesOpticsahsan shahNo ratings yet
- © 2014 Pearson Education, IncDocument54 pages© 2014 Pearson Education, IncIbrahim MNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument20 pagesPhysics Formula Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsJeshanth JsNo ratings yet
- LightDocument5 pagesLightnarayanaNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics (Theory)Document20 pagesRay Optics (Theory)Kumar Rohit100% (1)
- Wave and Optics DLPDocument8 pagesWave and Optics DLPlopezchinshin28No ratings yet
- Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument9 pagesLight - Reflection & RefractionKishore K.vNo ratings yet
- Our Eye As A Camera Refraction, Errors and Solutions.: DR - Ali.A.Taqi Fifth Year StudentsDocument44 pagesOur Eye As A Camera Refraction, Errors and Solutions.: DR - Ali.A.Taqi Fifth Year Studentsabigail100% (1)
- Light: Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument15 pagesLight: Light - Reflection and RefractionShabir KhanNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument25 pagesOpticsSam LoveNo ratings yet
- WP2 Light Waves (SDA) 2Document11 pagesWP2 Light Waves (SDA) 2matsweamogelang89No ratings yet
- Class X LP LightDocument1 pageClass X LP LightNiklesh SelvaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document33 pagesUnit 6mirdulsahuNo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesDocument78 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesWarren Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument6 pagesRay Optics and Optical InstrumentsJasdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument6 pagesScienceInkspireNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument27 pagesRay Optics and Optical InstrumentsChikchikchat ChatNo ratings yet
- Light - Refraction - Spherical Lens in One ShotDocument56 pagesLight - Refraction - Spherical Lens in One ShotRachit JainNo ratings yet
- Mirrors and Lenses: Ray Diagrams in A Plane MirrorDocument6 pagesMirrors and Lenses: Ray Diagrams in A Plane MirrorLabeenaNo ratings yet
- C 9,Ray Optics AshramDocument39 pagesC 9,Ray Optics AshramJawle AbhinavNo ratings yet
- 10 SC Phy LightDocument7 pages10 SC Phy LightAjay AnandNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light Printed Notes Class 8Document13 pagesReflection of Light Printed Notes Class 8Typist VBCNo ratings yet
- GD Class X Physics Chapter 11 Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument49 pagesGD Class X Physics Chapter 11 Human Eye and The Colourful WorldOfficial WorkNo ratings yet
- Science Notes For Class 10 Chapter 10 Light Reflection and RefractionDocument4 pagesScience Notes For Class 10 Chapter 10 Light Reflection and RefractionSaurabhNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 10 Light-Reflection and RefractionMohammedNo ratings yet
- Phy161 Lab Report 11Document10 pagesPhy161 Lab Report 11Javier Luis SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Optics 191 - TaggedDocument52 pagesChapter 5 Optics 191 - TaggedST4No ratings yet
- Physics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument19 pagesPhysics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsV3MON LOLNo ratings yet
- LIGHT FinalDocument32 pagesLIGHT Finalehan.ilrnestersNo ratings yet
- Optics Egt22460Document14 pagesOptics Egt22460vimukthi gunasinghaNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction - CBSE - XDocument7 pagesReflection and Refraction - CBSE - Xvidyamane23100% (1)
- Light and Mirror GRADE 10Document44 pagesLight and Mirror GRADE 10kimarie kinmon100% (1)
- Light, Reflection, Refraction - CBSE Class 10 PhysicsDocument7 pagesLight, Reflection, Refraction - CBSE Class 10 PhysicsGurukul24x794% (17)
- Optics: Lenses and Mirrors: (Completion Time: Approx. 2 H)Document10 pagesOptics: Lenses and Mirrors: (Completion Time: Approx. 2 H)Gabriel Eyapan100% (1)
- Cylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandCylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet