Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Insurance Contract - : Notes by Anusha Srinvasan Iyer Principles of Insurance Department of Commerce
Insurance Contract - : Notes by Anusha Srinvasan Iyer Principles of Insurance Department of Commerce
Uploaded by
Alan PeterCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- HR Audit Checklist PDFDocument6 pagesHR Audit Checklist PDFDiverseHRNo ratings yet
- CWCTDocument1 pageCWCTEng Tr0% (1)
- Certificate of Live BirthDocument2 pagesCertificate of Live BirthRoakh100% (1)
- Form SSA-3369-BKDocument10 pagesForm SSA-3369-BKMathis & MathisNo ratings yet
- What Is Risk ManagementDocument4 pagesWhat Is Risk Managementsudipta deyNo ratings yet
- Principles of InsuranceDocument5 pagesPrinciples of InsuranceayushNo ratings yet
- B&I Unit 4Document17 pagesB&I Unit 4saisri nagamallaNo ratings yet
- Principles & Types of InsuranceDocument6 pagesPrinciples & Types of InsuranceSudhansu Shekhar pandaNo ratings yet
- InsuranceDocument20 pagesInsuranceYvonne BarrackNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument4 pagesUntitled DocumentSiladitta PalNo ratings yet
- Insurance 1Document9 pagesInsurance 1ellengaoneNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document18 pagesAssignment 1Gokul SriramNo ratings yet
- Insurance Law (Definition, Nature and Function of Insurance) B. Principles of Insurance C. Kinds of InsuranceDocument13 pagesInsurance Law (Definition, Nature and Function of Insurance) B. Principles of Insurance C. Kinds of InsuranceAJAY TAJANo ratings yet
- INSURANCE (Updated)Document50 pagesINSURANCE (Updated)annafray7No ratings yet
- 18bco32c U1Document14 pages18bco32c U1Vipul TyagiNo ratings yet
- InsuranceDocument3 pagesInsuranceAzizi Mtumwa IddiNo ratings yet
- Principle of IndemnityDocument6 pagesPrinciple of Indemnitysonakshi182100% (1)
- ch-2 Principles of Insurance SRDocument4 pagesch-2 Principles of Insurance SRAmitNo ratings yet
- Principles of InsuranceDocument3 pagesPrinciples of InsuranceNikita DesaiNo ratings yet
- InsuranceDocument4 pagesInsuranceElle BadussyNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii BoirmDocument58 pagesUnit Iii Boirmmtechvlsitd labNo ratings yet
- Daniel AyoolaDocument10 pagesDaniel AyoolaSalim SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Types of Insurance ContractsDocument1 pageTypes of Insurance ContractsAMIT BHATIANo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document10 pagesChap 3shanmughipriya nagarajanNo ratings yet
- Insurance - Subrogation, Contribution, Re-InsuranceDocument26 pagesInsurance - Subrogation, Contribution, Re-InsuranceShivam kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Module 4 InsuranceDocument25 pagesModule 4 InsuranceSumiya YousefNo ratings yet
- Insurance - Exam Type Questions-1Document24 pagesInsurance - Exam Type Questions-1mufukamilamboNo ratings yet
- Principles of Insurance - 7ef9f744f095959c3b12c38e78 - 231016 - 190009Document9 pagesPrinciples of Insurance - 7ef9f744f095959c3b12c38e78 - 231016 - 190009Drunk funNo ratings yet
- PrincipleDocument3 pagesPrincipleMoh AdnanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Insurance PDF A6cd35c5Document4 pagesPrinciples of Insurance PDF A6cd35c5Mutende ChimfyendeNo ratings yet
- Insurance CompaniesDocument5 pagesInsurance CompaniesangelicamadscNo ratings yet
- Principles of InsuranceDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Insurancebeena antuNo ratings yet
- Banking and InsuranceDocument17 pagesBanking and InsuranceDeepak GhimireNo ratings yet
- Insurance & Risk Management JUNE 2022Document11 pagesInsurance & Risk Management JUNE 2022Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Accidental Insurance: Accident Al PoliciesDocument8 pagesAccidental Insurance: Accident Al PoliciesannieangeloNo ratings yet
- Iom Concept of InsuranceDocument4 pagesIom Concept of Insuranceowuor PeterNo ratings yet
- Insurance and Risk Management PowerPointDocument24 pagesInsurance and Risk Management PowerPointvidushi geraNo ratings yet
- Child Insurance PlanDocument72 pagesChild Insurance PlanAnvesh Pulishetty -BNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 PGI..Document6 pagesAssignment 1 PGI..Krishna RajputNo ratings yet
- Basics of Business Insurance - NotesDocument41 pagesBasics of Business Insurance - Notesjeganrajraj100% (1)
- InsuranceDocument7 pagesInsuranceraghunaikaNo ratings yet
- Life and General InsuranceDocument28 pagesLife and General InsuranceAravinda ShettyNo ratings yet
- Life and General Insurance - Bcom 5 Sem Ebook and NotesDocument28 pagesLife and General Insurance - Bcom 5 Sem Ebook and NotesEnoch Gilchrist100% (1)
- Business Services - Part 3: ObjectivesDocument14 pagesBusiness Services - Part 3: ObjectivesSanta GlenmarkNo ratings yet
- PrinciplesofinsuranceDocument14 pagesPrinciplesofinsuranceSenthil MN SNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheet - Insurance Lyst7304Document19 pagesSummary Sheet - Insurance Lyst7304smriti kumariNo ratings yet
- Insurance Domain Knowledge and BasicsDocument4 pagesInsurance Domain Knowledge and BasicsbadaradinniammannaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Insurance: Course Instructor: Nusrat FarzanaDocument16 pagesBasics of Insurance: Course Instructor: Nusrat FarzanamjrNo ratings yet
- Aid To Trade Insurance: Aditva SharmaDocument20 pagesAid To Trade Insurance: Aditva Sharmaaditva SharmaNo ratings yet
- Baei Pob InsuranceDocument5 pagesBaei Pob InsuranceAdelia WatkinsNo ratings yet
- Child Insurance PlanDocument72 pagesChild Insurance Plan6338250% (4)
- Banking and Insurance Unit III Study NotesDocument13 pagesBanking and Insurance Unit III Study NotesSekar M KPRCAS-CommerceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Fundamental Legal Principles of Insurace ContractDocument18 pagesChapter 9 Fundamental Legal Principles of Insurace ContractDaysha SullivanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Insurance: Risk Management, To HedgeDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Insurance: Risk Management, To HedgeifthisamNo ratings yet
- Institution That Offers A Person, Company, or Other Entity Reimbursement or Financial Protection Against Possible Future Losses or DamagesDocument16 pagesInstitution That Offers A Person, Company, or Other Entity Reimbursement or Financial Protection Against Possible Future Losses or DamagesHrishikesh DharNo ratings yet
- INSURANCEDocument11 pagesINSURANCESashNo ratings yet
- Summer T ReportsaddsadDocument78 pagesSummer T ReportsaddsadDivyaroop HarshwalNo ratings yet
- InsurancesDocument7 pagesInsuranceskidvictor16No ratings yet
- The Seven Principles of InsuranceDocument8 pagesThe Seven Principles of InsurancesafiqulislamNo ratings yet
- Remaining ProjectDocument81 pagesRemaining ProjectvickychapterNo ratings yet
- Insurance Project 1172407) VarDocument54 pagesInsurance Project 1172407) VarVarinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Brde 101 2016 2017Document8 pagesBrde 101 2016 2017kavyadeepamNo ratings yet
- ITR 1 Combined PDFDocument4 pagesITR 1 Combined PDFcallmeasthaNo ratings yet
- Chap 012Document36 pagesChap 012Shailesh VishvakarmaNo ratings yet
- CDA Dam Safety Guidelines 2013 Edition-ToCDocument7 pagesCDA Dam Safety Guidelines 2013 Edition-ToCDavid J. Cruz0% (1)
- Malwa Gramin BankDocument9 pagesMalwa Gramin BankJeshiNo ratings yet
- Highlights of The Plenary Proceedings of Thursday 16 APRIL 2020 1. The Sitting, Presided Over by The Rt. Hon. Speaker, Rebecca A. KadagaDocument4 pagesHighlights of The Plenary Proceedings of Thursday 16 APRIL 2020 1. The Sitting, Presided Over by The Rt. Hon. Speaker, Rebecca A. KadagaOkema LennyNo ratings yet
- California State Auditor: Child Welfare Services, Report 2011-101.1, October 2011Document96 pagesCalifornia State Auditor: Child Welfare Services, Report 2011-101.1, October 2011Rick ThomaNo ratings yet
- Crimes 3 MalaysiaDocument18 pagesCrimes 3 MalaysiaismailNo ratings yet
- Directive 2006-42-CE - Machinery PDFDocument63 pagesDirective 2006-42-CE - Machinery PDFeng13No ratings yet
- What Is NIOSH?: National Institute For Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)Document3 pagesWhat Is NIOSH?: National Institute For Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)haliza amirahNo ratings yet
- Ofw Information Sheet: Personal Data Change/s (If AnyDocument1 pageOfw Information Sheet: Personal Data Change/s (If AnyDan William BadiqueNo ratings yet
- Tor Project AssistantDocument4 pagesTor Project Assistantapi-304173542No ratings yet
- STATE OF NEW MEXICO v. BRIAN ADAMSDocument22 pagesSTATE OF NEW MEXICO v. BRIAN ADAMSDaily TimesNo ratings yet
- Orange County DA Chamberlain ReportDocument94 pagesOrange County DA Chamberlain ReportDarren Chaker100% (2)
- Child Welfare Waiver Demonstration Testimony of William C. BellDocument8 pagesChild Welfare Waiver Demonstration Testimony of William C. BellBeverly TranNo ratings yet
- Telecommunicator RealitiesDocument2 pagesTelecommunicator RealitiesFOX 61 Webstaff100% (1)
- App Form QuestionsDocument24 pagesApp Form QuestionsAnthony Rupac EscasinasNo ratings yet
- Health Care SystemDocument13 pagesHealth Care SystemApril Line Alfeche PantilloNo ratings yet
- (Liam Murphy, Thomas Nagel) The Myth of Ownership (BookFi)Document156 pages(Liam Murphy, Thomas Nagel) The Myth of Ownership (BookFi)JokoWidodoNo ratings yet
- Application For A Medicare Provider Number And/or Prescriber Number For A Medical PractitionerDocument5 pagesApplication For A Medicare Provider Number And/or Prescriber Number For A Medical PractitionerisyandsirNo ratings yet
- AAKAAR As The Name Represents To Shape Up The PersonalityDocument7 pagesAAKAAR As The Name Represents To Shape Up The Personalityhansdeep479No ratings yet
- UFC 3-601-02 08 Sep 2010Document65 pagesUFC 3-601-02 08 Sep 2010Brandon TrocNo ratings yet
- Ucsp LogoDocument8 pagesUcsp LogoRazhel Shane Capili JaroNo ratings yet
- Why Was The 1875 Public Health Act Passed - General Ppt. PresentationDocument10 pagesWhy Was The 1875 Public Health Act Passed - General Ppt. PresentationWill TeeceNo ratings yet
- Medicard Philippines, Inc. vs. CIR (G.R. No. 222743)Document21 pagesMedicard Philippines, Inc. vs. CIR (G.R. No. 222743)aitoomuchtvNo ratings yet
- Event Details and FormsDocument5 pagesEvent Details and FormsYesenia MerrillNo ratings yet
Insurance Contract - : Notes by Anusha Srinvasan Iyer Principles of Insurance Department of Commerce
Insurance Contract - : Notes by Anusha Srinvasan Iyer Principles of Insurance Department of Commerce
Uploaded by
Alan PeterOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Insurance Contract - : Notes by Anusha Srinvasan Iyer Principles of Insurance Department of Commerce
Insurance Contract - : Notes by Anusha Srinvasan Iyer Principles of Insurance Department of Commerce
Uploaded by
Alan PeterCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
INSURANCE CONTRACT -
An Insurance contract is also known as a contract of Indemnity. The indemnity
contract follows are the rules pertaining to essentials of General Contract such as
offer and acceptance, consideration, free consent etc. It also follows the rules
applicable to specific indemnity contract. These rules (specific to indemnity
contract) are also known as principles of Insurance namely uberrima fidei,
insurable interest, indemnity, causa proxima, contribution, subrogation and
mitigation of loss.
In an insurance contract, the insured proposes to the insurer to indemnify ( make
good a loss) in case of an happening of an adverse event. In return he offers him
premium as a consideration. On the other hand the insurer, promises to indemnify
the insured, in case of a happening of any adverse event financially, for a
consideration (premium)
Point to be noted here is there, by meaning of indemnification we mean the insured
is put back in the same financial position as before. Not a rupee more is given to
him. At any cost, the insured cannot be put into a better financial condition.
1.2 ECONOMIC FUNCTIONS OF INSURANCE
Insurance is a boon to any growing economy. General Insurance products such as
marine and fire, help a businessman to take risks. Assume Mr. A wants to start an
industry but is always worried of fires and floods , he would never be able to do
business peacefully. He would always think, what would happen to the crores of
investment if there is a fire. How will he come back to the same financial position.
Hard earned property or property at loan if destroyed, the owner goes into deep
debts. Business closes down for months. Till the time money is arranged to buy a
new factory, the danger of going out of business persists. But assume if an owner
has taken insurance for his property, if there is fire, the insurance company will
give him money (whatever is the sum assured). With that money , he can start
another factory quickly. The best part is , even for the number of months the
factory is shut down, under insurance he can claim loss of business. Similarly, all
types of insurance have economic functions say liability insurance takes care of
Notes by Anusha Srinvasan Iyer Principles of Insurance Department of Commerce.
third party claims, motor takes care of the insured's vehicles , health insurance
takes care of employees health, Engineering insurance helps the Government take
huge building, dam, flyover projects. Marine helps in sending articles to one place
to another safely, if items are lost in transit the insurance company pays.
1.3 PREMIUM
Premium is the cost paid by Insured to the insurer. Premiums are either paid
monthly, quarterly, half yearly depending on the convinience of the insured. For
General Insurance policies , the policies are renewed each year and a new premium
is fixed. But for life insurance, premium is either fixed for whole life or for fixed
term, depending on the type of policy. A point to remember about premium is that ,
if premium is not paid, the contract becomes void for lack of consideration. A very
popular question by students is that, if we buy a motor insurance policy and pay a
yearly premium of say 15000 Rs and nothing happens to the motor vehicle and
insurance company pays nothing, in that case, will the insurance company return
back any thing. The answer is 'no'. The insurance company promised you that ,
they will pay in case of the happening of the even.t The premium si a cost of the
promise. The whole year they kept the promise. They assumed the risk. If the
motor was insured for 15 lakh rupees, and something would have happened, the
insurers would have ended up paying money . Thus for assuming this risk they
charge money. Remember, the insured is transferring the risk to insurer and the
insurer assumes the risk and asks for premium.
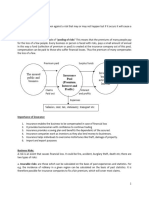
1.4 PRINCIPLES OF INSURANCE
Principles of insurance is the foundation on which the business of insurance is
built. If the understanding of priniciples or applicability of these principles go
wrong the whole concept of insurance is lost. Following are the principles in brief.
(Write examples with each principle clearly in your exam)
Utmost good faith/Uberima Fidei - This principle means that , both the insured
and insurer should not hide any details from each other. It is the insured who
knows everything about his subject matter and so he is responsible to tell
Notes by Anusha Srinvasan Iyer Principles of Insurance Department of Commerce.
everything to the insured. If the insured or insured do not reveal complete details,
the contract becomes voidable. For eg. The insured is suffering from an ailment
which he hides while buying a life insurance policy, then the insurer has every
right to repudiate the claim .
Insurable interest- This principle means that only the one who has
pecuiniary/financial interest in a particular subject matter can take an insurance
policy.
Indemnity- This principle says however big the sum insured is , only to the extent
of loss the insurance company is bound to indemnify. For eg- The sum insured is
50,000 for a Motor bike and if the motor bike meets with an accidents with repair
charges of 10,000, only 10,000 will be indemnified by the insurer.
Wherever , the principle of Indemnity applies, there principle of subrogation and
contribution also applies.
Subrogation - This principle says, that if there is a damage of subject matter and
the insurer is giving indemnifying the loss, the insured should inreturn surrender
the whole subject matter to the insurer. The insurer becomes the owner of the
damaged property, he can either sell of the scrap or can allow the insured to keep
the scrap and deduct the value of the scrap from the claim.
Contribution- Where the same subject matter is insured by two insurers , then
when there is a claim, both the insurers must contribute to indemnify in the ratios
of their sum insured. For eg - Sum insured from Company A is 5000 and Company
B is 10,000. If there is loss of Rs. 3000 then Insurance company A will give 1000
and Ins Co B will give 2000 Rs.
Mitigation of Loss - This principle says, the insured should at all times try to
minimize the loss . For eg, if there is a fire in a godown, the insured should try to
pull out things which are not yet burnt so as to damage greater damage. He has to
take steps so prevent from further losses. If it is proved that, he has not taken
proper steps for mitigation of loss then , then the claim can be repudiated by the
insurer.
Notes by Anusha Srinvasan Iyer Principles of Insurance Department of Commerce.
1.5 BROAD CATEGORIES OF INSURANCE
There are two broad categories of insurance -Life and General. While Life
insurance is all about insuring lives, General insurance is all about insuring
Properties against perils such as flood, fire etc
1.5.1 GENERAL INSURANCE
Fire Insurance - Where the properties insured are insured against perils such as
Fire, Flood, storm, Typhoon , Tempest, Earthquake etc. One must not think that
Fire means only Fire as a peril. Under the standard fire and all perils policy all the
above mentioned perils are covered.
MARINE - Marine policies can be divided into two categories, marine hull and
marine cargo. In marine hull, ships, ocean going vessels ,river vessels are insured
against fire, storm etc. In marine cargo policy, packages which are transported
from one place to another, either through air, sea , road or rail are covered.
MOTOR - Motor insurance policies cover the risks of vehicles meeting with
accidents and getting damaged. The own damage cover of motor vehicles give
claims when the owner's vehicle is damaged. Similarly, the third party cover ,
covers damages to other people's vehicles or damages to other persons caused by
the owner.
Liability Insurance - This insurance cover protects a person against third party
liabilities . For eg. A by mistake crashes into B's property and B's property gets
damaged. Now B will claim money from A for the damage that A has done to B. In
this case , had A been insured by a company, he would have been indemnified by
the insurance company in case B files a suit against . A fiduciary liability policy,
exclusively covers liabilities arising because of handling fiduciary liabilities. For
eg. If A is a trustee who manages properties entrusted to him, if something happens
to the property, the beneficiaries of the property would surely hold the trustee
responsible. In a such an event, the insurance company can pay on behalf of A, had
he taken a fiduciary liability insurance policy.
Notes by Anusha Srinvasan Iyer Principles of Insurance Department of Commerce.
HEALTH-- Here when a person falls sick all the medical expenses are taken care
off by insurance companies. They are insured against certain diseases.
PERSONAL ACCIDENT- This policy comes to rescue when a person meets with
an accident. This does not fall under health insurance. Under health insurance, a
person would have fallen sick by staying at home only, but here there has to be an
accident.
ENGINEERING - All big projects like, building constructions, dams, tunnel,
roads, flyover are risky projects. If while construction, if it falls it creates lots of
damages. Plus , again rebuilding process has to start. This policy can be taken by
Contractors and Principal both. If some damage happens during construction, the
insurance company can indemnify the money.
1.5.2 LIFE INSURANCE
There are primarily three types of life insurance plans -
1. Term plan - It is taken for a specific term. A person has to die within that term to
get money from the insurance company, This is the cheapest plan.
2. Pure endowment plan- A person has to survive a certain period to get the policy
money. This is more expensive than term plan
3. Endowment plan= This is a hybrid plan. It is acombination of both Term and
Pure endowement plan. So if a person dies within the term or a person survives a
term he gets the policy money. This is the most expensive of all the three plans.
Apart from these three, we have Unit linked Plans, where the premium money is
divided into two portions, investment and insurance. Every insured will get bare
minimum the insured amount but the investment money is invested in securities so
there is no gurantee of getting back the money.
*******************
Notes by Anusha Srinvasan Iyer Principles of Insurance Department of Commerce.
You might also like
- HR Audit Checklist PDFDocument6 pagesHR Audit Checklist PDFDiverseHRNo ratings yet
- CWCTDocument1 pageCWCTEng Tr0% (1)
- Certificate of Live BirthDocument2 pagesCertificate of Live BirthRoakh100% (1)
- Form SSA-3369-BKDocument10 pagesForm SSA-3369-BKMathis & MathisNo ratings yet
- What Is Risk ManagementDocument4 pagesWhat Is Risk Managementsudipta deyNo ratings yet
- Principles of InsuranceDocument5 pagesPrinciples of InsuranceayushNo ratings yet
- B&I Unit 4Document17 pagesB&I Unit 4saisri nagamallaNo ratings yet
- Principles & Types of InsuranceDocument6 pagesPrinciples & Types of InsuranceSudhansu Shekhar pandaNo ratings yet
- InsuranceDocument20 pagesInsuranceYvonne BarrackNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument4 pagesUntitled DocumentSiladitta PalNo ratings yet
- Insurance 1Document9 pagesInsurance 1ellengaoneNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document18 pagesAssignment 1Gokul SriramNo ratings yet
- Insurance Law (Definition, Nature and Function of Insurance) B. Principles of Insurance C. Kinds of InsuranceDocument13 pagesInsurance Law (Definition, Nature and Function of Insurance) B. Principles of Insurance C. Kinds of InsuranceAJAY TAJANo ratings yet
- INSURANCE (Updated)Document50 pagesINSURANCE (Updated)annafray7No ratings yet
- 18bco32c U1Document14 pages18bco32c U1Vipul TyagiNo ratings yet
- InsuranceDocument3 pagesInsuranceAzizi Mtumwa IddiNo ratings yet
- Principle of IndemnityDocument6 pagesPrinciple of Indemnitysonakshi182100% (1)
- ch-2 Principles of Insurance SRDocument4 pagesch-2 Principles of Insurance SRAmitNo ratings yet
- Principles of InsuranceDocument3 pagesPrinciples of InsuranceNikita DesaiNo ratings yet
- InsuranceDocument4 pagesInsuranceElle BadussyNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii BoirmDocument58 pagesUnit Iii Boirmmtechvlsitd labNo ratings yet
- Daniel AyoolaDocument10 pagesDaniel AyoolaSalim SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Types of Insurance ContractsDocument1 pageTypes of Insurance ContractsAMIT BHATIANo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document10 pagesChap 3shanmughipriya nagarajanNo ratings yet
- Insurance - Subrogation, Contribution, Re-InsuranceDocument26 pagesInsurance - Subrogation, Contribution, Re-InsuranceShivam kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Module 4 InsuranceDocument25 pagesModule 4 InsuranceSumiya YousefNo ratings yet
- Insurance - Exam Type Questions-1Document24 pagesInsurance - Exam Type Questions-1mufukamilamboNo ratings yet
- Principles of Insurance - 7ef9f744f095959c3b12c38e78 - 231016 - 190009Document9 pagesPrinciples of Insurance - 7ef9f744f095959c3b12c38e78 - 231016 - 190009Drunk funNo ratings yet
- PrincipleDocument3 pagesPrincipleMoh AdnanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Insurance PDF A6cd35c5Document4 pagesPrinciples of Insurance PDF A6cd35c5Mutende ChimfyendeNo ratings yet
- Insurance CompaniesDocument5 pagesInsurance CompaniesangelicamadscNo ratings yet
- Principles of InsuranceDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Insurancebeena antuNo ratings yet
- Banking and InsuranceDocument17 pagesBanking and InsuranceDeepak GhimireNo ratings yet
- Insurance & Risk Management JUNE 2022Document11 pagesInsurance & Risk Management JUNE 2022Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Accidental Insurance: Accident Al PoliciesDocument8 pagesAccidental Insurance: Accident Al PoliciesannieangeloNo ratings yet
- Iom Concept of InsuranceDocument4 pagesIom Concept of Insuranceowuor PeterNo ratings yet
- Insurance and Risk Management PowerPointDocument24 pagesInsurance and Risk Management PowerPointvidushi geraNo ratings yet
- Child Insurance PlanDocument72 pagesChild Insurance PlanAnvesh Pulishetty -BNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 PGI..Document6 pagesAssignment 1 PGI..Krishna RajputNo ratings yet
- Basics of Business Insurance - NotesDocument41 pagesBasics of Business Insurance - Notesjeganrajraj100% (1)
- InsuranceDocument7 pagesInsuranceraghunaikaNo ratings yet
- Life and General InsuranceDocument28 pagesLife and General InsuranceAravinda ShettyNo ratings yet
- Life and General Insurance - Bcom 5 Sem Ebook and NotesDocument28 pagesLife and General Insurance - Bcom 5 Sem Ebook and NotesEnoch Gilchrist100% (1)
- Business Services - Part 3: ObjectivesDocument14 pagesBusiness Services - Part 3: ObjectivesSanta GlenmarkNo ratings yet
- PrinciplesofinsuranceDocument14 pagesPrinciplesofinsuranceSenthil MN SNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheet - Insurance Lyst7304Document19 pagesSummary Sheet - Insurance Lyst7304smriti kumariNo ratings yet
- Insurance Domain Knowledge and BasicsDocument4 pagesInsurance Domain Knowledge and BasicsbadaradinniammannaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Insurance: Course Instructor: Nusrat FarzanaDocument16 pagesBasics of Insurance: Course Instructor: Nusrat FarzanamjrNo ratings yet
- Aid To Trade Insurance: Aditva SharmaDocument20 pagesAid To Trade Insurance: Aditva Sharmaaditva SharmaNo ratings yet
- Baei Pob InsuranceDocument5 pagesBaei Pob InsuranceAdelia WatkinsNo ratings yet
- Child Insurance PlanDocument72 pagesChild Insurance Plan6338250% (4)
- Banking and Insurance Unit III Study NotesDocument13 pagesBanking and Insurance Unit III Study NotesSekar M KPRCAS-CommerceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Fundamental Legal Principles of Insurace ContractDocument18 pagesChapter 9 Fundamental Legal Principles of Insurace ContractDaysha SullivanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Insurance: Risk Management, To HedgeDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Insurance: Risk Management, To HedgeifthisamNo ratings yet
- Institution That Offers A Person, Company, or Other Entity Reimbursement or Financial Protection Against Possible Future Losses or DamagesDocument16 pagesInstitution That Offers A Person, Company, or Other Entity Reimbursement or Financial Protection Against Possible Future Losses or DamagesHrishikesh DharNo ratings yet
- INSURANCEDocument11 pagesINSURANCESashNo ratings yet
- Summer T ReportsaddsadDocument78 pagesSummer T ReportsaddsadDivyaroop HarshwalNo ratings yet
- InsurancesDocument7 pagesInsuranceskidvictor16No ratings yet
- The Seven Principles of InsuranceDocument8 pagesThe Seven Principles of InsurancesafiqulislamNo ratings yet
- Remaining ProjectDocument81 pagesRemaining ProjectvickychapterNo ratings yet
- Insurance Project 1172407) VarDocument54 pagesInsurance Project 1172407) VarVarinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Brde 101 2016 2017Document8 pagesBrde 101 2016 2017kavyadeepamNo ratings yet
- ITR 1 Combined PDFDocument4 pagesITR 1 Combined PDFcallmeasthaNo ratings yet
- Chap 012Document36 pagesChap 012Shailesh VishvakarmaNo ratings yet
- CDA Dam Safety Guidelines 2013 Edition-ToCDocument7 pagesCDA Dam Safety Guidelines 2013 Edition-ToCDavid J. Cruz0% (1)
- Malwa Gramin BankDocument9 pagesMalwa Gramin BankJeshiNo ratings yet
- Highlights of The Plenary Proceedings of Thursday 16 APRIL 2020 1. The Sitting, Presided Over by The Rt. Hon. Speaker, Rebecca A. KadagaDocument4 pagesHighlights of The Plenary Proceedings of Thursday 16 APRIL 2020 1. The Sitting, Presided Over by The Rt. Hon. Speaker, Rebecca A. KadagaOkema LennyNo ratings yet
- California State Auditor: Child Welfare Services, Report 2011-101.1, October 2011Document96 pagesCalifornia State Auditor: Child Welfare Services, Report 2011-101.1, October 2011Rick ThomaNo ratings yet
- Crimes 3 MalaysiaDocument18 pagesCrimes 3 MalaysiaismailNo ratings yet
- Directive 2006-42-CE - Machinery PDFDocument63 pagesDirective 2006-42-CE - Machinery PDFeng13No ratings yet
- What Is NIOSH?: National Institute For Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)Document3 pagesWhat Is NIOSH?: National Institute For Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)haliza amirahNo ratings yet
- Ofw Information Sheet: Personal Data Change/s (If AnyDocument1 pageOfw Information Sheet: Personal Data Change/s (If AnyDan William BadiqueNo ratings yet
- Tor Project AssistantDocument4 pagesTor Project Assistantapi-304173542No ratings yet
- STATE OF NEW MEXICO v. BRIAN ADAMSDocument22 pagesSTATE OF NEW MEXICO v. BRIAN ADAMSDaily TimesNo ratings yet
- Orange County DA Chamberlain ReportDocument94 pagesOrange County DA Chamberlain ReportDarren Chaker100% (2)
- Child Welfare Waiver Demonstration Testimony of William C. BellDocument8 pagesChild Welfare Waiver Demonstration Testimony of William C. BellBeverly TranNo ratings yet
- Telecommunicator RealitiesDocument2 pagesTelecommunicator RealitiesFOX 61 Webstaff100% (1)
- App Form QuestionsDocument24 pagesApp Form QuestionsAnthony Rupac EscasinasNo ratings yet
- Health Care SystemDocument13 pagesHealth Care SystemApril Line Alfeche PantilloNo ratings yet
- (Liam Murphy, Thomas Nagel) The Myth of Ownership (BookFi)Document156 pages(Liam Murphy, Thomas Nagel) The Myth of Ownership (BookFi)JokoWidodoNo ratings yet
- Application For A Medicare Provider Number And/or Prescriber Number For A Medical PractitionerDocument5 pagesApplication For A Medicare Provider Number And/or Prescriber Number For A Medical PractitionerisyandsirNo ratings yet
- AAKAAR As The Name Represents To Shape Up The PersonalityDocument7 pagesAAKAAR As The Name Represents To Shape Up The Personalityhansdeep479No ratings yet
- UFC 3-601-02 08 Sep 2010Document65 pagesUFC 3-601-02 08 Sep 2010Brandon TrocNo ratings yet
- Ucsp LogoDocument8 pagesUcsp LogoRazhel Shane Capili JaroNo ratings yet
- Why Was The 1875 Public Health Act Passed - General Ppt. PresentationDocument10 pagesWhy Was The 1875 Public Health Act Passed - General Ppt. PresentationWill TeeceNo ratings yet
- Medicard Philippines, Inc. vs. CIR (G.R. No. 222743)Document21 pagesMedicard Philippines, Inc. vs. CIR (G.R. No. 222743)aitoomuchtvNo ratings yet
- Event Details and FormsDocument5 pagesEvent Details and FormsYesenia MerrillNo ratings yet