Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diabetes Treatment: Pancreatitis
Diabetes Treatment: Pancreatitis
Uploaded by
Safiya JamesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diabetes Treatment: Pancreatitis
Diabetes Treatment: Pancreatitis
Uploaded by
Safiya JamesCopyright:
Available Formats
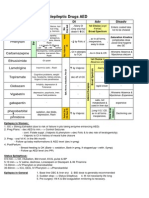
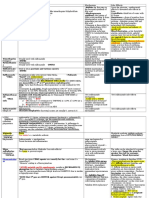
Diabetes Treatment
Type 2 Diabetes
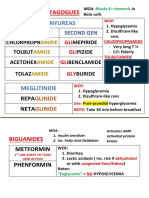
Metformin Decreases glucose output from First choice treatment
glycogen storage in the liver No effect on weight
Increases insulin sensitivity by No hypoglycemia
increasing glucose uptake Contraindications:
- Renal impairment (lactic acidosis)
Side effects:
- GI upset
Sulfonylureas Stimulate beta cells to release Second choice treatment
insulin. Contraindications:
Gliclazide - Obesity
Glipizide Side effects:
Glimepiride - Risk of hypoglycemia
Glibenclimide - Weight gain
Thiazolidinediones Increase insulin sensitivity in No hypoglycemia
adipose tissue and muscles by Side effects:
Pioglitazone binding to peroxisome - Weight gain
Rosiglitazone proliferator activated - Oedema
receptors (PPAR)-gamma & - Increase risk of fractures
regulating gene expression.
Acarbose Disaccharide inhibitor that Least effective drug
delays absorption of glucose Side effect:
after meals. - GI upset
GLP-1 analogues GLP – 1 is a peptide release Injected once or twice day
(Incretin based therapies) from the small intestine in No hypoglycemia
response to glucose absorption. Weight loss (can be used for obese
Exenatide (BD or Drug activates GLP-1 receptors patient)
Weekly) to increase insulin secretion Side effects:
Liraglutide (QD) and decrease glucagon - Nausea
Dulaglutide (Weekly) secretion. - Injection site reaction
Act in pancreas. - Pancreatitis
DPP 4 inhibitors DPP 4 is an enzyme that breaks Injected
(Incretin based therapies) down GLP-1. No hypoglycemia
Drug binds to DPP 4 and No weight gain
Sitagliptin inhibits its action increasing the Side effect:
Vildagliptin half-life of GLP-1. - Increase risk of cardiovascular
Saxagliptin Act in pancreas. problems in the long term
Linagliptin
SGLT-2 inhibitors SGLT-2 is transporter in Side effects:
nephron that allows glucose - Weight loss
Dapagliflozin reabsorption - Decrease blood pressure
Canagliflozin Drug inhibits SGLT2 in kidney. - Increase risk of genital and urinary
Empagliflozin tract infection
Liraglutide associated with reduced cardiovascular outcomes in long-term (LEADER) trial.
NB:
α-glucosidase inhibitors act in stomach.
Biguanides act in liver\meglintides act in pancreas.
Indications for Insulin in Type 2 Diabetes
Not meeting glycemic targets on maximum doses of OHAs
Decompensation during intercurrent illness, eg infection, injury
Uncontrolled weight loss
Perioperative in patients undergoing surgery
Pregnancy
Hepatic or renal disease
Allergy or other serious reaction to oral agents
Latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA)
Relief of glucose toxicity
Management of Type 1:
Monitoring glycemic control – finger prick, symptoms, HbA1c, blood ketone level.
Lifestyle modification
Insulin replacement – subcutaneous insulin or Islet replacement therapies
Involvement of multi-disciplinary team
Type 1 Diabetes
Basal – Bolus Insulin Basal/Nighttime insulin: suppresses Injected
glucose production between meals Side effects:
Basal: and overnight. (long term & provides - Hypoglycemia
Glargine 50% of daily requirement) - Weight gain
Detemir - Oedema
Bolus/Mealtime insulin: limits - Allergy
Bolus: hyperglycemia after meals (short
Glulisine term & provides 10% of daily
Aspart requirement)
Lispro/Humalog
Insulin pump Mimics normal pancreas function Injected
Costly
Side effects:
- Hypoglycemia
- Weight gain
- Oedema
- Allergy
- Infection
- Ketoacidosis
In type 1 DM; intensive glucose control (as opposed to cultural) has a greater effect on reducing retinopathy,
neuropathy and nephropathy.
You might also like
- Bridgeport Series I Milling Machne Repair ManualDocument134 pagesBridgeport Series I Milling Machne Repair Manualkxkvi1274502100% (6)
- Parts of A Bar.Document3 pagesParts of A Bar.MARY JOY VILLARUEL100% (1)
- Approach To Differential Diagnosis PDFDocument62 pagesApproach To Differential Diagnosis PDFanasNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology OutlineDocument11 pagesCardiovascular Pharmacology OutlineLhay de OcampoNo ratings yet
- Embryology MCQsDocument7 pagesEmbryology MCQsSafiya James100% (2)
- Pathology ReviewDocument26 pagesPathology ReviewSafiya James100% (1)
- Diabetes Type 2 HassanDocument26 pagesDiabetes Type 2 Hassanyash_acharya007100% (1)
- Prefix Suffix MnemonicsDocument5 pagesPrefix Suffix MnemonicsPj MontecilloNo ratings yet
- Prefix, Suffix of DrugsDocument6 pagesPrefix, Suffix of DrugsBriel Jake CabusasNo ratings yet
- Kaplan Notes. ExamenSO IMPORTANTDocument145 pagesKaplan Notes. ExamenSO IMPORTANTLisaNo ratings yet
- Drug Interactions: What Is An Interaction?Document4 pagesDrug Interactions: What Is An Interaction?Leyla MajundaNo ratings yet
- OSCEDocument16 pagesOSCESara KhalidNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEDocument3 pagesPharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEMitu Miressa تNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Anemias PDFDocument1 pageNinja - Anemias PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- IMG EmpAposterDocument1 pageIMG EmpAposterChiu LeoNo ratings yet
- Hmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, InteractionsDocument6 pagesHmg-Coa Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) : Side Effects, Contraindications, Interactionswaste78No ratings yet
- Clinical Use of Monoclonal Antibodies: Abciximab Infliximab TrastuzumabDocument15 pagesClinical Use of Monoclonal Antibodies: Abciximab Infliximab TrastuzumabAndleeb ImranNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Drug ChartDocument50 pagesPharmacology Drug ChartEssentialForLivingNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs AntidotesDocument3 pagesCommon Drugs AntidotesJhix JadraqueNo ratings yet
- Template Drug Card1Document1 pageTemplate Drug Card1Kay TaylorNo ratings yet
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFDocument21 pagesReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFAndres F. TorresNo ratings yet
- Common Signs and SymptomsDocument36 pagesCommon Signs and SymptomsJamil AimanNo ratings yet
- Drug Interactions 2 Paper PDFDocument2 pagesDrug Interactions 2 Paper PDFAzima AbdelrhamanNo ratings yet
- Common Medications UsedDocument3 pagesCommon Medications UsedRay Michael CasupananNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Drugs Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 pagesHypertension Drugs Cheat Sheet: by ViaGulzaib KhokharNo ratings yet
- Pass 2010 ScheduleDocument1 pagePass 2010 SchedulewldcrdNo ratings yet
- Whole Pharmacology Classification: Adrenergic Antagonists Alpha Adrenergic Antagonists Alpha 1 AntagonistsDocument17 pagesWhole Pharmacology Classification: Adrenergic Antagonists Alpha Adrenergic Antagonists Alpha 1 AntagonistsFlorina TrutescuNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action For Each Class of AntiDocument146 pagesMechanism of Action For Each Class of AntiReynaldo RiveraNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Anti-Coagulants PDFDocument3 pagesNinja - Anti-Coagulants PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Antiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE AdvDocument1 pageAntiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE Advrayooona88No ratings yet
- MnemonicsDocument3 pagesMnemonicsXyzhie McCrudenNo ratings yet
- Physiology Clinical Diagnosis Treatment: TSI AntibodiesDocument10 pagesPhysiology Clinical Diagnosis Treatment: TSI Antibodies85robertNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Review: Pharmacology Charlene Natale, BSN, RNDocument43 pagesNCLEX Review: Pharmacology Charlene Natale, BSN, RNMenly Susada100% (1)
- AntimicrobialsDocument1 pageAntimicrobialsRomaine Barrett100% (1)
- Pedia Stickers PDFDocument8 pagesPedia Stickers PDFAshNo ratings yet
- Lippin NotesDocument8 pagesLippin Noteswalt65100% (1)
- GastroenterologyDocument59 pagesGastroenterologyActeen MyoseenNo ratings yet
- Med CardsDocument4 pagesMed CardsSonia FernandesNo ratings yet
- Neuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartDocument5 pagesNeuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartMonica J Ortiz Pereira100% (1)
- Know The Normal ValuesDocument3 pagesKnow The Normal ValuesAngeline Monilla PanteNo ratings yet
- NERVOUS MnemonicsDocument4 pagesNERVOUS MnemonicsHimNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Anti-HTN PDFDocument6 pagesNinja - Anti-HTN PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- Pain and Inflammation Med ChartsDocument4 pagesPain and Inflammation Med Chartssurviving nursing school100% (1)
- Gout DrugsDocument1 pageGout DrugsMichael BrownNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Step 1 Antimicrobials ChartDocument6 pagesMicrobiology Step 1 Antimicrobials ChartM Patel100% (1)
- FINAL Hypertension Medication Summary SSDocument1 pageFINAL Hypertension Medication Summary SSronique reidNo ratings yet
- Classification of Drugs PDFDocument15 pagesClassification of Drugs PDFmuhammad ihtisham ul hassanNo ratings yet
- Summary of Antidiabetic Drugs PDFDocument3 pagesSummary of Antidiabetic Drugs PDFZinc YuloNo ratings yet
- Know Common Disease ManagementDocument14 pagesKnow Common Disease Managementcdx25No ratings yet
- Ischaemic Heart DiseaseDocument30 pagesIschaemic Heart DiseaseEB100% (1)
- Soap TemplateDocument3 pagesSoap TemplaterohitNo ratings yet
- NOAC ChartDocument2 pagesNOAC Chartsgod34No ratings yet
- Electrolytes ImbalancesDocument4 pagesElectrolytes ImbalancesPeter John Ruiz100% (1)
- Antibiotics Chart 1Document7 pagesAntibiotics Chart 1Vee MendNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of HypertensionDocument4 pagesPharmacology of HypertensionFlower100% (1)
- Antidotes To Common Medications: Medication AntidoteDocument1 pageAntidotes To Common Medications: Medication AntidoteshangguanlongkuiNo ratings yet
- Medication: Captopril (Capoten) Is An ACE Inhibitor and A Common Antihypertensive. Captopril Generic Name Contents (Hide)Document43 pagesMedication: Captopril (Capoten) Is An ACE Inhibitor and A Common Antihypertensive. Captopril Generic Name Contents (Hide)Kath Rubio0% (1)
- The Intern Pocket Card Surviving GraysDocument2 pagesThe Intern Pocket Card Surviving GraysKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Chart 2Document10 pagesAntibiotics Chart 2Vee MendNo ratings yet
- Shock PresentationDocument20 pagesShock Presentationrosalyn sugayNo ratings yet
- Northern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016Document48 pagesNorthern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016dreneavalentinstefanNo ratings yet
- 1 Nucleic AcidsDocument11 pages1 Nucleic AcidsSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- MM2 Cellular DifferentiationDocument2 pagesMM2 Cellular DifferentiationSafiya James100% (1)
- MM5 Nucleic Acids, DNA and RNADocument3 pagesMM5 Nucleic Acids, DNA and RNASafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Genetics - Chromosomal DisordersDocument3 pagesGenetics - Chromosomal DisordersSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Haemopoiesis: Composition of Whole Blood & Its ComponentsDocument8 pagesHaemopoiesis: Composition of Whole Blood & Its ComponentsSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Receptors: Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTK)Document5 pagesReceptors: Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTK)Safiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Na/K/Cl Co-Transporter (NKCC2)Document3 pagesDiuretics: Na/K/Cl Co-Transporter (NKCC2)Safiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Tell Them What You're Going To Tell Them. Tell Them. Tell Them What You Just Told Them. AristotleDocument17 pagesTell Them What You're Going To Tell Them. Tell Them. Tell Them What You Just Told Them. AristotleSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- JC1 Clinical Skills Task ListDocument2 pagesJC1 Clinical Skills Task ListSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Adult Stem Cell Additional InfoDocument1 pageAdult Stem Cell Additional InfoSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Sixth Form Government School: Thank You!Document1 pageSixth Form Government School: Thank You!Safiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Apt Contract ROSIYA COURT Furnished Nyrull ColletteDocument2 pagesApt Contract ROSIYA COURT Furnished Nyrull ColletteSafiya James100% (1)
- Plenary 4 2017Document14 pagesPlenary 4 2017Safiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Study TimetableDocument6 pagesStudy TimetableSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- The Passing of InfamyDocument1 pageThe Passing of InfamySafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Leaf Anatomy LabDocument4 pagesLeaf Anatomy LabSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Pre-Emancipation: Influential Factors in BritainDocument3 pagesPre-Emancipation: Influential Factors in BritainSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- CO2 in PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesCO2 in PhotosynthesisSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- How Does Obesity Cause DiabetesDocument3 pagesHow Does Obesity Cause DiabetesSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- HIV Vaccine Assessment Mark SchemeDocument1 pageHIV Vaccine Assessment Mark SchemeSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Rewards and Recognition in DR Reddy's by Zeba FathimaDocument82 pagesRewards and Recognition in DR Reddy's by Zeba Fathimazebafathima100% (1)
- Red Cross Red Crescent Magazine, No. 2, 2013Document32 pagesRed Cross Red Crescent Magazine, No. 2, 2013International Committee of the Red Cross100% (1)
- Physical Science Chapter 5 Ionic BondingDocument4 pagesPhysical Science Chapter 5 Ionic Bondingluis martinezNo ratings yet
- Restaurant - McdonaldsDocument9 pagesRestaurant - McdonaldsGABRIELA ELVIRA OSORIO MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Gujarat Animal Cruelty 387518Document5 pagesGujarat Animal Cruelty 387518Affan SayedNo ratings yet
- Philippine Christian University: College of Hospitality and Tourism ManagementDocument24 pagesPhilippine Christian University: College of Hospitality and Tourism ManagementJasmin Caye I. SantelicesNo ratings yet
- Red Beryl - Article - InColor Magazine-2Document2 pagesRed Beryl - Article - InColor Magazine-2JeremyNo ratings yet
- FST 01 PDFDocument12 pagesFST 01 PDFRitwika JanaNo ratings yet
- PP Ch2 3rdedDocument60 pagesPP Ch2 3rdedaying mugiwaraNo ratings yet
- Laparoscopic Bilateral Tubal LigationDocument2 pagesLaparoscopic Bilateral Tubal Ligationapi-3712326100% (1)
- Europass CV 111004 GalanisDocument2 pagesEuropass CV 111004 GalanisGeorge MastorakisNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication, Protein SynthesisDocument20 pagesDNA Replication, Protein SynthesisGarnetNo ratings yet
- HEALTH MELCs Grade 3 PDFDocument3 pagesHEALTH MELCs Grade 3 PDFMarcelina Ellar50% (2)
- Marcello Maggio. IGF-1, The Cross Road of The Nutritional, Inflammatory and Hormonal Pathways To FrailtyDocument22 pagesMarcello Maggio. IGF-1, The Cross Road of The Nutritional, Inflammatory and Hormonal Pathways To FrailtyFakhri KartanegaraNo ratings yet
- Section-1: Drilling Fluids CriteriaDocument8 pagesSection-1: Drilling Fluids CriteriaMohamed AbozeimaNo ratings yet
- Sludge TreatmentDocument34 pagesSludge TreatmentNurul Fatihah SyazwaniNo ratings yet
- Emkay Insurance Final ReportDocument73 pagesEmkay Insurance Final Reportrahulsogani123No ratings yet
- s555qw5w60101011010 Scalloppsnskskdndndn D Scalllpssond Sjsjsns S 3u373636191ir827472y152ta D D. DJDNDJFNFNF Ala. K K J N K nk755555511112727273737 11515152t2cawuwuwu272727 1116263636bllop - 1Document4 pagess555qw5w60101011010 Scalloppsnskskdndndn D Scalllpssond Sjsjsns S 3u373636191ir827472y152ta D D. DJDNDJFNFNF Ala. K K J N K nk755555511112727273737 11515152t2cawuwuwu272727 1116263636bllop - 1Red DiggerNo ratings yet
- TuberculosisDocument9 pagesTuberculosisIdasari DewiNo ratings yet
- RRM's ProfileDocument2 pagesRRM's ProfilemanjinderenerconNo ratings yet
- Ti N-Palladi Umcatalysts PDFDocument7 pagesTi N-Palladi Umcatalysts PDFBayu AnggaraNo ratings yet
- Construction ContractsDocument3 pagesConstruction Contractskat kaleNo ratings yet
- Nurs 3021 Journal OneDocument5 pagesNurs 3021 Journal Oneapi-313199824No ratings yet
- SPE-182811-MS Single-Well Chemical Tracer Test For Residual Oil Measurement: Field Trial and Case StudyDocument15 pagesSPE-182811-MS Single-Well Chemical Tracer Test For Residual Oil Measurement: Field Trial and Case StudySHOBHIT ROOHNo ratings yet
- Inconel - Alloy 050 - UNS N06950Document2 pagesInconel - Alloy 050 - UNS N06950Javeed A. KhanNo ratings yet
- Co AmoxiclavDocument1 pageCo AmoxiclavGrace DonatoNo ratings yet
- New Edited Gflmnhs Sosa DataDocument142 pagesNew Edited Gflmnhs Sosa DataMaura MartinezNo ratings yet
- Personality Theories and ModelsDocument66 pagesPersonality Theories and ModelsAndrei Băcanu100% (1)