Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 6: Statistical Inference
Chapter 6: Statistical Inference
Uploaded by
noOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 6: Statistical Inference
Chapter 6: Statistical Inference
Uploaded by
noCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 6: Statistical Inference
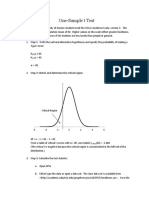
Inferences:
1. Confidence Interval: Point Estimator ± Margin of Error
2. Test of Hypothesis: Ho: guessing population value and use sample info to test it
Confidence Intervals:
Situation One: µ: Standard Deviation known alpha=size of error 1-alpha=Level of Confid.
𝜎
Formula: 𝑥 ± 𝑧𝛼 ∗ we can use CONFIDENCE.NORM(alpha, st. dev, n)
2 √𝑛
𝑠
Situation Two: µ: Standard deviation UNKNOWN! Formula: 𝑥 ± 𝑡𝛼 ∗ Excel: x-bar ± CONFIDENCE.T(alpha, s, n)
2 √𝑛
√𝑝(1−𝑝)
Situation Three: Proportions 𝑝 ± 𝑧𝛼 ∗
2 𝑛
Interpreting: In repeated sampling, 95% of the intervals will include the true µ. We are hoping our interval contains the actual µ.
Example 1: St. Dev known
N=40 3.2 ± z(.05/2) * .5/sqrt(40)
x-bar=3.2 3.2 ± {.15495 } ME For ME use CONFIDENCE.NORM(0.05.50.40)
st. dev=.5 CI: (3.045,3.355)
alpha=.05
Example 2: St. Dev Unknown
N=40 3.2 ± t.(.05/2) * .8/sqrt(40)
x-bar=3.2 CONFIDENCE.T(.05,.8,40)
s=.8 CI: (2.95,3.46)
alpha= .05
Example 3: Proportions
N=40 females are 25 out of 40 students so p-bar=25/40 alpha:.05
Therefore 0.625 ± 1.96 * sqrt(.625 * (1-.0625) / 40 = CI of (-0.15, .76)
Ho is true Ho is false
You might also like
- MidExam 6016201006 Muhammad Nahdi FebriansyahDocument9 pagesMidExam 6016201006 Muhammad Nahdi FebriansyahJoseGonzalezRomeroNo ratings yet
- UCCM2233 - Chp6.1 Estimation and Hypothesis Testing - Answer WbleDocument35 pagesUCCM2233 - Chp6.1 Estimation and Hypothesis Testing - Answer WbleVS ShirleyNo ratings yet
- Informative Speech OutlineDocument2 pagesInformative Speech Outlineno100% (1)
- Lecture 9Document12 pagesLecture 9maihonggiang004No ratings yet
- One-Sample T TestDocument4 pagesOne-Sample T Testjorge9000000No ratings yet
- Estimation and Confidence Intervals: Properties of Point EstimatesDocument14 pagesEstimation and Confidence Intervals: Properties of Point EstimatesdipanajnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7.1 - Estimation of ParametersDocument8 pagesLecture 7.1 - Estimation of ParametersJunior LafenaNo ratings yet
- Confidence IntervalsDocument6 pagesConfidence Intervalsandrew22No ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Statistical Inference by Dr. Javed IqbalDocument4 pagesLecture 5: Statistical Inference by Dr. Javed IqbalHamna AghaNo ratings yet
- Confidence Interval EstimationDocument62 pagesConfidence Interval EstimationVikrant LadNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document7 pagesWeek 2Indri Br SitumorangNo ratings yet
- Assignment02 - 60162020005 - Daud Wahyu Imani - Tugas Uji HipotesisDocument27 pagesAssignment02 - 60162020005 - Daud Wahyu Imani - Tugas Uji HipotesisDaud WahyuNo ratings yet
- Applied Statistics and Probability For Engineers Chapter - 8Document13 pagesApplied Statistics and Probability For Engineers Chapter - 8MustafaNo ratings yet
- : µ = 0 vs H: µ 6= 0. Previous work shows that σ = 2. A change in BMI of 1.5 is considered important to detect (if the true effect size is 1.5 or higherDocument5 pages: µ = 0 vs H: µ 6= 0. Previous work shows that σ = 2. A change in BMI of 1.5 is considered important to detect (if the true effect size is 1.5 or higherShreyas SatardekarNo ratings yet
- 260 ProjDocument3 pages260 ProjmoHAMMED HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 L1 L2Document7 pagesChapter 4 L1 L2SeMi NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Stats 2 NotesDocument17 pagesStats 2 Notesrachelmvaz99No ratings yet
- STAT G7 MODULE Confidence Intervals and Hypothesis TestingDocument23 pagesSTAT G7 MODULE Confidence Intervals and Hypothesis TestingR Jay Pangilinan HernoNo ratings yet
- Statistical TestsDocument24 pagesStatistical TestsSumit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Jfuture 202005025Document2 pagesJfuture 202005025devi kumarNo ratings yet
- Analisis Statistika: Materi 5 Inferensia Dari Contoh Besar (Inference From Large Samples)Document19 pagesAnalisis Statistika: Materi 5 Inferensia Dari Contoh Besar (Inference From Large Samples)Ma'ruf NurwantaraNo ratings yet
- HW12 SolDocument9 pagesHW12 SolLoy NasNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Statprob Q4Document15 pagesWeek 2 Statprob Q4Chris JonNo ratings yet
- Week 11 LectureDocument17 pagesWeek 11 LectureOlana SufiyanNo ratings yet
- Lecture21 HypothesisTest1Document53 pagesLecture21 HypothesisTest1Sonam AlviNo ratings yet
- Post-Exam 2 Practice Questions - Solutions 18.05, Spring 2014 Confidence IntervalsDocument7 pagesPost-Exam 2 Practice Questions - Solutions 18.05, Spring 2014 Confidence IntervalsIslamSharafNo ratings yet
- Point Estimation and Interval EstimationDocument4 pagesPoint Estimation and Interval EstimationAlexander EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Statistics ReviewerDocument5 pagesStatistics ReviewerMav CastilloNo ratings yet
- Statistics Part 3Document4 pagesStatistics Part 3Emilia CassidyNo ratings yet
- Estimating Population Values PPT at BEC DOMSDocument50 pagesEstimating Population Values PPT at BEC DOMSBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)No ratings yet
- Goal:: Estimation of ParametersDocument7 pagesGoal:: Estimation of ParametersJasper GabrielNo ratings yet
- Lc07 SL Estimation - PPT - 0Document48 pagesLc07 SL Estimation - PPT - 0Deni ChanNo ratings yet
- 00 Lab NotesDocument8 pages00 Lab Notesreddykavya2111No ratings yet
- Lectuer 21-ConfidenceIntervalDocument41 pagesLectuer 21-ConfidenceIntervalArslan ArshadNo ratings yet
- Discussion1 SolutionDocument5 pagesDiscussion1 Solutionana_paciosNo ratings yet
- B StatisticsDocument72 pagesB StatisticsAsima NoreenNo ratings yet
- Statistical Data Treatment: - Part 1 (Manual Calculations)Document51 pagesStatistical Data Treatment: - Part 1 (Manual Calculations)Cess MontemayorNo ratings yet
- IISER BiostatDocument87 pagesIISER BiostatPrithibi Bodle GacheNo ratings yet
- Chebyshev's Rule: Definitions: Sas Puts Out 2-Sided P-Values Rule/definitions ApplicationsDocument6 pagesChebyshev's Rule: Definitions: Sas Puts Out 2-Sided P-Values Rule/definitions ApplicationspetecadmusNo ratings yet
- 8 Interval EstimationDocument11 pages8 Interval EstimationMugahed Abdo Al-gahdariNo ratings yet
- Handout 4 - Statistical IntervalDocument13 pagesHandout 4 - Statistical Intervalabrilapollo.siaNo ratings yet
- Seventh LectureDocument31 pagesSeventh LectureSmith AlexNo ratings yet
- Confidence Intervals For A Single Sample: H.W. Kayondo C 1Document16 pagesConfidence Intervals For A Single Sample: H.W. Kayondo C 1shjahsjanshaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument23 pagesHypothesis TestingNidhiNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics With R For Engineers and Scientists 1St Edition Michael Akritas Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesProbability and Statistics With R For Engineers and Scientists 1St Edition Michael Akritas Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFEarlCollinsmapcs100% (11)
- Chapter 2 Approximation of Error 1 PDFDocument55 pagesChapter 2 Approximation of Error 1 PDFJomari Tobes SatorreNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - Estimation & Hypothesis One SampleDocument139 pagesCH 4 - Estimation & Hypothesis One SampleDrake AdamNo ratings yet
- 3 Round Off Error and ApproximationDocument37 pages3 Round Off Error and ApproximationFerry CaballasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document50 pagesLecture 7tomshave28No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 ReviewDocument6 pagesChapter 8 Reviewapi-3829767No ratings yet
- Point and Interval EstimationDocument10 pagesPoint and Interval EstimationJiten BendleNo ratings yet
- Braun Bootstrap2012 PDFDocument63 pagesBraun Bootstrap2012 PDFJoe OgleNo ratings yet
- Statistics Chp8-2Document35 pagesStatistics Chp8-2Jennifer LimerthaNo ratings yet
- STATQ3LAS10Document6 pagesSTATQ3LAS10respondekylamaeNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Chick PointDocument14 pagesWeek 6 Chick PointMohammad MazenNo ratings yet
- Stat Handout 2Document11 pagesStat Handout 2cmacblue42No ratings yet
- 1 Point Estimation: Parameter Estimation Kaustav Banerjee Decision Sciences Area, IIM LucknowDocument4 pages1 Point Estimation: Parameter Estimation Kaustav Banerjee Decision Sciences Area, IIM LucknowRajiv KumarNo ratings yet
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Probability and Statistics, Revised EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Probability and Statistics, Revised EditionNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Organizational ChartDocument1 pageOrganizational ChartnoNo ratings yet
- Regression Step by StepDocument1 pageRegression Step by StepnoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Economics NotesDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Economics NotesnoNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics Chapter 5Document2 pagesBusiness Analytics Chapter 5noNo ratings yet
- Organizational ChartDocument1 pageOrganizational ChartnoNo ratings yet
- Organizational Chart: CEO & Owner President Staff AccountantDocument1 pageOrganizational Chart: CEO & Owner President Staff AccountantnoNo ratings yet