Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Name: Aamir Muhammad & Saif Ur Rehman Topic: Switchyard, Types & Components Assigignment NO "1"
Name: Aamir Muhammad & Saif Ur Rehman Topic: Switchyard, Types & Components Assigignment NO "1"
Uploaded by
Aamir Mohammad100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
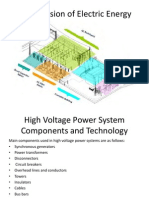
39 views3 pagesA switchyard is located at a power plant to maintain voltage levels for transmission or distribution. It consists of components like busbars, surge arrestors, insulators, isolators, circuit breakers, and transformers. There are two main types of switchyards: air insulated switchyards which use air as an insulator and are exposed; and gas insulated switchyards which use SF6 gas as an insulator inside enclosed metal enclosures. Key components of switchyards include busbars to receive and deliver power, insulators to support conductors, surge arrestors to protect from transients, and circuit breakers to isolate faulty parts. Circuit breakers can be vacuum, air, or SF6 gas based depending on the voltage
Original Description:
Components commonly used in Switchyard AIS
Original Title
Switch Yard
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA switchyard is located at a power plant to maintain voltage levels for transmission or distribution. It consists of components like busbars, surge arrestors, insulators, isolators, circuit breakers, and transformers. There are two main types of switchyards: air insulated switchyards which use air as an insulator and are exposed; and gas insulated switchyards which use SF6 gas as an insulator inside enclosed metal enclosures. Key components of switchyards include busbars to receive and deliver power, insulators to support conductors, surge arrestors to protect from transients, and circuit breakers to isolate faulty parts. Circuit breakers can be vacuum, air, or SF6 gas based depending on the voltage
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
39 views3 pagesName: Aamir Muhammad & Saif Ur Rehman Topic: Switchyard, Types & Components Assigignment NO "1"
Name: Aamir Muhammad & Saif Ur Rehman Topic: Switchyard, Types & Components Assigignment NO "1"
Uploaded by
Aamir MohammadA switchyard is located at a power plant to maintain voltage levels for transmission or distribution. It consists of components like busbars, surge arrestors, insulators, isolators, circuit breakers, and transformers. There are two main types of switchyards: air insulated switchyards which use air as an insulator and are exposed; and gas insulated switchyards which use SF6 gas as an insulator inside enclosed metal enclosures. Key components of switchyards include busbars to receive and deliver power, insulators to support conductors, surge arrestors to protect from transients, and circuit breakers to isolate faulty parts. Circuit breakers can be vacuum, air, or SF6 gas based depending on the voltage
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
NAME: AAMIR MUHAMMAD & SAIF UR REHMAN
TOPIC: SWITCHYARD, TYPES & COMPONENTS
ASSIGIGNMENT
NO “1”
SWITCHYARD:
Normally it is used for maintaining certain voltage level stepping up or down. Hence it is located in the
power plant for transmission or distribution. Switchyard consists of bus bar, surge arrestor, insulators,
isolators, earth switches, wave trap, circuit breaker, current transformer and voltage transformer
TYPES OF SWITCH YARD:
Following are the types of Switch Yard.
● AIR INSULATED SWITCHYARD (AIS):
It is the most common type used in power plant that uses air to insulate the different components of the
substation from each other as well as for grounding the charge. Substations rely on copper grounding on
equipment and in the ground to properly ground the system and make it safe. Since this type of system is
exposed to the open environment.
● GAS INSULATED SWITCHYARD (GIS):
A gas-insulated substation (GIS) uses a superior dielectric gas, SF6, at moderate pressure for phase-
to phase and phase-to-ground insulation. The high voltage conductors, circuit breaker interrupters,
switches, current transformers, and voltage transformers are in SF6 gas inside grounded metal
enclosures. A GIS is mostly used where space is expensive or not available. In a GIS the active parts
are protected from the deterioration from exposure to atmospheric air, moisture, contamination,
etc.
COMPONENTS OF SWITCH YARD:
● BUSBAR: it simply receives power from incoming circuits & delivers power to outgoing circuits.
● INSULATORS: they support conductors & insulate high current to conductors. Most commonly used
type of insulators is suspension type but post & strain type insulators are used in switchyard.
● SURGE ARRESTOR: It is connected between phase conductor and ground that prevents from
transient voltage/ surges from lightning.
● CURRENT TRANSFORMER: It is used for stepping down current for measurement & it is connected
in series with transmission line.
● VOLTAGE TRANSFORMER: It is used for stepping down Voltage for measurement & it is connected
in parallel with transmission line.
● ISOLATORS: It provides isolation from live parts for the purpose of maintenance & it is located at
either side of circuit breaker.
● RELAYS: It detects the fault & isolate the faulty part from rest of the system.
● WAVE TRAP: resonant circuit control in series with HV transmission lines to prevent from
transmission of high frequency signals.
● PLCC: power line carrier communication is used to communicate with grid or other control systems.
● CIRCUIT BREAKER: are automatic electrical devices that protect an electrical circuit caused by an
overload or fault on the line.
TYPES OF CIRCUIT BREAKER
1. VACUUM CIRCUIT BREAKER:
A breaker which used vacuum as an arc extinction medium is called a vacuum circuit breaker. In this
circuit breaker, the fixed and moving contact is enclosed in a permanently sealed vacuum interrupter.
Vacuum circuit breaker does not require any additional filling of oil or gas. Breaker unit is compact and
self-contained. It can be installed in any required orientation. Because of the above reasons together
with the economic advantage offered, vacuum circuit breaker has high acceptance (up to 40KV voltage
levels).
2. AIR CIRCUIT BREAKER:
Air blast circuit breaker is a suitable option to use where frequent operation is required because of
lesser arc energy. The risk of fire is eliminated in the operation of Air blast circuit breaker. Air blast
circuit breaker is small in size, because of the growth of dielectric strength is so rapid (which final
contact gap needed for arc extinction is very small). Arc quenching is much faster. It requires less
maintenance (up to 15KV voltage levels)
3. SF6 CIRCUIT BREAKER:
Due to the superior arc quenching property of sulphur hexafluoride gas (SF6), such circuit breakers have
very short arcing time. Since the dielectric strength of sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) gas is 2 to 3 times that
operation due unlike of air, such breakers can interrupt much larger currents. The sulphur hexafluoride
gas (SF6) circuit breaker gives noiseless operation due its closed gas circuit and no exhaust to
atmosphere unlike the air blast circuit breaker. It is used for high voltage application i.e., 33 KV – 132 KV
You might also like
- Visit On Substation ReportDocument13 pagesVisit On Substation ReportPravin Thakur50% (2)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- GisDocument30 pagesGisAbdevil75% (4)
- An Industrial Training PPT On 50mva, 132/33 KV Grid Sub StationDocument35 pagesAn Industrial Training PPT On 50mva, 132/33 KV Grid Sub Stationishfaq222100% (3)
- Group IV June 4,2013 EE 3303 Engr - Kenneth F. FajilanDocument170 pagesGroup IV June 4,2013 EE 3303 Engr - Kenneth F. Fajilanjenixson tamondong100% (2)
- Gas Insulated SwitchgearsDocument24 pagesGas Insulated Switchgearscody100% (3)
- Presentation On Substation, Including Latest AdvancementsDocument37 pagesPresentation On Substation, Including Latest AdvancementsAnjaneyakumarNo ratings yet
- Submitted To, Name-Mr. Ankush Tandon Sir (Assistant Professor)Document15 pagesSubmitted To, Name-Mr. Ankush Tandon Sir (Assistant Professor)Himanshu Soni100% (1)
- Electrical SubstationDocument16 pagesElectrical SubstationAjay Gahlot100% (3)
- Gas Insulated SwitchgearsDocument24 pagesGas Insulated Switchgearsemy1188No ratings yet
- On 220 KV GRID SUBSTATION (IG NAGAR JAIPUR)Document32 pagesOn 220 KV GRID SUBSTATION (IG NAGAR JAIPUR)TANISHK JHARWAL100% (1)
- Group 4 SwitchgearDocument10 pagesGroup 4 SwitchgearJordan Dator MontemayorNo ratings yet
- RRVPNL, 132 KV Gss (Gis) Old Power House Jodhpur (Raj.) : Bachelor of TechnologyDocument42 pagesRRVPNL, 132 KV Gss (Gis) Old Power House Jodhpur (Raj.) : Bachelor of TechnologyZombusterNo ratings yet
- Study of Substation Equipments & Protection: Konark Institute of Science & Technology BhubaneswarDocument19 pagesStudy of Substation Equipments & Protection: Konark Institute of Science & Technology BhubaneswarDev KumarNo ratings yet
- Sustation DesignDocument38 pagesSustation DesignFaheem FarooqNo ratings yet
- Switchgear - WikipediaDocument42 pagesSwitchgear - Wikipediahafiztanha450No ratings yet
- Electrical Substation General EquipmentsDocument22 pagesElectrical Substation General EquipmentsRanndolf JavierNo ratings yet
- Project - On Power Sub StationDocument22 pagesProject - On Power Sub StationRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Six Week Industrial Training at 66 KV SubDocument32 pagesSix Week Industrial Training at 66 KV SubGurinderdeep Singh67% (3)
- Gis - IntroductionDocument3 pagesGis - IntroductionsamjnanNo ratings yet
- SwitchgearDocument23 pagesSwitchgearAnonymous Yq9ibs100% (1)
- Switch Yard and Its EquipmentsDocument48 pagesSwitch Yard and Its Equipmentsamit joshi86% (14)
- SubstationDocument28 pagesSubstationPradeep Nagireddi100% (1)
- Switchgear PresentationDocument28 pagesSwitchgear PresentationSaniy Ahmad67% (3)
- Introduction To Switch Gear and ProtectionDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Switch Gear and Protectionpmankad100% (7)
- Modu LE5 SubstationDocument36 pagesModu LE5 SubstationRamya ShreyasNo ratings yet
- Switchgears and Other Equipments S RaoDocument114 pagesSwitchgears and Other Equipments S Rao2041016166.sourashishpatra100% (1)
- GowthamDocument38 pagesGowthamNavya PendurthiNo ratings yet
- SUBSTATIONDocument22 pagesSUBSTATIONAmrit Aggarwal100% (1)
- High Voltage Components PresentationsDocument28 pagesHigh Voltage Components Presentationschristian fruto100% (1)
- Switchyard FinalDocument6 pagesSwitchyard FinalPritam SamantaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On A 132KV GSS NANGAL-SHERPURDocument27 pagesPresentation On A 132KV GSS NANGAL-SHERPURmanmohan meenaNo ratings yet
- Power AssignmentDocument8 pagesPower AssignmentHaseeb AdilNo ratings yet
- By: - Achmad Rijal - Novarino HDocument14 pagesBy: - Achmad Rijal - Novarino HRam SinghNo ratings yet
- Darpan Report NewDocument66 pagesDarpan Report NewAnil Kumar JarwalNo ratings yet
- Major Electrical EquipmentsDocument52 pagesMajor Electrical EquipmentsGrant Arvin SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breakers: Presented by Ajay.S 11EE02Document28 pagesCircuit Breakers: Presented by Ajay.S 11EE02Ahmad Kalbounah0% (1)
- GIS PartsDocument8 pagesGIS Partserson1981100% (1)
- Kota Railway Summer TrainingDocument24 pagesKota Railway Summer TrainingSourabh VermaNo ratings yet
- Sub Stations 140318113806 Phpapp01Document51 pagesSub Stations 140318113806 Phpapp01JayadevDamodaranNo ratings yet
- Electrical Substation Switch Yard General EquipmentsDocument22 pagesElectrical Substation Switch Yard General EquipmentsAnand SwamiNo ratings yet
- Session: 2016 2019Document27 pagesSession: 2016 2019Manmohan MeenaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker: o o o o oDocument11 pagesCircuit Breaker: o o o o oSry Santos100% (1)
- Presentation On 220Kv Transmission Substation: By: Kauts Singh Patel ROLL NO. 2015031027 B.Tech Iv YearDocument17 pagesPresentation On 220Kv Transmission Substation: By: Kauts Singh Patel ROLL NO. 2015031027 B.Tech Iv YearadarshNo ratings yet
- Power Grid400Document9 pagesPower Grid400VIKAS GHATENo ratings yet
- Bd2 HomeworkDocument8 pagesBd2 HomeworkMhariecriszReazoNo ratings yet
- High Voltage TechniquesDocument108 pagesHigh Voltage Techniquesممشط75% (4)
- Switchgear and Protective DevicesDocument17 pagesSwitchgear and Protective DevicesAnonymous 5O6HavcVNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Lecture Notes EPS115Document3 pagesCHAPTER 2 Lecture Notes EPS115NGEH SAMUEL SHUNo ratings yet
- Substation High Voltage ComponentsDocument22 pagesSubstation High Voltage Componentsmukaram JahNo ratings yet
- Industrial Report On "Switch Gear and Protection" Government College of Engineering AmravatiDocument13 pagesIndustrial Report On "Switch Gear and Protection" Government College of Engineering AmravatiSominath HarneNo ratings yet
- Shivam Report On Substation VisitDocument18 pagesShivam Report On Substation VisitShivam KaushalNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- A Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileFrom EverandA Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileNo ratings yet
- Empowering Networks: A Comprehensive Guide to Medium Voltage SwitchgearFrom EverandEmpowering Networks: A Comprehensive Guide to Medium Voltage SwitchgearNo ratings yet
- مجموعة تجارب انظمة الزمن الحقيقيDocument45 pagesمجموعة تجارب انظمة الزمن الحقيقيSAGAAD AYAADNo ratings yet
- AD PWM IC InductionDocument41 pagesAD PWM IC InductionrigolafNo ratings yet
- Emtr Servicing Reconditioning of 1 Unit 7.5 KW, 40 HP, Cyclo Drive Induction Motor, 440V, 3phase. PPR No. 32278Document4 pagesEmtr Servicing Reconditioning of 1 Unit 7.5 KW, 40 HP, Cyclo Drive Induction Motor, 440V, 3phase. PPR No. 32278HazelNo ratings yet
- PLUS+1 Controllers: MC050-020 and MC050-022Document4 pagesPLUS+1 Controllers: MC050-020 and MC050-022vik_mdNo ratings yet
- I2 Sover USBDocument6 pagesI2 Sover USBGian Marco BoNo ratings yet
- Acer Travelmate 5310 5710 5710g Extensa 5210 5610 Wistron Dellen Rev Sa SCHDocument43 pagesAcer Travelmate 5310 5710 5710g Extensa 5210 5610 Wistron Dellen Rev Sa SCHЕвгений АвазачемNo ratings yet
- SIP5 7UT85-86-87 V09.20 Manual C094-1 en PDFDocument2,406 pagesSIP5 7UT85-86-87 V09.20 Manual C094-1 en PDFDanilo SilvaNo ratings yet
- N5900B 2 ManualDocument12 pagesN5900B 2 ManualYadgar ZanganaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics OneDocument59 pagesElectrostatics OneAkNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Aperture RadarDocument3 pagesSynthetic Aperture RadarLiviu LivadariuNo ratings yet
- Temperature Controlled FanDocument38 pagesTemperature Controlled FanJinil Vs0% (1)
- Sd.ma英文說明書 E-phaa-esda03 -l M型Document130 pagesSd.ma英文說明書 E-phaa-esda03 -l M型Wikmi IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Generatore MP10Document4 pagesGeneratore MP10Leonardo BruttiNo ratings yet
- MCCB Range: With Thermal - Magnetic ReleaseDocument2 pagesMCCB Range: With Thermal - Magnetic Releasevishal V PNo ratings yet
- 20-20 MpiDocument2 pages20-20 MpiLupiNo ratings yet
- Interconnect Components & Hardware: Catalog m65Document160 pagesInterconnect Components & Hardware: Catalog m65Semmi SemNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of Protection Relays Under CT SaturationDocument2 pagesBehaviour of Protection Relays Under CT Saturationvksharma13100% (1)
- ATS48 User ManualDocument85 pagesATS48 User Manualkythuat04 nteNo ratings yet
- ENmkb 237191 000 ENDocument20 pagesENmkb 237191 000 ENmohammadNo ratings yet
- Manual Bomba SumergibleDocument18 pagesManual Bomba SumergibleDavic LimachiNo ratings yet
- ATR4518R9 Antenna Triple Band PDFDocument2 pagesATR4518R9 Antenna Triple Band PDFMarcelo MontenegroNo ratings yet
- TM 3-4240-302-30-P-5 - AN - TSQ-73 - Power - Distr. - Unit - 1986Document72 pagesTM 3-4240-302-30-P-5 - AN - TSQ-73 - Power - Distr. - Unit - 1986Wurzel1946No ratings yet
- Automatic Hand Sanitizer Using IRDocument6 pagesAutomatic Hand Sanitizer Using IRsmartxdigital marketNo ratings yet
- LZQJ ManualDocument54 pagesLZQJ Manualthomaswangkoro100% (3)
- Acoustic Resonators White Paper 2015Document12 pagesAcoustic Resonators White Paper 2015chart328No ratings yet
- Power and Control Cable IEC 60502-1: Flame Retardant, Sunlight Resistant 90 °C / U /U 0,6/1 KVDocument3 pagesPower and Control Cable IEC 60502-1: Flame Retardant, Sunlight Resistant 90 °C / U /U 0,6/1 KVShashank SaxenaNo ratings yet
- 8085 PDFDocument74 pages8085 PDFGorla Ramu100% (1)
- Proakis ch05Document81 pagesProakis ch05OHNo ratings yet
- SFP512Document2 pagesSFP512ljubisaNo ratings yet