Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Partial Seizures 1
Partial Seizures 1
Uploaded by
R0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
108 views13 pagesThis document discusses drugs used for partial seizures. The main drugs discussed are carbamazepine, lamotrigine, valproate, and phenytoin. It provides information on their mechanisms of action, indications, dosages, and effectiveness for treating different types of partial seizures including simple partial seizures, complex partial seizures, and seizures that secondarily generalize. Other adjunctive or alternative treatment options are also listed.
Original Description:
Mbbs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses drugs used for partial seizures. The main drugs discussed are carbamazepine, lamotrigine, valproate, and phenytoin. It provides information on their mechanisms of action, indications, dosages, and effectiveness for treating different types of partial seizures including simple partial seizures, complex partial seizures, and seizures that secondarily generalize. Other adjunctive or alternative treatment options are also listed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
108 views13 pagesPartial Seizures 1
Partial Seizures 1
Uploaded by
RThis document discusses drugs used for partial seizures. The main drugs discussed are carbamazepine, lamotrigine, valproate, and phenytoin. It provides information on their mechanisms of action, indications, dosages, and effectiveness for treating different types of partial seizures including simple partial seizures, complex partial seizures, and seizures that secondarily generalize. Other adjunctive or alternative treatment options are also listed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 13
DRUGS
USED FOR PARTIAL SEIZURES
Mentor: Dr. Yogeeta Walke
• Carbamazepine
• Lamotrigine
• Valproate
• Phenytoin
GROUP MEMBERS
• Rea Fernandes
• Ritz Alfonso
• Reshma Salunkhe
• Samantha Pinto
• Rajashwini Sarnaik
• Saumya Pal
• Siddhi Savoiverekar
• Sharon Thomas
• Shefali Gauns
• Shiara Afonso
PARTIAL SEIZURES
1. Simple parPal seizures
• Convulsions -group of muscles or localized sensory disturbance
depending on area of cortex involved lasPng 1/2–1 min
• without loss of consciousness.
2. Complex parPal seizures (CPS, temporal lobe epilepsy, psychomotor)
• aZacks of bizarre and confused behaviour, purposeless movements,
emoPonal changes lasPng 1–2 min
• with impairment of consciousness.
• Aura o[en precedes.
• seizure focus-temporal lobe.
3. Simple parPal or complex parPal seizures secondarily generalized
• parPal seizure evolves into GTCS
• with loss of consciousness.
PHENYTOIN
MECHANISM
! Stabilizing influence on neuronal membrane
Blocks Na+ channels
Prolongs inacPvated state of voltage sensiPve neuronal Na+ channel
Prevents repePPve detonaPon of normal brain cells during
‘depolarizaPon shi[’
! TherapeuPc concentraPons
• High frequency discharges inhibited
• LiZle effect on normal low frequency discharges
• Which allow Na+ channels to recover
! Has no effect on resPng membrane potenPal: normal synapPc
transmission is not impaired.
! Does not interfere with kindling
INDICATIONS
• Simple parPal seizures
• Complex parPal seizures –added to
carbamazepine
• DOSE 100mg BD maximum 400mg/day
CARBAMAZEPINE
MECHANISM OF ACTION
• Na+ channels- prolongaPon of inacPvated
state
• Inhibits high frequency neuronal discharges
and presynapPc acPon -decreased transmiZer
release
• Inhibits kindling
INDICATIONS
• Most effecPve for CPS
• GTCS
• SPS
• Preferred in young girls -cosmePc side
effects of phenytoin (hirsuPsm)
• Dose:
! 200–400 mg TDS
! Children 15–30 mg/kg/day
LAMOTRIGINE
MECHANISM OF ACTION
! New anPconvulsant -carbamazepine-like acPon :
• Prolongs Na+ channel inacPvaPon and suppression of
high frequency firing
• Directly blocks voltage sensiPve Na+ channels thus
-stabilizing the presynapPc membrane
-prevenPng release of excitatory neurotransmiZers
(glutamate and aspartate) -broader-spectrum of
anPseizure efficacy.
• Does not antagonize PTZ seizures or block NMDA type
of glutamate receptors.
INDICATION
• Simple parPal seizures-add-on therapy in
cases with incomplete/poor response
• Complex parPal L-added in refractory cases.
• Dose: 50 mg/day iniPally, increase upto 300
mg/day as needed; not to be used in children.
VALPROATE
MECHANISM OF ACTION
MulPple mechanisms:
• Frequency-dependent prolongaPon of Na+
channel inacPvaPon
• Weak aZenuaPon of Ca2+ mediated ‘T’ current
• AugmentaPon of release of inhibitory transmiZer
GABA by
" inhibiPng its degradaPon (by GABA-
transaminase)
" increasing its synthesis from glutamic acid.
• Responses to exogenously applied GABA are not
altered
INDICATION
• AlternaPve/adjuvant drug for GTCS, SPS and
CPS
• Used with cauPon young children -hepaPc
toxicity
• Dose: Adults—
start with 200 mg TDS,
maximum 800 mg TDS
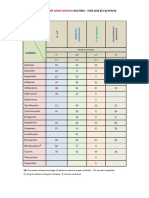
Type of seizure First choice drugs Second choice Add-on drugs
Alterna9ve Add-on drugs
drugs
simple parPal with Carbamazepine, Valproate, Lamotrigine,
or without Phenytoin Phenobarbitone GabapenPn,
generalizaPon Topiramate,
Primidone,
LevePracetam
Complex parPal Carbamazepine, GabapenPn, Clobazam,
with or without Valproate, Lamotrigine, Zonisamide,
generalizaPon Phenytoin LevePracetam Topiramate
You might also like
- Anti-Drug Campaign SpeechDocument2 pagesAnti-Drug Campaign SpeechGracel Gonzaga Eviota92% (12)
- AnticonvulsantDocument21 pagesAnticonvulsantSWATINo ratings yet
- Antiepilepticsnaser 160502063005Document30 pagesAntiepilepticsnaser 160502063005Vivek PandeyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of Epilepsy: Nandit P BDocument53 pagesPharmacotherapy of Epilepsy: Nandit P BNandit BanawalikarNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs 2019 Elearning PDFDocument39 pagesAntiepileptic Drugs 2019 Elearning PDFMalvika BabuNo ratings yet
- 3, Antiepileptic DrugsDocument39 pages3, Antiepileptic DrugsAbebe TilahunNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy Is Due To Sudden, Excessive Depolarization Of: Some or All Cerebral NeuronsDocument19 pagesEpilepsy Is Due To Sudden, Excessive Depolarization Of: Some or All Cerebral NeuronsMourian AmanNo ratings yet
- 2015 AntiepilepticsDocument36 pages2015 AntiepilepticsRumaidhil AbroryNo ratings yet
- Anti-Epileptic Drugs: - Classification of SeizuresDocument31 pagesAnti-Epileptic Drugs: - Classification of Seizuresdinesh33272No ratings yet
- 18aantiepileptic Drugs With ClobazamDocument29 pages18aantiepileptic Drugs With ClobazampabitraNo ratings yet
- Anti-Seizure Drugs MD4Document41 pagesAnti-Seizure Drugs MD4Sabeth MeyofNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs (Aed) : R. Anita. IndriyantiDocument36 pagesAntiepileptic Drugs (Aed) : R. Anita. Indriyantiandisti2323No ratings yet
- Drugs For Epilepsy: Lippincott, Chapter 12Document58 pagesDrugs For Epilepsy: Lippincott, Chapter 12Fourth YearNo ratings yet
- Dry Mouth: Prescribed For Newly Diagnosed, Mild DepressionDocument2 pagesDry Mouth: Prescribed For Newly Diagnosed, Mild DepressionAlya FerdausNo ratings yet
- 24 Antiseizure DrugsDocument71 pages24 Antiseizure DrugsThea MallariNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic DrugsDocument43 pagesAntiepileptic DrugsdrpraneethpremkumarNo ratings yet
- Sedative HypnoticsDocument27 pagesSedative HypnoticsPrecious FulgarinasNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy I IDocument57 pagesEpilepsy I IAhmad abu-dayyehNo ratings yet
- Anti EpilepticsDocument61 pagesAnti EpilepticsRamya RNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of MigraineDocument74 pagesPharmacotherapy of MigraineAvin GupthaNo ratings yet
- EpilepsyDocument11 pagesEpilepsyStella WatkinsNo ratings yet
- Mood StabDocument35 pagesMood StabAalia RanaNo ratings yet
- EpilepsyDocument11 pagesEpilepsyStella WatkinsNo ratings yet
- Cns Part 2 TransDocument3 pagesCns Part 2 TransAriNo ratings yet
- Anti-Epileptic Drugs: - Classification of SeizuresDocument31 pagesAnti-Epileptic Drugs: - Classification of SeizuresgopscharanNo ratings yet
- Null 1Document60 pagesNull 1tbuyinza21apNo ratings yet
- 14-Chapter 17-Drugs For EpilepsyDocument23 pages14-Chapter 17-Drugs For EpilepsyCandilicious10No ratings yet
- PriseChargeTherapEpilepsie Navarro 2015Document43 pagesPriseChargeTherapEpilepsie Navarro 2015Aya KheNo ratings yet
- 1) Selective Serotonin Reuptic Inhepetor (SSRI) - Xetine: Fluoxetine, Paroxetine, Sertraline, DoluexitineDocument13 pages1) Selective Serotonin Reuptic Inhepetor (SSRI) - Xetine: Fluoxetine, Paroxetine, Sertraline, DoluexitineSEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System Pharmacology: Elly Nurus SakinahDocument64 pagesCentral Nervous System Pharmacology: Elly Nurus Sakinahkareem92No ratings yet
- Tablas Farmacos SNCDocument75 pagesTablas Farmacos SNCServaNo ratings yet
- LcetamDocument40 pagesLcetampabitraNo ratings yet
- Antiseizure DrugsDocument10 pagesAntiseizure DrugsJoyce SumagaysayNo ratings yet
- Anti EpilepticsDocument29 pagesAnti Epilepticskeerthi sivayanamaNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs.Document32 pagesAntiepileptic Drugs.pabitraNo ratings yet
- AntiConvulsants Drugs in Brief PDFDocument28 pagesAntiConvulsants Drugs in Brief PDFSunilNo ratings yet
- Drug Treatment in Epilepsy: Martin Reed Pharmacy QEPH Miriam WilcherDocument60 pagesDrug Treatment in Epilepsy: Martin Reed Pharmacy QEPH Miriam WilcherBibek RajNo ratings yet
- Anti-Epileptics: Dr. Nishant B. Bhansali AP (Pharmacology)Document47 pagesAnti-Epileptics: Dr. Nishant B. Bhansali AP (Pharmacology)ankit ahirNo ratings yet
- Antiseizure AgentsDocument62 pagesAntiseizure Agentsakoeljames8543No ratings yet
- Cancer Topic DiscussionDocument13 pagesCancer Topic Discussionapi-610938913No ratings yet
- NPLEX Combination Review Neurology - A: Paul S. Anderson, ND Medical Board Review ServicesDocument83 pagesNPLEX Combination Review Neurology - A: Paul S. Anderson, ND Medical Board Review ServicesValeria AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptics Class PPT - DR Anoosha BhandarkarDocument64 pagesAntiepileptics Class PPT - DR Anoosha BhandarkaranooshabhandarkarNo ratings yet
- MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF CLINICAL PROBLEMS 9th EditionDocument1 pageMEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF CLINICAL PROBLEMS 9th EditionMeryPinkihanNo ratings yet
- CNS PNS DrugsDocument29 pagesCNS PNS DrugsMadel A. AlberioNo ratings yet
- 2 Antiepliptic-1Document56 pages2 Antiepliptic-1tofikshafi121No ratings yet
- 5-Pharmacology of EpilepsyDocument57 pages5-Pharmacology of EpilepsyEbenezer Frimpong-MansoNo ratings yet
- Anti EpiDocument27 pagesAnti EpiMuhammad Tariq RazaNo ratings yet
- Drug Treatment of EpilepsyDocument81 pagesDrug Treatment of EpilepsyAnifowose SamsonNo ratings yet
- AntidepressantsDocument4 pagesAntidepressantsAhmed MansourNo ratings yet
- Pharma - Pharmacotherapy of Depression and AnxietyDocument3 pagesPharma - Pharmacotherapy of Depression and Anxietylim.shaina26No ratings yet
- Mayra Pagan: Pharmacology-NursingDocument50 pagesMayra Pagan: Pharmacology-NursingmayraNo ratings yet
- Cerebyx: Chan: BZS, Barbs, Topiramate Synthesis: Gabapentin Gaba Metab: Valproaic AcDocument3 pagesCerebyx: Chan: BZS, Barbs, Topiramate Synthesis: Gabapentin Gaba Metab: Valproaic AcGabriel FriedmanNo ratings yet
- Handout 2563 OpioidsDocument84 pagesHandout 2563 OpioidsPiya TangNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic DrugsDocument63 pagesAntiepileptic Drugsvpd100% (1)
- Peran Apoteker Dalam Pencapaian Epilepsi Yang TerkendaliDocument46 pagesPeran Apoteker Dalam Pencapaian Epilepsi Yang TerkendaliFina Ahmad FitrianaNo ratings yet
- Conventional Antiepileptic Drugs: Presented by Dr. Mehnaz MahmoodaDocument41 pagesConventional Antiepileptic Drugs: Presented by Dr. Mehnaz MahmoodaMehediNo ratings yet
- Eti Nurwening Sholikhah: Department of Pharmacology & Therapy Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah MadaDocument43 pagesEti Nurwening Sholikhah: Department of Pharmacology & Therapy Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah MadaadystiNo ratings yet
- ANTICONVULSANDocument18 pagesANTICONVULSANAndi Firda IndiraNo ratings yet
- Barbiturates: of Action of GABA. Independent of GABADocument10 pagesBarbiturates: of Action of GABA. Independent of GABAAvi WerdesheimNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteFrom EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Ottimizzazione del trattamento delle fluttuazioni motorie nella malattia di ParkinsonFrom EverandFast Facts: Ottimizzazione del trattamento delle fluttuazioni motorie nella malattia di ParkinsonNo ratings yet
- Graver Catalog 2012 PDFDocument76 pagesGraver Catalog 2012 PDFAskar HarisNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker: Authorized/approved VaccinesDocument8 pagesCOVID-19 Vaccine Tracker: Authorized/approved VaccinestucchaNo ratings yet
- Clarisa Bsph3y1-2 PTQM311 Assignelementswk5Document2 pagesClarisa Bsph3y1-2 PTQM311 Assignelementswk5Crisamor Clarisa100% (1)
- 5 Reaction KineticsDocument15 pages5 Reaction KineticsPamela Ann Taclob0% (1)
- PHARMACY MANAGEMENT PROJECT Ahmad IbitoyDocument116 pagesPHARMACY MANAGEMENT PROJECT Ahmad IbitoyHamna BadarNo ratings yet
- Fatal Side Effects: Medicine Patents Under The MicroscopeDocument61 pagesFatal Side Effects: Medicine Patents Under The MicroscopeOxfamNo ratings yet
- Buletin Farmasi 09/2013Document12 pagesBuletin Farmasi 09/2013afiq83No ratings yet
- Toxicology: Drugs and Poisons Forensic ScienceDocument22 pagesToxicology: Drugs and Poisons Forensic SciencecuambyahooNo ratings yet
- OrogelDocument2 pagesOrogelAbu SayedNo ratings yet
- NBCODocument2 pagesNBCObraveheart14No ratings yet
- To Use Kamias As Crack Heel RemoverDocument22 pagesTo Use Kamias As Crack Heel RemoverRenfred Paul TejeroNo ratings yet
- Asia3 Product List 2 PDFDocument17 pagesAsia3 Product List 2 PDFYoussef KaidNo ratings yet
- Botika BillDocument3 pagesBotika BillGirielynPoLaguismaNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug DeliveryDocument73 pagesTransdermal Drug DeliveryHairuddin To100% (2)
- Respiratory SystemDocument176 pagesRespiratory Systemwordlife360No ratings yet
- Gram-Negative Bacteria: Antibiogram of Bacteria - Year 2020 (Icu at Kfafh)Document2 pagesGram-Negative Bacteria: Antibiogram of Bacteria - Year 2020 (Icu at Kfafh)jen nalusNo ratings yet
- Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: An Evolutionary, Epidemiologic, and Therapeutic OdysseyDocument12 pagesMethicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: An Evolutionary, Epidemiologic, and Therapeutic OdysseyFelicia HalimNo ratings yet
- Azep Nasal SprayDocument3 pagesAzep Nasal SprayGaurav LoyalkaNo ratings yet
- Compounding in Hospital SettingDocument22 pagesCompounding in Hospital Settingkhangsiean89100% (1)
- Lidocaine - HPLCDocument3 pagesLidocaine - HPLCRoger (Sisfarma)No ratings yet
- Guideline For Treatment of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Guided by TheDocument16 pagesGuideline For Treatment of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Guided by TheLydia LydiaNo ratings yet
- Animal ScreeningDocument15 pagesAnimal ScreeningbbdddNo ratings yet
- Pt. Rania Jaya Farmarindo Daftar Harga Jual PersediaanDocument22 pagesPt. Rania Jaya Farmarindo Daftar Harga Jual PersediaanLalu EyiqNo ratings yet
- Extravasations DiagramDocument1 pageExtravasations DiagramJohnNo ratings yet
- 2014 Consensus Guidelines For The Management of PonvDocument29 pages2014 Consensus Guidelines For The Management of PonvHumaira Azmi100% (1)
- Pharmacy Resume Review Rubric PDFDocument3 pagesPharmacy Resume Review Rubric PDFsara elalfyNo ratings yet
- Shrooq Pharma Vaccant Product ListDocument10 pagesShrooq Pharma Vaccant Product ListangelicakhanNo ratings yet
- POPM IndianJAnaesth505345-128624 - 000208Document10 pagesPOPM IndianJAnaesth505345-128624 - 000208venkayammaNo ratings yet
- Case Study of UTIDocument6 pagesCase Study of UTIAmina TariqNo ratings yet