Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summary: Outline The Process Involved in Genetic Engineering
Summary: Outline The Process Involved in Genetic Engineering
Uploaded by
Angeline BruceOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summary: Outline The Process Involved in Genetic Engineering
Summary: Outline The Process Involved in Genetic Engineering
Uploaded by
Angeline BruceCopyright:
Available Formats
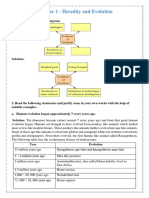
Summary: Outline the process involved in genetic engineering
Traditional Breeding
Occurs between closely related organisms.
Genetic exchange occurs in reproductive cells, and occurs between related
chromosomes.
Through homologous recombination.
Amount of DNA and spacing between genes remain the same.
Genetic Engineering
The use of technology to change the genetic makeup of living things for human
purposes.
Is human-made and can subject to human and other errors.
Involves any gene from any organism, alive or dead, or synthesized in a lab.
Occurs in somatic cells.
Insertion into chromosomes occurs randomly.
DNA Cloning
The process of making multiple, identical copies of a particular piece of DNA
Summary: Discuss the application of recombinant DNA.
Recombinant DNA is the term used to describe the combination of two DNA strands
that are constructed artificially.
Applications in Medicine
Insulin- Recombinant DNA technology has allowed the scientist to develop
human insulin by using the bacteria as a host cell and it is also available in the
market. This hormone is responsible for controlling the glucose level in humans.
Vaccines- Recombinant DNA technology enables the scientists to develop
vaccines by cloning the gene used for protective antigen protein.
Human growth hormones- Scientist have developed many growth hormones
using recombinant DNA technology. It is responsible for growth, reproduction of
cells and regeneration in humans as well as animals. The disease of dwarfism is
treated with this hormone.
Gene Therapy- Genetic engineering may one day enable the medicinal scientists
to replace the defective genes responsible for hereditary diseases with normal
genes. This new system of therapy is called gene therapy.
Summary: Describe the general features of history of life on earth, including
generally accepted dates and sequence of geologic time scale and characteristics
of major groups of organism present during this time of period.
Geologic Time Scale - a tabular representation of the major divisions of the history of
Earth.
Divisions of Geologic Time Scale:
Eon- longest division that spans hundreds to thousands of millions of years ago.
Era- division that span time periods of tens to hundreds of millions of years.
Period- division that spans no more than one hundred million yeays.
Epoch- smallest division that is characterized by distinctive organisms.
Four Eons of Geologic Time Scale:
Hadean - 4.6 to 3.9 billion years ago.
Archean - 3.9 to 2.5 billion years ago
Proterozoic – 2.5 billion years ago to 540 million years ago.
Phanerozoic – 540 million years ago through today and divided into three
eras.
Eras in Geologic Time Scale
Precambrian - 4600 to 542 million years ago and considered as the oldest era.
Paleozoic – 570 to 250 million years ago, known as Age of Amphibians, Fishes
and invertebrates, and divided into six periods; Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian,
Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian.
Mesozoic- lasted from 250 million years ago to 65 million years ago, known as
time of reptiles and divided into three periods; Triassic Jurassic and Cretaceous.
Cenozoic- 65 million years ago to present days and development of modern
mammals and human beings. It is divided into two periods; Tertiary and
Quaternary.
Periods under the Paleozoic Era
Cambrian- 540 to 500 million years ago. Explosion of life forms. First shellfish,
primitive fish, trilobites, corals and mollusks.
You might also like
- What Are Common Interview Questions PDFDocument2 pagesWhat Are Common Interview Questions PDFAngeline Bruce100% (2)
- What Are Common Interview Questions PDFDocument2 pagesWhat Are Common Interview Questions PDFAngeline Bruce100% (2)
- Iot Based Doorbell Using Raspberry PiDocument18 pagesIot Based Doorbell Using Raspberry PiSiri talasala100% (1)
- Assignment 8 Biology EssayDocument6 pagesAssignment 8 Biology Essayjanna conawayNo ratings yet
- Rule 1030 - Training and Acreditation of Personnel On OSHDocument12 pagesRule 1030 - Training and Acreditation of Personnel On OSHrobinrubina100% (1)
- Lotus and F1 EnginesDocument10 pagesLotus and F1 EnginesshahrizalNo ratings yet
- Apple Laptop Price ListDocument130 pagesApple Laptop Price ListMauricio PiñerosNo ratings yet
- Manual ReebokDocument13 pagesManual ReebokSerguei Esquivel SeredínNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 NotesDocument97 pagesGeneral Biology 2 NotesMacky NohayNo ratings yet
- (REVIEWER) General Biology 2 3rd QT Reviewer (Summary of Lessons 6-9)Document10 pages(REVIEWER) General Biology 2 3rd QT Reviewer (Summary of Lessons 6-9)mhenly.estanislaoNo ratings yet
- Hand OutDocument50 pagesHand Out8rvxjshnbtNo ratings yet
- Forum/Open Discussion: - Lesson 1: Genetics, Evolution and Origin of Biodiversity ObjectivesDocument13 pagesForum/Open Discussion: - Lesson 1: Genetics, Evolution and Origin of Biodiversity ObjectivesArianne PoleaNo ratings yet
- GenBio2 Q3 M4 6 Learner PDFDocument48 pagesGenBio2 Q3 M4 6 Learner PDFFlores Carl JosephNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Gen BioDocument9 pagesModule 2 Gen BioCasimero CabungcalNo ratings yet
- Local Media2007381616359617278-1Document13 pagesLocal Media2007381616359617278-1Angelo D. AmorNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry BiodiversityDocument18 pagesBiochemistry BiodiversitybenchihebNo ratings yet
- Evidences of EvolutionDocument5 pagesEvidences of EvolutionAnthony CreationNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument7 pagesBiologyreesespufffNo ratings yet
- What Is LifeDocument4 pagesWhat Is LifeMaria FerreyraNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Quarter 2Document2 pagesEarth and Life Science Quarter 2Jonathan R. YadaoNo ratings yet
- BSE102 - Lecture 2 - Biology-Study of LifeDocument11 pagesBSE102 - Lecture 2 - Biology-Study of LifeShreyans KothariNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 EvolutionDocument61 pagesLesson 6 EvolutionCRIS EDISON VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- Protein Fish LabAnswersDocument14 pagesProtein Fish LabAnswersrahmi93No ratings yet
- Lesson-5 BiodiversityDocument5 pagesLesson-5 BiodiversityLucky JalecoNo ratings yet
- 1.1.3.16. Humans Report On Their Own Peculiarities: 22 Chapter 1. I. Introduction To The CellDocument1 page1.1.3.16. Humans Report On Their Own Peculiarities: 22 Chapter 1. I. Introduction To The CellAnna YepNo ratings yet
- GENBIODocument8 pagesGENBIOFaith MagluyanNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 (Chelsea's Answers)Document10 pagesGeneral Biology 2 (Chelsea's Answers)Aisel SorilankaNo ratings yet
- Jean-Claude Bertrand, Philippe Normand, Bernard Ollivier, Télesphore Sime-Ngando - Prokaryotes and Evolution-Springer International Publishing (2018)Document401 pagesJean-Claude Bertrand, Philippe Normand, Bernard Ollivier, Télesphore Sime-Ngando - Prokaryotes and Evolution-Springer International Publishing (2018)Vianney BeraudNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document21 pagesGeneral Biology 2gabrielNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes - Blueprint of Life by Ahmad Shah IdilDocument33 pagesBiology Notes - Blueprint of Life by Ahmad Shah Idilcody jamesNo ratings yet
- Biol 233 Uofc Review PackageDocument15 pagesBiol 233 Uofc Review PackagePeter KimNo ratings yet
- Reviewer G-12Document8 pagesReviewer G-12Kresha Belle MercadoNo ratings yet
- Microbiome Integrative MedicineDocument8 pagesMicrobiome Integrative Medicine23bhaga100% (1)
- Definition of Biological Science. Biological Science Is A Branch ofDocument11 pagesDefinition of Biological Science. Biological Science Is A Branch ofAlyssa DianneNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified OrganismsDocument3 pagesGenetically Modified OrganismsSandip ThapaNo ratings yet
- Anthropology 1020Document21 pagesAnthropology 1020api-311356019100% (1)
- BiologyDocument2 pagesBiology1 1No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 EvolutionDocument8 pagesChapter 4 EvolutionYuri MiyaNo ratings yet
- 2ND Quarter ReviewerDocument2 pages2ND Quarter ReviewerEam OsarNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life NotesDocument11 pagesEarth and Life NotesAdrienne MercurioNo ratings yet
- Genetics 1.1 ResumeDocument102 pagesGenetics 1.1 ResumemiertschinkNo ratings yet
- Las 5 Bio2 PDFDocument13 pagesLas 5 Bio2 PDFPeanut BlobNo ratings yet
- General Biology Reviewer 2023Document11 pagesGeneral Biology Reviewer 2023Eunice AniceteNo ratings yet
- Theories of EvolutionDocument5 pagesTheories of EvolutionMehar FathimaNo ratings yet
- Evidence of EvolutionDocument40 pagesEvidence of EvolutionMarco ZoletaNo ratings yet
- STS NotesDocument7 pagesSTS Notesalona MabungaNo ratings yet
- Determine The Interrelatedness of Society (Week 8-9)Document6 pagesDetermine The Interrelatedness of Society (Week 8-9)Florelyn GocotanoNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument25 pagesBiodiversityジェノンベンNo ratings yet
- Heridity and EvulationDocument7 pagesHeridity and Evulationkrushnakadam0029No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Biodiversity ScriptDocument7 pagesChapter 4 Biodiversity ScriptApodedNo ratings yet
- Biology ArticleDocument6 pagesBiology ArticleOktario RuntulaloNo ratings yet
- BOL 2006 Biology NotesDocument35 pagesBOL 2006 Biology NotesSteven XuNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 - The Origin and Diversity of LifeDocument33 pagesGeneral Biology 2 - The Origin and Diversity of LifeJohn OliquianoNo ratings yet
- 6 (9 Files Merged) PDFDocument328 pages6 (9 Files Merged) PDFPhillip BarnettNo ratings yet
- ELS ReviewerDocument2 pagesELS ReviewerKeren Missha LagarteraNo ratings yet
- Sbi3u IsuDocument13 pagesSbi3u IsuSabrina RuncoNo ratings yet
- G10 Evolution Unit Test Study Guide PDFDocument4 pagesG10 Evolution Unit Test Study Guide PDFIva TerzievaNo ratings yet
- Biology Project TRANSGENIC ANIMALS Class 12Document19 pagesBiology Project TRANSGENIC ANIMALS Class 12Shaik FaisalNo ratings yet
- Partialllllllevolution and Origin of BiodiversityDocument29 pagesPartialllllllevolution and Origin of Biodiversityroses the cupcakeNo ratings yet
- 1st Reading EFBDocument7 pages1st Reading EFBMu TiaraNo ratings yet
- Kepy 01 07 29 EtextDocument11 pagesKepy 01 07 29 Etextmradul guptaNo ratings yet
- Comprehention 05Document25 pagesComprehention 05osamaNo ratings yet
- Review: 1. What Is The Difference Between Needham and Spallanzani's Experiment?Document54 pagesReview: 1. What Is The Difference Between Needham and Spallanzani's Experiment?bae joohyunNo ratings yet
- Evolutionary Psychiatry Glossary 2Document15 pagesEvolutionary Psychiatry Glossary 2Nenad MilosevicNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.6 Biology Careers in The Twenty-First Century: Living and InteractingDocument2 pagesLesson 1.6 Biology Careers in The Twenty-First Century: Living and InteractingAlexa Mae TinongaNo ratings yet
- T H G P: HE Uman Enome RojectDocument28 pagesT H G P: HE Uman Enome RojectUpendra Sharma Sulibele100% (1)
- Life Script: How the Human Genome Discoveries Will Transform Medicine and Enhance Your HealthFrom EverandLife Script: How the Human Genome Discoveries Will Transform Medicine and Enhance Your HealthRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Acet2015 - Simulated Exam Set B - Section 7 - Verbal Analogy 8.28.2015 PDFDocument2 pagesAcet2015 - Simulated Exam Set B - Section 7 - Verbal Analogy 8.28.2015 PDFAngeline BruceNo ratings yet
- Notes - English (Grammar)Document3 pagesNotes - English (Grammar)Angeline BruceNo ratings yet
- Idioms (English and Filipino)Document7 pagesIdioms (English and Filipino)Angeline BruceNo ratings yet
- Upcat 2018 Reviewer Reading Comprehension English I. LovelessnessDocument8 pagesUpcat 2018 Reviewer Reading Comprehension English I. LovelessnessAngeline BruceNo ratings yet
- What Are Common Interview QuestionsDocument6 pagesWhat Are Common Interview QuestionsAngeline BruceNo ratings yet
- Bird Box ReviewDocument1 pageBird Box ReviewAngeline BruceNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety Awareness SymposiumDocument1 pageFire Safety Awareness SymposiumAngeline BruceNo ratings yet
- 07Document1 page07Danny ArimaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Difficult TopicsDocument2 pagesTeaching Difficult TopicsSunil PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Electronique de Puissance L2 S1Document28 pagesElectronique de Puissance L2 S1Cheikh Brahim ElkhadarNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of A Box Culvert1Document7 pagesAnalysis and Design of A Box Culvert1Uwua DanielNo ratings yet
- Reflector Antennas PDFDocument78 pagesReflector Antennas PDFsankararao gullipalliNo ratings yet
- STEAM USE in CORRUGATORS PDFDocument3 pagesSTEAM USE in CORRUGATORS PDFArtur SilvaNo ratings yet
- Jsa Brick WorkDocument4 pagesJsa Brick WorkRavi thokalNo ratings yet
- BSS 10 10 - 2E: B-3-2.1 End Deflector Type Ball ScrewsDocument3 pagesBSS 10 10 - 2E: B-3-2.1 End Deflector Type Ball ScrewsWonka AzuleNo ratings yet
- CheCal Culminating Activity - Alliones, Cairo, Consus, Daisog, Manadong, Mara - BSCHE2ADocument13 pagesCheCal Culminating Activity - Alliones, Cairo, Consus, Daisog, Manadong, Mara - BSCHE2AGalrichber ManadongNo ratings yet
- Iom P031Document12 pagesIom P031LeandroJairHerreraBallestasNo ratings yet
- Cable Gland: Type 153 IndustrialDocument2 pagesCable Gland: Type 153 IndustrialLucas ElliottNo ratings yet
- uP9011Q DS F0000Document15 pagesuP9011Q DS F0000Blue StacksNo ratings yet
- Avro CanadaDocument1 pageAvro CanadaElie ObeidNo ratings yet
- QlikSense Course ContentDocument4 pagesQlikSense Course ContentSatyam GargNo ratings yet
- SAD Chaper8Document33 pagesSAD Chaper8VJ Tang100% (1)
- Delta Performan G45Document23 pagesDelta Performan G45oscar.diaz.joveNo ratings yet
- Ionic Formulas Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesIonic Formulas Lesson Planapi-357585508No ratings yet
- Web Viva Questions & AnswersDocument8 pagesWeb Viva Questions & Answersget_togetherNo ratings yet
- FAG E1 - Spherical - Roller - Bearings - WL - 43170Document27 pagesFAG E1 - Spherical - Roller - Bearings - WL - 43170MarioNo ratings yet
- Python Simple Snake Game v1.0Document6 pagesPython Simple Snake Game v1.0Horas100% (1)
- 01-07-2021-1625129537-6-Impact - Ijrhal-14. Ijrhal - Design and Analysis of FlexvatorDocument4 pages01-07-2021-1625129537-6-Impact - Ijrhal-14. Ijrhal - Design and Analysis of FlexvatorImpact JournalsNo ratings yet
- Dental Casting DefectsDocument86 pagesDental Casting Defectsdennu101100% (3)
- ABB Price Book 452Document1 pageABB Price Book 452EliasNo ratings yet
- 6.8 Western (6.8 Western) : SAAMI New Cartridge & ChamberDocument2 pages6.8 Western (6.8 Western) : SAAMI New Cartridge & ChamberDeanNo ratings yet
- Java Mail To Yahoo and Gmail AccountsDocument2 pagesJava Mail To Yahoo and Gmail AccountsAshishKumarMishraNo ratings yet