Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 viewsGrapeRootstock Chart
GrapeRootstock Chart
Uploaded by
Techgear Medan1. The document describes characteristics of important rootstocks for California vineyards, including their tolerance to nematodes, drought, salinity, and vigor influence on scion growth.
2. Some rootstocks that are tolerant to nematodes and drought include St. George, 1103P, and 140Ru, while rootstocks like 5BB, 5C, and Salt Creek are adapted to moist clay soils.
3. Growers must consider the soil type and mineral nutrition needs of their scion varieties when selecting a rootstock to ensure proper adaptation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- D5 Fortified Wines - An Accompaniment To The WSET Level 4 Diploma in Wines by Wine Spirit Education TrustDocument74 pagesD5 Fortified Wines - An Accompaniment To The WSET Level 4 Diploma in Wines by Wine Spirit Education TrustMatt HuntNo ratings yet
- Phase 2 NVC Habitat Survey Roudsea Wood and Mosses NNRDocument20 pagesPhase 2 NVC Habitat Survey Roudsea Wood and Mosses NNRapi-658315367100% (1)
- Giuseppe Concone Lyrical Studies For Trumpet em CDocument37 pagesGiuseppe Concone Lyrical Studies For Trumpet em CClistenes AndréNo ratings yet
- Introduction Watermelon (Citrullus Lanatus) Is An ImportantDocument9 pagesIntroduction Watermelon (Citrullus Lanatus) Is An ImportantparmardhavalNo ratings yet
- Glassware - F & - B Service EquipmentsDocument3 pagesGlassware - F & - B Service EquipmentsRajeev MathurNo ratings yet
- Cook's Illustrated 069Document36 pagesCook's Illustrated 069vicky61050% (2)
- Dossier Armand BrignacDocument15 pagesDossier Armand BrignacAnonymous 2Buf6xOegSNo ratings yet
- Rootstocks 24347Document4 pagesRootstocks 24347Rogerio GomesNo ratings yet
- Helliwell Provincial Park TEM 2001 Map LegendDocument3 pagesHelliwell Provincial Park TEM 2001 Map LegendKathy DunsterNo ratings yet
- At The End of Mill Road v1Document2 pagesAt The End of Mill Road v1qjwltxqxzrzxdxdhamNo ratings yet
- Lower-Level Categories in Soil Taxonomy: SubordersDocument5 pagesLower-Level Categories in Soil Taxonomy: SubordersGian Franco ValenciaNo ratings yet
- (Lesson 2, Module 3) How Ore Minerals Are Found, Mined & Processed For Human Use - SAUT - EXCDocument1 page(Lesson 2, Module 3) How Ore Minerals Are Found, Mined & Processed For Human Use - SAUT - EXCLydill Ann SautNo ratings yet
- Cerny 1991Document40 pagesCerny 1991HKTanoliNo ratings yet
- WEE'" Tony Williams: Is of ToDocument1 pageWEE'" Tony Williams: Is of Tocoo11No ratings yet
- Resource and Development Part C - Soil ResourceDocument7 pagesResource and Development Part C - Soil ResourceDarsh TodiNo ratings yet
- Geology and Exploration of Gold Placer DDocument14 pagesGeology and Exploration of Gold Placer Dyonathan tsegayeNo ratings yet
- Zodiac Degree InfluencesDocument13 pagesZodiac Degree InfluencesAnton KühnlächnerNo ratings yet
- ABRSM Grade 8 Theory TopicDocument1 pageABRSM Grade 8 Theory Topicdaphnelee.0821No ratings yet
- Irish Base Metal Deposits Field Trip SummaryDocument25 pagesIrish Base Metal Deposits Field Trip SummaryKenShin BlacKNo ratings yet
- Appendix I Departure Analysis TableDocument8 pagesAppendix I Departure Analysis TablelewiscreekNo ratings yet
- Valuation Report of MayadeviDocument7 pagesValuation Report of Mayadevi236ksfeNo ratings yet
- Richardspost Subduction Pdac 2019Document27 pagesRichardspost Subduction Pdac 2019Salvador SánchezNo ratings yet
- Vocabagrams PDFDocument1 pageVocabagrams PDFmaruf048No ratings yet
- Geo LN 1 Types of SoDocument2 pagesGeo LN 1 Types of SoParveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Geoscience Examination Package: For Geoscience Graduates (Petroleum Companies Exams)Document18 pagesGeoscience Examination Package: For Geoscience Graduates (Petroleum Companies Exams)Dana AbkhNo ratings yet
- We Three Kings2Document1 pageWe Three Kings2Paolo RomeroNo ratings yet
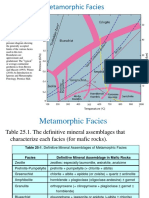
- Metamorphic FaciesDocument48 pagesMetamorphic FaciesNisha Singh100% (2)
- Exogenic Force Agents of Gradation Landforms (Weathering, Erosion, Deposition) SoilDocument1 pageExogenic Force Agents of Gradation Landforms (Weathering, Erosion, Deposition) SoilApichayaNo ratings yet
- University of Minnesota: Soil Test ReportDocument2 pagesUniversity of Minnesota: Soil Test ReportJose Cuadros LoayzaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 45 (PYQ Series 3) Notes ENGLISHDocument10 pagesLECTURE 45 (PYQ Series 3) Notes ENGLISHkeshavsharma6767No ratings yet
- Test 2 Answer SheetDocument4 pagesTest 2 Answer SheetAdi AlshtiwiNo ratings yet
- Geometry FormulaDocument12 pagesGeometry FormulaMiahSalitaNo ratings yet
- Formula 2Document6 pagesFormula 2Juven LuzorataNo ratings yet
- (L4) - (JLD 3.0) - Gravitation - 30th September.Document56 pages(L4) - (JLD 3.0) - Gravitation - 30th September.Dida CowernNo ratings yet
- Type of Soil Formation of Soil Characteristi C Feature Major CropDocument3 pagesType of Soil Formation of Soil Characteristi C Feature Major CropJenish PadshalaNo ratings yet
- Geo de La Minera Toqui PDFDocument29 pagesGeo de La Minera Toqui PDFDaniel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Igneous Rocks Desc ID Table Empty - Dropdown Menus 2.0Document7 pagesLab 2 Igneous Rocks Desc ID Table Empty - Dropdown Menus 2.0Kristika RaguthasNo ratings yet
- BHG Garden Plan Soften FenceDocument3 pagesBHG Garden Plan Soften Fenceargai ritaNo ratings yet
- Urubamba FinalDocument11 pagesUrubamba FinalJulissa Andrea Tahua MorenoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21 New Meta Facies 2 SP2017 Web BasedDocument58 pagesLecture 21 New Meta Facies 2 SP2017 Web BasedBharat MohaanaNo ratings yet
- AP Env Sci Cram Chart 2021Document1 pageAP Env Sci Cram Chart 2021高瑞韩No ratings yet
- GravitationDocument2 pagesGravitationgokulkrishna2k7No ratings yet
- Heb A Alphabet 2nded 2017Document18 pagesHeb A Alphabet 2nded 2017AlondraNo ratings yet
- GM Aid - Random Encounters - Generic RPGDocument1 pageGM Aid - Random Encounters - Generic RPGDon PerryNo ratings yet
- Basic Data of The Soil RegionsDocument23 pagesBasic Data of The Soil RegionsamicoadrianoNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 2 - Cordillera RealDocument12 pagesCapitulo 2 - Cordillera RealLeo VelascoNo ratings yet
- Koppen KemeDocument1 pageKoppen KemeunoporquezmartinNo ratings yet
- Porphyry Cu-Mo-Au and Related Epithermal Systems: Part 6: Post-Subduction DepositsDocument22 pagesPorphyry Cu-Mo-Au and Related Epithermal Systems: Part 6: Post-Subduction DepositsHugo Poma100% (1)
- Formation Evaluation: Water Saturation - SWDocument16 pagesFormation Evaluation: Water Saturation - SWPuji WastoyoNo ratings yet
- An Investigation Into The Palynological Properties of Fen Peast Through Multiple Pollen Profiles From SE England - WallerDocument12 pagesAn Investigation Into The Palynological Properties of Fen Peast Through Multiple Pollen Profiles From SE England - Wallerwolfspider1No ratings yet
- Vocabulary Game: Fauna Is AnotherDocument2 pagesVocabulary Game: Fauna Is AnotherIsabel M Moya SeguraNo ratings yet
- Cause and EffectDocument1 pageCause and EffectalexNo ratings yet
- RuneQuest Game Aid - Weather TablesDocument1 pageRuneQuest Game Aid - Weather Tablesrutius100% (1)
- 1st VideoDocument7 pages1st VideoManish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sami Gilgit Field PDFDocument24 pagesSami Gilgit Field PDFSamiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Description:: Class: Holothuroidea (Sea Cucumbers)Document8 pagesDescription:: Class: Holothuroidea (Sea Cucumbers)Karl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Kingmaker Mapa3Document1 pageKingmaker Mapa3Cristian BenzNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Soil Description 2006-9Document10 pagesGuidelines For Soil Description 2006-9JOSENo ratings yet
- Tugas 3 Geologi Pengembangan Wilayah: Inem Nurhasanah 2017 69 009Document4 pagesTugas 3 Geologi Pengembangan Wilayah: Inem Nurhasanah 2017 69 009Laras AdillahusnaNo ratings yet
- Eneralized: Vers FORDocument61 pagesEneralized: Vers FORAli RezaNo ratings yet
- Siang Petrografi Batuan GranitoidDocument37 pagesSiang Petrografi Batuan GranitoidDeskaNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic Facies UGDocument20 pagesMetamorphic Facies UGcrocin idlyNo ratings yet
- Microdistillers H - September 2022Document91 pagesMicrodistillers H - September 2022Rodolfo RivadeneyraNo ratings yet
- Soogil Drink MenuDocument2 pagesSoogil Drink MenuEater NYNo ratings yet
- 08 Chapter 2Document27 pages08 Chapter 2KV DeepikaNo ratings yet
- Jmbfs 1181 YalcinDocument5 pagesJmbfs 1181 YalcinvalentinaNo ratings yet
- Wine ListDocument17 pagesWine ListeatlocalmenusNo ratings yet
- Apple Wine RecipeDocument2 pagesApple Wine RecipeFred smithNo ratings yet
- Liquor Price in DelhiDocument78 pagesLiquor Price in DelhilolNo ratings yet
- Guava Value Added ProductsDocument7 pagesGuava Value Added Productsusha kumariNo ratings yet
- Determination of Amino Acid Profiles of Grapes and Wines by HPLC-MSDocument1 pageDetermination of Amino Acid Profiles of Grapes and Wines by HPLC-MSAshis BorahNo ratings yet
- Lonicera CaeruleaDocument8 pagesLonicera Caerulea62991No ratings yet
- Eezaa Foods International PVT - LTD: Quality Assurance Specification Cover SheetDocument7 pagesEezaa Foods International PVT - LTD: Quality Assurance Specification Cover SheetPariksha AryaNo ratings yet
- Distilare UjssmDocument2 pagesDistilare UjssmCosmin ManNo ratings yet
- KSBCL Price ListDocument595 pagesKSBCL Price ListVijay Perumalsamy0% (1)
- The Lincoln Beverage MenuDocument17 pagesThe Lincoln Beverage MenuMixologyNo ratings yet
- SUJ Bar Essentials Supply Checklist PDFDocument5 pagesSUJ Bar Essentials Supply Checklist PDFCosmin DospinescuNo ratings yet
- Wine Australia Compliance Guide June 2016Document28 pagesWine Australia Compliance Guide June 2016eduardo3000No ratings yet
- D5 Fortified Wine Topics - AnswersDocument13 pagesD5 Fortified Wine Topics - AnswersIvan ClavierNo ratings yet
- Tourism in MoldovaDocument1 pageTourism in MoldovaDumitru PlamadealaNo ratings yet
- Beverage Bioflavouring and BioproductionDocument14 pagesBeverage Bioflavouring and BioproductionsmakinpanglinkNo ratings yet
- Speak The Culture - FranceDocument308 pagesSpeak The Culture - Franceanca_cristinaa100% (4)
- Tarporley Talk February 2012Document84 pagesTarporley Talk February 2012Talkabout PublishingNo ratings yet
- Food & Beverage Service: Frequently Asked Questions in InterviewDocument13 pagesFood & Beverage Service: Frequently Asked Questions in Interviewsudharaj30No ratings yet
- Winegrapes EbookDocument699 pagesWinegrapes EbookDritanRukaNo ratings yet
- The PH Scale Is From 0 - 14: HealthyDocument11 pagesThe PH Scale Is From 0 - 14: HealthybcamperoNo ratings yet
- Summer Cocktail ListDocument1 pageSummer Cocktail ListChris HughesNo ratings yet
GrapeRootstock Chart
GrapeRootstock Chart
Uploaded by
Techgear Medan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views1 page1. The document describes characteristics of important rootstocks for California vineyards, including their tolerance to nematodes, drought, salinity, and vigor influence on scion growth.
2. Some rootstocks that are tolerant to nematodes and drought include St. George, 1103P, and 140Ru, while rootstocks like 5BB, 5C, and Salt Creek are adapted to moist clay soils.
3. Growers must consider the soil type and mineral nutrition needs of their scion varieties when selecting a rootstock to ensure proper adaptation.
Original Description:
grape universe
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document describes characteristics of important rootstocks for California vineyards, including their tolerance to nematodes, drought, salinity, and vigor influence on scion growth.
2. Some rootstocks that are tolerant to nematodes and drought include St. George, 1103P, and 140Ru, while rootstocks like 5BB, 5C, and Salt Creek are adapted to moist clay soils.
3. Growers must consider the soil type and mineral nutrition needs of their scion varieties when selecting a rootstock to ensure proper adaptation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views1 pageGrapeRootstock Chart
GrapeRootstock Chart
Uploaded by
Techgear Medan1. The document describes characteristics of important rootstocks for California vineyards, including their tolerance to nematodes, drought, salinity, and vigor influence on scion growth.
2. Some rootstocks that are tolerant to nematodes and drought include St. George, 1103P, and 140Ru, while rootstocks like 5BB, 5C, and Salt Creek are adapted to moist clay soils.
3. Growers must consider the soil type and mineral nutrition needs of their scion varieties when selecting a rootstock to ensure proper adaptation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Characteristics of important rootstocks for California vineyards
Nematode Resistance Tolerance Influence on scion
Phylloxera Root Dagger Wet Ease of
Rootstock Vitis parentage Drought Salinity Lime Vigor mineral nutrition7 Soil adaptation Other characteristics
resistance knot (Xiphinema index) soil propagation
Riparia Gloire riparia H1 M-H M L M L L L N, P = L; K, Mg = L-M Deep, well-drained, fertile, moist soils H Early maturation; scions tend to overbear
St. George L-M shallow soils; N = H; K = H ; P = L on low P soils; Fruit set problems with some scions; latent virus
rupestris H2 L L L-M M-H L H Deep and gravelly soils H
(Rupestris du lot) H-deep soils H on high P soils tolerant
N = L-M; P = M
SO4 berlandieri x riparia H M M L-M M L-M M-H L-M Moist, clay soils M Noted as a cool region rootstock
K = M-H; Mg = M
N = M-H; P, K, Zn = M Susceptible to phytophthora root rot; adapted
5BB berlandieri x riparia H M-H M M L M M-H M Moist, clay soils H
Ca, Mg = M-H to high vigor varieties
N = L; P, K = M
5C berlandieri x riparia H M M L L-M M M-H L-M Moist, clay soils H –
Mg = M-H; Zn = L-M
420A Mgt berlandieri x riparia H L-M L L M L M-H L-M N, P, K = L; Mg = M; Zn = LM Fine-textured, fertile soils M Scions tend to overbear when young
99R berlandieri x rupestris H M L-M M-H L M M M-H P = M; K = H; Mg = M Tolerant of acid soil M Young scions may develop slowly
N = M; P = H
110R berlandieri x rupestris H L L M-H5 L M M M-H Hillside, gravelly and acid soils L-M Develops slowly in wet soils
K = L-M; Mg, Zn = M
140Ru berlandieri x rupestris H L L H L H H H N = M-H; P, Mg = H; K = L Adapted to drought and acid soils M Does poorly in non-irrigated, low K soils
N = M-H
1103P berlandieri x rupestris H M L M-H M M-H M H Adapted to drought and saline soils H –
P, Mg = H; K, Zn = L-M
N = M-H
3309 C riparia x rupestris H2 L L M L-M L-M L L-M Deep soils H Sensitive to latent viruses; tolerant of cold injury
P, Ca = L; K, Mg, Zn = M
N, K = M-H
101-14 Mgt riparia x rupestris M2 M-H M L L M L M Moist clay soils H Tolerates wet soils
P, Mg, Ca = L; Zn = M
Schwarzmann riparia x rupestris H M M-H M M M-H M M N, P = M; K = M-H; Mg = L Moist, deep soils H –
44-53 M riparia x (cordifolia x rupestris) H L – M M L L M N = L-M; P, Mg, Ca = L; K = H High Mg soils H Readily Mg deficient in low Mg soils
Best on fertile, med to fine textured
1616 C acerifolia x riparia H M-H M-H L M M L M N = L; K = M-H H Poor on infertile, sandy soils
soils; tolerates acid soils
Salt Creek N, P = H
champinii H H M H L-M M-H M-H H Sandy, infertile L Tolerant to Phytophthora
(Ramsey) K = M-H; Zn, Mn = L
Dog Ridge champinii M-H H M H L-M M-H M VH N, P = H; K = M; Zn = L V. sandy, infertile L Promotes excess vigor, poor fruit set
Harmony 1613 (solonis x Othello) x Dog Ridge L3
L-M 4
M-H M-H L L-M M H N = L; P = M; K = H; Zn = L-M Sandy loams and loamy sands H –
Freedom 1613 (solonis x Othello) x Dog Ridge L3 H4 H H L M M H N, P, K = H; Mg = M; Zn, Mn = L Sands to sandy loams M-H Sensitive to latent viruses
Poor on coarse, sandy soils due to low
039-16 vinifera x rotundifolia H L H L M L L H N, K = H; P = L-M; Zn = L VL Tolerant of fanleaf virus
root knot nematode tolerance
RS -3 Ramsey x Schwarzman – H H – – – – M-H – – – –
RS - 9 Ramsey x Schwarzman – H H – – – – L – – – –
UCD GRN-1
V. rupestris x M. rotundifolia VH VH4 VH M – M-H6 – M-H – – – –
(8909-05)
UCS GRN-2 (V. rufotomentosa x (Dog Ridge x
VH VH4 VH M – M – M – – – –
(9363-16) Riparia Gloire)) x Riparia Gloire
UCD GRN-3 (V. rufotomentosa x (Dog Ridge x
H VH4 VH M-H – M – M-H – – – –
(9365-43) Riparia Gloire)) x V. champinii c9038
UCD GRN-4 (V. rufotomentosa x (Dog Ridge x
H VH4 VH H – M – M-H – – – –
(9365-85) Riparia Gloire)) x V. champinii c9038
UCD GRN-5 (Ramsey x Riparia Gloire) x V.
M-H VH4 VH H – M – H – – – –
(9407-14) champinii c9021
1
Ratings: VL = very low; L = low; M = medium; H = high; VH = very high. 5
Once established
2
Will support populations of phylloxera but will not form tuberosities. 6
Recent experimentation has shown fairly strong salt tolerance
3
The degree of long-term phylloxera resistance is questionable due to the unknown Vitis vinifera parentage of these rootstocks. 7
Influence on scion mineral nutrition refers to comparative petiole tissue levels of nutritional elements
4
Resistence is based on most species of root knot nematodes, but not all. Characteristics of important rootstocks for California vineyards, courtesy of University of California, Davis, updated Dec. 2014 by Dr. Andy Walker
You might also like
- D5 Fortified Wines - An Accompaniment To The WSET Level 4 Diploma in Wines by Wine Spirit Education TrustDocument74 pagesD5 Fortified Wines - An Accompaniment To The WSET Level 4 Diploma in Wines by Wine Spirit Education TrustMatt HuntNo ratings yet
- Phase 2 NVC Habitat Survey Roudsea Wood and Mosses NNRDocument20 pagesPhase 2 NVC Habitat Survey Roudsea Wood and Mosses NNRapi-658315367100% (1)
- Giuseppe Concone Lyrical Studies For Trumpet em CDocument37 pagesGiuseppe Concone Lyrical Studies For Trumpet em CClistenes AndréNo ratings yet
- Introduction Watermelon (Citrullus Lanatus) Is An ImportantDocument9 pagesIntroduction Watermelon (Citrullus Lanatus) Is An ImportantparmardhavalNo ratings yet
- Glassware - F & - B Service EquipmentsDocument3 pagesGlassware - F & - B Service EquipmentsRajeev MathurNo ratings yet
- Cook's Illustrated 069Document36 pagesCook's Illustrated 069vicky61050% (2)
- Dossier Armand BrignacDocument15 pagesDossier Armand BrignacAnonymous 2Buf6xOegSNo ratings yet
- Rootstocks 24347Document4 pagesRootstocks 24347Rogerio GomesNo ratings yet
- Helliwell Provincial Park TEM 2001 Map LegendDocument3 pagesHelliwell Provincial Park TEM 2001 Map LegendKathy DunsterNo ratings yet
- At The End of Mill Road v1Document2 pagesAt The End of Mill Road v1qjwltxqxzrzxdxdhamNo ratings yet
- Lower-Level Categories in Soil Taxonomy: SubordersDocument5 pagesLower-Level Categories in Soil Taxonomy: SubordersGian Franco ValenciaNo ratings yet
- (Lesson 2, Module 3) How Ore Minerals Are Found, Mined & Processed For Human Use - SAUT - EXCDocument1 page(Lesson 2, Module 3) How Ore Minerals Are Found, Mined & Processed For Human Use - SAUT - EXCLydill Ann SautNo ratings yet
- Cerny 1991Document40 pagesCerny 1991HKTanoliNo ratings yet
- WEE'" Tony Williams: Is of ToDocument1 pageWEE'" Tony Williams: Is of Tocoo11No ratings yet
- Resource and Development Part C - Soil ResourceDocument7 pagesResource and Development Part C - Soil ResourceDarsh TodiNo ratings yet
- Geology and Exploration of Gold Placer DDocument14 pagesGeology and Exploration of Gold Placer Dyonathan tsegayeNo ratings yet
- Zodiac Degree InfluencesDocument13 pagesZodiac Degree InfluencesAnton KühnlächnerNo ratings yet
- ABRSM Grade 8 Theory TopicDocument1 pageABRSM Grade 8 Theory Topicdaphnelee.0821No ratings yet
- Irish Base Metal Deposits Field Trip SummaryDocument25 pagesIrish Base Metal Deposits Field Trip SummaryKenShin BlacKNo ratings yet
- Appendix I Departure Analysis TableDocument8 pagesAppendix I Departure Analysis TablelewiscreekNo ratings yet
- Valuation Report of MayadeviDocument7 pagesValuation Report of Mayadevi236ksfeNo ratings yet
- Richardspost Subduction Pdac 2019Document27 pagesRichardspost Subduction Pdac 2019Salvador SánchezNo ratings yet
- Vocabagrams PDFDocument1 pageVocabagrams PDFmaruf048No ratings yet
- Geo LN 1 Types of SoDocument2 pagesGeo LN 1 Types of SoParveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Geoscience Examination Package: For Geoscience Graduates (Petroleum Companies Exams)Document18 pagesGeoscience Examination Package: For Geoscience Graduates (Petroleum Companies Exams)Dana AbkhNo ratings yet
- We Three Kings2Document1 pageWe Three Kings2Paolo RomeroNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic FaciesDocument48 pagesMetamorphic FaciesNisha Singh100% (2)
- Exogenic Force Agents of Gradation Landforms (Weathering, Erosion, Deposition) SoilDocument1 pageExogenic Force Agents of Gradation Landforms (Weathering, Erosion, Deposition) SoilApichayaNo ratings yet
- University of Minnesota: Soil Test ReportDocument2 pagesUniversity of Minnesota: Soil Test ReportJose Cuadros LoayzaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 45 (PYQ Series 3) Notes ENGLISHDocument10 pagesLECTURE 45 (PYQ Series 3) Notes ENGLISHkeshavsharma6767No ratings yet
- Test 2 Answer SheetDocument4 pagesTest 2 Answer SheetAdi AlshtiwiNo ratings yet
- Geometry FormulaDocument12 pagesGeometry FormulaMiahSalitaNo ratings yet
- Formula 2Document6 pagesFormula 2Juven LuzorataNo ratings yet
- (L4) - (JLD 3.0) - Gravitation - 30th September.Document56 pages(L4) - (JLD 3.0) - Gravitation - 30th September.Dida CowernNo ratings yet
- Type of Soil Formation of Soil Characteristi C Feature Major CropDocument3 pagesType of Soil Formation of Soil Characteristi C Feature Major CropJenish PadshalaNo ratings yet
- Geo de La Minera Toqui PDFDocument29 pagesGeo de La Minera Toqui PDFDaniel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Igneous Rocks Desc ID Table Empty - Dropdown Menus 2.0Document7 pagesLab 2 Igneous Rocks Desc ID Table Empty - Dropdown Menus 2.0Kristika RaguthasNo ratings yet
- BHG Garden Plan Soften FenceDocument3 pagesBHG Garden Plan Soften Fenceargai ritaNo ratings yet
- Urubamba FinalDocument11 pagesUrubamba FinalJulissa Andrea Tahua MorenoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21 New Meta Facies 2 SP2017 Web BasedDocument58 pagesLecture 21 New Meta Facies 2 SP2017 Web BasedBharat MohaanaNo ratings yet
- AP Env Sci Cram Chart 2021Document1 pageAP Env Sci Cram Chart 2021高瑞韩No ratings yet
- GravitationDocument2 pagesGravitationgokulkrishna2k7No ratings yet
- Heb A Alphabet 2nded 2017Document18 pagesHeb A Alphabet 2nded 2017AlondraNo ratings yet
- GM Aid - Random Encounters - Generic RPGDocument1 pageGM Aid - Random Encounters - Generic RPGDon PerryNo ratings yet
- Basic Data of The Soil RegionsDocument23 pagesBasic Data of The Soil RegionsamicoadrianoNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 2 - Cordillera RealDocument12 pagesCapitulo 2 - Cordillera RealLeo VelascoNo ratings yet
- Koppen KemeDocument1 pageKoppen KemeunoporquezmartinNo ratings yet
- Porphyry Cu-Mo-Au and Related Epithermal Systems: Part 6: Post-Subduction DepositsDocument22 pagesPorphyry Cu-Mo-Au and Related Epithermal Systems: Part 6: Post-Subduction DepositsHugo Poma100% (1)
- Formation Evaluation: Water Saturation - SWDocument16 pagesFormation Evaluation: Water Saturation - SWPuji WastoyoNo ratings yet
- An Investigation Into The Palynological Properties of Fen Peast Through Multiple Pollen Profiles From SE England - WallerDocument12 pagesAn Investigation Into The Palynological Properties of Fen Peast Through Multiple Pollen Profiles From SE England - Wallerwolfspider1No ratings yet
- Vocabulary Game: Fauna Is AnotherDocument2 pagesVocabulary Game: Fauna Is AnotherIsabel M Moya SeguraNo ratings yet
- Cause and EffectDocument1 pageCause and EffectalexNo ratings yet
- RuneQuest Game Aid - Weather TablesDocument1 pageRuneQuest Game Aid - Weather Tablesrutius100% (1)
- 1st VideoDocument7 pages1st VideoManish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sami Gilgit Field PDFDocument24 pagesSami Gilgit Field PDFSamiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Description:: Class: Holothuroidea (Sea Cucumbers)Document8 pagesDescription:: Class: Holothuroidea (Sea Cucumbers)Karl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Kingmaker Mapa3Document1 pageKingmaker Mapa3Cristian BenzNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Soil Description 2006-9Document10 pagesGuidelines For Soil Description 2006-9JOSENo ratings yet
- Tugas 3 Geologi Pengembangan Wilayah: Inem Nurhasanah 2017 69 009Document4 pagesTugas 3 Geologi Pengembangan Wilayah: Inem Nurhasanah 2017 69 009Laras AdillahusnaNo ratings yet
- Eneralized: Vers FORDocument61 pagesEneralized: Vers FORAli RezaNo ratings yet
- Siang Petrografi Batuan GranitoidDocument37 pagesSiang Petrografi Batuan GranitoidDeskaNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic Facies UGDocument20 pagesMetamorphic Facies UGcrocin idlyNo ratings yet
- Microdistillers H - September 2022Document91 pagesMicrodistillers H - September 2022Rodolfo RivadeneyraNo ratings yet
- Soogil Drink MenuDocument2 pagesSoogil Drink MenuEater NYNo ratings yet
- 08 Chapter 2Document27 pages08 Chapter 2KV DeepikaNo ratings yet
- Jmbfs 1181 YalcinDocument5 pagesJmbfs 1181 YalcinvalentinaNo ratings yet
- Wine ListDocument17 pagesWine ListeatlocalmenusNo ratings yet
- Apple Wine RecipeDocument2 pagesApple Wine RecipeFred smithNo ratings yet
- Liquor Price in DelhiDocument78 pagesLiquor Price in DelhilolNo ratings yet
- Guava Value Added ProductsDocument7 pagesGuava Value Added Productsusha kumariNo ratings yet
- Determination of Amino Acid Profiles of Grapes and Wines by HPLC-MSDocument1 pageDetermination of Amino Acid Profiles of Grapes and Wines by HPLC-MSAshis BorahNo ratings yet
- Lonicera CaeruleaDocument8 pagesLonicera Caerulea62991No ratings yet
- Eezaa Foods International PVT - LTD: Quality Assurance Specification Cover SheetDocument7 pagesEezaa Foods International PVT - LTD: Quality Assurance Specification Cover SheetPariksha AryaNo ratings yet
- Distilare UjssmDocument2 pagesDistilare UjssmCosmin ManNo ratings yet
- KSBCL Price ListDocument595 pagesKSBCL Price ListVijay Perumalsamy0% (1)
- The Lincoln Beverage MenuDocument17 pagesThe Lincoln Beverage MenuMixologyNo ratings yet
- SUJ Bar Essentials Supply Checklist PDFDocument5 pagesSUJ Bar Essentials Supply Checklist PDFCosmin DospinescuNo ratings yet
- Wine Australia Compliance Guide June 2016Document28 pagesWine Australia Compliance Guide June 2016eduardo3000No ratings yet
- D5 Fortified Wine Topics - AnswersDocument13 pagesD5 Fortified Wine Topics - AnswersIvan ClavierNo ratings yet
- Tourism in MoldovaDocument1 pageTourism in MoldovaDumitru PlamadealaNo ratings yet
- Beverage Bioflavouring and BioproductionDocument14 pagesBeverage Bioflavouring and BioproductionsmakinpanglinkNo ratings yet
- Speak The Culture - FranceDocument308 pagesSpeak The Culture - Franceanca_cristinaa100% (4)
- Tarporley Talk February 2012Document84 pagesTarporley Talk February 2012Talkabout PublishingNo ratings yet
- Food & Beverage Service: Frequently Asked Questions in InterviewDocument13 pagesFood & Beverage Service: Frequently Asked Questions in Interviewsudharaj30No ratings yet
- Winegrapes EbookDocument699 pagesWinegrapes EbookDritanRukaNo ratings yet
- The PH Scale Is From 0 - 14: HealthyDocument11 pagesThe PH Scale Is From 0 - 14: HealthybcamperoNo ratings yet
- Summer Cocktail ListDocument1 pageSummer Cocktail ListChris HughesNo ratings yet