Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Membangkitkan Signal: All TT - SF
Membangkitkan Signal: All TT - SF
Uploaded by
Isa Mahfudi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
100 views8 pagesThe document contains 10 experiments on generating and analyzing different types of signals in MATLAB. It summarizes the coding used to generate signals like sine waves, dirac delta functions, rectangular functions, and more. It also tests functions for analog to digital conversion and audio aliasing.
Original Description:
.
Original Title
Iman
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document contains 10 experiments on generating and analyzing different types of signals in MATLAB. It summarizes the coding used to generate signals like sine waves, dirac delta functions, rectangular functions, and more. It also tests functions for analog to digital conversion and audio aliasing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
100 views8 pagesMembangkitkan Signal: All TT - SF
Membangkitkan Signal: All TT - SF
Uploaded by
Isa MahfudiThe document contains 10 experiments on generating and analyzing different types of signals in MATLAB. It summarizes the coding used to generate signals like sine waves, dirac delta functions, rectangular functions, and more. It also tests functions for analog to digital conversion and audio aliasing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
MEMBANGKITKAN SIGNAL
Nama : Iman Saptiadi
Nosis : 20170239-E
Kelas : T.Telkommil
Codingan Matlab Bentuk sinyal
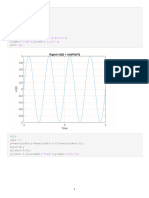
Percobaan 1 close all
clear tt_sf
samples = 10000; %jumlah sample
samp_freq = 20 %frekuensi sample
nyq = samp_freq/2 %Batas frekunsi
Nyquist sample
samp_time = samples/samp_freq;
%waktu sampling
freq = 4 %frekuensi gelombang
sinus
t = [0:samples-1]; %jumlah waktu
sample
tt = t/10000; %Setiap titik
adalah 0.1 mdetik,di plot menjadi
1 detik
size(tt);
sint = sin(tt);
radfreq = freq*(2*pi)/1;
sint2 = sin(radfreq*tt);
%Frekuensi radial adalah radfreq,
sedangkan Hz adalah radfreq/
(2*pi)
plot(tt, sint2, 'k')
title('radfreq plot')
pause(1)
if nyq - freq < 0 alias = nyq -
abs(nyq-freq), end
cnt = 1;
for ii = 1:samp_time:samples
tt_sf(cnt) = ii/samples;
cnt=cnt+1;
Percobaan 2 end
if ii < samples tt_sf(cnt) =
samples/10000; end
sint3 = sin(radfreq*tt_sf);
hold on
tt_sf_sze = size(tt_sf,2)
plot(tt_sf, sint3, 'r')
figure, plot(tt_sf, sint3, 'r.'),
hold on,plot(tt, sint2)
'k'
% Dirac
N = 10; %number of samples
n = -N/2:N/2; %vector
d = [zeros(1,N/2) 1
zeros(1,N/2)];
figure; %display
stem(n,d);
xlabel('n');
ylabel('/delta(n)');
title('Dirac function');
axis([-N/2 N/2 0 1.1]);
Percobaan 3 %Rect function
M = 3;
N = 10; %number of samples
n = -N/2:N/2; %vector
Rect = [zeros(1,N/2-M)
ones(1,2*M+1) zeros(1,N/2-M)];
%logic for rect
figure; %display
stem(n,Rect);
xlabel('n');
ylabel('rect');
title('Rect function');
axis([-N/2 N/2 0 1.1]);
Percobaan 4 %sign function
N = 10; %Number of samples
n = -N/2:N/2; %vector
u = [zeros(1,N/2) 1 ones(1,N/2)];
%logic
sign function
x = 2.*u-1;
figure; %display
stem(n,x);
xlabel('n');
ylabel('x(n)');
title('Sign function');
axis([-N/2 N/2 -1 1]);
Percobaan 5 %Sine function test
[x,t]=sin_NU(1000,10,0.5);
figure(7);
plot(t,x);
xlabel('time');
ylabel('signal');
title('sin_NU function test');
Sin_NU function[x,t] = sin_NU(fs, f0, T)
t = 0:1/fs:T;
x = sin(2*pi*f0*t);
end
Percobaan 6 %Sine function
L = 50;
n = [-L:L];
Ts = 0.1;
x = zeros(1,length(n));
x(n~=0) = sin(pi*n(n~=0)*Ts)./
(pi*n(n~=0)*Ts);
x(n==0) = 1;
figure;
stem(n,x);
xlabel('n');
ylabel('sin');
title('Sinc function');
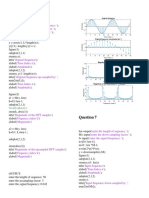
Percobaan 7 %Sine function
L = 20;
n = 0:L-1;
f0 = 100;
fs = 1000;
x0 = 1;
x = x0*sin(2*pi*f0/fs*n);
figure;
stem(n,x);
xlabel('n');
ylabel('sin');
title('sine');
axis([-1 L -1.1 1.1]);
Percobaan 8 % Unit step function
N = 10;
n = -N/2:N/2;
u = [zeros(1,N/2) 1 ones(1,N/2)];
step
figure;
stem(n,u);
xlabel('n');
ylabel('u(n)');
title('Unit step function');
axis([-N/2 N/2 0 1.1]);
Percobaan 9 T = 2;
f0 = 1000;
fs1 = 20000;
fs2 = 1500;
[x1, t1] = sin_NU(fs1, f0,T);
[x2, t2] = sin_NU(fs2, f0,T);
figure;
plot(t1,x1,t2,x2,'LineWidth',3.0),
axis([0, 0.005, -1.1, 1.1])
legend('High Frequency','Low frequency')
xlabel('Time')
ylabel('signals')
title('Audio aliasing');
%%%
soundsc(x1,fs1)
%%%
soundsc(x2,fs2)
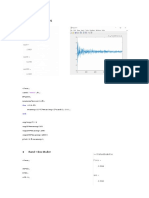
Percobaan 10 % ADC_NU function test
R = 10;
B = 3;
x = -5:15;
y = adc_NU(x,R,B);
t = 0:length(x)-1;
figure(11)
plot(t,x,t,y)
plot(t,x,'g-*','Linewidth',2.2)
hold on
stem(t,y,'filled','Linewidth',2.2)
hold off
title('Ramp function unipolar
quantization')
xlabel('Time in sec')
ylabel('signal magnitude in volts')
axis([-0.1,20.1,-5.1,15.1])
adc_NU function y = adc_NU(x, R, B)
level = [0:R/(2^B):R-R/(2^B)];
temp = [-inf,(level(2:end)-R/
(2^(B+1))),inf];
y = zeros(1,length(x));
for i = 1:length(level)
y = y + (x >= temp(i)).*(x <
temp(i+1)).*level(i);
end
You might also like
- Mix Design Lab ReportDocument11 pagesMix Design Lab Reportnagasaba100% (3)
- VTU DSP Lab Manual 5th Sem E C Matlab Programs and CCS Studio ProgramsDocument63 pagesVTU DSP Lab Manual 5th Sem E C Matlab Programs and CCS Studio ProgramsSona Uttappa50% (2)
- Lab ManualDocument49 pagesLab ManualDeepika PalrajNo ratings yet
- P1 - 16 and Quantization... DCDocument8 pagesP1 - 16 and Quantization... DCsana aminNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Chinese Codes Safety Concept, Material Resistance, Load CombinationsDocument66 pagesPresentation of Chinese Codes Safety Concept, Material Resistance, Load CombinationsdaeealiNo ratings yet
- Stahlton Prospekt NZS3101Document24 pagesStahlton Prospekt NZS3101Anonymous dK9Qi2XjNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 Zani AkbariDocument7 pagesTugas 1 Zani AkbariIsa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- Open Ended Exp DSPDocument55 pagesOpen Ended Exp DSPTilak shastriNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledSanjay ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- DSP Lab ManualDocument51 pagesDSP Lab ManualShahin4220No ratings yet
- CT 303 Digital Communications Lab 9: Heer Gohil 201901135Document25 pagesCT 303 Digital Communications Lab 9: Heer Gohil 201901135H GNo ratings yet
- FitsumDocument6 pagesFitsumFetsum LakewNo ratings yet
- CompreDocument3 pagesCompreAbhishek GangwarNo ratings yet
- Matlab Assignment 22bec038Document20 pagesMatlab Assignment 22bec038Diya ShahNo ratings yet
- 15LEB369Document7 pages15LEB369s.r.No ratings yet
- Part-A Experiments Using Matlab: DSP Lab ManualDocument40 pagesPart-A Experiments Using Matlab: DSP Lab ManualSharth KumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 2: Communication Signals: Generation and InterpretationDocument8 pagesExperiment # 2: Communication Signals: Generation and InterpretationMaha AliNo ratings yet
- Digitalcom Lab Manual NewDocument26 pagesDigitalcom Lab Manual NewAkanksha DixitNo ratings yet
- FO7C70BFCC81Document15 pagesFO7C70BFCC81fundaliNo ratings yet
- DSP Using MatlabDocument10 pagesDSP Using MatlabYounus AliNo ratings yet
- Constanta Depi MatlabDocument7 pagesConstanta Depi MatlabAdrian HurmuzNo ratings yet
- Thi NghiemDocument22 pagesThi NghiemshiNo ratings yet
- SCE3101 Lab 2 - Code PDFDocument6 pagesSCE3101 Lab 2 - Code PDFCharlene ChetcutiNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document7 pagesLab 4OSAMA HARAMINE SINAN 1802015No ratings yet
- Experiment 1 1. (A) Generation of (I) Delta (T) (Ii) U (T) (Iii) R (T) (Iv) Parabolic Function (V) Signum Function (Vi) Sinc FunctionDocument31 pagesExperiment 1 1. (A) Generation of (I) Delta (T) (Ii) U (T) (Iii) R (T) (Iv) Parabolic Function (V) Signum Function (Vi) Sinc FunctionAnjali AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Assignment DSP 1Document17 pagesAssignment DSP 1chetan sharmaNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document9 pagesExp 2Mohammad HasnainNo ratings yet
- Working With Wavelets: Task 1: Shannon WaveletDocument13 pagesWorking With Wavelets: Task 1: Shannon WaveletAvni RajpalNo ratings yet
- DSP Lab ManualDocument20 pagesDSP Lab ManualRavi RavikiranNo ratings yet
- AkanshaKhandelwalMCA (SE) 2ndsemDocument35 pagesAkanshaKhandelwalMCA (SE) 2ndsemAkansha KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- DSP Lab Manual 19 Nov 20111Document35 pagesDSP Lab Manual 19 Nov 20111TapasRoutNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document20 pagesExp 2Rohit JainNo ratings yet
- MPMCDocument12 pagesMPMCBadal kumarNo ratings yet
- DSP Lab ReportDocument23 pagesDSP Lab Reportopensource liveNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocument55 pagesDigital Signal ProcessingArdrick BoscoNo ratings yet
- DSP Record EndDocument91 pagesDSP Record Endpapa pepaamNo ratings yet
- Matlab Code For Basic DSP Signals MATLAB PROGRAM TO DISPLAY THE PROPERTIES OF DISCRETE FOURIER TRANSFORM (DFT)Document16 pagesMatlab Code For Basic DSP Signals MATLAB PROGRAM TO DISPLAY THE PROPERTIES OF DISCRETE FOURIER TRANSFORM (DFT)Sabithkk2007No ratings yet
- DSP RecordDocument85 pagesDSP Recordjas wanthNo ratings yet
- Lab ExerciseDocument4 pagesLab Exercise20BEC098 PANKAJNo ratings yet
- % File NVD4B - Sim1.m: FunctionDocument9 pages% File NVD4B - Sim1.m: FunctionNguyễn Vũ Minh ViệtNo ratings yet
- BSL Lab ManualDocument67 pagesBSL Lab ManualKranthi Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Excercise 1: %generation of Unit Impulse: %generation of Ramp SignalDocument3 pagesExcercise 1: %generation of Unit Impulse: %generation of Ramp Signalmsd91No ratings yet
- FS 2cycles SawtoothDocument2 pagesFS 2cycles SawtoothSHAHZEB AFRIDINo ratings yet
- Experiment No. - 1: Aim: Software Used: MATLAB TheoryDocument18 pagesExperiment No. - 1: Aim: Software Used: MATLAB TheoryKumar RajeshwarNo ratings yet
- Mece218-Lab Study 1 PDFDocument1 pageMece218-Lab Study 1 PDFNeslihan YılmazNo ratings yet
- HW 9Document3 pagesHW 9api-516646274No ratings yet
- KTCK Câu 1Document11 pagesKTCK Câu 1HOANG PHI HUNG NGUYENNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document24 pagesLab 1Sai Prasad ReddyNo ratings yet
- DSP 72Document42 pagesDSP 72SakethNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Lab: Practical RecordDocument30 pagesDigital Signal Processing Lab: Practical RecordAnveshGopalamNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocument23 pagesDigital Signal ProcessingSanjay PalNo ratings yet
- DSP Final LabDocument30 pagesDSP Final Labdesi boyNo ratings yet
- Lab DSPDocument29 pagesLab DSPaftab_harisNo ratings yet
- DSP LAB 1to 6Document12 pagesDSP LAB 1to 6daddyplays25No ratings yet
- DSP Lab ExamDocument7 pagesDSP Lab ExamUzair AhmedNo ratings yet
- Principles of Communication Engineering PracticalDocument30 pagesPrinciples of Communication Engineering PracticalTechniworkNo ratings yet
- Lab # 5 Discrete Time Fourier Transform: ObjectiveDocument14 pagesLab # 5 Discrete Time Fourier Transform: ObjectiveUmar KhanNo ratings yet
- Try 1Document1 pageTry 1Shreyansh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- DSP PracticalDocument25 pagesDSP PracticalDurgesh DhoreNo ratings yet
- Labsheet1 EAC22065Document5 pagesLabsheet1 EAC22065ANANTHAKRISHNAN MNo ratings yet
- SCilab LAb ReportDocument26 pagesSCilab LAb ReportVilayat AliNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Tugas 1 Zani AkbariDocument7 pagesTugas 1 Zani AkbariIsa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- 8x8 LED Matrix MAX7219 Tutorial With Scrolling Text & Android Control Via Bluetooth - HowToMechatronicsDocument43 pages8x8 LED Matrix MAX7219 Tutorial With Scrolling Text & Android Control Via Bluetooth - HowToMechatronicsIsa Mahfudi100% (1)
- Click: International Journal of Smart Grid and Clean EnergyDocument4 pagesClick: International Journal of Smart Grid and Clean EnergyIsa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- Dynamic VAWT Darrieus by Changing Angle of Attack To Reach Maximum EfficiencyDocument1 pageDynamic VAWT Darrieus by Changing Angle of Attack To Reach Maximum EfficiencyIsa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- A Matlab Tour of Morphological Filtering: EE465: Introduction To Digital Image Processing 1Document20 pagesA Matlab Tour of Morphological Filtering: EE465: Introduction To Digital Image Processing 1Isa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- Alphabet and Number Recognition of Indonesian Sign Language Using SIFT AlgorithmDocument7 pagesAlphabet and Number Recognition of Indonesian Sign Language Using SIFT AlgorithmIsa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- Research Logbook: Master of Applied Science in Electrical Engineering (Magister Terapan Teknik Elektro)Document4 pagesResearch Logbook: Master of Applied Science in Electrical Engineering (Magister Terapan Teknik Elektro)Isa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- Gammu Phone DatabaseDocument3 pagesGammu Phone DatabaseIsa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- Implementation Morphology Methods For Sign Language Recognition On Increasing The Extraction Process CharacteristicsDocument1 pageImplementation Morphology Methods For Sign Language Recognition On Increasing The Extraction Process CharacteristicsIsa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- Single Line Diagram GI Cilegon Baru 150kVDocument1 pageSingle Line Diagram GI Cilegon Baru 150kVIsa Mahfudi100% (1)
- GSM Uplink and Downlink Frequency - EHowDocument3 pagesGSM Uplink and Downlink Frequency - EHowIsa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- GSM (Global System For Mobile Communications) Is An Open, Digital Cellular Technology Used For Transmitting Mobile Voice and DDocument7 pagesGSM (Global System For Mobile Communications) Is An Open, Digital Cellular Technology Used For Transmitting Mobile Voice and DIsa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- Classified Ads - Job VacancyDocument12 pagesClassified Ads - Job VacancyIsa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- MSK Modulation - GMSK Modulation - GMSK Modulator and DemodulatorDocument6 pagesMSK Modulation - GMSK Modulation - GMSK Modulator and DemodulatorIsa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- Mobile Internet Applications RTD 704 /7Document26 pagesMobile Internet Applications RTD 704 /7Isa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- 20 FREE SIP Softphones VoIP InsiderDocument31 pages20 FREE SIP Softphones VoIP InsiderIsa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- Konfigurasi Network Element - Switching PT Telkom Divre V Jawa TimurDocument34 pagesKonfigurasi Network Element - Switching PT Telkom Divre V Jawa TimurIsa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- Discribe About Laboratorium TelekomunicationDocument1 pageDiscribe About Laboratorium TelekomunicationIsa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- Applicant LetterDocument25 pagesApplicant LetterIsa MahfudiNo ratings yet
- Practice of AffineDocument5 pagesPractice of AffineJesy servbNo ratings yet
- Autonomous Reinforcement Learning-BioloidDocument7 pagesAutonomous Reinforcement Learning-Bioloiddarkot1234No ratings yet
- Catalog PneuSeals PDE3351-EN PDFDocument116 pagesCatalog PneuSeals PDE3351-EN PDFEmerson OliveiraNo ratings yet
- 2 3 1 Overview of Geotechnical Design of Bridges and Provisions of UK National Annex For EN1997 1Document15 pages2 3 1 Overview of Geotechnical Design of Bridges and Provisions of UK National Annex For EN1997 1Martha LacerdaNo ratings yet
- Steps in ABG Analysis Using The Tic-Tac-Toe MethodDocument4 pagesSteps in ABG Analysis Using The Tic-Tac-Toe MethodSeanmarie CabralesNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis of A Microgrid Using ETAP: April 2015Document6 pagesPower System Analysis of A Microgrid Using ETAP: April 2015Adoos KhalidNo ratings yet
- Shear Capacity of Circular Sections OnlineDocument63 pagesShear Capacity of Circular Sections Onlinenitinchavan30No ratings yet
- NE203 Assignment3 V1Document2 pagesNE203 Assignment3 V1Sumit KumarNo ratings yet
- Vajiram CSP20 CA Test 1Document71 pagesVajiram CSP20 CA Test 1annushaNo ratings yet
- Appendix A - Nonmandatory Acceptable Astm EditionsDocument10 pagesAppendix A - Nonmandatory Acceptable Astm EditionsWeniton OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Floating Production Storage and Offloading VesselDocument6 pagesFloating Production Storage and Offloading VesselartletNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibrations Experiment Leaf PDFDocument9 pagesMechanical Vibrations Experiment Leaf PDFfariskolej4946No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer - N 2018Document76 pagesHeat Transfer - N 2018suryadtp suryadtpNo ratings yet
- Plane Electromagnetic Waves: Dr. Rakhesh Singh Kshetrimayum Dr. Rakhesh Singh KshetrimayumDocument55 pagesPlane Electromagnetic Waves: Dr. Rakhesh Singh Kshetrimayum Dr. Rakhesh Singh KshetrimayumRitesh BadhaiNo ratings yet
- Separator All Oil and Gas SpreadsheetDocument22 pagesSeparator All Oil and Gas SpreadsheetSatria 'igin' Girindra Nugraha100% (1)
- ENGR 313: Introduction To Materials Science and EngineeringDocument7 pagesENGR 313: Introduction To Materials Science and EngineeringTracey HowardNo ratings yet
- Resonance and Induction Tutorial: Jack DeruiterDocument19 pagesResonance and Induction Tutorial: Jack DeruiterDanish AhmedNo ratings yet
- Subscription For Journals For The Year 2020 Sub. PeriodDocument10 pagesSubscription For Journals For The Year 2020 Sub. PeriodB VAMSI KRISHNANo ratings yet
- Study Guide: Segments, Angles, and InequalitiesDocument4 pagesStudy Guide: Segments, Angles, and InequalitiesCaseyRodenNo ratings yet
- hw2 NewDocument9 pageshw2 Newkaliman2010No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument173 pagesElectromagnetic WavesatiqdhepNo ratings yet
- 2017 Yuan Hierarchical Motion Planning For Multi-Steering Tractor-Trailer Mobile Robots With On-Axle Hitching PDFDocument11 pages2017 Yuan Hierarchical Motion Planning For Multi-Steering Tractor-Trailer Mobile Robots With On-Axle Hitching PDFSubhajeet RathNo ratings yet
- Performance Measurements On A Thermoacoustic Refrigerator Driven at High AmplitudesDocument7 pagesPerformance Measurements On A Thermoacoustic Refrigerator Driven at High AmplitudessaekNo ratings yet
- SFD and BMD Made EasyDocument16 pagesSFD and BMD Made EasyHimalFernandoNo ratings yet
- Pauli Matrices: 1 Algebraic PropertiesDocument6 pagesPauli Matrices: 1 Algebraic PropertiesAnthony RogersNo ratings yet
- Civil Soe and Syllabus 2014-15 For Old Course PDFDocument104 pagesCivil Soe and Syllabus 2014-15 For Old Course PDFYogesh KherdeNo ratings yet
- MCQs With SolutionDocument4 pagesMCQs With SolutionPinalNo ratings yet