Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Static Electricity Is The Imbalance of Positive and Negative Charge
Static Electricity Is The Imbalance of Positive and Negative Charge
Uploaded by
neelaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Static Electricity Is The Imbalance of Positive and Negative Charge
Static Electricity Is The Imbalance of Positive and Negative Charge
Uploaded by
neelaCopyright:
Available Formats
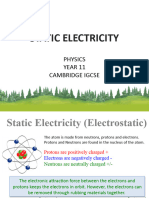
What is Static Electricity?
Rubbing a polythene strip on wool causes some of the outer electrons in the wool to move over to
the polythene strip. As the polythene gains electrons it becomes negatively charged. The wool
looses electrons and is left with a net positive charge (more protons to electrons).
Static electricity is caused by the transfer of charge.
Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons and electrons each with their own properties.
Protons have a Positive (+) charge.
Electrons have a Negative (-) charge.
Neutrons are Neutral (no charge).
The positive charges (protons) are held in the nucleus of the atom.
The negative charges (electrons) are spread in orbits around the nucleus.
The protons and neutrons are held very tightly in the nucleus. But some of the electrons are held
very loosely and can move from one atom to another. If an atom looses an electron the number of
protons (positive charges) exceeds the number of electrons (negative charges) and the atom is
positively charged.
If an atom gains an electron the number of protons (positive charges) is lesser than the number of
electrons (negative charges) and the atom is negatively charged.
One method in which electrons can be moved or transferred is by rubbing two insulators together.
Rubbing causes friction between the two surfaces increasing the surface contact and allowing more
electrons to be transferred. The object which looses electrons becomes positively charged and the
one that gains the electrons becomes negatively charged.
Therefore,
Static Electricity is the imbalance of Positive and Negative Charge
Attraction & Repulsion
Rubbing a polythene strip on wool causes some of the outer electrons in the wool to move over to
the polythene strip. As the polythene gains electrons it becomes negatively charged. The wool
looses electrons and is left with a net positive charge (more protons to electrons).
Only the negative electrons move. The positive protons remained fixed in the atoms nucleus.
Rubbing materials to generate charge only works for insulated objects. Conductors direct the charge
flow to earth.
When two electrically charged bodies are brought together they exert a force on each other.
Electrically charged objects may attract or repel each other or attract small uncharged objects place
near them.
Opposite charges attract. Like charges Repel.
Example
Balloon
A balloon can be made to stick to a wall by using the principles of electrostatics.
When a balloon is rubbed against clothes the negative electrons from the clothes get transferred to
the balloon making the balloon negatively charged. When the balloon is placed near a wall or ceiling
(a neutral object) it stays there and doesn’t fall. This is because the negative charge of the balloon
repels some of the electrons in the wall or ceiling away from the surface. This results in an overall
positively charged surface causing the negatively charged balloon to be attracted (remember
opposite charges attract).
The separated charges in the wall or ceiling are called INDUCED charges.
http://passmyexams.co.uk/GCSE/physics/attraction-and-repulsion-of-charged-bodies.html
You might also like
- Ib PPT 6 SL PDFDocument23 pagesIb PPT 6 SL PDFzarna nirmal rawalNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges: What Is Atom?Document5 pagesElectric Charges: What Is Atom?Alif Rachmat RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Electricity 01 - Electric ChargeDocument16 pagesElectricity 01 - Electric ChargeAli SalamehNo ratings yet
- Q3 - Lesson 1 PDFDocument85 pagesQ3 - Lesson 1 PDFTimothy Francisco100% (1)
- What Is Static ElectricityDocument3 pagesWhat Is Static ElectricityBrian Yosua PratamaNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument19 pagesAtomic StructureElmarNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics 2022 KatikamuDocument24 pagesElectrostatics 2022 KatikamuWAFULA BRIAN OKANYANo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Structure, Bonding and Main Group ChemistryDocument7 pagesUnit 1: Structure, Bonding and Main Group ChemistryJosh ColeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.1 ChemistryDocument7 pagesUnit 1.1 ChemistryHumoon AfsardeirNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Electric Force and Electric FieldDocument58 pagesLecture - Electric Force and Electric FieldnafsNo ratings yet
- 1st WeekDocument5 pages1st WeekNanzkie Andrei SamanNo ratings yet
- Aether and Structure of ElectronDocument7 pagesAether and Structure of ElectrondllabarreNo ratings yet
- ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELD (Edited)Document38 pagesELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELD (Edited)paperNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Notes and WorksheetsDocument8 pagesChapter 22 Notes and WorksheetscelinelizabethNo ratings yet
- 115 PPT Electrostatics Origin Electrostatics CapacitanceDocument67 pages115 PPT Electrostatics Origin Electrostatics CapacitanceErojo, Kyeane Red N.No ratings yet
- Static ElectricityDocument23 pagesStatic ElectricityMehboob KhanNo ratings yet
- AtomsfinalDocument55 pagesAtomsfinallaizfeerNo ratings yet
- Phys 3Document5 pagesPhys 3Wyndle PachecaNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity: Lesson 1 - Basic Terminology & ConceptsDocument77 pagesStatic Electricity: Lesson 1 - Basic Terminology & ConceptsDERRICKKEANNo ratings yet
- 1 Static Electricity NoteDocument2 pages1 Static Electricity Noteapi-266021217No ratings yet
- Static Note Igcse 08Document10 pagesStatic Note Igcse 08Ghazi DallyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 1Document22 pagesChemistry Unit 1JoshuaCookNo ratings yet
- Static ElectricityDocument4 pagesStatic ElectricityMuhammad Wasil KhanNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism (Part2)Document26 pagesElectricity and Magnetism (Part2)ShinjiNo ratings yet
- TECHNICAL TERMS 1st Lesson WordDocument5 pagesTECHNICAL TERMS 1st Lesson Wordmhariz encinasNo ratings yet
- Methods of ChargingDocument5 pagesMethods of Chargingjackkingsman19No ratings yet
- Electr Ic Forces Charge Interactions: Opposites (+/-) Attract and Likes (+/+ or - / - ) RepelDocument8 pagesElectr Ic Forces Charge Interactions: Opposites (+/-) Attract and Likes (+/+ or - / - ) Repelapi-27085921No ratings yet
- SKMJ - Static ElectricityDocument18 pagesSKMJ - Static Electricitykhumaira.jamariNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity: An Interactive Module For BGSCE Physics Created by Mrs. C. Saunders - NeelyDocument18 pagesStatic Electricity: An Interactive Module For BGSCE Physics Created by Mrs. C. Saunders - NeelyChristanique McIntoshNo ratings yet
- Electric CurrentDocument20 pagesElectric CurrentBik WodeNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 LM 1Document7 pagesPhysics 2 LM 1Nina Aida Bautista PaduaNo ratings yet
- EEC 124 Week OneDocument18 pagesEEC 124 Week OneOlisaemeka EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Physics-Static and Current ElectricityDocument10 pagesPhysics-Static and Current ElectricityCodeen WhiteNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade 7 Unit 8Document31 pagesPhysics Grade 7 Unit 8kidanemariam HabtemariamNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument44 pagesPhysics ProjectAvnish TewariNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment: in Physics 2Document7 pagesLaboratory Experiment: in Physics 2Charles ContridasNo ratings yet
- Periodic TrendsDocument19 pagesPeriodic TrendsgehgehkkNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 NotesDocument18 pagesUnit 7 Notesyooh9814No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument15 pagesPhysicsジョンNo ratings yet
- Electricity Is The ScienceDocument3 pagesElectricity Is The Scienceanon_522631638No ratings yet
- Electrostatics - Direct Current PDFDocument76 pagesElectrostatics - Direct Current PDFRita UmutoniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 PhysicsDocument2 pagesChapter 22 Physicsapi-261669796No ratings yet
- Periodic Trends and The Octet RuleDocument5 pagesPeriodic Trends and The Octet Rule10chirag10No ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument7 pagesPhysics NotesSoe ThiriNo ratings yet
- Physics ResearchDocument4 pagesPhysics ResearchYzza Veah EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics BasicsDocument5 pagesElectrostatics Basicspurnendu.dhalNo ratings yet
- Triboelectric Series and Induction ChargingDocument6 pagesTriboelectric Series and Induction ChargingDanielle Danica Alcuizar BaguioNo ratings yet
- Thorn Lighting Electrical TheoryDocument60 pagesThorn Lighting Electrical TheoryRahul MishraNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The AtomDocument2 pagesThe Structure of The Atomapi-666588628No ratings yet
- Conduction and InductionDocument29 pagesConduction and Inductionalkinani.faithNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Electrostatics r1Document20 pagesModule 5 - Electrostatics r1Gabriel RamosNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering MT-144-NSU (Theory)Document39 pagesBasic Electrical & Electronics Engineering MT-144-NSU (Theory)Asad KhokharNo ratings yet
- Note 3 ADocument24 pagesNote 3 Apalmer okiemuteNo ratings yet
- Nature of Electricity and Concept of ElectricityDocument2 pagesNature of Electricity and Concept of ElectricityArianna Faith LaxamanaNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Civil Engineering and Architecture: Kaunas University of TechnologyDocument8 pagesFaculty of Civil Engineering and Architecture: Kaunas University of TechnologyDar MudasirNo ratings yet
- The Structure of MatterDocument3 pagesThe Structure of MatterFull StudyNo ratings yet
- Static ElectricityDocument25 pagesStatic ElectricityZwe Htut NaingNo ratings yet
- KS3 Static Electricity Gap-FillDocument1 pageKS3 Static Electricity Gap-FillSophie Wyatt-SmithNo ratings yet
- Static ElectricityDocument21 pagesStatic Electricitydiala alazraiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PhysicsDocument3 pagesReviewer in PhysicsBeatrice MararacNo ratings yet
- Physics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPhysics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 3.design and Analysis of PistonDocument66 pages3.design and Analysis of PistonNaresh DamaNo ratings yet
- Projet Proposal For The Construction of A Marcet BoilerDocument5 pagesProjet Proposal For The Construction of A Marcet BoilerOjiSofttouchCharlesNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Department Journals Level 4: Holding InformationDocument6 pagesChemical Engineering Department Journals Level 4: Holding Informationmubi_loveNo ratings yet
- MR Dmaper PPT NewDocument21 pagesMR Dmaper PPT NewDinesh KhatriNo ratings yet
- Ariel Calculation MethodDocument6 pagesAriel Calculation MethodSubrata Mukherjee100% (1)
- Exam 3Document8 pagesExam 3Molibeli TaeleNo ratings yet
- Advances in Solar Energy Volume 17 - D Yogi GoswamiDocument337 pagesAdvances in Solar Energy Volume 17 - D Yogi Goswamianhttp.nevigroupNo ratings yet
- Cema Standar 502-2001 PDFDocument10 pagesCema Standar 502-2001 PDFjavier alvarez100% (1)
- Crane SafetiesDocument38 pagesCrane SafetiesSamar Rustagi100% (1)
- Unit 2 ReviewDocument15 pagesUnit 2 Reviewapi-336093393No ratings yet
- Separating Solids From LiquidsDocument4 pagesSeparating Solids From LiquidsLei Yin100% (1)
- Assg 2 MaterialDocument6 pagesAssg 2 MaterialAKMAL RIZAL BIN ZAINI A21EM0017No ratings yet
- PC1220R Infino LotteDocument1 pagePC1220R Infino LotteSCAR GONZALEzNo ratings yet
- Packed Tower Specification Sheet: Bed NumberDocument2 pagesPacked Tower Specification Sheet: Bed NumberJane UchulNo ratings yet
- Gear Box NoiseDocument3 pagesGear Box NoiseKumar SanthanamNo ratings yet
- Nano Scale Porous Silicon Microcavity Optical Sensor Device For The Detection of Methyl ParathionDocument7 pagesNano Scale Porous Silicon Microcavity Optical Sensor Device For The Detection of Methyl ParathionhesoyamyecgaaaNo ratings yet
- Ipc2012 90235Document9 pagesIpc2012 90235Marcelo Varejão CasarinNo ratings yet
- Pericyclic Practice QuestionsDocument3 pagesPericyclic Practice QuestionsAashnaNo ratings yet
- AFS 2211 - FUNDAMENTALS OF FOOD CHEMISTRY - Water PDFDocument40 pagesAFS 2211 - FUNDAMENTALS OF FOOD CHEMISTRY - Water PDFderrickNo ratings yet
- EBSD and EDS Characterization of High Entropy AlloysDocument4 pagesEBSD and EDS Characterization of High Entropy Alloyskelsiu1No ratings yet
- Em-I PBLDocument2 pagesEm-I PBLraza ahmadNo ratings yet
- 01 Thermal ExpansionDocument9 pages01 Thermal ExpansionKarina FerrerNo ratings yet
- Analysis Pressure Build Up and DrawdownDocument23 pagesAnalysis Pressure Build Up and DrawdownUzumaki28100% (1)
- The Dynamic Two-Fluid Model OLGA: Theory and ApplicationDocument18 pagesThe Dynamic Two-Fluid Model OLGA: Theory and ApplicationmgaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Compression of A Helical SpringDocument12 pagesLab 1 - Compression of A Helical SpringHaroon Rashidi75% (4)
- Punching Shear For FoundationsDocument2 pagesPunching Shear For FoundationsFeroz Khan PatthanNo ratings yet
- Daikin ErrorsDocument2 pagesDaikin ErrorsPatrizio_MNo ratings yet
- Material Specification: Mechanical Property RequirementsDocument2 pagesMaterial Specification: Mechanical Property RequirementsNguyễn Tấn HảiNo ratings yet
- Walter F. Stewart, Stephen S. Woods, Harold Deck Beeson-Safe Use of Oxygen and Oxygen Systems_ Guidelines for Oxygen System Desing, Materials Selection, Operations, Storage, and Transportation (Astm M.pdfDocument113 pagesWalter F. Stewart, Stephen S. Woods, Harold Deck Beeson-Safe Use of Oxygen and Oxygen Systems_ Guidelines for Oxygen System Desing, Materials Selection, Operations, Storage, and Transportation (Astm M.pdfksvvijNo ratings yet