Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Qsns On Chemical Kinetics
Qsns On Chemical Kinetics
Uploaded by
prathmfed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
55 views1 page1. For a chemical reaction involving ammonia and oxygen, calculate the rates of disappearance of ammonia and formation of water given the rate of formation of NO is provided.
2. The rate of appearance of an underlined product is directly proportional to the rate of disappearance of the underlined reactant.
3. Calculate the average rates of reaction in atm/s and mol/L s for the reaction of NO and O3 using data provided about changes in pressure and time.
Original Description:
chemsitry
Original Title
qsns on chemical kinetics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. For a chemical reaction involving ammonia and oxygen, calculate the rates of disappearance of ammonia and formation of water given the rate of formation of NO is provided.
2. The rate of appearance of an underlined product is directly proportional to the rate of disappearance of the underlined reactant.
3. Calculate the average rates of reaction in atm/s and mol/L s for the reaction of NO and O3 using data provided about changes in pressure and time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
55 views1 pageQsns On Chemical Kinetics
Qsns On Chemical Kinetics
Uploaded by
prathmfed1. For a chemical reaction involving ammonia and oxygen, calculate the rates of disappearance of ammonia and formation of water given the rate of formation of NO is provided.
2. The rate of appearance of an underlined product is directly proportional to the rate of disappearance of the underlined reactant.
3. Calculate the average rates of reaction in atm/s and mol/L s for the reaction of NO and O3 using data provided about changes in pressure and time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
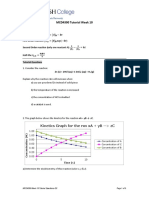
CHEMICAL KINETICS (BASICS/RATE OF REACTION/ORDER/MOLECULARITY) CODE: 2019-20/1
1. Ammonia and oxygen react at high 6. For a reaction nA product, if
temperature as: the rate constant and the rate of
4NH3 + 5O2 4NO + 6H2O. reaction are equal, what is the order
In an expt, the rate of formation of of reaction?
NO is 3.6x10-3 Ms-1. Calculate a) rate A) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3
of disappearance of ammonia and 7. For a hypothetical reaction, A B it
b) rate of formation of water. is found that the rate constant is x s-1.
2. In the following reaction, how is the By what factor the rate is increased if
rate of appearance of the underlined the initial concentration of A is
product related to the rate of tripled?
disappearance of the underlined A) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
reactant? 8. The rate of reaction 3A + 2B
BrO3- + 5Br- + 6H+ 3Br2 + 3H2O products is given by rate expression,
d[Br2] 5 −d[Br−] r= k [A] [B]2. If A is taken in excess, the
a) 𝑑𝑡
=3 𝑑𝑡
d[Br2] −d[Br−] order of the reaction would be
b) =
𝑑𝑡 𝑑𝑡 a) 3 b) 2 c) 1 d) 5
d[Br2] 1 −d[Br−]
c) = 9. The rate of a gaseous reaction is given
𝑑𝑡 3 𝑑𝑡
d)
d[Br2] 3 −d[Br−]
= by the expression k [A]2 [B]3. The
𝑑𝑡 5 𝑑𝑡
volume of the reaction vessel is
3. I) For the reaction at 273K (gases)
suddenly reduced to one-half of the
NO + O3 NO2 + O2. It is
initial volume. The reaction rate
observed that the pressure of NO falls
relative to the original rate will be
from 700mm Hg to 500mm Hg in
a) 1/24 b) 1/32 c) 32 d) 24
250s. Calculate the average rate of
10. The rate constant of the reaction
reaction in atm/s.
depends on
a) 1.053x10-3 b) 1.053x10-4
a) temperature
c) 2.053x10-3 d) 2.053x10-4
b) initial concentration of reactants
II) Also, calculate the average rate of
c) time of reaction d) extent of rxn
reaction in mol/L s.
11. For non-stoichiometric reaction
a) 4.7x10-5 b) 5.9x10-5
2A + B C + D . the following data
c) 3.2x10-5 d) 9.8x10-5
were obtained in 3 expts. All at 298K.
4. For a rxn, 2NO + 2H2 N2 + 2H2O
Initial [A] Initial [B] Initial rate of
the following data were obtained:
formation of C
[NO] mol/L [H2] mol/L rate 0.1M 0.1M 1.2x10-3
1. 5x10-3 2.5x10-3 3x10-5 0.1M 0.2M 1.2x10-3
2. 15x10-3 2.5x10-3 9x10-5 0.2M 0.1M 2.4x10-3
-3 -3 3.6x10-4
3. 15x10 10x10 The rate law for the formation of C is
Calculate the order of reaction and a) r= k [A] [B]2 b) r= k [A]
rate constant. c) r= k [A] [B] d) r= k [A]2 [B]
a) 2,2.4 b) 1,1.4 c) 3,2.4 d) 0,1.4
12. For elementary reaction, M N the
5. The rate constant for the reaction rate of disappearance of M increases
2N2O5 4NO2 + O2 is 3x10-5s-1. If by a factor of 8 upon doubling the
the rate is 2.4x10-5 mol/L s, then the concentration of M. the order of
initial concentration of N2O5 is: reaction with respect to M is:
a) 1.4 b) 1.2 c) 0.04 d) 0.8 A) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
You might also like
- CRE - Diagnostic Exam (USA)Document2 pagesCRE - Diagnostic Exam (USA)Kuo SarongNo ratings yet
- Sb200tg Thermo KingDocument121 pagesSb200tg Thermo KingEdu Edy100% (3)
- DPP-01 Chemical KineticsDocument1 pageDPP-01 Chemical Kineticsprathmfed100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Chemical Kinetics - ExercisesDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Chemical Kinetics - Exercisestran huyNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry by Prince Sir: Chemical Kinetics DPP-1Document4 pagesPhysical Chemistry by Prince Sir: Chemical Kinetics DPP-1PunisherNo ratings yet
- F6 AL Chemistry (Tutorial 11) : (I) Multiple ChoicesDocument4 pagesF6 AL Chemistry (Tutorial 11) : (I) Multiple Choicesfire historyNo ratings yet
- PLTL Ch. 16 AssignmentDocument6 pagesPLTL Ch. 16 AssignmentJules BrunoNo ratings yet
- Practice Final CHE1112Document13 pagesPractice Final CHE1112dancer88838No ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics AssignmentDocument15 pagesChemical Kinetics AssignmentVanshdip RawatNo ratings yet
- Chemistry File 4Document4 pagesChemistry File 4Pawan Kumar100% (1)
- Chemical Kinetics 1Document103 pagesChemical Kinetics 1drvssssmcrobertganjNo ratings yet
- Deodhar Classes PDF 2Document6 pagesDeodhar Classes PDF 2Aditya MoreNo ratings yet
- MCD4390 Week 10 Tutorial QuestionsDocument5 pagesMCD4390 Week 10 Tutorial QuestionsGabbar100% (1)
- 08a. Chemical Kinetics SheetDocument33 pages08a. Chemical Kinetics SheetVIKRANTH KUMAR JAKKOJUNo ratings yet
- JH PC Chemical Kinetics DPP 22 To 34Document18 pagesJH PC Chemical Kinetics DPP 22 To 34The IndianNo ratings yet
- 101DPP 1 Chemical Kinetics C4U Sahendra KumarDocument3 pages101DPP 1 Chemical Kinetics C4U Sahendra KumarR K Meena JhopadiNo ratings yet
- Chm271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesChm271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical Kineticsfiefy zmrNo ratings yet
- CHM271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesCHM271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical KineticsisfaNo ratings yet
- Chm271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesChm271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical KineticsisfaNo ratings yet
- Deodhar Classes PDF 1Document6 pagesDeodhar Classes PDF 1Aditya MoreNo ratings yet
- CH 12 Prac Test Kinetics1Document15 pagesCH 12 Prac Test Kinetics1NolemNo ratings yet
- Deodhar Classes Edited PDF 12Document6 pagesDeodhar Classes Edited PDF 12Aditya MoreNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics-1Document50 pagesChemical Kinetics-1telangtanushreeNo ratings yet
- Xii - Chemistry - QPDocument6 pagesXii - Chemistry - QPJHADESWAR RESIDENTIAL COLLEGENo ratings yet
- Question On Chemical Kinetics-MA 2022Document12 pagesQuestion On Chemical Kinetics-MA 2022Sangay ChodenNo ratings yet
- 102 MSJC 13Document11 pages102 MSJC 13noelNo ratings yet
- Application of Rate ReactionDocument10 pagesApplication of Rate ReactionRahmawati PutrianasariNo ratings yet
- Ch123 Exam II Practice Exam Spring2011Document7 pagesCh123 Exam II Practice Exam Spring2011christopher92530% (1)
- EDUC 3136 A TeST 1 Reaction Kinetics 2023 PDFDocument11 pagesEDUC 3136 A TeST 1 Reaction Kinetics 2023 PDFKgaugelo FenyaneNo ratings yet
- Ntu 2008 ChemDocument6 pagesNtu 2008 ChemAgitya Putra KusumaNo ratings yet
- 05 - Chemical Kinetics (Level) .PDF Module-6-1Document15 pages05 - Chemical Kinetics (Level) .PDF Module-6-1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet 2Document3 pagesChemistry Worksheet 2LemontNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Chemical KineticsDocument10 pagesChapter 13 Chemical KineticsJacob McPhersonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics - Practice SheetDocument17 pagesChemical Kinetics - Practice Sheetnepogi1509No ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument11 pagesChemical KineticssamarthNo ratings yet
- Practice Rate Law ProblemsDocument6 pagesPractice Rate Law ProblemsPatriciaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-Manual CH1002Document18 pagesTutorial-Manual CH1002Gift Chulu100% (2)
- Worksheet 1 KineticsDocument1 pageWorksheet 1 KineticsarshbirksidhuNo ratings yet
- CH-4 Kinetics MaterialDocument18 pagesCH-4 Kinetics MaterialBishal MishraNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument4 pagesChemical KineticssathishNo ratings yet
- 10th ChemistryDocument4 pages10th ChemistrySana AshfaqNo ratings yet
- 4.chemical Kinetics KCET PYQsDocument2 pages4.chemical Kinetics KCET PYQsPunith kumar100% (4)
- QP - Chemistry - 12 - Set 1Document6 pagesQP - Chemistry - 12 - Set 1Akash SureshNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper Term IIDocument3 pagesSample Question Paper Term IIKafeel ShahNo ratings yet
- Revision Note Chemical KineticsDocument20 pagesRevision Note Chemical KineticsAprillia ChanNo ratings yet
- Bài tập Động hóa học chương 2Document2 pagesBài tập Động hóa học chương 2Thảo PhươngNo ratings yet
- Practice Rate Law ProblemsDocument12 pagesPractice Rate Law ProblemsCatrina RiveraNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics LectureDocument22 pagesChemical Kinetics LectureMohamed MegahedNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Class 12 2024Document10 pagesSample Paper Class 12 2024jinturay1212No ratings yet
- OCR - Chemistry - Module 5 Part 1 - GraspIT ANSWERS - A LevelDocument10 pagesOCR - Chemistry - Module 5 Part 1 - GraspIT ANSWERS - A LevelSigourney MarshNo ratings yet
- 11 HalfDocument6 pages11 HalfsgrnaharantuNo ratings yet
- Revisin Test - Chemical KineticsDocument4 pagesRevisin Test - Chemical KineticsSABIQNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics FinalDocument7 pagesChemical Kinetics Finalaxiliya6No ratings yet
- Chemistry QP5Document5 pagesChemistry QP5Jinendra UvarajNo ratings yet
- CH13 Practice ExamDocument8 pagesCH13 Practice ExamAnonymous WI0nbsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 HOME WITH ANSDocument7 pagesChapter 14 HOME WITH ANSSerpicoNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL KINETICS FinalDocument6 pagesCHEMICAL KINETICS FinalBOTHRA CLASSESNo ratings yet
- NEET Sample (Model-5) Question Paper With Answer Keys - Free PDF DownloadDocument40 pagesNEET Sample (Model-5) Question Paper With Answer Keys - Free PDF Downloadt.nishar61258No ratings yet
- Kinetics Lec-1 NEET ChalisaDocument35 pagesKinetics Lec-1 NEET Chalisaashustarguy005No ratings yet
- Sample Question Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics and BiologyDocument5 pagesSample Question Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics and BiologyDhanashreeNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsFrom EverandElectrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsAndrzej LewenstamNo ratings yet
- QSN Bank On Coordination Compounds 2012-2022Document10 pagesQSN Bank On Coordination Compounds 2012-2022prathmfedNo ratings yet
- DPP-01 Chemical KineticsDocument1 pageDPP-01 Chemical Kineticsprathmfed100% (1)
- QSN Bank On Aldehydes 2012-2022Document26 pagesQSN Bank On Aldehydes 2012-2022prathmfedNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Coordination CompoundsDocument8 pagesAssignment On Coordination CompoundsprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Cblechpl 06125Document9 pagesCblechpl 06125prathmfedNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics 2020-2022Document6 pagesChemical Kinetics 2020-2022prathmfedNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Aldehydes-Ketones-Carboxylic AcidsDocument2 pagesAssignment On Aldehydes-Ketones-Carboxylic AcidsprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Solid State, Solutions and KineticsDocument12 pagesAssignment On Solid State, Solutions and KineticsprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Nomenclature of Aldehyde-KetonesDocument2 pagesAssignment On Nomenclature of Aldehyde-KetonesprathmfedNo ratings yet
- DPP 02Document1 pageDPP 02prathmfedNo ratings yet
- Yet QSNS On Mole ConceptDocument2 pagesYet QSNS On Mole ConceptprathmfedNo ratings yet
- MCQS'S On Solutions MARKS: 50X4 200M TIME:150MIN: Y Y X X Y Y X XDocument1 pageMCQS'S On Solutions MARKS: 50X4 200M TIME:150MIN: Y Y X X Y Y X XprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics (Order/First Order/Half - Life) Code: 2019-20/3Document1 pageChemical Kinetics (Order/First Order/Half - Life) Code: 2019-20/3prathmfedNo ratings yet
- Jee Advanced Test On EquilibriaDocument2 pagesJee Advanced Test On EquilibriaprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Classification of PlantsDocument12 pagesClassification of Plantsprathmfed100% (1)
- Lesson 7 EnergyDocument16 pagesLesson 7 EnergyprathmfedNo ratings yet
- School Lesson PlanDocument17 pagesSchool Lesson PlanprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 WorkDocument15 pagesLesson 2 WorkprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Niit Most Effective Social Media Platform TodayDocument24 pagesNiit Most Effective Social Media Platform Todayprathmfed50% (4)
- Method 3 Gas Analysis For Carbon Dioxide, Oxygen, Excess Air, and Dry Molecular WeightDocument17 pagesMethod 3 Gas Analysis For Carbon Dioxide, Oxygen, Excess Air, and Dry Molecular WeightAhmad RyderNo ratings yet
- SRS 400 A 475 GPMDocument12 pagesSRS 400 A 475 GPMrhusseinpos4765No ratings yet
- The Stall Chart - Varying Flow Secondary - Constant Inlet Temperature - Constant Outlet TemperatureDocument8 pagesThe Stall Chart - Varying Flow Secondary - Constant Inlet Temperature - Constant Outlet TemperatureSandra FerrellNo ratings yet
- OSHA Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs) - Tabla 2Document4 pagesOSHA Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs) - Tabla 2ivan20175029bNo ratings yet
- C10 Silicone MSDSDocument8 pagesC10 Silicone MSDSlukasjoNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectroscopy: - : Presented By:-Amruta S. Sambarekar 1 Year M.Pharm Dept. of Pharmaceutics M M C P, BelgaumDocument56 pagesMass Spectroscopy: - : Presented By:-Amruta S. Sambarekar 1 Year M.Pharm Dept. of Pharmaceutics M M C P, Belgaumsaurabh chaturvediNo ratings yet
- A05 1032 PDFDocument2 pagesA05 1032 PDFArgile-assholeNo ratings yet
- Journal of The Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers Volume 45 Issue 6 2014 (Doi 10.1016/j.jtice.2014.05.012) Ameduri, Bruno - Recent Advances in The Controlled Radical (Co) Polymerization of FluoDocument10 pagesJournal of The Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers Volume 45 Issue 6 2014 (Doi 10.1016/j.jtice.2014.05.012) Ameduri, Bruno - Recent Advances in The Controlled Radical (Co) Polymerization of FluoRyan Eka JuniawanNo ratings yet
- Brominator Pages ExtractDocument2 pagesBrominator Pages ExtractSatya SharmaNo ratings yet
- TheQuestforTheCures 11EpisodeTranscriptsEbookDocument273 pagesTheQuestforTheCures 11EpisodeTranscriptsEbookanon_59594913850% (2)
- AUBF LAB - Chemical Examination of UrineDocument7 pagesAUBF LAB - Chemical Examination of Urinecdsteenkamp18No ratings yet
- Finishing Agents & Specialty ChemicalsDocument4 pagesFinishing Agents & Specialty Chemicals950 911No ratings yet
- Important Books For IITDocument13 pagesImportant Books For IITChennaiSuperkings100% (2)
- KaMin™ 2000C - Calcined Kaolin ClayDocument1 pageKaMin™ 2000C - Calcined Kaolin Claymarco_ravelo_10No ratings yet
- Raj1 PDFDocument35 pagesRaj1 PDFAvdhoot Gautam100% (1)
- Form 3 Module Chapter 4 Reativity of MetalsDocument11 pagesForm 3 Module Chapter 4 Reativity of Metalsgrace_lo_1100% (1)
- Brochure ZA ProductGuideDocument16 pagesBrochure ZA ProductGuideAli MasyhurNo ratings yet
- 30247073B V11.21 DSC3 Brochure EN LRDocument24 pages30247073B V11.21 DSC3 Brochure EN LRthoanp1990No ratings yet
- EASA Mod 7A BK 5 Elect CableDocument59 pagesEASA Mod 7A BK 5 Elect CableVasco M C Santos100% (1)
- AMPHOTERIC L Tech DataDocument3 pagesAMPHOTERIC L Tech Datadedete100% (1)
- Molar Concentration Step-By-Step Working Out Using Titration ResultsDocument3 pagesMolar Concentration Step-By-Step Working Out Using Titration Resultsshania chambersNo ratings yet
- Dry Eyes Drug TreatmentDocument3 pagesDry Eyes Drug Treatmentlu100% (1)
- AMPALAYA (Momordica Charantia) LEAVES EXTRACT As An Alternative MolluscicideDocument28 pagesAMPALAYA (Momordica Charantia) LEAVES EXTRACT As An Alternative MolluscicideSchievvie AbanillaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Plaque Control PedoDocument54 pagesMechanical Plaque Control PedoFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocument6 pagesAgarose Gel ElectrophoresisJêyà BharathìNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Analysis: Product Code: Q11007 Batch No: 6498201120 Qualigens Mfg. Date: November 2020Document2 pagesCertificate of Analysis: Product Code: Q11007 Batch No: 6498201120 Qualigens Mfg. Date: November 2020pervaz anwer0% (1)
- Lattner Instruction Manual 2005 - WLF ModelsDocument87 pagesLattner Instruction Manual 2005 - WLF Modelsethen223No ratings yet
- Composites: ASTM D7264 Flexural Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite MaterialsDocument2 pagesComposites: ASTM D7264 Flexural Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite MaterialsnileshbagaleNo ratings yet
- Ncr18650 DatasheetDocument1 pageNcr18650 DatasheetDNIndustryNo ratings yet