Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sonographic Anatomy of The Neck - The Suprahyoid Region - Abstract
Sonographic Anatomy of The Neck - The Suprahyoid Region - Abstract
Uploaded by
jmccoyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sonographic Anatomy of The Neck - The Suprahyoid Region - Abstract
Sonographic Anatomy of The Neck - The Suprahyoid Region - Abstract
Uploaded by
jmccoyCopyright:
Available Formats
Sonographic anatomy of the neck: The suprahyoid region - ScienceDirect Page 1 of 3
Journals & Books
Create account Sign in
Get Access Share Export
Journal of Ultrasound
Volume 14, Issue 3, September 2011, Pages 130-135
Sonographic anatomy of the neck: The suprahyoid region
A. Gervasio , G. D’Orta, I. Mujahed, A. Biasio
Show more
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jus.2011.06.001 Get rights and content
Abstract
The suprahyoid region extends from the base of the skull to the hyoid bone and
includes the pharyngeal, parapharyngeal, parotid, carotid, masticator, retropharyngeal,
and perivertebral spaces, as well as the oral cavity. The areas that can be explored by
ultrasound include the parotid, carotid, and masticator spaces; the oral cavity; the
submandibular and sublingual spaces; the floor of the mouth; and the root of the
tongue. The parotid space contains the parotid gland and the excretory duct of Steno,
the facial nerve, the external carotid artery, the retromandibular vein, and the
intraparotid lymph nodes. The carotid space in the suprahyoid region of the neck
contains the internal carotid artery, the internal jugular vein, cranial nerves IX to XII,
and the sympathetic plexus. Only some parts of the masticator space can be explored
sonographically: these include the masseter muscle, the zygomatic arch and the outer
cortex of the ramus of the mandible, and the suprazygomatic portion of the temporalis
muscle. The submandibular space houses the submandibular gland, the submental and
submandibular lymph nodes, and the anterior belly of digastric muscle. The facial
artery and vein and the lower loop of the hypoglossal nerve all pass through the
submandibular space. The sublingual space includes the sublingual gland, the deep
portion of the submandibular gland and its main excretory duct, the hypoglossal nerve
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S197134951100035X?via%3Dihub 5/9/19
You might also like
- Cosmetic Otoplasty 2018 DBDocument11 pagesCosmetic Otoplasty 2018 DBcirugia plastica uisNo ratings yet
- Abstract - Sonographic Anatomy of The Neck - Suprahyoid RegionDocument1 pageAbstract - Sonographic Anatomy of The Neck - Suprahyoid RegionjmccoyNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Anatomy of The Neck - The Infrahyoid Region - AbstractDocument1 pageUltrasound Anatomy of The Neck - The Infrahyoid Region - AbstractjmccoyNo ratings yet
- Sushma 3rd Seminar Arterial Supply and Venous Drainage of HeadDocument63 pagesSushma 3rd Seminar Arterial Supply and Venous Drainage of HeadDrSushma NareshNo ratings yet
- Regjionet 2Document105 pagesRegjionet 2Rijad Musli100% (1)
- Salivary Gland AnatomyDocument38 pagesSalivary Gland AnatomyAlex HaileyesusNo ratings yet
- Fascialspaceinfections 140219122023 Phpapp01Document58 pagesFascialspaceinfections 140219122023 Phpapp01muhamed sayedNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Head and NeckDocument176 pagesMuscles of The Head and Neckpianistgirl99No ratings yet
- Case Report CSOMDocument13 pagesCase Report CSOMNashria RusdhyNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development of Cranial Base: SeminarDocument34 pagesGrowth and Development of Cranial Base: SeminarMNSNo ratings yet
- US Anatomy of The Neck 2Document5 pagesUS Anatomy of The Neck 2Ignacio Navarrete LorenzonNo ratings yet
- 210190Document6 pages210190meher chohanNo ratings yet
- Carlson 2000Document13 pagesCarlson 2000Mamadou DIENENo ratings yet
- Deep Neck Infection 051005Document43 pagesDeep Neck Infection 051005Vishal GauravNo ratings yet
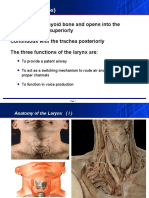
- Anatomy and Physiology of LarynxDocument37 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Larynxsuci100% (2)
- Head Neck and Oral CavityDocument41 pagesHead Neck and Oral Cavitymeharnigar123No ratings yet
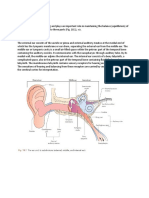
- Exterior and Middle EarDocument26 pagesExterior and Middle EarAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Head and Face: Dr. Muh. Iqbal Basri, M.Kes, SP.SDocument34 pagesHead and Face: Dr. Muh. Iqbal Basri, M.Kes, SP.SamiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter V - Human Anatomy: 7-Resources & Indexes Module 8-AbbreviationsDocument4 pagesChapter V - Human Anatomy: 7-Resources & Indexes Module 8-AbbreviationsIndranil SinhaNo ratings yet
- Imaging The Oral Cavity - Key Concepts For The Radiologist - PMCDocument24 pagesImaging The Oral Cavity - Key Concepts For The Radiologist - PMCVilaseca224466No ratings yet
- Ve Summary ChartDocument10 pagesVe Summary ChartMoliNo ratings yet
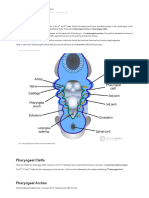
- The Pharyngeal Arches - Clefts - Pouches - Embryology - TeachMeAnatomyDocument4 pagesThe Pharyngeal Arches - Clefts - Pouches - Embryology - TeachMeAnatomypinkrawpineappleNo ratings yet
- RADI AnatomyDocument37 pagesRADI AnatomyAmanda AmaroNo ratings yet
- II - 51. The Parotid Salivary GlandDocument5 pagesII - 51. The Parotid Salivary GlandAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck Anatomy: A. Arsalan, MD M. Martin MD, DMD October 4-5, 2017Document53 pagesHead and Neck Anatomy: A. Arsalan, MD M. Martin MD, DMD October 4-5, 2017aaamirrrNo ratings yet
- The Infratemporal FossaDocument5 pagesThe Infratemporal FossaxxyumeNo ratings yet
- Larynx (Voice Box)Document59 pagesLarynx (Voice Box)alfaz lakhaniNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy SyllabusDocument3 pagesGeneral Anatomy SyllabusPatricia patriciaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Tables-Arteries of The Head and NeckDocument20 pagesAnatomy Tables-Arteries of The Head and NeckTracie YWNo ratings yet
- Anatomyofthe Auditory SystemDocument6 pagesAnatomyofthe Auditory System32. Nguyễn Tiến Thái SơnNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of EarDocument17 pagesAnatomy of Earkresha solankiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology THT - Dr. AriefDocument88 pagesAnatomy and Physiology THT - Dr. AriefGilbert Sterling OctaviusNo ratings yet
- Lecture Medskull - ModofiedDocument88 pagesLecture Medskull - ModofiedNikolai SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Parotid GlandDocument2 pagesParotid Glandneleh grayNo ratings yet
- Deep Neck Space Infections: Best Viewed As A Powerpoint Slideshow To Insure That Overlays Are SeenDocument43 pagesDeep Neck Space Infections: Best Viewed As A Powerpoint Slideshow To Insure That Overlays Are SeenGilang Kurnia HirawatiNo ratings yet
- Human Function AnatomyDocument8 pagesHuman Function AnatomyaishbiyaNo ratings yet
- The Anatomical Record - ) SakamotoDocument9 pagesThe Anatomical Record - ) SakamotoIngridNatalyYomayuzaNo ratings yet
- Found 903118732 4683Document2 pagesFound 903118732 4683Bogdan Robert CNo ratings yet
- 7 Submandibular Region-Dr - GosaiDocument14 pages7 Submandibular Region-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Pharynx NotesDocument8 pagesPharynx Notesm0rat0r1umNo ratings yet
- Craneo Sobotta PDFDocument111 pagesCraneo Sobotta PDFMaria Teresa AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Plastic Surgery Board NotesDocument69 pagesPlastic Surgery Board Notesseandarcy600100% (1)
- PPP LarynxDocument65 pagesPPP LarynxAnkur MittalNo ratings yet
- Diffuse Otitis Externa: Case ReportDocument21 pagesDiffuse Otitis Externa: Case ReportKalvin DersingNo ratings yet
- External EarDocument3 pagesExternal EarbarbacumlaudeNo ratings yet
- Imaging The Oral Cavity 2011Document14 pagesImaging The Oral Cavity 2011Vivie SantidamrongkulNo ratings yet
- Skull Base Embryology: A Multidisciplinary ReviewDocument10 pagesSkull Base Embryology: A Multidisciplinary ReviewJulio AbarzuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 139 Anatomy of The Skull Base Temporal Bone External Ear and Middle Ear Larry G Duckert - CompressDocument12 pagesChapter 139 Anatomy of The Skull Base Temporal Bone External Ear and Middle Ear Larry G Duckert - CompressWudieNo ratings yet
- Triangles of NeckDocument6 pagesTriangles of NeckDr santoshNo ratings yet
- Pharynx: DissectionDocument23 pagesPharynx: DissectionrajtanniruNo ratings yet
- A Study of Auricle Morphology For Identification in IndiansDocument8 pagesA Study of Auricle Morphology For Identification in IndiansRohin GargNo ratings yet
- Fowl Course 214Document10 pagesFowl Course 214Mohamed MaherNo ratings yet
- Case2 Osteo MuscullusDocument2 pagesCase2 Osteo Muscullussyifa salsabila defci putriNo ratings yet
- ანატომია ზეპირიDocument22 pagesანატომია ზეპირიmaNo ratings yet
- Facial NerveDocument23 pagesFacial NerveAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The FaceDocument24 pagesAnatomy of The Faceashley nicholeNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Hearing and EarDocument10 pagesThe Physiology of Hearing and EarMustafam98No ratings yet
- CT Neck Anatomy DemystifiedDocument26 pagesCT Neck Anatomy DemystifiedTapi imaging centre Vyara dist TapiNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- Osteopathic Fascia Treatment Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesOsteopathic Fascia Treatment Peripheral Nervous SystemjmccoyNo ratings yet
- Chiropractic and Energy Medicine A Shared HistoryDocument28 pagesChiropractic and Energy Medicine A Shared HistoryjmccoyNo ratings yet
- Median Arcuate Ligament SyndromeDocument2 pagesMedian Arcuate Ligament SyndromejmccoyNo ratings yet
- Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension PDFDocument34 pagesIdiopathic Intracranial Hypertension PDFjmccoyNo ratings yet
- JMDH 7 011 Skin Fascia and ScarsDocument14 pagesJMDH 7 011 Skin Fascia and ScarsjmccoyNo ratings yet
- Neurological Manifestations of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome(s)Document14 pagesNeurological Manifestations of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome(s)jmccoy100% (2)
- Saliva Transit and GERDDocument6 pagesSaliva Transit and GERDjmccoyNo ratings yet
- Abstract - Sonographic Anatomy of The Neck - Suprahyoid RegionDocument1 pageAbstract - Sonographic Anatomy of The Neck - Suprahyoid RegionjmccoyNo ratings yet
- Study of Children With AerophagiaDocument7 pagesStudy of Children With AerophagiajmccoyNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Facet Pain ArticleDocument24 pagesLumbar Facet Pain ArticlejmccoyNo ratings yet
- Diastasis Recti 0038 1661380Document7 pagesDiastasis Recti 0038 1661380jmccoyNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Anatomy of The Neck - The Infrahyoid Region - AbstractDocument1 pageUltrasound Anatomy of The Neck - The Infrahyoid Region - AbstractjmccoyNo ratings yet
- Passive and Active Contributions To Glenohumeral StabilityDocument5 pagesPassive and Active Contributions To Glenohumeral StabilityjmccoyNo ratings yet
- The Innervation of The Soft Palate MusclesDocument7 pagesThe Innervation of The Soft Palate MusclesjmccoyNo ratings yet