Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Chapter 1
Chemistry Chapter 1
Uploaded by
MriganKar XonoWallOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Chapter 1
Chemistry Chapter 1
Uploaded by
MriganKar XonoWallCopyright:
Available Formats
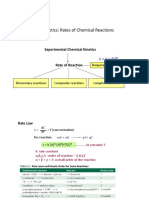
CHEMICAL KINETICS
change∈concentration change∈ pressure
Rate of RXn = change ∈time = change∈time
∆ C C 2−C1
Rate of RXn =
∆C
∆t
=
∆P
∆t ( ∆t
=
t 2−t 1 )
UNIT OF RATE OF RXn:
n ∆C molL−1
Rate of RX = ∆t
=
T
= molL-1T-1.
RECIPROCAL RULE OF MOLAR COEFFICIENT:
For the given reaction,
αA + βB γC + δD
Rate of RXn = α
1
[ – d[A]
dt ] 1
= β [ – d [B]
dt ] = γ
1
[ ]
d [C ]
dt
1
= δ [ ].
d [ D]
dt
RATE LAW AND RATE CONSTANT:
For the given reaction,
αA + βB γC + δD
Rate law is –
RATE = k [ A ] x [ B ] y
where k is called RATE CONSTANT and
x is the order of reaction w.r.t A and y w.r.t B.
For ELEMENTARY RXn or SLOW STEP or RATE DETERMINING RXn (R.D.S).
RATE = k [ A ] α [ B ] β
SPECIFIC RXn RATE:
when A = B = 1 molL-1 then,
Rate = k
UNIT OF RATE CONSTANT:
Say αA P
Rate = k[A]n n is the order of reaction.
Rate [ molL−1]T −1
K= n =
[ A] [molL−1 ]n
K = [mol L-1]1-n T-1
Rate constant of:
Zero order reaction is: mol L-1 s-1.
First order reaction is: s-1.
Second order reaction is: mol-1 L s-1.
INTEGRATED EQn OF ZERO ORDER RXn:
C0 - Ct = Kt
C0
Half Life of Zero Order Rxn : t1/2 =
2k
INTEGRATED EQn OF FIRST ORDER RXn:
ln C −ln C =kt
0 t
2.303 log 2
Half Life of Zero Order Rxn : t 1 /2 =
k
INTEGRATED EQn OF SECOND ORDER RXn:
1 1
− =kt
Ct C0
1
Half Life of Zero Order Rxn : t 1 /2 =
C0 k
ARRHENIUS EQUATION:
K = Ae-Ea/RT.
K is the Rate Constant.
A is the Arrhenius eqn/constant parameter.
Ea is the activation energy.
R is the Universal Gas constant [R = 8.314].
T represents Temperature [in Kelvin].
e is the exponent.
Arrhenius Equation in Tempr T1 and T2 and Rate Const. K1 and K2.
K2
log ( )=
Ea
(1 1
−
K 1 2.303 R T 1 T 2 )
PSEUDO OF 1st ORDER REACTION:
Rate = k’[A]1
where, Order =1 and Molecularity = 2.
You might also like
- Pressure Check Connection Pressure A40fDocument3 pagesPressure Check Connection Pressure A40fBudi Rohmani100% (3)
- Chemical Kinetics: For The Given ReactionDocument3 pagesChemical Kinetics: For The Given ReactionMriganKar XonoWallNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9. Kinetics: Rates of Chemical ReactionsDocument11 pagesChapter 9. Kinetics: Rates of Chemical ReactionsAtiya SultanaNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument43 pagesChemical KineticsJohn SlyNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry 2 Midterm Note I. Reaction Kinetic:: 1. Some ConceptsDocument9 pagesPhysical Chemistry 2 Midterm Note I. Reaction Kinetic:: 1. Some ConceptsTrung VõNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics 1Document4 pagesChemical Kinetics 1deepanjan881No ratings yet
- Chemical KineticDocument44 pagesChemical KineticVibhor100% (1)
- Chemical Kinetics (Edustudy Point) - Pages-DeletedDocument6 pagesChemical Kinetics (Edustudy Point) - Pages-DeletedMudil MathurNo ratings yet
- Lecturers CHEMICAL KINETICSDocument36 pagesLecturers CHEMICAL KINETICSb.hamdi160No ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics PDFDocument3 pagesChemical Kinetics PDFHari KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument4 pagesChemical KineticsSaurabh yadavNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE Main Advanced Physical Chemistry 12th Chemical Kinetics PDFDocument44 pagesIIT JEE Main Advanced Physical Chemistry 12th Chemical Kinetics PDFSesha Sai Kumar50% (4)
- Chemical Kinetics 13thDocument32 pagesChemical Kinetics 13thRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Kinetika Kimia s1Document28 pagesKinetika Kimia s1Umiia RuhunussaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Chemical KineticsDocument30 pagesChapter - Chemical KineticsMD.IRFAN UDDIN AHMED MEHEDINo ratings yet
- 2024 Recapitulation Part 2 Chapter 12-13Document26 pages2024 Recapitulation Part 2 Chapter 12-13Mạnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document46 pagesChapter 6Yahya Alhaddi KA201 18No ratings yet
- CH E 441 Ex1 Spring 05Document6 pagesCH E 441 Ex1 Spring 05Jhon Barzola PalominoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 38Document5 pagesLecture 38Hagere EthiopiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14. Enzyme KineticsDocument44 pagesChapter 14. Enzyme KineticsKalai VaniNo ratings yet
- 2024 Recapitulation Part 2 Chapter 12-13Document26 pages2024 Recapitulation Part 2 Chapter 12-13httam12022005No ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument4 pagesChemical Kineticsmandhareneel06No ratings yet
- Slides - 10 01 12 PDFDocument5 pagesSlides - 10 01 12 PDFsandypu08No ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics1Document59 pagesChemical Kinetics1Fernando MattiucciNo ratings yet
- 11.1 Reaction Rate 3Document24 pages11.1 Reaction Rate 3Avicenna Ibnu Bahrin100% (1)
- Rate of Reaction: Appearance of Products (P) (P2) - (P1)Document3 pagesRate of Reaction: Appearance of Products (P) (P2) - (P1)Pardeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics FinalDocument52 pagesChemical Kinetics FinalnotrealsikeNo ratings yet
- 13 LectureDocument41 pages13 Lectureasfass sfasfasfasNo ratings yet
- Chapter Chemical Kinetics CHE 121Document38 pagesChapter Chemical Kinetics CHE 121iqbal-cheNo ratings yet
- Video 2. Rate LawsDocument7 pagesVideo 2. Rate LawsEvelyn LaraNo ratings yet
- Chem 102-General Chemistry Lecture 9 SMDocument23 pagesChem 102-General Chemistry Lecture 9 SMTakesure Mgcini MaphosaNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticszzDocument29 pagesChemical KineticszzfailurewasteworthlessNo ratings yet
- Skf3023 Lecture 1Document33 pagesSkf3023 Lecture 1NOR SANISAH BINTI ARSADNo ratings yet
- Steady StateDocument30 pagesSteady Statesus023No ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes Ch04 Chemical KineticsDocument4 pages12 Chemistry Notes Ch04 Chemical KineticssrideviNo ratings yet
- Chap. 8 Reaction Kinetics: (1) Definition of Reaction RateDocument6 pagesChap. 8 Reaction Kinetics: (1) Definition of Reaction RateArasuNo ratings yet
- Explain Reaction MechanismDocument5 pagesExplain Reaction MechanismQuynh NhuNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument32 pagesChemical KineticsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Thermoelectricity DefinitionsDocument22 pagesThermoelectricity DefinitionspavecuNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Formula SheetDocument1 pageKinetics Formula SheetdfasdfNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics - Short NotesDocument2 pagesChemical Kinetics - Short Notesrjrahul453lNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chem Notes Question Bank Chemical Kinetics PDFDocument23 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chem Notes Question Bank Chemical Kinetics PDFAshika D ChandavarkarNo ratings yet
- Enzyme KineticsDocument28 pagesEnzyme Kineticsghislain22.kevinNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument16 pagesHeat Transferprasanna0% (1)
- CH 7 - Chemical KineticsDocument60 pagesCH 7 - Chemical KineticsCharbel RahmeNo ratings yet
- Esssential Water Chemistry I-2Document12 pagesEsssential Water Chemistry I-2Mers AbeNo ratings yet
- Slide 1 PDFDocument58 pagesSlide 1 PDFTeeranun NakyaiNo ratings yet
- 028 CSTR Startup PDFDocument3 pages028 CSTR Startup PDFAnalytics ClubNo ratings yet
- Rate Law and The Eyring EquationDocument11 pagesRate Law and The Eyring EquationManjunath.RNo ratings yet
- Fourier's Law: Module 2: Steady-State Heat ConductionDocument3 pagesFourier's Law: Module 2: Steady-State Heat ConductionJohnAdistubNo ratings yet
- Fourier's Law: Module 2: Steady-State Heat ConductionDocument3 pagesFourier's Law: Module 2: Steady-State Heat ConductionJohnAdistubNo ratings yet
- Fourier's Law: Module 2: Steady-State Heat ConductionDocument3 pagesFourier's Law: Module 2: Steady-State Heat ConductionJohnAdistubNo ratings yet
- Rates of Chemical Reactions: Kinetics 1Document68 pagesRates of Chemical Reactions: Kinetics 1K CabeguinNo ratings yet
- Chemical-Kinetics-Ppt XIIDocument41 pagesChemical-Kinetics-Ppt XIIAnonymous RuslwNZZlNo ratings yet
- PPG - Kinetika KimiaDocument42 pagesPPG - Kinetika KimiamuaffifahNo ratings yet
- Collision Theory: - Reactions in Solutions: - Activated Complex Theory: and The Motion of Molecules Through These Surfaces: - TheDocument20 pagesCollision Theory: - Reactions in Solutions: - Activated Complex Theory: and The Motion of Molecules Through These Surfaces: - Thecmc107No ratings yet
- 2a REACTION RATEDocument17 pages2a REACTION RATEMinh ThànhNo ratings yet
- UIL Chemistry Reference Materials: 1 EquationsDocument2 pagesUIL Chemistry Reference Materials: 1 EquationsAnonymous BsqwX1jsNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- UFAD PresentationDocument42 pagesUFAD Presentationsenthilarasu5No ratings yet
- Properties of Reservoir Fluids: Why Do We Study Phase Behavior?Document9 pagesProperties of Reservoir Fluids: Why Do We Study Phase Behavior?Ali RostamiNo ratings yet
- Pipe Is Under Clamping ForceDocument7 pagesPipe Is Under Clamping Forcejosediaz141No ratings yet
- 3744-Article Text-13502-1-10-20210616Document4 pages3744-Article Text-13502-1-10-20210616micahelNo ratings yet
- Avd - Vddci102Document8 pagesAvd - Vddci102faisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Test API RP 1111Document2 pagesTest API RP 1111Nguyễn QuânNo ratings yet
- Ex.112 - Effects of Slipping Along Screws and Back Pressure On Energy Dissipation and Backflows in A Twin Screw ExtruderDocument10 pagesEx.112 - Effects of Slipping Along Screws and Back Pressure On Energy Dissipation and Backflows in A Twin Screw ExtruderjacksayshiNo ratings yet
- Heat Pump - Refrigeration and LiquefactionDocument72 pagesHeat Pump - Refrigeration and LiquefactionhananNo ratings yet
- SH SH4: 2-Pole 4-PoleDocument20 pagesSH SH4: 2-Pole 4-Polemarpaung saberindoNo ratings yet
- Competency: Mass Transfer-I Course Code: 3340502Document7 pagesCompetency: Mass Transfer-I Course Code: 3340502Dope WorldNo ratings yet
- Answer2example2 PDFDocument3 pagesAnswer2example2 PDFAffandy AhmadNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic Lift at Reynolds Numbers BelowDocument2 pagesAerodynamic Lift at Reynolds Numbers BelowTaekevNo ratings yet
- Drill - Pipe - GradesDocument1 pageDrill - Pipe - GradesQuality controllerNo ratings yet
- Assignment Petroleum LabDocument5 pagesAssignment Petroleum LabsaimaliNo ratings yet
- SOP - 01 - Surface Well Testing SOP Index - Rev11Document5 pagesSOP - 01 - Surface Well Testing SOP Index - Rev11HasnainNo ratings yet
- Mus (PPT 1)Document14 pagesMus (PPT 1)Sagar GawdeNo ratings yet
- Wilo Datasheet - International - en - 2161331 - Cronoline Il 150 325 37 4 s1 Ie3Document5 pagesWilo Datasheet - International - en - 2161331 - Cronoline Il 150 325 37 4 s1 Ie3suwono radukNo ratings yet
- Geometry Sim ScaleDocument233 pagesGeometry Sim ScaleViníciusGonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Ashrae ChartDocument2 pagesAshrae Chartsophia arellanoNo ratings yet
- Heat Recovery Unit: FeaturesDocument4 pagesHeat Recovery Unit: FeaturesEldin JelecNo ratings yet
- Study Report G-02 RevbDocument21 pagesStudy Report G-02 RevbRiandi HartartoNo ratings yet
- Hydrogenation of Vegetable OilsDocument7 pagesHydrogenation of Vegetable OilsKroya HunNo ratings yet
- Electrical Submersible Pumping (ESP) System Fundamentals: Dr. M. GhareebDocument25 pagesElectrical Submersible Pumping (ESP) System Fundamentals: Dr. M. Ghareebramzi aidliNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Sharp Crested Weirs - Francis FormulaDocument8 pagesRectangular Sharp Crested Weirs - Francis FormulaRenvil PedernalNo ratings yet
- Lift Station - Design ProjectDocument30 pagesLift Station - Design ProjectChristian DoriaNo ratings yet
- Normal Design: Depressurize From Design Pressure To 50% in 15 MinutesDocument2 pagesNormal Design: Depressurize From Design Pressure To 50% in 15 Minutesmatteo2009No ratings yet
- BuTech Low Pressure Valves, Fittings and TubingDocument14 pagesBuTech Low Pressure Valves, Fittings and TubingNicolas AguilarNo ratings yet
- Distillation Matlab CodeDocument8 pagesDistillation Matlab CodeSaurab Devanandan0% (1)
- Avk Combination Air Valve, PN 16 701/95-010: For Wastewater, Reinforced Polyamide, Compact DesignDocument2 pagesAvk Combination Air Valve, PN 16 701/95-010: For Wastewater, Reinforced Polyamide, Compact Designkad-7No ratings yet