Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cars
Cars
Uploaded by
ivanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cars
Cars
Uploaded by
ivanCopyright:
Available Formats
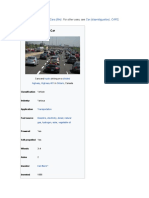
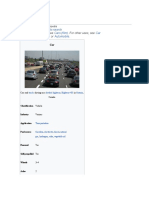
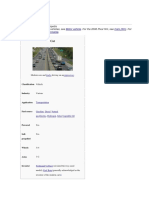
A car (or automobile) is a wheeled motor vehicle used for transportation.
Most
definitions of car say they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have
four tires, and mainly transport people rather than goods.[2][3]
Cars came into global use during the 20th century, and developed economies depend
on them. The year 1886 is regarded as the birth year of the modern car when German
inventor Karl Benz patented his Benz Patent-Motorwagen. Cars became widely
available in the early 20th century. One of the first cars accessible to the masses
was the 1908 Model T, an American car manufactured by the Ford Motor Company. Cars
were rapidly adopted in the US, where they replaced animal-drawn carriages and
carts, but took much longer to be accepted in Western Europe and other parts of the
world.
Cars have controls for driving, parking, passenger comfort, and safety, and
controlling a variety of lights. Over the decades, additional features and controls
have been added to vehicles, making them progressively more complex. These include
rear reversing cameras, air conditioning, navigation systems, and in-car
entertainment. Most cars in use in the 2010s are propelled by an internal
combustion engine, fueled by the combustion of fossil fuels. Electric cars, which
were invented early in the history of the car, began to become commercially
available in 2008.
There are costs and benefits to car use. The costs include acquiring the vehicle,
interest payments (if the car is financed), repairs and maintenance, fuel,
depreciation, driving time, parking fees, taxes, and insurance.[4] The costs to
society include maintaining roads, land use, road congestion, air pollution, public
health, health care, and disposing of the vehicle at the end of its life. Road
traffic accidents are the largest cause of injury-related deaths worldwide.[5]
The benefits include on-demand transportation, mobility, independence, and
convenience.[6] The societal benefits include economic benefits, such as job and
wealth creation from the automotive industry, transportation provision, societal
well-being from leisure and travel opportunities, and revenue generation from the
taxes. People's ability to move flexibly from place to place has far-reaching
implications for the nature of societies.[7] There are around 1 billion cars in use
worldwide. The numbers are increasing rapidly, especially in China, India and other
newly industrialized countries.[8]
You might also like
- LUBS5217M Seminar 1 Questions 2016-2017Document27 pagesLUBS5217M Seminar 1 Questions 2016-2017akshra7gjNo ratings yet
- Car Rental Business PlanDocument18 pagesCar Rental Business PlanShanoi Walker-GayleNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesLiterature ReviewMuhammad Irfan Dogar100% (1)
- Supercharged! Design, Testing and Installation of Supercharger Systems by Corky Bell - Chapter 2: Acquiring A Supercharged VehicleDocument8 pagesSupercharged! Design, Testing and Installation of Supercharger Systems by Corky Bell - Chapter 2: Acquiring A Supercharged VehicleBentley Publishers67% (3)
- Test 3 Reading Passage 1 Questions 1-6 New-Age TransportDocument4 pagesTest 3 Reading Passage 1 Questions 1-6 New-Age TransportPrince54% (13)
- Volvo 940 Owners Manual 1991Document205 pagesVolvo 940 Owners Manual 1991NopNo ratings yet
- Car Say They Run Primarily On Roads, Seat One To Eight People, Have FourDocument1 pageCar Say They Run Primarily On Roads, Seat One To Eight People, Have FourDerrick BaltimoreNo ratings yet
- Ethanol Flexible-Fuel VehiclesDocument1 pageEthanol Flexible-Fuel VehicleslatchanyananaNo ratings yet
- Citation NeededDocument1 pageCitation NeededDexterNo ratings yet
- Cars Came Into Global Use During The 20th Century, and Developed EconomiesDocument5 pagesCars Came Into Global Use During The 20th Century, and Developed EconomiestjasaNo ratings yet
- CarDocument1 pageCarinbawNo ratings yet
- Rise of Motorized VehiclesDocument2 pagesRise of Motorized VehiclesMauyrNo ratings yet
- Recarch CarDocument1 pageRecarch CarBhupender AswalNo ratings yet
- მანქანა მაგარია ტოიოტა პრიუს ხოარ გადაობDocument1 pageმანქანა მაგარია ტოიოტა პრიუს ხოარ გადაობdachi apkhazavaNo ratings yet
- WkiDocument1 pageWkiAle IlovanNo ratings yet
- Modern Cars and Driving On An In, Canada: Trucks Expressway OntarioDocument2 pagesModern Cars and Driving On An In, Canada: Trucks Expressway OntariosudinorangeNo ratings yet
- For Other Types of Motorized Vehicles, See - For Other Uses, See,, andDocument5 pagesFor Other Types of Motorized Vehicles, See - For Other Uses, See,, andbluesparkles013No ratings yet
- Cars (Film) Car (Disambiguation) Cars Automobile: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orDocument3 pagesCars (Film) Car (Disambiguation) Cars Automobile: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orAndrei SlabakovNo ratings yet
- Reference:WikipediaDocument1 pageReference:Wikipediagnoble30No ratings yet
- CarDocument1 pageCarSuryansh RajputNo ratings yet
- Jump To Navigationjump To Search: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orDocument2 pagesJump To Navigationjump To Search: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See,, orFrances camille TumbagaNo ratings yet
- FDFXDocument1 pageFDFXMahmoud Al NuaimiNo ratings yet
- CARSDocument8 pagesCARSRajbir SinghNo ratings yet
- CarDocument1 pageCarSzsbxbhxdhdhdNo ratings yet
- AutomobileDocument1 pageAutomobileschoolemail bellaNo ratings yet
- Accident Avoid Automatic Steering System Final ReportDocument40 pagesAccident Avoid Automatic Steering System Final ReportAlmubeenNo ratings yet
- A Car or Automobile Is A Motor Vehicle With WheelsDocument2 pagesA Car or Automobile Is A Motor Vehicle With WheelsAlin VoicuNo ratings yet
- CarsDocument2 pagesCarssaleha3695No ratings yet
- Safari - 08-Jun-2020 at 12:31 PM 3Document1 pageSafari - 08-Jun-2020 at 12:31 PM 3Santosh J Yadav's FriendNo ratings yet
- Cars and TechnologiesDocument1 pageCars and TechnologiesRupak adhikariNo ratings yet
- Jump To Navigation Jump To Search: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For The Country, See - For Other Uses, See,, orDocument30 pagesJump To Navigation Jump To Search: For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For The Country, See - For Other Uses, See,, orLeonard IonutNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of CarsDocument1 pageThe Evolution of CarsmikkelNo ratings yet
- All About CarsDocument16 pagesAll About Carsapi-255581071No ratings yet
- For Other Types of Motorized Vehicles, See - For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See andDocument4 pagesFor Other Types of Motorized Vehicles, See - For The 2006 Pixar Film, See - For Other Uses, See andewbNo ratings yet
- Car HistoryDocument15 pagesCar HistoryprakashNo ratings yet
- Etymology: Source - WikipediaDocument3 pagesEtymology: Source - WikipediaWolfMensch1216No ratings yet
- Title The Automobile Revolution A JDocument2 pagesTitle The Automobile Revolution A JromohacNo ratings yet
- Tata Motors 2012: Fuel and Propulision TechnologiesDocument88 pagesTata Motors 2012: Fuel and Propulision TechnologiesParth AggarwalNo ratings yet
- History of CarsDocument21 pagesHistory of CarsGayle OmisolNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Mobility A Journey Through The History of CarsDocument3 pagesThe Evolution of Mobility A Journey Through The History of Carsa_s_1_5No ratings yet
- Car ReviewDocument3 pagesCar Reviewerwand21No ratings yet
- Cars Say That They Run Primarily On Roads, Seat One To Eight People, Have FourDocument9 pagesCars Say That They Run Primarily On Roads, Seat One To Eight People, Have FourShrinivas_shprNo ratings yet
- POM SC045 Study ReportDocument6 pagesPOM SC045 Study ReportRushikesh PatilNo ratings yet
- CarsDocument5 pagesCarsPawan KumarNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of AutomobilesDocument2 pagesThe Evolution of Automobilesrjn46189nezidcomNo ratings yet
- Automotive Industry AnalysisDocument31 pagesAutomotive Industry AnalysisSaif Muhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument56 pagesINTRODUCTIONkoolvansh692No ratings yet
- Wiki Loves Food - Wikipedia Photo Contest. Upload Pictures of Indian Food and Win PrizesDocument24 pagesWiki Loves Food - Wikipedia Photo Contest. Upload Pictures of Indian Food and Win PrizesgadmaleNo ratings yet
- Lucas TVS ProjectDocument58 pagesLucas TVS ProjectSourav Roy0% (1)
- Describe The Car IndustryDocument3 pagesDescribe The Car IndustryLillian KobusingyeNo ratings yet
- Natural SciencesDocument13 pagesNatural Sciencesxxmahnoor21No ratings yet
- The World of AutomobilesDocument3 pagesThe World of AutomobilesAmogus MogusNo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysisDocument12 pagesSwot Analysispoonamy09No ratings yet
- Cars StudyDocument2 pagesCars StudyFfkfj djdjfjNo ratings yet
- Research On AutomobilesDocument12 pagesResearch On Automobilesanoopv1102No ratings yet
- Cars and Trucks Driving On A Divided Highway, Highway 401 in Ontario, CanadaDocument24 pagesCars and Trucks Driving On A Divided Highway, Highway 401 in Ontario, CanadaToday NewsNo ratings yet
- Car HistoryDocument3 pagesCar HistoryfranklinNo ratings yet
- Scientific PaperDocument9 pagesScientific Paperapi-317125318No ratings yet
- The Evolution of Cars Over TimeDocument1 pageThe Evolution of Cars Over TimediogoNo ratings yet
- Nama: Raina Fishecella Nim: C100220187: Transportation (Car)Document1 pageNama: Raina Fishecella Nim: C100220187: Transportation (Car)Farid AzisNo ratings yet
- CarsDocument2 pagesCarsda. f1tnessNo ratings yet
- The Road To Muscle CarDocument15 pagesThe Road To Muscle Carvishal HarshNo ratings yet
- Page SemiDocument39 pagesPage SemiBallon DopeNo ratings yet
- Dr. Kavita Sasidharan Kulkarni, Supervisor, School of BusinessDocument2 pagesDr. Kavita Sasidharan Kulkarni, Supervisor, School of Businesssakshi gulatiNo ratings yet
- PDF IELTS Obj 5 Lesson 2Document18 pagesPDF IELTS Obj 5 Lesson 2Antonio SgròNo ratings yet
- Auto Parts AccessoriesDocument129 pagesAuto Parts Accessoriesjaytech O. kerimNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle ReportDocument9 pagesElectric Vehicle ReportAnurag MishraNo ratings yet
- Department of Vocational Education & Training: Industrial Training Institute, Aundh, Pune - 07Document43 pagesDepartment of Vocational Education & Training: Industrial Training Institute, Aundh, Pune - 07Joint Chief Officer, MB MHADANo ratings yet
- Sample Business Plan For Spare PartsDocument6 pagesSample Business Plan For Spare Partsm00d18sr100% (1)
- Impact of Customer Satisfaction On Brand Preference of CarDocument4 pagesImpact of Customer Satisfaction On Brand Preference of CarvdocxNo ratings yet
- Drivers ' and Conductors' Views On The Causes and Ways of Preventing Workplace Violence in The Road Passenger Transport Sector in Maputo City, MozambiqueDocument11 pagesDrivers ' and Conductors' Views On The Causes and Ways of Preventing Workplace Violence in The Road Passenger Transport Sector in Maputo City, MozambiqueReign PedrosaNo ratings yet
- IELTS Reading Matching Paragraph InformationDocument11 pagesIELTS Reading Matching Paragraph InformationShokirjon TolibjonovNo ratings yet
- BM4211 Assignment - 1st Coursework - ExampleDocument17 pagesBM4211 Assignment - 1st Coursework - ExampleArun AGNo ratings yet
- Final Project (5) - MergedDocument48 pagesFinal Project (5) - MergedSudarNo ratings yet
- Ezekiel John Roque 2015707041Document3 pagesEzekiel John Roque 2015707041Keizer DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Digital Transformation in The Automotive IndustryDocument8 pagesDigital Transformation in The Automotive IndustryKal Gyimesi100% (2)
- Toefl 1998-01 ListeningDocument5 pagesToefl 1998-01 ListeningSilvia Juliana RincónNo ratings yet
- 1931 Tesla Electric CarDocument4 pages1931 Tesla Electric Carstone.people5124100% (2)
- What's Under The Bonnet?: Car ExpensesDocument2 pagesWhat's Under The Bonnet?: Car Expensesliehuan wangNo ratings yet
- 2019 Urban Mobility Report From Texas A&M Transportation InstituteDocument50 pages2019 Urban Mobility Report From Texas A&M Transportation InstituteKERANewsNo ratings yet
- Market Strategies of TeslaDocument6 pagesMarket Strategies of TeslaMd. Asiqul AlamNo ratings yet
- We Should Only Be Allowed To Drive 4 Days A WeekDocument2 pagesWe Should Only Be Allowed To Drive 4 Days A WeekMallo KaiNo ratings yet
- Soal BudgetingDocument2 pagesSoal BudgetingnoortiaNo ratings yet
- Practice Automotive Industries Tarea 2Document3 pagesPractice Automotive Industries Tarea 2Oscar FerNo ratings yet
- Sách - Ielts Writing Task 2 For IntermediateDocument61 pagesSách - Ielts Writing Task 2 For IntermediateNhật PhongNo ratings yet
- University of Education Lower Mall Campus, LahoreDocument27 pagesUniversity of Education Lower Mall Campus, LahoreSeemab Sheikh QurashiNo ratings yet
- Jaguar Land-Rover: A Customer Centric OrganizationDocument15 pagesJaguar Land-Rover: A Customer Centric OrganizationAnmol Shukla100% (1)
- Corcoran Simon Ielts Advice and Tips 2010 2018Document147 pagesCorcoran Simon Ielts Advice and Tips 2010 2018Karina Boyko100% (1)