Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PSA 4 Beds 12 Steps
PSA 4 Beds 12 Steps
Uploaded by
odeinatus0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views2 pagesThis document describes the steps in a pressure swing adsorption (PSA) process. It introduces abbreviations for the steps: AD for adsorption, PR for pressurizing, PG for purging, PPE for pressurizing pressure equalization, and DPE for depressurizing pressure equalization. It then describes a four-bed PSA process that includes additional pressure equalization steps - first depressurizing pressure equalization (FDPE), first pressurizing pressure equalization (FPPE), second depressurizing pressure equalization (SDPE), and second pressurizing pressure equalization (SPPE) - to improve recovery of hydrogen compared to a basic two-bed process.
Original Description:
psa separation
Original Title
PSA 4 beds 12 steps
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes the steps in a pressure swing adsorption (PSA) process. It introduces abbreviations for the steps: AD for adsorption, PR for pressurizing, PG for purging, PPE for pressurizing pressure equalization, and DPE for depressurizing pressure equalization. It then describes a four-bed PSA process that includes additional pressure equalization steps - first depressurizing pressure equalization (FDPE), first pressurizing pressure equalization (FPPE), second depressurizing pressure equalization (SDPE), and second pressurizing pressure equalization (SPPE) - to improve recovery of hydrogen compared to a basic two-bed process.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views2 pagesPSA 4 Beds 12 Steps
PSA 4 Beds 12 Steps
Uploaded by
odeinatusThis document describes the steps in a pressure swing adsorption (PSA) process. It introduces abbreviations for the steps: AD for adsorption, PR for pressurizing, PG for purging, PPE for pressurizing pressure equalization, and DPE for depressurizing pressure equalization. It then describes a four-bed PSA process that includes additional pressure equalization steps - first depressurizing pressure equalization (FDPE), first pressurizing pressure equalization (FPPE), second depressurizing pressure equalization (SDPE), and second pressurizing pressure equalization (SPPE) - to improve recovery of hydrogen compared to a basic two-bed process.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
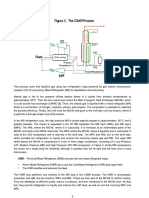
AD Adsorbing
PR Pressurizing
PG Purging
Pressurizing pressure equalization (PPE)
Depressurizing pressure equalization (D
Blowdown (BD) Damp
Pressurizing pressure equalization (PPE)
First depressurizing pressure equalization (FDPE)
First pressurizing pressure equalization (FPPE)
Second depressurizing pressure equalization (SDPE)
Second pressurizing pressure equalization (SPPE).
depressurizing pressure equalization (DPE) corresponding to the PPE step, (iv)
countercurrent depressurization/blowdown to atmosphere(BD), (v) purge with H2
product (PG), and (vi) pressurizing
pressure equalization (PPE) up to an average pressure between the beds.
In the present study, the experiments are focused on making improvements in both the
purity and recovery instead of only the purity. Because a high-pressure H2 mixture was
supplied to the PSA process, a large H2 loss was expected from the two-bed PSA
process. To recognize the improvement degree in the recovery by increasing the
number of adsorption beds and pressure equalization steps, the four-bed PSA process
with twice the pressure equalization steps was designed as shown in Fig. 2(b). In
addition, the following additional four steps were added to the cyclic sequence of the
two-bed PSA: first depressurizing pressure equalization (FDPE), first pressurizing
pressure equalization (FPPE), second depressurizing pressure equalization (SDPE),
and second pressurizing pressure equalization (SPPE). Therefore, the bed could be
pressurized using a three-stage pressurization (the first and second pressurizing
pressure equalization steps and feed pressurization step). One of the important
operating parameters in PSA operation is the purge-to-feed flow-rate ratio (P/F ratio),
which was calculated with the following equation: P=F ratio ¼
You might also like
- Convergent & Convergent-Divergent Nozzle Performance Lab ReportDocument25 pagesConvergent & Convergent-Divergent Nozzle Performance Lab ReportAkmal Aiman100% (1)
- Aspen Plus: Aspen Plus Model of The CO Capture Process by DepgDocument23 pagesAspen Plus: Aspen Plus Model of The CO Capture Process by DepgGodstandNo ratings yet
- Bilevel VentilationDocument18 pagesBilevel VentilationBonehead7No ratings yet
- Aspen Plus DEPG ModelDocument23 pagesAspen Plus DEPG ModelAmir JoonNo ratings yet
- Ther 1 - 111114Document33 pagesTher 1 - 111114So Nny0% (1)
- Section 5Document100 pagesSection 5Brayan Dali Nattez VargasNo ratings yet
- Shams Pulmonary Quiz 2Document16 pagesShams Pulmonary Quiz 2tylermedNo ratings yet
- Dead Space Analysis at Different Levels of Positive End-Expiratory Pressure in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Patients. JCC 2018Document8 pagesDead Space Analysis at Different Levels of Positive End-Expiratory Pressure in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Patients. JCC 2018Emiliano GogniatNo ratings yet
- An Investigation On Gas Lift Performance Curve in An Oil-Producing WellDocument15 pagesAn Investigation On Gas Lift Performance Curve in An Oil-Producing WellPenélope MqzNo ratings yet
- End Inspiratory Pause Prolongation in ARDSDocument8 pagesEnd Inspiratory Pause Prolongation in ARDSMaxi BoniniNo ratings yet
- AbgDocument66 pagesAbgindyaphdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Pressure: 5.1 Pressure and Its UnitsDocument14 pagesChapter 5: Pressure: 5.1 Pressure and Its UnitsMohammed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation Part 1 AnswersDocument3 pagesMechanical Ventilation Part 1 AnswersDikka Aziz100% (1)
- Study of The Pressure Drop of Dense Phase Gas-Solid Flow Through NozzleDocument5 pagesStudy of The Pressure Drop of Dense Phase Gas-Solid Flow Through NozzleMuhammad Adnan LaghariNo ratings yet
- Pressure Gain Combustion MethodsDocument8 pagesPressure Gain Combustion MethodsMax MustermannNo ratings yet
- SPE 176284 MS With Cover Page v2Document14 pagesSPE 176284 MS With Cover Page v2Adelia Dwi cahyaniNo ratings yet
- Effect of PEEP On Dead Space in An Experimental Model of ARDSDocument10 pagesEffect of PEEP On Dead Space in An Experimental Model of ARDSFernando SousaNo ratings yet
- BFP Performance Assessment Article HelpfulDocument10 pagesBFP Performance Assessment Article HelpfulUdhayakumar VenkataramanNo ratings yet
- Aspen Plus DEPG Model PDFDocument23 pagesAspen Plus DEPG Model PDFGodstandNo ratings yet
- Choke Sizing & Propiedaes de Los FluidosDocument149 pagesChoke Sizing & Propiedaes de Los FluidosJose RojasNo ratings yet
- The Engineering of Hydrogen PeroxideDocument12 pagesThe Engineering of Hydrogen PeroxideDian Ahmad BudianaNo ratings yet
- Editorial Bob y JesúsDocument2 pagesEditorial Bob y JesúsEmiliano GogniatNo ratings yet
- New Method To Estimate FFL With WFT DataDocument10 pagesNew Method To Estimate FFL With WFT DataPaolo MartiniNo ratings yet
- 2012 Yan SEG New Model Pore PressureDocument5 pages2012 Yan SEG New Model Pore PressureDewantari BrahmaniNo ratings yet
- 4.basf - 855 - e 17 (TC) - Ima Spain - Up ScalinDocument27 pages4.basf - 855 - e 17 (TC) - Ima Spain - Up ScalinPaqui Miranda GualdaNo ratings yet
- 5.0 Pneumatic System: Head and PressureDocument17 pages5.0 Pneumatic System: Head and PressureChidiebere Samuel OkogwuNo ratings yet
- Blood GasDocument31 pagesBlood GasHusna Nur FitrianaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Loss CorrelationsDocument50 pagesPressure Loss CorrelationsRMolina65No ratings yet
- Measurement of Lung Volumes by Plethysmography: Ers/Ats Workshop Report SeriesDocument13 pagesMeasurement of Lung Volumes by Plethysmography: Ers/Ats Workshop Report SeriesCarlos Cortez MansillaNo ratings yet
- Gas GradientDocument11 pagesGas Gradientamir_hayfaNo ratings yet
- Exercise Permeability QDocument7 pagesExercise Permeability QsidikNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control: Sukanta Kumar Dash, Syamalendu S. BandyopadhyayDocument11 pagesInternational Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control: Sukanta Kumar Dash, Syamalendu S. BandyopadhyayYogesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Losses How To Determine How To Use: NumberDocument8 pagesHydraulic Losses How To Determine How To Use: NumberRamanamurthy PalliNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Seal Capacity Determinations: Conventional Cores vs. CuttingsDocument12 pagesComparison of Seal Capacity Determinations: Conventional Cores vs. CuttingsAnonymous OaXCZFVNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 YvonneDocument39 pagesChapter 7 YvonneMarija SaricNo ratings yet
- Gas Compression With The Liquid Jet PumpDocument13 pagesGas Compression With The Liquid Jet PumprezarossNo ratings yet
- 01 Why Do We Need Artificial LiftDocument55 pages01 Why Do We Need Artificial LiftReza Ramadhan0% (1)
- Test Bank For Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation 5th Edition CairoDocument13 pagesTest Bank For Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation 5th Edition Cairochowryurduq0krhNo ratings yet
- CSSC 200900060Document6 pagesCSSC 200900060Eva SilviaNo ratings yet
- Material Balance EquationDocument10 pagesMaterial Balance EquationMurtez100% (1)
- Accepted Manuscript: Separation and Purification TechnologyDocument36 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Separation and Purification Technologyeti apriyantiNo ratings yet
- Multi Phase PR - DropDocument43 pagesMulti Phase PR - Dropmts1234No ratings yet
- PPM L3Document17 pagesPPM L3baban omerNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Multi-Step Pressure Swing Adsorption Process For Production of Pure Hydrogen With High RecoveryDocument6 pagesSimulation of Multi-Step Pressure Swing Adsorption Process For Production of Pure Hydrogen With High RecoveryAgam HanasichulaNo ratings yet
- Pore Pressure Prediction: Ajiri Praise Edo Percy OjogboDocument11 pagesPore Pressure Prediction: Ajiri Praise Edo Percy OjogboPercy OjogboNo ratings yet
- Effect of Sub Cooling and Superheating On Vapour Compression Refrigeration Systems Using R-22 Alternative RefrigerantsDocument11 pagesEffect of Sub Cooling and Superheating On Vapour Compression Refrigeration Systems Using R-22 Alternative RefrigerantsMalayPatelNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature Table 1. Nomenclature: J K K Kx K P P r r µ T Z L φ A DDocument12 pagesNomenclature Table 1. Nomenclature: J K K Kx K P P r r µ T Z L φ A Dمصطفى محمد عباسNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Analysis of Continuous Gas Lift Valve Positioning Methods and Its Application With Ms Excel & VbaDocument8 pagesA Comparative Analysis of Continuous Gas Lift Valve Positioning Methods and Its Application With Ms Excel & VbaArpan BiswasNo ratings yet
- H3 ManualDocument4 pagesH3 Manualmegameca007No ratings yet
- Determination of Certified Relieving CapacitiesDocument6 pagesDetermination of Certified Relieving CapacitiesGustavo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Well Control EquationsDocument13 pagesWell Control EquationsShaho Abdulqader Mohamedali100% (1)
- Pressure Loss CorrelationsDocument57 pagesPressure Loss Correlationseandresmar100% (1)
- Abg 3Document43 pagesAbg 3Montasir AhmedNo ratings yet
- CFD Modelling of Air Flow Field, Mean Age of Air and CO2 Distributions Inside A BedroomDocument10 pagesCFD Modelling of Air Flow Field, Mean Age of Air and CO2 Distributions Inside A BedroomBart Kemper, P.E.No ratings yet
- Sjet34a383 389Document7 pagesSjet34a383 389Raja GoldenNo ratings yet
- Static Pressure and Pressure Head in FluidsDocument5 pagesStatic Pressure and Pressure Head in FluidsMjay JayNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Natural Gas: From Coal, Dry Biomass, and Power-to-Gas ApplicationsFrom EverandSynthetic Natural Gas: From Coal, Dry Biomass, and Power-to-Gas ApplicationsTilman J. SchildhauerNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsFrom EverandRespiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsJian-Xin ZhouNo ratings yet
- NavitelNavigator - Quick Start Guide - 9 - QSG - ENDocument2 pagesNavitelNavigator - Quick Start Guide - 9 - QSG - ENodeinatusNo ratings yet
- Process of LNG Plant PDFDocument26 pagesProcess of LNG Plant PDFodeinatus100% (3)
- 45Document136 pages45odeinatusNo ratings yet
- Youtube Tricks MUO SheetDocument1 pageYoutube Tricks MUO SheetodeinatusNo ratings yet
- Akai Awbr 305 Im en GR Ro 8 Jan 2016Document54 pagesAkai Awbr 305 Im en GR Ro 8 Jan 2016odeinatusNo ratings yet
- Tunisia - Nawara Southern Tunisian Gas Pipeline - ESIA Executive SummaryDocument28 pagesTunisia - Nawara Southern Tunisian Gas Pipeline - ESIA Executive SummaryodeinatusNo ratings yet
- n2 Psa LindeDocument3 pagesn2 Psa LindeodeinatusNo ratings yet
- NX 300h FWD: Business FWD Hybrid Business FWD HybridDocument6 pagesNX 300h FWD: Business FWD Hybrid Business FWD HybridodeinatusNo ratings yet
- Router Manual ZTE MF253VDocument17 pagesRouter Manual ZTE MF253VodeinatusNo ratings yet
- BMW 3Document2 pagesBMW 3odeinatusNo ratings yet
- Player PDFDocument1 pagePlayer PDFodeinatusNo ratings yet
- BP Alaska Safety Handbook (BP ASH) PDFDocument130 pagesBP Alaska Safety Handbook (BP ASH) PDFVan Sot100% (2)
- Witnessing Matrix SGP GEN 00 U PR 852061 001 - 2Document22 pagesWitnessing Matrix SGP GEN 00 U PR 852061 001 - 2odeinatusNo ratings yet
- Air Products AP-C3MR™ LNG ProcessDocument1 pageAir Products AP-C3MR™ LNG ProcessodeinatusNo ratings yet
- BP Attach B Permit To Work PDFDocument16 pagesBP Attach B Permit To Work PDFodeinatusNo ratings yet
- BP - Golden Rules - Download From Step Change Web Site PDFDocument16 pagesBP - Golden Rules - Download From Step Change Web Site PDFodeinatusNo ratings yet