Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Scan0054 PDF
Scan0054 PDF
Uploaded by
Jayson Jonson AraojoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Scan0054 PDF
Scan0054 PDF
Uploaded by
Jayson Jonson AraojoCopyright:
Available Formats
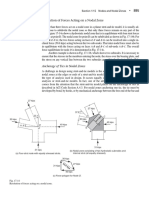
106 REPULSION-TYPE MOTORS
IlLUSTRATIONS-CHAPTER 2 107
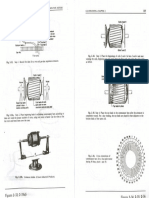
Fig, 2-37_ Cross connections of
commutator bars for a six-pole motor
having 36 bars, pitch I and 13_
Fig. 2-4Q. A wave connection showing dead coil. Thiscoil must remain unconnected
when there are more coils than bars. '
35 36 1
34
33
32
31
30
29
Fig. 2-38. Cross connections of
28 commutator bars for an eight-pole motor
27 having 36 bars, pitch 1 and 10.
26 11
25 12
24 13 Fig. 2-41. The method of placing a jumper between two bars to take the place of a
23 14 coil. This is used when there is an even number of coils and one bar more than the
22 15
number of coils.
21 20 19 18 17 16
~2434445 1 2 3
41 4 Coils 1 and 2
40 56
39
38 7 f='=
~
~ 8 """
Fig. 2-39. A four-pole, wave-wound ~ 9 f== -=
r= -=
armature must have an odd number of
• bars in the commutator. If there is an
35
34
10
11
~ i==
f==
=
-== b
even number of bars, two must be 33 12
. shorted. . 32
31
~
13
14
15
\f= =-==-
"
16
29 17 Fig. 2-42. The first two coils of a wave-wound armature in place: Note that this
2827 1918 armature is wound exactly as a lap armature, except that the beginning leads are placed
26252423222120 away from the center of the coil.
Figures 2-37; 2-38; 2-39
Fizures 2-40: 2-41; 2-42
You might also like
- Ejercicios RMS PDFDocument2 pagesEjercicios RMS PDFNicolás CanaríaNo ratings yet
- MINTZBERGDocument32 pagesMINTZBERGgeezee10004464100% (2)
- Figures 2 32 2-33a B: Repulsion-Type Motors I Lustra Ions-Chapter 2Document1 pageFigures 2 32 2-33a B: Repulsion-Type Motors I Lustra Ions-Chapter 2Jayson Jonson AraojoNo ratings yet
- Algebra PDFDocument12 pagesAlgebra PDFHafid Gando100% (1)
- Alarms - 66 Block and CablingDocument8 pagesAlarms - 66 Block and CablingBeto RNo ratings yet
- Anderson BridgeDocument8 pagesAnderson Bridgevaishnavi87No ratings yet
- Lss 2t - RL - S S RL Is - S:RL: AlgebraDocument1 pageLss 2t - RL - S S RL Is - S:RL: AlgebraNaigell SolomonNo ratings yet
- NAS (3rd) May2019Document3 pagesNAS (3rd) May2019SANJAY SHARMANo ratings yet
- Four Roses DoilyDocument2 pagesFour Roses Doilydonredaa13No ratings yet
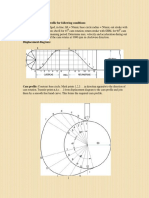
- Solved Problems (1) Draw The Cam Profile For Following ConditionsDocument6 pagesSolved Problems (1) Draw The Cam Profile For Following Conditionsrakesh kumarNo ratings yet
- 3 D 91654 Fed 96 C 76 ADocument7 pages3 D 91654 Fed 96 C 76 APhuriwat ChantraworawitNo ratings yet
- Re-Design The Wing of The C-212-400 PDFDocument6 pagesRe-Design The Wing of The C-212-400 PDFMaurizio BernasconiNo ratings yet
- EEA101L Expt#3 RamosDocument11 pagesEEA101L Expt#3 RamosKhen RamosNo ratings yet
- Mecanismos ProblemaDocument2 pagesMecanismos ProblemaManuel ChavezNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity (Practice Questions PDFDocument33 pagesCurrent Electricity (Practice Questions PDFSakshamNo ratings yet
- James Stewart Chapter 13 - Book Eight EditionDocument3 pagesJames Stewart Chapter 13 - Book Eight Editionabdulrehman gNo ratings yet
- ZNO Maths - 240326 - 132040Document5 pagesZNO Maths - 240326 - 132040Марина ДіденкоNo ratings yet
- Áreas de BrodmannDocument1 pageÁreas de BrodmannAni RiveraNo ratings yet
- 15-20W Class AB Audio AmplifierDocument4 pages15-20W Class AB Audio AmplifierhsNo ratings yet
- Tnc 135 Точка По ТочкаDocument21 pagesTnc 135 Точка По ТочкаaLexusNo ratings yet
- Fii HiDocument28 pagesFii Himimilos84No ratings yet
- "%Iagay%Y:Aa: Y An4Batc KaDocument2 pages"%Iagay%Y:Aa: Y An4Batc Kagigito0825No ratings yet
- Movement 2 - MarimbaDocument2 pagesMovement 2 - Marimbaoscar fundoNo ratings yet
- Algebra and Trigonometry 10th Edition Larson Solutions ManualDocument37 pagesAlgebra and Trigonometry 10th Edition Larson Solutions Manualacraspedalucchesezsl3q100% (15)
- Lecture 10Document35 pagesLecture 10Adarsh PriyaranjanNo ratings yet
- Diseño de Columnas de Concreto Basado en ACI 318-14Document1 pageDiseño de Columnas de Concreto Basado en ACI 318-14zenon mitha huarachiNo ratings yet
- Section4 8Document23 pagesSection4 8Amna OmerNo ratings yet
- ECE 3144 Lecture 8: Dr. Rose Q. Hu Electrical and Computer Engineering Department Mississippi State UniversityDocument10 pagesECE 3144 Lecture 8: Dr. Rose Q. Hu Electrical and Computer Engineering Department Mississippi State UniversityGopakumar G NairNo ratings yet
- ER CircuitosElectricosDocument2 pagesER CircuitosElectricosLito PelosNo ratings yet
- I Li LL kYADocument1 pageI Li LL kYANathan BrongcanoNo ratings yet
- EL 404 Circuit & Field TheoryDocument57 pagesEL 404 Circuit & Field Theorykaruppusamymari100% (1)
- Damian Hall Assignment7 DctheoryDocument18 pagesDamian Hall Assignment7 DctheoryDamian HallNo ratings yet
- Bridging Course P1L3Document7 pagesBridging Course P1L3Jayson BayogoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Keplers LawDocument3 pagesUnit 3 Keplers LawSagar ChaulagaiNo ratings yet
- Manual SIWAREX WP521 WP522 en - PDF Page 23Document1 pageManual SIWAREX WP521 WP522 en - PDF Page 23Cristi CrseNo ratings yet
- Three: Khulna University of Engineering TechnologyDocument10 pagesThree: Khulna University of Engineering TechnologyAfiat Khan TahsinNo ratings yet
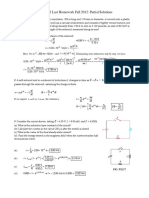
- Physics 42 Last Homework Fall 2012: Partial Solutions: NA L A R N N R N NDocument6 pagesPhysics 42 Last Homework Fall 2012: Partial Solutions: NA L A R N N R N NJustine J TibaijukaNo ratings yet
- Ceig DairyDocument10 pagesCeig DairyAmeerNo ratings yet
- D 4 Development of Beam EquationsDocument1 pageD 4 Development of Beam EquationsAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Test MHF4U - Fatima YahyaDocument2 pagesUnit 6 Test MHF4U - Fatima YahyafatimatumbiNo ratings yet
- TeoríaDocument1 pageTeoríaLeire BarandiaranNo ratings yet
- Design ExampleDocument4 pagesDesign ExampleEngr Sher KhanNo ratings yet
- Design ExampleDocument4 pagesDesign ExampleEngr Sher KhanNo ratings yet
- Repair Parts Sheet Pro Series Electric Torque Wrench Pump Model ZU4Document16 pagesRepair Parts Sheet Pro Series Electric Torque Wrench Pump Model ZU4Jhon VargasNo ratings yet
- A424 - OhmLaw2 2Document1 pageA424 - OhmLaw2 2Arnold KeNo ratings yet
- CC3 Chapter 9 ReviewDocument2 pagesCC3 Chapter 9 ReviewstellaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker Time / Current Curves (Earth Current) : With Without WithDocument1 pageCircuit Breaker Time / Current Curves (Earth Current) : With Without WithCarlos MoralesNo ratings yet
- Ass KeysDocument3 pagesAss KeysSuDheer KumarNo ratings yet
- Juntas CardanDocument30 pagesJuntas CardanAlonso FernandoNo ratings yet
- +2 Physics EM FinalDocument8 pages+2 Physics EM FinalThamizhan Cyber SolutionsNo ratings yet
- DL 541Document3 pagesDL 541Gagan SLNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Circuits - Ee8351 - November-December-2018Document3 pagesDigital Logic Circuits - Ee8351 - November-December-2018FOR STUDENTSNo ratings yet
- Ac Structured Q PDFDocument9 pagesAc Structured Q PDFabdul halimNo ratings yet
- DC Generator & Motor TheoryDocument12 pagesDC Generator & Motor TheoryMuhammad ArshedNo ratings yet
- Ejemplo Diseño A TensionDocument11 pagesEjemplo Diseño A TensionLucia MurilloNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices 9th Edition - CHP 3 Basic ProblemsDocument4 pagesElectronic Devices 9th Edition - CHP 3 Basic ProblemsThivhulawi MukondeleliNo ratings yet
- Aura Ai-2 Pipeline ProtectionDocument1 pageAura Ai-2 Pipeline ProtectionLeonardo Mondragon RiosNo ratings yet
- EE182221 DC Machines Ep2 UploadDocument14 pagesEE182221 DC Machines Ep2 UploadWarayut KampeerawatNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering - Indian Institute of Technology KharagpurDocument2 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering - Indian Institute of Technology KharagpurArkadebSenguptaNo ratings yet
- The Boogie Man BL Es: Piz 3 5 6 Contraba SDocument2 pagesThe Boogie Man BL Es: Piz 3 5 6 Contraba SMarco ScicliNo ratings yet
- Matheng Skript 1213Document227 pagesMatheng Skript 1213Jayson Jonson AraojoNo ratings yet
- Addition Hori 7Document1 pageAddition Hori 7Jayson Jonson AraojoNo ratings yet
- Addition of Numbers 1 10Document2 pagesAddition of Numbers 1 10Jayson Jonson AraojoNo ratings yet
- Addition - No Regrouping: Name: DateDocument2 pagesAddition - No Regrouping: Name: DateJayson Jonson AraojoNo ratings yet
- Addition Without Carrying 3Document2 pagesAddition Without Carrying 3Jayson Jonson AraojoNo ratings yet
- Addition With Regrouping: Name: DateDocument2 pagesAddition With Regrouping: Name: DateJayson Jonson AraojoNo ratings yet
- Midterm MathDocument3 pagesMidterm MathJayson Jonson AraojoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Management-Business FunctionsDocument8 pagesEngineering Management-Business FunctionsJayson Jonson AraojoNo ratings yet
- Unit-2: Linear Data Structure StackDocument37 pagesUnit-2: Linear Data Structure StackDivyes P100% (1)
- Sustainable Architecture and Building Design (SABD) PDFDocument19 pagesSustainable Architecture and Building Design (SABD) PDFShivachandran Sivanesan67% (3)
- Arbor APS STT - Unit 03 - Virtual Deployment - 25jan2018Document26 pagesArbor APS STT - Unit 03 - Virtual Deployment - 25jan2018masterlinh2008No ratings yet
- Joint Ventures in SingaporeDocument13 pagesJoint Ventures in SingaporesochealaoNo ratings yet
- Program Mechanics Sy 2021-2022Document10 pagesProgram Mechanics Sy 2021-2022Deogracia BorresNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Data BookDocument19 pagesMachine Design Data BookSunnyChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2020-12-24 at 11.13.39Document35 pagesScreenshot 2020-12-24 at 11.13.39Finca NurizzatiNo ratings yet
- Eka Bangun Utomo: EducationDocument1 pageEka Bangun Utomo: EducationEKANo ratings yet
- Weekly Report JAK2 - Tier III Data Center Project (8 Januari 2020)Document27 pagesWeekly Report JAK2 - Tier III Data Center Project (8 Januari 2020)Ilafya Nur IsninaNo ratings yet
- How Many Lumens To Light A Room - Modern - PlaceDocument8 pagesHow Many Lumens To Light A Room - Modern - PlaceMailah HapinNo ratings yet
- I Don't KnowDocument225 pagesI Don't KnowNew ThinkingNo ratings yet
- Environmental Awareness QuotesDocument21 pagesEnvironmental Awareness QuotesJaveed AktharNo ratings yet
- CNG Refuelling - English Final 100504Document8 pagesCNG Refuelling - English Final 100504Worldwide Equipment SolutionsNo ratings yet
- SP 11-Control of Externally Provided Products, Process and ServicesDocument11 pagesSP 11-Control of Externally Provided Products, Process and Servicesisooffice38000No ratings yet
- Addons Free Part 1Document2 pagesAddons Free Part 1Alfa RebornNo ratings yet
- Tools Used in Food PreparationDocument33 pagesTools Used in Food PreparationJohn Nelson A Picones100% (5)
- Lab - Fossil EvidenceDocument3 pagesLab - Fossil Evidenceapi-223694170No ratings yet
- Green Building Designing Innovation in India A Literature Review PDFDocument8 pagesGreen Building Designing Innovation in India A Literature Review PDFBulbul SahuNo ratings yet
- Art StylesDocument34 pagesArt StylesAdrienne Dave MojicaNo ratings yet
- Pdms Catalogue GenerationDocument26 pagesPdms Catalogue GenerationAou UgohNo ratings yet
- A. Palko - Pregnant PolytraumaDocument60 pagesA. Palko - Pregnant PolytraumaLazar VučetićNo ratings yet
- LP 1 Music Q3Document4 pagesLP 1 Music Q3Hazel Rubas SamsonNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Air Quality Impacts On Women and Children in The Accra MetropolisDocument118 pagesAssessment of Air Quality Impacts On Women and Children in The Accra MetropolisJeff Derbi-OkaeNo ratings yet
- Iot Based Real Time Potholes Detection System Using Image Processing TechniquesDocument5 pagesIot Based Real Time Potholes Detection System Using Image Processing TechniquesanjaleemanageNo ratings yet
- Collection Review Men S Key Items A W 21 22 Cut SewDocument10 pagesCollection Review Men S Key Items A W 21 22 Cut SewRitu JainNo ratings yet
- APA Format For Annotated Bibliographies: Updated For 5th EditionDocument3 pagesAPA Format For Annotated Bibliographies: Updated For 5th EditionSafat Al Mamun RonoNo ratings yet
- Canopius Reinsurance AG Financial Condition Report 2018Document50 pagesCanopius Reinsurance AG Financial Condition Report 2018saxobobNo ratings yet
- Modifications of Conventional Rigid and Flexible Methods For Mat Foundation DesignDocument156 pagesModifications of Conventional Rigid and Flexible Methods For Mat Foundation Designapirakq100% (1)
- Design and Implementation of A Computerized Information Management System in Seismic Data ProcessingDocument8 pagesDesign and Implementation of A Computerized Information Management System in Seismic Data Processinganyak1167032No ratings yet