Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical Engineering Assgn Question
Electrical Engineering Assgn Question
Uploaded by
amit621988Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical Engineering Assgn Question
Electrical Engineering Assgn Question
Uploaded by
amit621988Copyright:
Available Formats
JSS Academy of Technical Education,
C-20/1, Sector-62, Noida - 201301 (U.P), India
Electrical Engineering Department
SUBJECT: Basic Electrical Engineering SESSION: 2018-19 (EVEN)
SUBJECT CODE: KEE-201 SECTION: B-7, Faculty: Mr. Amit Kr. Roy
ASSIGNMENT-1 (Based on Unit-1)
NOTE: Assignment to be done in a separate assignment note book.
Date of Submission: 15/02/2019
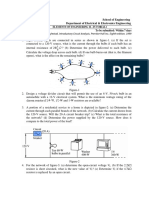
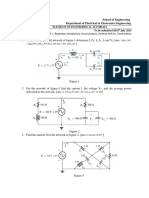
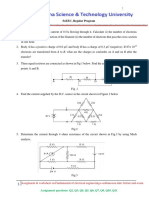
1. For the given circuit of Fig. 1, calculate the current in 6-ohm resistance using source
transformation.
Fig. 1 Fig. 2
2. Determine the power consumed in the 2-ohm resistor for the circuit of Fig. 2.
3. Determine the current in the 2ohm resistance using mesh analysis.
4. Using nodal analysis determine the voltage drop across 4-ohm, 8-ohm and 16-ohm resistances.
5. Determine current Ix in the given network using source transformation techniques.
6. Calculate the node voltage for the network shown in fig. 6.
7. Calculate the current supplied by the voltage sources in Fig. 7.
8. Determine the current in 2-ohm resistor using superposition theorem in Fig. 8.
JSS Academy of Technical Education,
C-20/1, Sector-62, Noida - 201301 (U.P), India
Electrical Engineering Department
Fig. 6 Fig. 7 Fig. 8
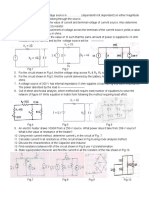
9. Determine the Thevenin’s equivalent across A-B for the given network of Fig. 9;
Fig. 9 Fig. 10
10. Find the current in 6-ohm resistor using Thevenin’s theorem for the network of Fig. 10.
11. Using Norton’s theorem calculate the current in 6-ohm resistor in the electrical circuit of Fig.
11.
12. Using Norton’s theorem calculate the current in 10-ohm resistance for the electrical network if
Fig. 12.
Fig. 11
Fig. 12
13. Derive the equivalent resistance reduction technique of Star-Delta transformation (Star
to Delta & Delta to Star).
14. Calculate the equivalent resistance between terminal A-B and between terminal AC for the
network shown as per Fig. 13.
15. Calculate the equivalent resistance between terminal X-Y for the network of Fig. 14.
Fig. 13 Fig. 14
You might also like
- Doctors at Noida ExtensionDocument2 pagesDoctors at Noida Extensionamit62198880% (5)
- Employee Information System DocumentationDocument46 pagesEmployee Information System Documentationarwin1076% (49)
- Kathmandu School of Engineering University Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument3 pagesKathmandu School of Engineering University Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringUrgen TamangNo ratings yet
- EE Assignment 23-24 Sem 1Document7 pagesEE Assignment 23-24 Sem 1Triggered CreatorNo ratings yet
- QUESTION BANK Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument7 pagesQUESTION BANK Basic Electrical EngineeringChirag ShakyaNo ratings yet
- EE Uptu Old QuesDocument1 pageEE Uptu Old Quesm_mustaqeemNo ratings yet
- BEE Model Paper 1Document7 pagesBEE Model Paper 1Nikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Model Questions EEE Cat-IDocument4 pagesModel Questions EEE Cat-IIKNo ratings yet
- 2002UNIT2PAPER2Document16 pages2002UNIT2PAPER2petey78No ratings yet
- Kathmandu School of Engineering University Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument3 pagesKathmandu School of Engineering University Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineeringkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- R07a1ec02-Electrical Circuit AnalysisDocument8 pagesR07a1ec02-Electrical Circuit AnalysisSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Seat No.: - F.E. (First Semester) EXAMINATION, 2023 Basic Electrical Engineering (2019 PATTERN) TimeDocument7 pagesSeat No.: - F.E. (First Semester) EXAMINATION, 2023 Basic Electrical Engineering (2019 PATTERN) TimeNikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Solution Tutorial 1 Ent162 (Extra Notes)Document10 pagesSolution Tutorial 1 Ent162 (Extra Notes)Wan LynnNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-02-24 at 12.47.29 AMDocument20 pagesScreenshot 2024-02-24 at 12.47.29 AMAws QhtNo ratings yet
- LAB 9 EE NewDocument9 pagesLAB 9 EE NewtengyanNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Nit Rraipur Assignment 1Document4 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Nit Rraipur Assignment 125. Tejas RajabhojNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits ThoeryDocument3 pagesElectrical Circuits ThoerySrini R KNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (May Aug2015)Document5 pagesAssignment 1 (May Aug2015)Gy LiawNo ratings yet
- ES Unit-1Document48 pagesES Unit-1Mazin VoraNo ratings yet
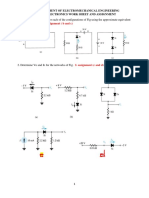
- Determine The Current I For Each of The Configurations of Fig Using The Approximate Equivalent Model For The DiodeDocument7 pagesDetermine The Current I For Each of The Configurations of Fig Using The Approximate Equivalent Model For The DiodeDaniel KetemawNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document6 pagesAssignment 1Aswathy ManojNo ratings yet
- r05010203 Electrical CircuitsDocument14 pagesr05010203 Electrical CircuitsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- bt21R0718 p1 18 11 09rahulDocument30 pagesbt21R0718 p1 18 11 09rahulAnonymous nTxB1EPvNo ratings yet
- Expt - 3 - Verification of Reciprocity Theorem For Ac CircuitsDocument3 pagesExpt - 3 - Verification of Reciprocity Theorem For Ac CircuitsChaitanya Vivek DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Expt - 3 - Verification of Reciprocity Theorem For Ac CircuitsDocument3 pagesExpt - 3 - Verification of Reciprocity Theorem For Ac CircuitsChaitanya Vivek Deshpande0% (1)
- Tracing Current-Voltage Curve of Solar Panel BasedDocument8 pagesTracing Current-Voltage Curve of Solar Panel BasedMihai BogdanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet No. 2Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet No. 2Anshu JindalNo ratings yet
- HHW Class12 New PDFDocument58 pagesHHW Class12 New PDFSannidhi ShettyNo ratings yet
- OctoberNovember 2020Document2 pagesOctoberNovember 2020Karlapati Sai KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document5 pagesAssignment 2pappuyadav1996No ratings yet
- Principles of Electronic Communication Winter 2019 Question PaperDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Electronic Communication Winter 2019 Question PaperPRANAV CNo ratings yet
- R09 Set No. 2Document8 pagesR09 Set No. 2Samiullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Roorkee EEN-112: Electrical Science Tutorial Sheet - 04Document2 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Roorkee EEN-112: Electrical Science Tutorial Sheet - 04Kumar ShivamNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesBasic Electrical EngineeringBisam Binod KhanalNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3 - 242Document5 pagesSheet 3 - 242mahmoudaliabdelaziz11No ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 2: Nodal-Voltage Analysis Methods: EET140 Electric Circuit 1 SEM 1 2017/2018Document8 pagesTUTORIAL 2: Nodal-Voltage Analysis Methods: EET140 Electric Circuit 1 SEM 1 2017/2018Izzuddin ZahidiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1AemalkhanNo ratings yet
- 9A02305 Electrical CircuitsDocument8 pages9A02305 Electrical CircuitssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Class: XII Subject: PHYSICSDocument22 pagesClass: XII Subject: PHYSICSSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Department: RESIT FINAL ASSIGNMENT: Semester-2, 2019-20 EEPW2251: Electrical Power TechnologyDocument3 pagesEngineering Department: RESIT FINAL ASSIGNMENT: Semester-2, 2019-20 EEPW2251: Electrical Power TechnologyFarooq KhanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank BeeDocument25 pagesQuestion Bank Beedhruv goraiNo ratings yet
- ENGG112 Tutorial 6Document4 pagesENGG112 Tutorial 6Rojan PradhanNo ratings yet
- BE ENG111 Assignment1Document7 pagesBE ENG111 Assignment1Risky romiosNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering1Document3 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering1Nikash SubediNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics 2017 18 Pre Board Exam PDFDocument8 pages12 Physics 2017 18 Pre Board Exam PDFAshish ChaharNo ratings yet
- OutputDocument130 pagesOutput18131A0230 GEDDU TARUN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Tracing Current-Voltage Curve of Solar Panel Based On Labview Arduino InterfacingDocument8 pagesTracing Current-Voltage Curve of Solar Panel Based On Labview Arduino InterfacingHabes NoraNo ratings yet
- EED 101 - Tut 1Document5 pagesEED 101 - Tut 1GaneshKannaNo ratings yet
- 130901-2 Circuit & Networks Gtu 3rd Sem PaperDocument2 pages130901-2 Circuit & Networks Gtu 3rd Sem PaperShailesh SankdasariyaNo ratings yet
- Anant Achievement Classes Physics TestDocument2 pagesAnant Achievement Classes Physics TestUTSAV JAINNo ratings yet
- Bee Lab ManualDocument62 pagesBee Lab ManualSwetha VanamNo ratings yet
- Funda Worksheet On Chapter 1&2 - 2Document3 pagesFunda Worksheet On Chapter 1&2 - 2Ezedin NegashNo ratings yet
- 2010 Conference On Precision Electromagnetic MeasurementsDocument2 pages2010 Conference On Precision Electromagnetic MeasurementsluisNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument2 pagesBasic Electrical EngineeringAdhikari SushilNo ratings yet
- Holiday Homework Class: XII Subject: PhysicsDocument3 pagesHoliday Homework Class: XII Subject: PhysicsAlind GuptaNo ratings yet
- IEE Tutorial 1Document6 pagesIEE Tutorial 1wwinnerNo ratings yet
- WWW - Studyhaunters.blogspot - In: Question Paper Code: 22115Document5 pagesWWW - Studyhaunters.blogspot - In: Question Paper Code: 22115Sriram JNo ratings yet
- CT May June 2011 PDFDocument5 pagesCT May June 2011 PDFthangalakshmipr9728No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Subject:: 2019-20 (EVEN) Subject Code: Roe-086 Section: Ee-ADocument1 pageSubject:: 2019-20 (EVEN) Subject Code: Roe-086 Section: Ee-Aamit621988No ratings yet
- Unit-3 MHD Part-1Document12 pagesUnit-3 MHD Part-1amit621988No ratings yet
- Zkad 003Document16 pagesZkad 003amit621988No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2amit621988100% (1)
- Unit-3 MHD Part-2Document12 pagesUnit-3 MHD Part-2amit621988No ratings yet
- Unit-3 Fuel CellDocument14 pagesUnit-3 Fuel Cellamit621988100% (1)
- First Year FormatDocument28 pagesFirst Year Formatamit621988No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2amit621988No ratings yet
- First Year FormatDocument28 pagesFirst Year Formatamit621988No ratings yet
- Gazet3 d09 NewDocument254 pagesGazet3 d09 Newamit621988No ratings yet
- Infosys TrainingDocument5 pagesInfosys Trainingamit621988No ratings yet
- CIA-III 2018-19 Even Kee 201Document2 pagesCIA-III 2018-19 Even Kee 201amit621988No ratings yet
- Fluid MachineryDocument18 pagesFluid Machineryamit621988No ratings yet
- Completed Done Developed Done Setupistobedone 80%: Research Area: Tentative TitleDocument1 pageCompleted Done Developed Done Setupistobedone 80%: Research Area: Tentative Titleamit621988No ratings yet
- Notice: Jss MahavidhyapeethaDocument1 pageNotice: Jss Mahavidhyapeethaamit621988No ratings yet
- Duty Anti Ragging17-1Document32 pagesDuty Anti Ragging17-1amit621988No ratings yet
- S. No. Name of The Faculty Achievements Significant Events PublicationDocument2 pagesS. No. Name of The Faculty Achievements Significant Events Publicationamit621988No ratings yet
- Data Warehousing: A Tool For The Outcomes Assessment ProcessDocument5 pagesData Warehousing: A Tool For The Outcomes Assessment Processamit621988No ratings yet
- Content Beyond Syllabus For "Fundamentals of E.M Theory" 3 Year, 5 Semester, Subject Code: EEC-508 Faculty: Mr. Amit Kr. RoyDocument1 pageContent Beyond Syllabus For "Fundamentals of E.M Theory" 3 Year, 5 Semester, Subject Code: EEC-508 Faculty: Mr. Amit Kr. Royamit621988No ratings yet
- Final Call IICPE2016Document1 pageFinal Call IICPE2016amit621988No ratings yet
- Alternators - ConstructionDocument17 pagesAlternators - Constructionamit621988No ratings yet
- Process Fired Heaters/Furnaces in RefineriesDocument4 pagesProcess Fired Heaters/Furnaces in Refineriesamit621988No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Oscilloscope Function Generator)Document12 pagesChapter 3 (Oscilloscope Function Generator)che syakirNo ratings yet
- Ambo University Institute of Technology Department of Computer ScienceDocument78 pagesAmbo University Institute of Technology Department of Computer ScienceNuredin Abdumalik100% (1)
- Scanning Into LaserficheDocument3 pagesScanning Into LaserficheMarco SánchezNo ratings yet
- User Manual For FLYINSONODocument30 pagesUser Manual For FLYINSONONAYAN PATELNo ratings yet
- Discover The AREST Framework - Easily Control Your Arduino, Raspberry Pi & ESP8266 ProjectsDocument203 pagesDiscover The AREST Framework - Easily Control Your Arduino, Raspberry Pi & ESP8266 ProjectstariqNo ratings yet
- Dell DR Series System Interoperability Guide For Releases 3.2.6.1 and 3.2.0.2Document29 pagesDell DR Series System Interoperability Guide For Releases 3.2.6.1 and 3.2.0.2Gokul VeNo ratings yet
- Design and Performance Analysis of D-STATCOM For Non-Linear Load Composite CompensationDocument2 pagesDesign and Performance Analysis of D-STATCOM For Non-Linear Load Composite CompensationDavidMaighlNo ratings yet
- ICOM IC-7700 BrochureDocument12 pagesICOM IC-7700 Brochuregus289No ratings yet
- 03 IAB BasicsDocument62 pages03 IAB BasicsMohamed SakrNo ratings yet
- Excellent Perimeter Protection: With Hikvision + OPTEXDocument2 pagesExcellent Perimeter Protection: With Hikvision + OPTEXawadalmekawyNo ratings yet
- La-A998p R01 Szso40 PDFDocument58 pagesLa-A998p R01 Szso40 PDFJoselo LópezNo ratings yet
- CPV 363 MFDocument9 pagesCPV 363 MFSergio MuriloNo ratings yet
- 1SDC007408G0201 - WP Ats 021 022 enDocument36 pages1SDC007408G0201 - WP Ats 021 022 enSemih GençNo ratings yet
- Layers and Types of CloudDocument4 pagesLayers and Types of CloudRocky ArunnNo ratings yet
- Panasonic - CF-19FHGAXxM Service ManualDocument90 pagesPanasonic - CF-19FHGAXxM Service ManualGraku MartínNo ratings yet
- Muslim Ladies College AL 2021Document7 pagesMuslim Ladies College AL 2021IQAM IFTHIKARNo ratings yet
- Alcatel-Lucent Omniswitch 2260: Websmart+ Gigabit Ethernet Lan Switch FamilyDocument7 pagesAlcatel-Lucent Omniswitch 2260: Websmart+ Gigabit Ethernet Lan Switch FamilyAsnake TegenawNo ratings yet
- MST30 & MST155M Series of Multi Service Transmission Equipment User ManualDocument39 pagesMST30 & MST155M Series of Multi Service Transmission Equipment User ManualHuỳnh PhongNo ratings yet
- Understanding Group Policy Part 1 of 3: Rick ClausDocument34 pagesUnderstanding Group Policy Part 1 of 3: Rick ClausmaneeiyerNo ratings yet
- G 4 DocumentationDocument33 pagesG 4 DocumentationEsku LuluNo ratings yet
- Presented By:-: Temperature Controlled DC FanDocument19 pagesPresented By:-: Temperature Controlled DC FanAkash HalliNo ratings yet
- E InvitationDocument67 pagesE InvitationNeha SoniNo ratings yet
- CA BlazeMeter Beyond Open SourceDocument3 pagesCA BlazeMeter Beyond Open Sourcegh0st23No ratings yet
- DirectSOFT Comm Link ProblemsDocument4 pagesDirectSOFT Comm Link Problemsdzireyes94No ratings yet
- Microsoft: Networking:: AD, Group Policy, Domain, - Tcp/Ip (SNMP, SMTP, Pop3, Ras, DNS, DHCPDocument3 pagesMicrosoft: Networking:: AD, Group Policy, Domain, - Tcp/Ip (SNMP, SMTP, Pop3, Ras, DNS, DHCPMadhu SrvNo ratings yet
- 39Document15 pages39李德军No ratings yet
- IGBT Power Module: BSM 75 GD 120 DN2Document10 pagesIGBT Power Module: BSM 75 GD 120 DN2Alvin NguyenNo ratings yet
- Cariaga Standardized Test 20itemsDocument3 pagesCariaga Standardized Test 20itemsCristina Rhain WinterNo ratings yet
- Eaton-Ceag-El-Cps-Datasheet-V-Cg-Se 4-400 W-GBDocument1 pageEaton-Ceag-El-Cps-Datasheet-V-Cg-Se 4-400 W-GBjibin georgeNo ratings yet