Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 viewsBP Elevation & FP Depression (Chapter 7)
BP Elevation & FP Depression (Chapter 7)
Uploaded by
megha sharmaThis document discusses how to calculate boiling point elevation and freezing point depression when adding a solute to a solvent. It defines boiling point elevation and freezing point depression formulas using van't Hoff factor, molality, and constants specific to each solvent. The document provides an example calculation for a 7.187m NaCl solution in water, finding the boiling point is elevated to 107.35°C and freezing point is depressed to -26.7°C.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Task 1 53 BP 19 RP F 0.35849 From Physical ChemistryDocument12 pagesTask 1 53 BP 19 RP F 0.35849 From Physical ChemistrysyavinaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11 Boiling Point ElevationDocument2 pagesExperiment 11 Boiling Point ElevationHanna Gwyneth DollanoNo ratings yet
- Chem FormulasDocument24 pagesChem FormulasReniela Dela PazNo ratings yet
- Solution Part 4Document92 pagesSolution Part 4abuthahir1.mcaNo ratings yet
- Random Notes Class 12 ChemistryDocument87 pagesRandom Notes Class 12 Chemistryankitajamatia06No ratings yet
- Dollano, HAnnaGwyneth - Experiment 11 Boiling Point ElevationDocument2 pagesDollano, HAnnaGwyneth - Experiment 11 Boiling Point ElevationHanna Gwyneth DollanoNo ratings yet
- Colligative 1Document26 pagesColligative 1miguelcarlosavila81No ratings yet
- Simple Mixtures Colligative Properties: Chapter 7: SlideDocument32 pagesSimple Mixtures Colligative Properties: Chapter 7: SlideputriNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties: Nathaniel P. DugosDocument32 pagesColligative Properties: Nathaniel P. DugossololexzibNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Handoutsworksheet Brinell ValencianoDocument8 pagesWeek 5 Handoutsworksheet Brinell ValencianoPortgas D. AceNo ratings yet
- LESSON 6 Colligative PropertiesDocument39 pagesLESSON 6 Colligative PropertiesPatricia Flores100% (2)
- Colligative PropertiesDocument4 pagesColligative PropertiesDECA JALUENo ratings yet
- Gen - Chem 2 Q3 Week 5 With QA Beta 1Document17 pagesGen - Chem 2 Q3 Week 5 With QA Beta 1Andrhea Peralta100% (1)
- Changes in Vapour Pressure. (Vapour Pressure Lowering) : V - P Depends Only On The SolventDocument5 pagesChanges in Vapour Pressure. (Vapour Pressure Lowering) : V - P Depends Only On The SolventMarthy DayagNo ratings yet
- PT 2 - ChemDocument4 pagesPT 2 - ChemAlthea ErielNo ratings yet
- Formulae Solutions (Amit Sir) ParadiseDocument4 pagesFormulae Solutions (Amit Sir) Paradiseravitiwari5497No ratings yet
- Calculation On BPE FPDDocument17 pagesCalculation On BPE FPDstephniedayaoNo ratings yet
- Statement of The Problem: % RecoveryDocument5 pagesStatement of The Problem: % RecoveryAnthon ToledanoNo ratings yet
- Colligative PropertiesDocument27 pagesColligative PropertiesKofoworola MikailNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of SolutionDocument7 pagesColligative Properties of SolutionBianca GeagoniaNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocument17 pagesColligative Properties of SolutionsananahahNo ratings yet
- Boiling Point ElevationDocument2 pagesBoiling Point ElevationHannah Kristen NimoNo ratings yet
- Prac-8 - Colligative PropertiesDocument15 pagesPrac-8 - Colligative PropertiesCristiano PassarelliNo ratings yet
- Target: Figure 1. Citrus Fruits Sprayed With WaterDocument7 pagesTarget: Figure 1. Citrus Fruits Sprayed With WaterGrace AmarNo ratings yet
- Freezing Point DepressionDocument3 pagesFreezing Point DepressionFarid HossainNo ratings yet
- Colligative Prop. ContinuationDocument4 pagesColligative Prop. ContinuationBianca GeagoniaNo ratings yet
- 8.1HW Colligative Properties-SolDocument5 pages8.1HW Colligative Properties-SolabcdNo ratings yet
- Boiling Point ElevationDocument23 pagesBoiling Point Elevationopolla nianorNo ratings yet
- PDF - Colligative Property 2Document1 pagePDF - Colligative Property 2Yakshit JunejaNo ratings yet
- Colligative PropertiesDocument3 pagesColligative PropertiesCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- 2020 CHEE2001 Week 8 Tutorial SlidesDocument26 pages2020 CHEE2001 Week 8 Tutorial SlidesMuntaha ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Solutions: Points To RememberDocument15 pagesUnit 2 Solutions: Points To RememberHarpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Liquid Solution: Vapour PressureDocument4 pagesLiquid Solution: Vapour PressureAnshu BhawsarNo ratings yet
- Calculate The Vapor Pressure at 25C of An Aqueous Solution That Is 5Document7 pagesCalculate The Vapor Pressure at 25C of An Aqueous Solution That Is 5Charsea ReighNo ratings yet
- Simple Mixture DrShikin 2Document54 pagesSimple Mixture DrShikin 2PutriNo ratings yet
- 3rd Qtr-2nd Long TestDocument2 pages3rd Qtr-2nd Long Testedward henry caoileNo ratings yet
- Collogative Properties: Vapor Pressure LoweringDocument2 pagesCollogative Properties: Vapor Pressure LoweringKryzler KayeNo ratings yet
- Phase Equilibria: One-Component Systems Solutions of NonelectrolytesDocument50 pagesPhase Equilibria: One-Component Systems Solutions of NonelectrolyteskarinaNo ratings yet
- Collogative Properties: Vapor Pressure LoweringDocument3 pagesCollogative Properties: Vapor Pressure LoweringJunell TadinaNo ratings yet
- Stem08 Final LessonDocument22 pagesStem08 Final Lessonsunooyah95No ratings yet
- Co Lligat Ive PropertiesDocument9 pagesCo Lligat Ive PropertiesRizwan AliNo ratings yet
- chm431 2020 ps12 2020 AnsDocument7 pageschm431 2020 ps12 2020 AnsDede RohayatiNo ratings yet
- PT 2 - Dilution and Colligative Properties Worksheet-1Document4 pagesPT 2 - Dilution and Colligative Properties Worksheet-1Althea ErielNo ratings yet
- Colligative PropertiesDocument15 pagesColligative Propertiesprabs20069178No ratings yet
- Австри 2011 ХариултDocument12 pagesАвстри 2011 ХариултGerel BayrmagnaiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Potential in Mixtures: Partial Molar Quantities Thermodynamics of Mixing The Chemical Potentials of LiquidsDocument61 pagesChemical Potential in Mixtures: Partial Molar Quantities Thermodynamics of Mixing The Chemical Potentials of Liquidsjayven minguillanNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties: Take Out A Calculator, Paper and Pencil To Work Problems While Watching The VideoDocument17 pagesColligative Properties: Take Out A Calculator, Paper and Pencil To Work Problems While Watching The Videogymnast1No ratings yet
- Solutions Short NotesDocument3 pagesSolutions Short NotesbiriyanilaabarNo ratings yet
- Mass Balance With ExcelDocument22 pagesMass Balance With ExcelGarcia RaphNo ratings yet
- Solutions - Short Notes - Vijeta Series Class-10thDocument3 pagesSolutions - Short Notes - Vijeta Series Class-10thAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Solutions - Short Notes - Lakshya NEET 2.0 2024Document3 pagesSolutions - Short Notes - Lakshya NEET 2.0 2024umamahfarooq75No ratings yet
- Chemistyi XII Solution (Assg L-3)Document6 pagesChemistyi XII Solution (Assg L-3)Ritabrata DeNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties SolutionsDocument32 pagesColligative Properties SolutionsYeNo ratings yet
- Bag I. Chap 7Document33 pagesBag I. Chap 7Yola EfriantiNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 2Document15 pages12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 2aesthetic rushNo ratings yet
- Colligative PropertiesDocument7 pagesColligative Propertiesakshatjn100% (1)
- Solutions CLASS 12 PDF QUESTIONSDocument35 pagesSolutions CLASS 12 PDF QUESTIONSJampa SaicharanNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Problems - Freezing Point Depression and Other Solution Properties With AnswersDocument16 pagesAP Chemistry Problems - Freezing Point Depression and Other Solution Properties With AnswersCameron Kaye ColamboNo ratings yet
- Colligative PropertiesDocument7 pagesColligative PropertiesadwinanilNo ratings yet
- Blockbuster Problems Chemistry QnsDocument121 pagesBlockbuster Problems Chemistry Qnstrinathreddy3300No ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science G8Q3.5Document3 pagesReviewer in Science G8Q3.5SSGNo ratings yet
- Extraction and Distribution CoefficientDocument3 pagesExtraction and Distribution CoefficientSaeed KhawamNo ratings yet
- Pulp & Paper-SystemGuide-0221Document8 pagesPulp & Paper-SystemGuide-0221Surung P. Kreison (CARBOLINE)No ratings yet
- Unit Test 4 Alchemist Science Academy PDFDocument10 pagesUnit Test 4 Alchemist Science Academy PDFAanchal PathakNo ratings yet
- Dynamon NRG 1030 (Ac)Document4 pagesDynamon NRG 1030 (Ac)Rodolfo Deudor CondezoNo ratings yet
- Paper and Surface Chemicals - Part2 PDFDocument13 pagesPaper and Surface Chemicals - Part2 PDFHgagselim SelimNo ratings yet
- General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: An Integrated ApproachDocument100 pagesGeneral, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: An Integrated ApproachRon SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Quality of WaterDocument27 pagesQuality of WaterSuresh Varma Kopanathi0% (1)
- Methanol Storage and HandlingDocument2 pagesMethanol Storage and HandlingSlim ToumiNo ratings yet
- 2005 Kodera - Determination of Free Chlorine Based On Anodic Voltammetry Using Platinum, Gold and Glassy Caron ElectrodesDocument6 pages2005 Kodera - Determination of Free Chlorine Based On Anodic Voltammetry Using Platinum, Gold and Glassy Caron ElectrodestovarsaNo ratings yet
- Fuels and CombustionDocument41 pagesFuels and CombustionranveerNo ratings yet
- PDF 2D Metal Carbides and Nitrides Mxenes Structure Properties and Applications Babak Anasori Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF 2D Metal Carbides and Nitrides Mxenes Structure Properties and Applications Babak Anasori Ebook Full Chapterpaul.popp121100% (8)
- Detergent Ingredient Database Final Report (DID-list) PDFDocument13 pagesDetergent Ingredient Database Final Report (DID-list) PDFherrumbeNo ratings yet
- MSDS-kramco 750Document2 pagesMSDS-kramco 750marosnaxNo ratings yet
- PC3150 PDFDocument8 pagesPC3150 PDFMaffone NumerounoNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 1Document8 pagesExperiment No 1Rhoellet VenzonNo ratings yet
- APV Corrosion Handbook 1035 01 08 2008 PDFDocument44 pagesAPV Corrosion Handbook 1035 01 08 2008 PDFFaboNo ratings yet
- ISO 8501-3 Prep PDFDocument6 pagesISO 8501-3 Prep PDFAdnan HussainNo ratings yet
- Assignment L01-T4Document8 pagesAssignment L01-T4MawareNo ratings yet
- Pasar PDFDocument70 pagesPasar PDFRalph Carlo EvidenteNo ratings yet
- CBSE 12 Chemistry Question Term2Document4 pagesCBSE 12 Chemistry Question Term2R roseNo ratings yet
- F T. Topolimero. 24022020Document2 pagesF T. Topolimero. 24022020FedericoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument13 pagesUntitledjennifer lohNo ratings yet
- Xanthan Gum Its Biopharmaceutical Applications: An OverviewDocument14 pagesXanthan Gum Its Biopharmaceutical Applications: An OverviewmaizhafiraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Quantitative Color ReactionsDocument5 pagesExperiment 2: Quantitative Color ReactionsIson DyNo ratings yet
- KNER Propellant IgnitionDocument2 pagesKNER Propellant IgnitionBa RiNo ratings yet
- Query4 PDFDocument1 pageQuery4 PDFAlessandro1975No ratings yet
- Review For Test 2 ch3 and ch4Document5 pagesReview For Test 2 ch3 and ch4Alison VelázquezNo ratings yet
- Enzymes 1Document95 pagesEnzymes 1Hawi kelbessaNo ratings yet
BP Elevation & FP Depression (Chapter 7)
BP Elevation & FP Depression (Chapter 7)
Uploaded by
megha sharma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views1 pageThis document discusses how to calculate boiling point elevation and freezing point depression when adding a solute to a solvent. It defines boiling point elevation and freezing point depression formulas using van't Hoff factor, molality, and constants specific to each solvent. The document provides an example calculation for a 7.187m NaCl solution in water, finding the boiling point is elevated to 107.35°C and freezing point is depressed to -26.7°C.
Original Description:
bp and fp elevation class 12
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses how to calculate boiling point elevation and freezing point depression when adding a solute to a solvent. It defines boiling point elevation and freezing point depression formulas using van't Hoff factor, molality, and constants specific to each solvent. The document provides an example calculation for a 7.187m NaCl solution in water, finding the boiling point is elevated to 107.35°C and freezing point is depressed to -26.7°C.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views1 pageBP Elevation & FP Depression (Chapter 7)
BP Elevation & FP Depression (Chapter 7)
Uploaded by
megha sharmaThis document discusses how to calculate boiling point elevation and freezing point depression when adding a solute to a solvent. It defines boiling point elevation and freezing point depression formulas using van't Hoff factor, molality, and constants specific to each solvent. The document provides an example calculation for a 7.187m NaCl solution in water, finding the boiling point is elevated to 107.35°C and freezing point is depressed to -26.7°C.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
A.
Romero 2008
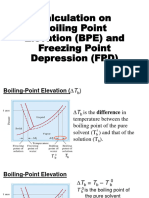
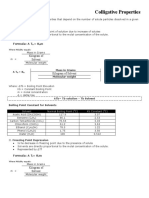
Calculating Boiling Point Elevation and Freezing Point Depression
CHEM 30A
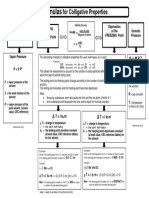
Boiling Point Elevation:
Change in BP
(add this number to the Tb = i Kb m
normal BP) mol solute
molality (m) =
kg solvent
mol particles constant (different for each solvent)
van’t Hoff factor =
mol of solute
BP = BPnormal + Tb
Freezing Point Depression:
Change in FP
(subtract this number Tf = i Kf m
from the normal FP)
FP = FPnormal – Tf
Example: What are the BP and FP of a 7.187m NaCl solution?
For water: Kb = 0.512 ºC · kg H2O / mol particles
Kf = 1.86 ºC · kg H2O / mol particles
2 mol particles 0.512 ºC · kg H2O 7.187 mol NaCl
Tb = i Kb m = = 7.35 ºC
1 mol NaCl mol particles 1 kg H2O
BPsoln = BPnormal + Tb = 100.00ºC + 7.35ºC = 107.35ºC
2 mol particles 1.86 ºC · kg H2O 7.187 mol NaCl
Tf = i Kf m = = 26.7 ºC
1 mol NaCl mol particles 1 kg H2O
FPsoln = FPnormal - Tf = 0.00ºC – 26.7ºC = –26.7ºC
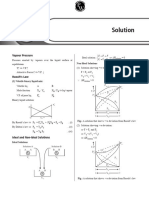
Pure Water w/
Water Solute
gas
BP 107.35ºC
100ºC
liquid to the range of temperatures over which the solution
to
FP 0ºC is a liquid is colligatively extended on both ends
solid –26.7ºC
You might also like
- Task 1 53 BP 19 RP F 0.35849 From Physical ChemistryDocument12 pagesTask 1 53 BP 19 RP F 0.35849 From Physical ChemistrysyavinaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11 Boiling Point ElevationDocument2 pagesExperiment 11 Boiling Point ElevationHanna Gwyneth DollanoNo ratings yet
- Chem FormulasDocument24 pagesChem FormulasReniela Dela PazNo ratings yet
- Solution Part 4Document92 pagesSolution Part 4abuthahir1.mcaNo ratings yet
- Random Notes Class 12 ChemistryDocument87 pagesRandom Notes Class 12 Chemistryankitajamatia06No ratings yet
- Dollano, HAnnaGwyneth - Experiment 11 Boiling Point ElevationDocument2 pagesDollano, HAnnaGwyneth - Experiment 11 Boiling Point ElevationHanna Gwyneth DollanoNo ratings yet
- Colligative 1Document26 pagesColligative 1miguelcarlosavila81No ratings yet
- Simple Mixtures Colligative Properties: Chapter 7: SlideDocument32 pagesSimple Mixtures Colligative Properties: Chapter 7: SlideputriNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties: Nathaniel P. DugosDocument32 pagesColligative Properties: Nathaniel P. DugossololexzibNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Handoutsworksheet Brinell ValencianoDocument8 pagesWeek 5 Handoutsworksheet Brinell ValencianoPortgas D. AceNo ratings yet
- LESSON 6 Colligative PropertiesDocument39 pagesLESSON 6 Colligative PropertiesPatricia Flores100% (2)
- Colligative PropertiesDocument4 pagesColligative PropertiesDECA JALUENo ratings yet
- Gen - Chem 2 Q3 Week 5 With QA Beta 1Document17 pagesGen - Chem 2 Q3 Week 5 With QA Beta 1Andrhea Peralta100% (1)
- Changes in Vapour Pressure. (Vapour Pressure Lowering) : V - P Depends Only On The SolventDocument5 pagesChanges in Vapour Pressure. (Vapour Pressure Lowering) : V - P Depends Only On The SolventMarthy DayagNo ratings yet
- PT 2 - ChemDocument4 pagesPT 2 - ChemAlthea ErielNo ratings yet
- Formulae Solutions (Amit Sir) ParadiseDocument4 pagesFormulae Solutions (Amit Sir) Paradiseravitiwari5497No ratings yet
- Calculation On BPE FPDDocument17 pagesCalculation On BPE FPDstephniedayaoNo ratings yet
- Statement of The Problem: % RecoveryDocument5 pagesStatement of The Problem: % RecoveryAnthon ToledanoNo ratings yet
- Colligative PropertiesDocument27 pagesColligative PropertiesKofoworola MikailNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of SolutionDocument7 pagesColligative Properties of SolutionBianca GeagoniaNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocument17 pagesColligative Properties of SolutionsananahahNo ratings yet
- Boiling Point ElevationDocument2 pagesBoiling Point ElevationHannah Kristen NimoNo ratings yet
- Prac-8 - Colligative PropertiesDocument15 pagesPrac-8 - Colligative PropertiesCristiano PassarelliNo ratings yet
- Target: Figure 1. Citrus Fruits Sprayed With WaterDocument7 pagesTarget: Figure 1. Citrus Fruits Sprayed With WaterGrace AmarNo ratings yet
- Freezing Point DepressionDocument3 pagesFreezing Point DepressionFarid HossainNo ratings yet
- Colligative Prop. ContinuationDocument4 pagesColligative Prop. ContinuationBianca GeagoniaNo ratings yet
- 8.1HW Colligative Properties-SolDocument5 pages8.1HW Colligative Properties-SolabcdNo ratings yet
- Boiling Point ElevationDocument23 pagesBoiling Point Elevationopolla nianorNo ratings yet
- PDF - Colligative Property 2Document1 pagePDF - Colligative Property 2Yakshit JunejaNo ratings yet
- Colligative PropertiesDocument3 pagesColligative PropertiesCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- 2020 CHEE2001 Week 8 Tutorial SlidesDocument26 pages2020 CHEE2001 Week 8 Tutorial SlidesMuntaha ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Solutions: Points To RememberDocument15 pagesUnit 2 Solutions: Points To RememberHarpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Liquid Solution: Vapour PressureDocument4 pagesLiquid Solution: Vapour PressureAnshu BhawsarNo ratings yet
- Calculate The Vapor Pressure at 25C of An Aqueous Solution That Is 5Document7 pagesCalculate The Vapor Pressure at 25C of An Aqueous Solution That Is 5Charsea ReighNo ratings yet
- Simple Mixture DrShikin 2Document54 pagesSimple Mixture DrShikin 2PutriNo ratings yet
- 3rd Qtr-2nd Long TestDocument2 pages3rd Qtr-2nd Long Testedward henry caoileNo ratings yet
- Collogative Properties: Vapor Pressure LoweringDocument2 pagesCollogative Properties: Vapor Pressure LoweringKryzler KayeNo ratings yet
- Phase Equilibria: One-Component Systems Solutions of NonelectrolytesDocument50 pagesPhase Equilibria: One-Component Systems Solutions of NonelectrolyteskarinaNo ratings yet
- Collogative Properties: Vapor Pressure LoweringDocument3 pagesCollogative Properties: Vapor Pressure LoweringJunell TadinaNo ratings yet
- Stem08 Final LessonDocument22 pagesStem08 Final Lessonsunooyah95No ratings yet
- Co Lligat Ive PropertiesDocument9 pagesCo Lligat Ive PropertiesRizwan AliNo ratings yet
- chm431 2020 ps12 2020 AnsDocument7 pageschm431 2020 ps12 2020 AnsDede RohayatiNo ratings yet
- PT 2 - Dilution and Colligative Properties Worksheet-1Document4 pagesPT 2 - Dilution and Colligative Properties Worksheet-1Althea ErielNo ratings yet
- Colligative PropertiesDocument15 pagesColligative Propertiesprabs20069178No ratings yet
- Австри 2011 ХариултDocument12 pagesАвстри 2011 ХариултGerel BayrmagnaiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Potential in Mixtures: Partial Molar Quantities Thermodynamics of Mixing The Chemical Potentials of LiquidsDocument61 pagesChemical Potential in Mixtures: Partial Molar Quantities Thermodynamics of Mixing The Chemical Potentials of Liquidsjayven minguillanNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties: Take Out A Calculator, Paper and Pencil To Work Problems While Watching The VideoDocument17 pagesColligative Properties: Take Out A Calculator, Paper and Pencil To Work Problems While Watching The Videogymnast1No ratings yet
- Solutions Short NotesDocument3 pagesSolutions Short NotesbiriyanilaabarNo ratings yet
- Mass Balance With ExcelDocument22 pagesMass Balance With ExcelGarcia RaphNo ratings yet
- Solutions - Short Notes - Vijeta Series Class-10thDocument3 pagesSolutions - Short Notes - Vijeta Series Class-10thAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Solutions - Short Notes - Lakshya NEET 2.0 2024Document3 pagesSolutions - Short Notes - Lakshya NEET 2.0 2024umamahfarooq75No ratings yet
- Chemistyi XII Solution (Assg L-3)Document6 pagesChemistyi XII Solution (Assg L-3)Ritabrata DeNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties SolutionsDocument32 pagesColligative Properties SolutionsYeNo ratings yet
- Bag I. Chap 7Document33 pagesBag I. Chap 7Yola EfriantiNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 2Document15 pages12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 2aesthetic rushNo ratings yet
- Colligative PropertiesDocument7 pagesColligative Propertiesakshatjn100% (1)
- Solutions CLASS 12 PDF QUESTIONSDocument35 pagesSolutions CLASS 12 PDF QUESTIONSJampa SaicharanNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Problems - Freezing Point Depression and Other Solution Properties With AnswersDocument16 pagesAP Chemistry Problems - Freezing Point Depression and Other Solution Properties With AnswersCameron Kaye ColamboNo ratings yet
- Colligative PropertiesDocument7 pagesColligative PropertiesadwinanilNo ratings yet
- Blockbuster Problems Chemistry QnsDocument121 pagesBlockbuster Problems Chemistry Qnstrinathreddy3300No ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science G8Q3.5Document3 pagesReviewer in Science G8Q3.5SSGNo ratings yet
- Extraction and Distribution CoefficientDocument3 pagesExtraction and Distribution CoefficientSaeed KhawamNo ratings yet
- Pulp & Paper-SystemGuide-0221Document8 pagesPulp & Paper-SystemGuide-0221Surung P. Kreison (CARBOLINE)No ratings yet
- Unit Test 4 Alchemist Science Academy PDFDocument10 pagesUnit Test 4 Alchemist Science Academy PDFAanchal PathakNo ratings yet
- Dynamon NRG 1030 (Ac)Document4 pagesDynamon NRG 1030 (Ac)Rodolfo Deudor CondezoNo ratings yet
- Paper and Surface Chemicals - Part2 PDFDocument13 pagesPaper and Surface Chemicals - Part2 PDFHgagselim SelimNo ratings yet
- General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: An Integrated ApproachDocument100 pagesGeneral, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: An Integrated ApproachRon SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Quality of WaterDocument27 pagesQuality of WaterSuresh Varma Kopanathi0% (1)
- Methanol Storage and HandlingDocument2 pagesMethanol Storage and HandlingSlim ToumiNo ratings yet
- 2005 Kodera - Determination of Free Chlorine Based On Anodic Voltammetry Using Platinum, Gold and Glassy Caron ElectrodesDocument6 pages2005 Kodera - Determination of Free Chlorine Based On Anodic Voltammetry Using Platinum, Gold and Glassy Caron ElectrodestovarsaNo ratings yet
- Fuels and CombustionDocument41 pagesFuels and CombustionranveerNo ratings yet
- PDF 2D Metal Carbides and Nitrides Mxenes Structure Properties and Applications Babak Anasori Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF 2D Metal Carbides and Nitrides Mxenes Structure Properties and Applications Babak Anasori Ebook Full Chapterpaul.popp121100% (8)
- Detergent Ingredient Database Final Report (DID-list) PDFDocument13 pagesDetergent Ingredient Database Final Report (DID-list) PDFherrumbeNo ratings yet
- MSDS-kramco 750Document2 pagesMSDS-kramco 750marosnaxNo ratings yet
- PC3150 PDFDocument8 pagesPC3150 PDFMaffone NumerounoNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 1Document8 pagesExperiment No 1Rhoellet VenzonNo ratings yet
- APV Corrosion Handbook 1035 01 08 2008 PDFDocument44 pagesAPV Corrosion Handbook 1035 01 08 2008 PDFFaboNo ratings yet
- ISO 8501-3 Prep PDFDocument6 pagesISO 8501-3 Prep PDFAdnan HussainNo ratings yet
- Assignment L01-T4Document8 pagesAssignment L01-T4MawareNo ratings yet
- Pasar PDFDocument70 pagesPasar PDFRalph Carlo EvidenteNo ratings yet
- CBSE 12 Chemistry Question Term2Document4 pagesCBSE 12 Chemistry Question Term2R roseNo ratings yet
- F T. Topolimero. 24022020Document2 pagesF T. Topolimero. 24022020FedericoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument13 pagesUntitledjennifer lohNo ratings yet
- Xanthan Gum Its Biopharmaceutical Applications: An OverviewDocument14 pagesXanthan Gum Its Biopharmaceutical Applications: An OverviewmaizhafiraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Quantitative Color ReactionsDocument5 pagesExperiment 2: Quantitative Color ReactionsIson DyNo ratings yet
- KNER Propellant IgnitionDocument2 pagesKNER Propellant IgnitionBa RiNo ratings yet
- Query4 PDFDocument1 pageQuery4 PDFAlessandro1975No ratings yet
- Review For Test 2 ch3 and ch4Document5 pagesReview For Test 2 ch3 and ch4Alison VelázquezNo ratings yet
- Enzymes 1Document95 pagesEnzymes 1Hawi kelbessaNo ratings yet