Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IFM Assignment #
IFM Assignment #
Uploaded by
Brian ThompsonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IFM Assignment #
IFM Assignment #
Uploaded by
Brian ThompsonCopyright:
Available Formats
NUST Business School
International Financial Management
Assignment # 03
Submitted To:
Mr. Muhammad Arshad
Submitted By:
Mohsin Sarfraz
EMBA-2K16
Date: 17 April, 2019.
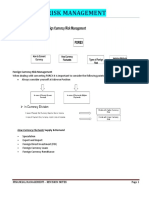
Exchange Rate:
An exchange rate is the value of one nation's currency versus the currency of
another nation or economic zone.
Direct Quote:
A quote, which is expressed as Rupees per unit of a foreign currency is referred to
as a Direct Quote.
Indirect Quote:
A quote, which is expressed as foreign currency per unit of Rupee or per Rs. 100 is
referred to as an Indirect Quote
Direct Quote = 1/ Indirect Quote
Cross Exchange Rate:
A cross rate is an exchange rate of two currencies expressed in a third different
currency, such as the exchange rate between the euro and the yuan expressed
in yen.
Currency Appreciation:
Currency appreciation is an increase in the value of country’s currency with respect
to one or more foreign currencies, typically in a floating exchange rate system in
which no official currency value is maintained.
Currency Depreciation:
Currency depreciation is the loss of value of a country's currency with respect to one
or more foreign reference currencies, typically in a floating exchange rate system in
which no official currency value is maintained.
Nominal Exchange Rate:
A nominal exchange rate is the rate at which you can exchange one currency for
another. Nominal rates are quoted in the paper and posted at the foreign exchange
kiosks.
Real Exchange Rate:
Real exchange rates provide an inflation adjusted measure of a currency’s
purchasing power. It is important to adjust for inflation because both inflation and
nominal exchange rate movements affect a firm’s cost position relative to
international rivals.
You might also like
- Chapter 15 International FinanceDocument31 pagesChapter 15 International FinanceSANANDITA DASGUPTA 1723585100% (1)
- X5 GT Wiring DiagramDocument2 pagesX5 GT Wiring DiagramBrian Thompson0% (1)
- IBF NotesDocument35 pagesIBF NotesAsad Shah100% (1)
- International FinanceDocument6 pagesInternational FinancevenigvNo ratings yet
- IFM Notes 1Document90 pagesIFM Notes 1Tarini MohantyNo ratings yet
- Topic 8-Macroeconomics OpenEconomyDocument47 pagesTopic 8-Macroeconomics OpenEconomyPradeep VarshneyNo ratings yet
- International Banking - 1 1.1 Exchange Rates and Forex Business 1.2 Basics of Forex Derivatives 1.3corresponding Banking and NRI AccountsDocument24 pagesInternational Banking - 1 1.1 Exchange Rates and Forex Business 1.2 Basics of Forex Derivatives 1.3corresponding Banking and NRI Accountsvijay_vmrNo ratings yet
- The Meaning of Foreign ExchangeDocument5 pagesThe Meaning of Foreign ExchangeRohini ManiNo ratings yet
- Chapte R: International Financial ManagementDocument24 pagesChapte R: International Financial ManagementNiket GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iii: Foreign Exchange Determination Systems &international InstitutionsDocument97 pagesUnit - Iii: Foreign Exchange Determination Systems &international InstitutionsShaziyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Foreign Exchange Market: By: Roshan Rudra Kumar Samanna Srinivas Sanath Kumar Sandeep KumarDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Foreign Exchange Market: By: Roshan Rudra Kumar Samanna Srinivas Sanath Kumar Sandeep KumarSandeep MadivalNo ratings yet
- The Foreign Exchange MarketDocument17 pagesThe Foreign Exchange MarketReemaNo ratings yet
- International Finance April 2023 CmV1 Wai 3Document7 pagesInternational Finance April 2023 CmV1 Wai 3Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- IFM Question Bank Solved FinalDocument34 pagesIFM Question Bank Solved FinalRavindra BabuNo ratings yet
- فوزيDocument11 pagesفوزيبدر الدين عبد العاليNo ratings yet
- Foriegn MarketsDocument38 pagesForiegn MarketsBasavarajNo ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange RateDocument3 pagesForeign Exchange RatesamchannuNo ratings yet
- The Foreign Exchange Market: Prepared For Class Discussion by Prof - SuryanarayananDocument28 pagesThe Foreign Exchange Market: Prepared For Class Discussion by Prof - Suryanarayananchhavi nahataNo ratings yet
- Echange Rate Mechanism: 1. Direct Quote 2. Indirect QuoteDocument4 pagesEchange Rate Mechanism: 1. Direct Quote 2. Indirect QuoteanjankumarNo ratings yet
- Effects of Foreign Currency Exchange RatesDocument14 pagesEffects of Foreign Currency Exchange RatesAddi Såïñt GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Arbitrade (I.F.M.) FinalDocument3 pagesArbitrade (I.F.M.) Final0012 Shah Md. Arafat [C]No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Foreign Exchange and Balance of Payments Foreign Exchange Market Meaning & Definition of Foreign ExchangeDocument26 pagesUnit 2 Foreign Exchange and Balance of Payments Foreign Exchange Market Meaning & Definition of Foreign ExchangeKaran C VNo ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange Market: Dr. Amit Kumar SinhaDocument67 pagesForeign Exchange Market: Dr. Amit Kumar SinhaAmit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Foreign Exchange Market, Exchange Rate DeterminationDocument7 pagesLesson 3 - Foreign Exchange Market, Exchange Rate DeterminationChocodie cocodieNo ratings yet
- 2.07 Capital Flows and The FX Market - AnswersDocument21 pages2.07 Capital Flows and The FX Market - Answersgustavo eichholzNo ratings yet
- International Business FinanceDocument39 pagesInternational Business FinanceArinaSofiyaNo ratings yet
- (TCQT) Slide - Group 1Document53 pages(TCQT) Slide - Group 1hoangminh01122019No ratings yet
- GROUP 3 Foreign Exchange Risk and ManagementDocument11 pagesGROUP 3 Foreign Exchange Risk and Managementsejal bohraNo ratings yet
- Multinational Financial Managment 07062022 015959pmDocument21 pagesMultinational Financial Managment 07062022 015959pmShahbaz QureshiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 PDFDocument29 pagesModule 2 PDFRAJASAHEB DUTTANo ratings yet
- Wa0005.Document5 pagesWa0005.Kinza IqbalNo ratings yet
- Assignment IFDocument2 pagesAssignment IFMohammad SaqibNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 FIDocument9 pagesChapter 7 FIsitina.at.lunarNo ratings yet
- Multinational Accounting: Foreign Currency Transactions and Financial InstrumentsDocument88 pagesMultinational Accounting: Foreign Currency Transactions and Financial InstrumentsVitaNo ratings yet
- International Finance ManagementDocument33 pagesInternational Finance ManagementAkshay SinghNo ratings yet
- Jakarta Interbank Spot Dollar Rate (JISDOR) As The Reference Rate: Is It Effective?Document12 pagesJakarta Interbank Spot Dollar Rate (JISDOR) As The Reference Rate: Is It Effective?predy hartantoNo ratings yet
- International FinanceDocument7 pagesInternational Financenemik007No ratings yet
- Kavita IbDocument19 pagesKavita IbKaranPatilNo ratings yet
- AskxdjDocument17 pagesAskxdjWaqas Asghar GorayaNo ratings yet
- Nominal and Real Effective Exchange RateDocument8 pagesNominal and Real Effective Exchange RateDeepanshi AhujaNo ratings yet
- Forex MarketDocument18 pagesForex MarketneetuNo ratings yet
- CH 7 - The Foreign Exchange MarketDocument29 pagesCH 7 - The Foreign Exchange Marketabdullahnadeem7744No ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange RateDocument29 pagesForeign Exchange RateakshaynnaikNo ratings yet
- 2000 CHP 10 FX MarketDocument32 pages2000 CHP 10 FX Marketoutkast32No ratings yet
- Module 3Document4 pagesModule 3Abhishek AbhiNo ratings yet
- International Financial Markets Part 2Document9 pagesInternational Financial Markets Part 2truthoverloveNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10-Foreign Exchange MarketDocument42 pagesLecture 10-Foreign Exchange MarketfarahNo ratings yet
- Forex Market in IndiaDocument24 pagesForex Market in IndiaHarshUpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Overview of Exchange Rate SystemsDocument21 pagesChapter 12 - Overview of Exchange Rate SystemsjagritiNo ratings yet
- Adv. Financial Acc 2 Chapter 11Document88 pagesAdv. Financial Acc 2 Chapter 11LegnaNo ratings yet
- IPPTChap 010Document33 pagesIPPTChap 010Roro FooNo ratings yet
- International Business: by Charles W.L. HillDocument33 pagesInternational Business: by Charles W.L. Hilllovelyday9876No ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange: UNIT-5Document7 pagesForeign Exchange: UNIT-5Pika PikachuNo ratings yet
- Ma. Eleanor T. FernandezDocument14 pagesMa. Eleanor T. FernandezDiane OlivasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 (Theories of Exchange Rates - PPP, IfE, IRP)Document6 pagesAssignment 2 (Theories of Exchange Rates - PPP, IfE, IRP)doraemonNo ratings yet
- FOREX & Interest RiskDocument11 pagesFOREX & Interest Riskpercy mapetereNo ratings yet
- MF0015 - International Financial Management - Set - 2Document10 pagesMF0015 - International Financial Management - Set - 2Shilpa PokharkarNo ratings yet
- IFM Question Bank SolvedDocument11 pagesIFM Question Bank SolvedRavindra Babu100% (1)
- Theories of Exchange RateDocument37 pagesTheories of Exchange Ratedranita@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- TAPES-R Guide October 2011 - To Be Updated PDFDocument10 pagesTAPES-R Guide October 2011 - To Be Updated PDFBrian ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Installation Instruction of 5-Phase Motor: Connection DiagramDocument4 pagesInstallation Instruction of 5-Phase Motor: Connection DiagramBrian ThompsonNo ratings yet
- UV Data SheetDocument15 pagesUV Data SheetBrian ThompsonNo ratings yet
- PH Type Stepping Motors: - $I Ec-If C .TionsDocument1 pagePH Type Stepping Motors: - $I Ec-If C .TionsBrian ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Na1-Pk5 Na1-5 e CataDocument10 pagesNa1-Pk5 Na1-5 e CataBrian ThompsonNo ratings yet
- SBS Instalment Plans at 0% Markup With No Processing Fee: Petrol Generators Petrol Generators Inverter TypeDocument2 pagesSBS Instalment Plans at 0% Markup With No Processing Fee: Petrol Generators Petrol Generators Inverter TypeBrian ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Assessment CreteriaDocument20 pagesAssessment CreteriaBrian ThompsonNo ratings yet
- SBS Instalment Plans at 0% Markup With No Processing Fee: Terms and ConditionsDocument2 pagesSBS Instalment Plans at 0% Markup With No Processing Fee: Terms and ConditionsBrian ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Gait Lab System: The System Must Included Following,: Sr. # Items QtyDocument4 pagesGait Lab System: The System Must Included Following,: Sr. # Items QtyBrian ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Conflict Management Group-EMBA !ST GroupworkDocument2 pagesConflict Management Group-EMBA !ST GroupworkBrian ThompsonNo ratings yet
- 3D1 For 13 PlanerDocument32 pages3D1 For 13 PlanerBrian ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Raheel Abbas MS76Document5 pagesRaheel Abbas MS76Brian ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Afirm ALAC Patient Measurement Form For TTP: Patient Name Male Female Adult ChildDocument2 pagesAfirm ALAC Patient Measurement Form For TTP: Patient Name Male Female Adult ChildBrian ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Summary of RDocument2 pagesSummary of RBrian ThompsonNo ratings yet
- ConstitutionDocument22 pagesConstitutionBrian ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Emg ProtocolDocument14 pagesEmg ProtocolBrian ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 For March 27 17Document2 pagesAssignment 1 For March 27 17Brian ThompsonNo ratings yet