Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsSecond Law of Motion
Second Law of Motion
Uploaded by
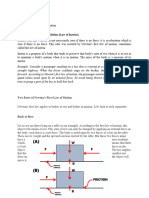
Mohammad UmairThe Second Law of Motion states that the force acting on an object equals its mass times its acceleration, written as F=ma. This means that a greater force is needed to accelerate a more massive object, and applying the same force will cause a less massive object to accelerate more. The force is a vector quantity, having both magnitude and direction, and can be a single force or the net force from multiple forces combined on an object.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Physics Definition List Form 4 & Form 5Document34 pagesPhysics Definition List Form 4 & Form 5ruslawati92% (12)
- Idealization in MechanicsDocument2 pagesIdealization in MechanicsReashma Ps40% (5)
- NSLDocument1 pageNSLfranklin.yin2020No ratings yet
- Second Law-Law of Acceleration-OkDocument11 pagesSecond Law-Law of Acceleration-OkMariegold LagatNo ratings yet
- Physics: First Law (Law of Inertia)Document2 pagesPhysics: First Law (Law of Inertia)Kumanan CultureshockNo ratings yet
- Experiment 101 Newton'S Second Law of Motion AnalysisDocument5 pagesExperiment 101 Newton'S Second Law of Motion AnalysisJerome LangitNo ratings yet
- Notes-Laws of MotionDocument3 pagesNotes-Laws of MotionJocel BaquilarNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesLaws of MotionCJay ArnauNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation: /R) WhereDocument1 pageNewton's Law of Universal Gravitation: /R) WhereCris HovaNo ratings yet
- Newton Laws of Motion: Trajectory - inDocument10 pagesNewton Laws of Motion: Trajectory - inpriyanka429No ratings yet
- Newton LawDocument5 pagesNewton Lawdva222No ratings yet
- Contact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcesDocument6 pagesContact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcesBethlehem CuradaNo ratings yet
- Newton Law of MotionDocument1 pageNewton Law of MotionbrostaNo ratings yet
- Newton Laws of MotionDocument1 pageNewton Laws of MotionShantanu DwivediNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity SheetsDocument4 pagesLearning Activity SheetsJoshua BarontoyNo ratings yet
- LAWS of Motion SCIENCE 8Document14 pagesLAWS of Motion SCIENCE 8Gregg LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Ewton S AWS OF Otion: The Fundamental Laws of Newtonian DynamicsDocument74 pagesEwton S AWS OF Otion: The Fundamental Laws of Newtonian Dynamicsapi-37284110% (1)
- Chapter-3 Newton's LawsDocument8 pagesChapter-3 Newton's LawsMd Najmul HudaNo ratings yet
- Newton'S Laws Newton's Laws of Motion Are Three: Philosophiae Naturalis Principia MathematicaDocument1 pageNewton'S Laws Newton's Laws of Motion Are Three: Philosophiae Naturalis Principia MathematicaKusuma MahadikaNo ratings yet
- Matter and Energy. Topic 8-Newton S Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesMatter and Energy. Topic 8-Newton S Laws of MotionAlexa MartínezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Mechanics - Newton's Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Mechanics - Newton's Laws of Motiontekeje7802No ratings yet
- Physics: Class 9th (KPK)Document41 pagesPhysics: Class 9th (KPK)MobeenKhanNo ratings yet
- Newton's Three Law of MotionDocument3 pagesNewton's Three Law of MotionArlyn Pong Pling PioNo ratings yet
- A.2 Forces & Momentum: The Three Laws of MotionDocument16 pagesA.2 Forces & Momentum: The Three Laws of MotionVedant PatnaikNo ratings yet
- Stability - ForceDocument17 pagesStability - Forcelife & logicNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean TheoremDocument2 pagesPythagorean TheoremGuNo ratings yet
- Capiz State UniversityDocument1 pageCapiz State UniversityJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- E101 - AgustinDocument21 pagesE101 - AgustinSeth Jarl G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Momentum - Is A Physics Term It Refers To The Quantity of Motion That An Object Has. Momentum Can Be Defined As "Mass in Motion."Document6 pagesMomentum - Is A Physics Term It Refers To The Quantity of Motion That An Object Has. Momentum Can Be Defined As "Mass in Motion."taneaturcu919No ratings yet
- Force - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument25 pagesForce - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJay SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Newt 2Document3 pagesNewt 2Tyro SpiedNo ratings yet
- Project File LawsDocument5 pagesProject File LawsSonaNo ratings yet
- Interactions and ForceDocument2 pagesInteractions and Forcezhungjian586No ratings yet
- Aguila123 OdtDocument2 pagesAguila123 OdtAnonymous M7EKcmNA9kNo ratings yet
- Law of AccelerationDocument2 pagesLaw of Accelerationchristianlozada000No ratings yet
- Moodle Activity 2Document1 pageMoodle Activity 2Ilaitia RavunikauNo ratings yet
- The Laws of MotionDocument15 pagesThe Laws of MotionAmar Poñado BagacinaNo ratings yet
- Second Law of MotoinDocument2 pagesSecond Law of MotoinAli_Ramadan1997No ratings yet
- AstronomyDocument115 pagesAstronomyhariharanphysics02No ratings yet
- Dynamics NotesDocument3 pagesDynamics NotesShamsherNo ratings yet
- CE 2107 ϕshbol FUTURAMADocument210 pagesCE 2107 ϕshbol FUTURAMA21-06116No ratings yet
- Newton'S Three Laws of Motion: by Aybak Basuony Dont Hate On Me This Presentation Was Done On My PhoneDocument6 pagesNewton'S Three Laws of Motion: by Aybak Basuony Dont Hate On Me This Presentation Was Done On My PhoneAybak BasuonyNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Translatory Motion Newton Laws of Motion:-First Law of Motion: - StatementDocument17 pagesDynamics of Translatory Motion Newton Laws of Motion:-First Law of Motion: - Statementasadaliawanatd1No ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Friction Laboratory Report: Air Resistance Refers To The ForcesDocument6 pagesExperiment 4: Friction Laboratory Report: Air Resistance Refers To The ForcesMan DejeloNo ratings yet
- FORCE and MOTIONDocument3 pagesFORCE and MOTIONKristineMaeFernandezCarmeloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 DynamicsDocument12 pagesChapter 3 DynamicsMuhammadSultanNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document - EditedDocument1 pageUntitled Document - EditedOdeteNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Newton MechanicsDocument16 pagesCh1 Newton MechanicsRana JahanzaibNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument31 pagesLaws of MotionManas ThakurNo ratings yet
- Center of Gravity & Hooks LawDocument1 pageCenter of Gravity & Hooks Lawnandana jammulaNo ratings yet
- Statistics of Rigid BodiesDocument7 pagesStatistics of Rigid BodiesAphaedes AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Newton's Laws of Motion: Particle Dynamics IDocument5 pagesChapter 5: Newton's Laws of Motion: Particle Dynamics Idilovan_têlîNo ratings yet
- NEWTON's 1st, 2nd & 3rd LawsDocument20 pagesNEWTON's 1st, 2nd & 3rd LawsNorKamilahMakhtarNo ratings yet
- Three Laws of MotionDocument22 pagesThree Laws of MotionCamille Neriza FeLicianoNo ratings yet
- Newton's Third Law: Contact Interactions (Normal, Frictional, Tensional, and Applied Forces Are Examples ofDocument4 pagesNewton's Third Law: Contact Interactions (Normal, Frictional, Tensional, and Applied Forces Are Examples ofRayudu VVSNo ratings yet
- Application of Three Laws of Motion On A RocketDocument1 pageApplication of Three Laws of Motion On A RocketAngelica CabreraNo ratings yet
- Forces: Briefly Explained by Max de RooijDocument1 pageForces: Briefly Explained by Max de RooijMax De RooijNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of Elements ListDocument7 pagesPeriodic Table of Elements ListMin YoongiNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument1 pageDefinitionsMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- FluidDocument1 pageFluidMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Hex ColoursDocument1 pageHex ColoursMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Boilers: Introduction and ClassificationDocument3 pagesBoilers: Introduction and ClassificationMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Transforms of Some Basic FunctionsDocument1 pageTransforms of Some Basic FunctionsMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Thin Column BucklingDocument1 pageThin Column BucklingMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Non-Homogeneous EquationsDocument1 pageNon-Homogeneous EquationsMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Islamiyat AssignmentDocument15 pagesIslamiyat AssignmentMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- 5070 s17 QP All PDFDocument116 pages5070 s17 QP All PDFMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Newton 3 LawsDocument1 pageNewton 3 LawsMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- ImprovementsDocument1 pageImprovementsMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- A Dart GunDocument1 pageA Dart GunMohammad Umair100% (1)
- A HammerDocument1 pageA HammerMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- The Equation For WorkDocument1 pageThe Equation For WorkMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Mechanical EnergyDocument1 pageMechanical EnergyMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- It's All Uphill Interactive It's All Uphill InteractiveDocument1 pageIt's All Uphill Interactive It's All Uphill InteractiveMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Store EnergyDocument1 pageStore EnergyMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
Second Law of Motion
Second Law of Motion
Uploaded by
Mohammad Umair0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageThe Second Law of Motion states that the force acting on an object equals its mass times its acceleration, written as F=ma. This means that a greater force is needed to accelerate a more massive object, and applying the same force will cause a less massive object to accelerate more. The force is a vector quantity, having both magnitude and direction, and can be a single force or the net force from multiple forces combined on an object.
Original Description:
newton law
Original Title
2nd law
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe Second Law of Motion states that the force acting on an object equals its mass times its acceleration, written as F=ma. This means that a greater force is needed to accelerate a more massive object, and applying the same force will cause a less massive object to accelerate more. The force is a vector quantity, having both magnitude and direction, and can be a single force or the net force from multiple forces combined on an object.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageSecond Law of Motion
Second Law of Motion
Uploaded by
Mohammad UmairThe Second Law of Motion states that the force acting on an object equals its mass times its acceleration, written as F=ma. This means that a greater force is needed to accelerate a more massive object, and applying the same force will cause a less massive object to accelerate more. The force is a vector quantity, having both magnitude and direction, and can be a single force or the net force from multiple forces combined on an object.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
The Second Law of Motion describes what happens to a massive body when it is acted upon by an
external force. It states, "The force acting on an object is equal to the mass of that object times its
acceleration." This is written in mathematical form as F = ma, where F is force, m is mass, and a is
acceleration. The bold letters indicate that force and acceleration are vector quantities, which means
they have both magnitude and direction. The force can be a single force, or it can be the vector sum of
more than one force, which is the net force after all the forces are combined.
You might also like
- Physics Definition List Form 4 & Form 5Document34 pagesPhysics Definition List Form 4 & Form 5ruslawati92% (12)
- Idealization in MechanicsDocument2 pagesIdealization in MechanicsReashma Ps40% (5)
- NSLDocument1 pageNSLfranklin.yin2020No ratings yet
- Second Law-Law of Acceleration-OkDocument11 pagesSecond Law-Law of Acceleration-OkMariegold LagatNo ratings yet
- Physics: First Law (Law of Inertia)Document2 pagesPhysics: First Law (Law of Inertia)Kumanan CultureshockNo ratings yet
- Experiment 101 Newton'S Second Law of Motion AnalysisDocument5 pagesExperiment 101 Newton'S Second Law of Motion AnalysisJerome LangitNo ratings yet
- Notes-Laws of MotionDocument3 pagesNotes-Laws of MotionJocel BaquilarNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesLaws of MotionCJay ArnauNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation: /R) WhereDocument1 pageNewton's Law of Universal Gravitation: /R) WhereCris HovaNo ratings yet
- Newton Laws of Motion: Trajectory - inDocument10 pagesNewton Laws of Motion: Trajectory - inpriyanka429No ratings yet
- Newton LawDocument5 pagesNewton Lawdva222No ratings yet
- Contact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcesDocument6 pagesContact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcesBethlehem CuradaNo ratings yet
- Newton Law of MotionDocument1 pageNewton Law of MotionbrostaNo ratings yet
- Newton Laws of MotionDocument1 pageNewton Laws of MotionShantanu DwivediNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity SheetsDocument4 pagesLearning Activity SheetsJoshua BarontoyNo ratings yet
- LAWS of Motion SCIENCE 8Document14 pagesLAWS of Motion SCIENCE 8Gregg LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Ewton S AWS OF Otion: The Fundamental Laws of Newtonian DynamicsDocument74 pagesEwton S AWS OF Otion: The Fundamental Laws of Newtonian Dynamicsapi-37284110% (1)
- Chapter-3 Newton's LawsDocument8 pagesChapter-3 Newton's LawsMd Najmul HudaNo ratings yet
- Newton'S Laws Newton's Laws of Motion Are Three: Philosophiae Naturalis Principia MathematicaDocument1 pageNewton'S Laws Newton's Laws of Motion Are Three: Philosophiae Naturalis Principia MathematicaKusuma MahadikaNo ratings yet
- Matter and Energy. Topic 8-Newton S Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesMatter and Energy. Topic 8-Newton S Laws of MotionAlexa MartínezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Mechanics - Newton's Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Mechanics - Newton's Laws of Motiontekeje7802No ratings yet
- Physics: Class 9th (KPK)Document41 pagesPhysics: Class 9th (KPK)MobeenKhanNo ratings yet
- Newton's Three Law of MotionDocument3 pagesNewton's Three Law of MotionArlyn Pong Pling PioNo ratings yet
- A.2 Forces & Momentum: The Three Laws of MotionDocument16 pagesA.2 Forces & Momentum: The Three Laws of MotionVedant PatnaikNo ratings yet
- Stability - ForceDocument17 pagesStability - Forcelife & logicNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean TheoremDocument2 pagesPythagorean TheoremGuNo ratings yet
- Capiz State UniversityDocument1 pageCapiz State UniversityJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- E101 - AgustinDocument21 pagesE101 - AgustinSeth Jarl G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Momentum - Is A Physics Term It Refers To The Quantity of Motion That An Object Has. Momentum Can Be Defined As "Mass in Motion."Document6 pagesMomentum - Is A Physics Term It Refers To The Quantity of Motion That An Object Has. Momentum Can Be Defined As "Mass in Motion."taneaturcu919No ratings yet
- Force - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument25 pagesForce - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJay SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Newt 2Document3 pagesNewt 2Tyro SpiedNo ratings yet
- Project File LawsDocument5 pagesProject File LawsSonaNo ratings yet
- Interactions and ForceDocument2 pagesInteractions and Forcezhungjian586No ratings yet
- Aguila123 OdtDocument2 pagesAguila123 OdtAnonymous M7EKcmNA9kNo ratings yet
- Law of AccelerationDocument2 pagesLaw of Accelerationchristianlozada000No ratings yet
- Moodle Activity 2Document1 pageMoodle Activity 2Ilaitia RavunikauNo ratings yet
- The Laws of MotionDocument15 pagesThe Laws of MotionAmar Poñado BagacinaNo ratings yet
- Second Law of MotoinDocument2 pagesSecond Law of MotoinAli_Ramadan1997No ratings yet
- AstronomyDocument115 pagesAstronomyhariharanphysics02No ratings yet
- Dynamics NotesDocument3 pagesDynamics NotesShamsherNo ratings yet
- CE 2107 ϕshbol FUTURAMADocument210 pagesCE 2107 ϕshbol FUTURAMA21-06116No ratings yet
- Newton'S Three Laws of Motion: by Aybak Basuony Dont Hate On Me This Presentation Was Done On My PhoneDocument6 pagesNewton'S Three Laws of Motion: by Aybak Basuony Dont Hate On Me This Presentation Was Done On My PhoneAybak BasuonyNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Translatory Motion Newton Laws of Motion:-First Law of Motion: - StatementDocument17 pagesDynamics of Translatory Motion Newton Laws of Motion:-First Law of Motion: - Statementasadaliawanatd1No ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Friction Laboratory Report: Air Resistance Refers To The ForcesDocument6 pagesExperiment 4: Friction Laboratory Report: Air Resistance Refers To The ForcesMan DejeloNo ratings yet
- FORCE and MOTIONDocument3 pagesFORCE and MOTIONKristineMaeFernandezCarmeloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 DynamicsDocument12 pagesChapter 3 DynamicsMuhammadSultanNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document - EditedDocument1 pageUntitled Document - EditedOdeteNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Newton MechanicsDocument16 pagesCh1 Newton MechanicsRana JahanzaibNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument31 pagesLaws of MotionManas ThakurNo ratings yet
- Center of Gravity & Hooks LawDocument1 pageCenter of Gravity & Hooks Lawnandana jammulaNo ratings yet
- Statistics of Rigid BodiesDocument7 pagesStatistics of Rigid BodiesAphaedes AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Newton's Laws of Motion: Particle Dynamics IDocument5 pagesChapter 5: Newton's Laws of Motion: Particle Dynamics Idilovan_têlîNo ratings yet
- NEWTON's 1st, 2nd & 3rd LawsDocument20 pagesNEWTON's 1st, 2nd & 3rd LawsNorKamilahMakhtarNo ratings yet
- Three Laws of MotionDocument22 pagesThree Laws of MotionCamille Neriza FeLicianoNo ratings yet
- Newton's Third Law: Contact Interactions (Normal, Frictional, Tensional, and Applied Forces Are Examples ofDocument4 pagesNewton's Third Law: Contact Interactions (Normal, Frictional, Tensional, and Applied Forces Are Examples ofRayudu VVSNo ratings yet
- Application of Three Laws of Motion On A RocketDocument1 pageApplication of Three Laws of Motion On A RocketAngelica CabreraNo ratings yet
- Forces: Briefly Explained by Max de RooijDocument1 pageForces: Briefly Explained by Max de RooijMax De RooijNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of Elements ListDocument7 pagesPeriodic Table of Elements ListMin YoongiNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument1 pageDefinitionsMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- FluidDocument1 pageFluidMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Hex ColoursDocument1 pageHex ColoursMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Boilers: Introduction and ClassificationDocument3 pagesBoilers: Introduction and ClassificationMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Transforms of Some Basic FunctionsDocument1 pageTransforms of Some Basic FunctionsMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Thin Column BucklingDocument1 pageThin Column BucklingMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Non-Homogeneous EquationsDocument1 pageNon-Homogeneous EquationsMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Islamiyat AssignmentDocument15 pagesIslamiyat AssignmentMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- 5070 s17 QP All PDFDocument116 pages5070 s17 QP All PDFMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Newton 3 LawsDocument1 pageNewton 3 LawsMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- ImprovementsDocument1 pageImprovementsMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- A Dart GunDocument1 pageA Dart GunMohammad Umair100% (1)
- A HammerDocument1 pageA HammerMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- The Equation For WorkDocument1 pageThe Equation For WorkMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Mechanical EnergyDocument1 pageMechanical EnergyMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- It's All Uphill Interactive It's All Uphill InteractiveDocument1 pageIt's All Uphill Interactive It's All Uphill InteractiveMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Store EnergyDocument1 pageStore EnergyMohammad UmairNo ratings yet