Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Integumentary System: Exercise
The Integumentary System: Exercise
Uploaded by
VaraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Integumentary System: Exercise
The Integumentary System: Exercise
Uploaded by
VaraCopyright:
Available Formats
ighapmLre07pg143_146 5/12/04 12:54 PM Page 143 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts:
NAME ___________________________________ LAB TIME/DATE _______________________
REVIEW SHEET
exercise
The Integumentary
System
Basic Structure of the Skin
7
1. Complete the following statements by writing the appropriate word or phrase on the correspondingly numbered blank:
The two basic tissues of which the skin is composed are dense irregular 1. stratified squamous epithelium
connective tissue, which makes up the dermis, and 1 , which forms the epi-
dermis. The tough water-repellent protein found in the epidermal cells is called 2. keratin
2 . The pigments melanin and 3 contribute to skin color. A localized
concentration of melanin is referred to as a 4 . 3. carotene
4. freckle
2. Four protective functions of the skin are Prevents dessication, protects against thermal damage, prevents bacterial invasion, and
protects against UV radiation. .
3. Using the key choices, choose all responses that apply to the following descriptions.
Key: a. stratum basale d. stratum lucidum g. reticular layer
b. stratum corneum e. stratum spinosum h. epidermis as a whole
c. stratum granulosum f. papillary layer i. dermis as a whole
d; stratum lucidum 1. translucent cells in thick skin containing keratin fibrils
b & d; strata corneum and lucidum 2. dead cells
f; papillary layer 3. dermis layer responsible for fingerprints
i; dermis (or f, g) 4. vascular region
h; epidermis 5. major skin area that produces derivatives (nails and hair)
a; stratum basale 6. epidermal region exhibiting the most rapid cell division
b; stratum corneum 7. scalelike dead cells, full of keratin, that constantly slough off
e; stratum spinosum 8. mitotic cells filled with intermediate filaments
i; dermis (or g) 9. has abundant elastic and collagenic fibers
a; stratum basale 10. location of melanocytes and Merkel cells
e; stratum spinosum 11. area where weblike prekeratin filaments first appear
f; papillary layer 12. region of areolar connective tissue
Review Sheet 7 143
ighapmLre07pg143_146 5/12/04 12:54 PM Page 144 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts:
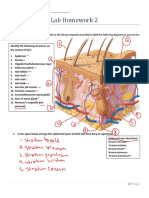
4. Label the skin structures and areas indicated in the accompanying diagram of thin skin. Then, complete the statements that
follow.
Hair shaft
Stratum corneum
Stratum granulosum
Stratum spinosum
Epidermis
Stratum basale
(layers)
Dermal papillae
Hair root
Sebaceous gland
Dermis Hair follicle
Arrector pili muscle
Reticular layer
Sweat gland
Blood vessel
Subcutaneous
tissue or
Hair bulb
hypodermis Nerve fiber
Adipose cells
Pacinian corpuscle
(deep pressure receptor)
a. Laminated (or lamellated) granules extruded from the keratinocytes prevent water loss by diffusion through
the epidermis.
b. Fibers in the dermis are produced by fibroblasts .
c. Glands that respond to rising androgen levels are the sebaceous (and apocrine sweat) glands.
d. Phagocytic cells that occupy the epidermis are called Langerhans’ cells .
e. A unique touch receptor formed from a stratum basale cell and a nerve fiber is a Merkel disc .
f. What layer is present in thick skin but not in thin skin? Stratum lucidum
g. What cell-to-cell structures hold the cells of the stratum spinosum tightly together? Desmosomes
5. What substance is manufactured in the skin (but is not a secretion) to play a role elsewhere in the body?
Vitamin D
144 Review Sheet 7
ighapmLre07pg143_146 5/12/04 12:54 PM Page 145 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts:
6. List the sensory receptors found in the dermis of the skin. Pain, pressure, touch, heat, and cold.
7. A nurse tells a doctor that a patient is cyanotic. Define cyanosis. A blue cast to the skin.
What does its presence imply? Inadequate oxygenation of the blood.
8. What is the mechanism of a suntan? When exposed to UV radiation, the melanocytes produce more protective melanin and the skin
becomes more brown in color.
9. What is a bedsore (decubitus ulcer) ? Localized area of tissue necrosis and death.
Why does it occur? Pressure areas (points of increased pressure over bony areas) restrict the blood supply to the area.
10. Some injections hurt more than others. On the basis of what you have learned about skin structure, can you determine why
this is so? It depends on the relative number of pain receptors stimulated.
Appendages of the Skin
11. Using key choices, respond to the following descriptions.
Key: a. arrector pili d. hair follicle g. sweat gland—apocrine
b. cutaneous receptors e. nail h. sweat gland—eccrine
c. hair f. sebaceous glands
f; sebaceous glands 1. produces an accumulation of oily material that is known as a blackhead
a; arrector pili 2. tiny muscles, attached to hair follicles, that pull the hair upright during fright or
cold
h; sweat gland—eccrine 3. perspiration glands with a role in temperature control
d; hair follicle 4. sheath formed of both epithelial and connective tissues
g; sweat gland—apocrine 5. less numerous type of perspiration-producing gland; found mainly in the pubic
and axillary regions
f; sebaceous glands 6. found everywhere on body except palms of hands and soles of feet
c, e; hair, nail 7. primarily dead/keratinized cells
b; cutaneous receptors 8. specialized nerve endings that respond to temperature, touch, etc
f; sebaceous glands 9. its secretion is a lubricant for hair and skin
e; nail 10. “sports” a lunula and a cuticle
Review Sheet 7 145
ighapmLre07pg143_146 5/12/04 12:54 PM Page 146 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts:
12. Describe two integumentary system mechanisms that help in regulating body temperature. (1) When capillary blood flow to
the skin is enhanced (by nervous system controls), heat radiates from the skin surface; restriction of blood flow conserves body heat. (2)
Activity of sweat glands, i.e., when perspiration evaporates from the skin surface, heat is lost.
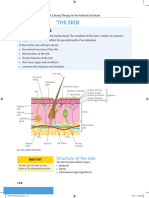
13. Several structures or skin regions are listed below. Identify each by matching its letter with the appropriate area on the figure.
a. Adipose cells
f
b. Dermis
e
c. Epidermis
b
d. Hair follicle
e. Hair shaft
d
f. Sloughing stratum corneum cells a
Plotting the Distribution of Sweat Glands
14. With what substance in the bond paper does the iodine painted on the skin react? The starch
15. Based on class data, which skin area—the forearm or palm of hand—has more sweat glands? Palm
Was this an expected result? Yes Explain. For most people, hands sweat more than the forearm.
Which other body areas would, if tested, prove to have a high density of sweat glands? Face, axillae
16. What organ system controls the activity of the eccrine sweat glands? Nervous system (sympathetic division)
Dermography: Fingerprinting
17. Why can fingerprints be used to identify individuals?
Everyone’s fingerprints are genetically distinct.
18. Name the three common fingerprint patterns.
loops , arches , and whorls
146 Review Sheet 7
You might also like
- Integumentary System Study Guide AnswersDocument4 pagesIntegumentary System Study Guide Answersapi-33050097583% (6)
- Lab 8 - Dichotomous KeyDocument5 pagesLab 8 - Dichotomous KeyCzarine Kay Nopre PamaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Web QuestDocument5 pagesMuscular System Web Questaidibwahab0% (1)
- The Integumentary SystemDocument33 pagesThe Integumentary SystemMica BernardoNo ratings yet
- Radiacid 0208Document7 pagesRadiacid 0208Максим ХилоNo ratings yet
- History of Home Economics in The CaribbeanDocument33 pagesHistory of Home Economics in The Caribbeanshemina armorer100% (1)
- Autobiography Rubric: Category 4 3 2 1Document1 pageAutobiography Rubric: Category 4 3 2 1CarminaCarillo100% (1)
- 03 Builder Teachers ManualDocument33 pages03 Builder Teachers Manualapi-262368157100% (1)
- Week 6 Work Sheet 14Document3 pagesWeek 6 Work Sheet 14Jennifer EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Medical TerminologyDocument14 pagesMedical TerminologyCharmy UbiñaNo ratings yet
- Disorder/Condition/Disease Pathophysiology Clinical Manifestations Assessment and Diagnostic StudiesDocument9 pagesDisorder/Condition/Disease Pathophysiology Clinical Manifestations Assessment and Diagnostic StudiesKasey C. PintoNo ratings yet
- Axial Skeleton SkullDocument36 pagesAxial Skeleton SkulltiiandiNo ratings yet
- You Are What You AbsorbDocument17 pagesYou Are What You AbsorbaligaramNo ratings yet
- Human Body PowerPointDocument62 pagesHuman Body PowerPointusmcdoc113597No ratings yet
- Lymphatic System: Presented byDocument55 pagesLymphatic System: Presented bySHAIK SHABEENA100% (1)
- 03 Busy Bee Teachers ManualDocument32 pages03 Busy Bee Teachers Manualapi-262368157No ratings yet
- Hair Shaft DisordersDocument3 pagesHair Shaft DisordersLakshya J BasumataryNo ratings yet
- The Human Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesThe Human Skeletal System201090182No ratings yet
- Human Body Systems: The Human Body Is Divided Into Many Systems Which Enable The Organism To Carry On Life FunctionsDocument63 pagesHuman Body Systems: The Human Body Is Divided Into Many Systems Which Enable The Organism To Carry On Life FunctionsKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Labour Bag (NHS)Document2 pagesLabour Bag (NHS)Jenny PattonNo ratings yet
- HaircuttingDocument5 pagesHaircuttingTribo LuminiscenteNo ratings yet
- Of The: Lovely M. PatriarcaDocument24 pagesOf The: Lovely M. PatriarcaMarlyn Laurio-patriarcaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology PretestDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology PretestMary Regine BalacuitNo ratings yet
- 10 Dos and Don'ts For Beautiful Skin: The Golden RuleDocument10 pages10 Dos and Don'ts For Beautiful Skin: The Golden RuleSharmNo ratings yet
- Hazard Awareness, Identification, Recognition, and Control For Beauty and Grooming ProfessionalsDocument108 pagesHazard Awareness, Identification, Recognition, and Control For Beauty and Grooming ProfessionalsSho aibNo ratings yet
- General Science Unit 4-5 PDFDocument90 pagesGeneral Science Unit 4-5 PDFwildwolfNo ratings yet
- Understanding Alzheimers DiseaseDocument24 pagesUnderstanding Alzheimers DiseaseAre Pee EtcNo ratings yet
- The Earliest Weeks of PregnancyDocument23 pagesThe Earliest Weeks of PregnancyAnaleah MalayaoNo ratings yet
- Abbreviations and SymbolsDocument11 pagesAbbreviations and SymbolsMarc BNo ratings yet
- Hair Growth Regime BuilderDocument16 pagesHair Growth Regime BuilderVictor NuñezNo ratings yet
- ToriLev AnatomyOfThePig-web PDFDocument8 pagesToriLev AnatomyOfThePig-web PDFStanislava KanjevacNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument4 pagesSkinKatjaMarieNo ratings yet
- Layette Preparation Handout-1Document2 pagesLayette Preparation Handout-1alainea100% (1)
- Axial Skeleton PDFDocument48 pagesAxial Skeleton PDFSharadambigai SamarasanNo ratings yet
- A To Z Medical TerminologyDocument16 pagesA To Z Medical TerminologyBobNathanaelNo ratings yet
- Diabetes WorksheetDocument2 pagesDiabetes WorksheetAstrid TelloNo ratings yet
- Morality As Duty:: Immanuel Kant's Arguments in GroundworkDocument57 pagesMorality As Duty:: Immanuel Kant's Arguments in GroundworkAlyssa Marie SantosNo ratings yet
- Motivation & Self-EsteemDocument9 pagesMotivation & Self-EsteemAmirthaNo ratings yet
- The Skin (Integumentary System)Document4 pagesThe Skin (Integumentary System)Darlin Maree JamonNo ratings yet
- 01-INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM TheoryDocument9 pages01-INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Theorykapil RajputplNo ratings yet
- M06 Mari2603 07 Se C06Document4 pagesM06 Mari2603 07 Se C06LENARD GUINSATAONo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System: Powerpoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community CollegeDocument62 pagesThe Integumentary System: Powerpoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community CollegetanarNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio IIIDocument4 pagesEjercicio IIIedgarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document47 pagesChapter 5Beaune V. VillarazaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PptintegsystemDocument64 pagesChapter 5 PptintegsystemlorinsyacderminnatNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet 5 The Skin A28 Group1Document2 pagesWork Sheet 5 The Skin A28 Group1Japet Floyd AlipioNo ratings yet
- HIstology Experiment 12Document5 pagesHIstology Experiment 12Pearlregine Cianne MirandaNo ratings yet
- Unit VI Powerpoint 2018Document19 pagesUnit VI Powerpoint 2018Steve Sullivan100% (3)
- BSci 103 Laboratory - Exercise 2 - BURDIOS H.Document13 pagesBSci 103 Laboratory - Exercise 2 - BURDIOS H.Haide Naya BurdiosNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument15 pagesUntitledSwitzel Smyle Goh PuyaoanNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System IncludesDocument29 pagesIntegumentary System IncludesRhena TogoresNo ratings yet
- CH 05Document28 pagesCH 05Nestor BalboaNo ratings yet
- 6 Integumentary SystemDocument4 pages6 Integumentary SystemPrincess kyle anicoyNo ratings yet
- Woreta Health Science and Business College Dr. Ayana Wasse (MD, SCR)Document25 pagesWoreta Health Science and Business College Dr. Ayana Wasse (MD, SCR)Eyachew TewabeNo ratings yet
- ANAT 1 Lab Homework 2 - JMDocument2 pagesANAT 1 Lab Homework 2 - JMJadeanna MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Integumentary SystemDocument26 pagesChapter 6 Integumentary SystemPrinces Eunice DenostaNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth & DifferentiationDocument25 pagesPlant Growth & DifferentiationAntarnet AntarNo ratings yet
- Beauty Therapy 1Document6 pagesBeauty Therapy 1Ekram MagedNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Concept Book AtfDocument159 pagesDermatology Concept Book AtfDaksh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Tissue Engineering For Skin TransplantationDocument5 pagesChapter 17 Tissue Engineering For Skin Transplantationmaf_oliveiraNo ratings yet
- Astm A325Document8 pagesAstm A325Nacer KisyNo ratings yet
- Geography Chapter 7 Land SupplyDocument9 pagesGeography Chapter 7 Land SupplydenrabyNo ratings yet
- Childhood EducationDocument19 pagesChildhood EducationCharlyn Mae Abedes EbuengaNo ratings yet
- MFG Fiberglass Column Forms Product SheetDocument3 pagesMFG Fiberglass Column Forms Product SheetAboalmaail AlaminNo ratings yet
- 5-7 - English - Revision - Qns 2Document26 pages5-7 - English - Revision - Qns 2addyNo ratings yet
- Strilube 3125 TDSDocument2 pagesStrilube 3125 TDSchetanNo ratings yet
- Aecc 2 EnvsDocument12 pagesAecc 2 Envssaha7003810868No ratings yet
- Transposition: Shubhangi ShuklaDocument24 pagesTransposition: Shubhangi ShuklaShubhangi ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Building ServicesDocument108 pagesBuilding ServicesSilvinus Clisson Pragash50% (2)
- Riser Clamps SpecificationDocument36 pagesRiser Clamps SpecificationasaiNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportsDocument18 pagesLab ReportsLana RaedNo ratings yet
- Traulsen RLT - ALT Freezer DUTDocument2 pagesTraulsen RLT - ALT Freezer DUTwsfc-ebayNo ratings yet
- Circuit Makes Simple High Voltage Inverter: ArticleDocument3 pagesCircuit Makes Simple High Voltage Inverter: ArticleAmador Garcia IIINo ratings yet
- Basics of HFFR ExtrusionDocument7 pagesBasics of HFFR ExtrusionYiğit IlgazNo ratings yet
- Psychological TheoriesDocument19 pagesPsychological TheoriesYapieeNo ratings yet
- NSK Wheel Bearings: Produced Worldwide To One StandardDocument6 pagesNSK Wheel Bearings: Produced Worldwide To One StandardCarlo AguiluzNo ratings yet
- Workbook PDFDocument145 pagesWorkbook PDFRecordTrac - City of OaklandNo ratings yet
- Petronas-PTS 32.37.20.10-Sep. 2008-Instrument Signal Lines 6Document1 pagePetronas-PTS 32.37.20.10-Sep. 2008-Instrument Signal Lines 6amoghimiNo ratings yet
- Jaggery Making: How To Make Jaggery?Document5 pagesJaggery Making: How To Make Jaggery?Subham BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Rele Ups CyberDocument4 pagesRele Ups CyberFrancisco Javier Duran MejiasNo ratings yet
- Informasi Umum PLTSDocument20 pagesInformasi Umum PLTSmass_rc100No ratings yet
- Letter To Parents (RVHS Incident)Document2 pagesLetter To Parents (RVHS Incident)dontspreadaboutmeNo ratings yet
- ELSci Q2 Lesson 6 - Organ Systems of Representative AnimalsDocument51 pagesELSci Q2 Lesson 6 - Organ Systems of Representative AnimalsItsClarence100% (2)
- A Grand Rounds Presentation To Medical Doctors On End of Life DiscussionsDocument17 pagesA Grand Rounds Presentation To Medical Doctors On End of Life DiscussionsShivan A.C.No ratings yet
- Sheep Diseases - The Farmers Guide - 2nd Edition - July 2015Document84 pagesSheep Diseases - The Farmers Guide - 2nd Edition - July 2015Raghu NathaNo ratings yet
- Titan Aviation 30000l Semi Trailer Refueller PDFDocument4 pagesTitan Aviation 30000l Semi Trailer Refueller PDFcloudysunNo ratings yet
- PolityDocument10 pagesPolityKedar BhasmeNo ratings yet
- Biology Laboratory ManualDocument314 pagesBiology Laboratory ManualLeroyJones91% (11)
- 20T Wheat Flour Milling PlantDocument12 pages20T Wheat Flour Milling Plantshio29100% (2)