Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Neurotransmitters
Types of Neurotransmitters
Uploaded by
sophia0agulto-10 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
105 views4 pagesThis document summarizes different types of neurotransmitters, including their locations, effects, functions, and related disorders. It discusses four main categories: (1) acetylcholine and monoamines like dopamine and serotonin, found throughout the central and peripheral nervous systems; (2) amino acid neurotransmitters such as glutamate and GABA, the most prevalent in the brain; (3) neuropeptides produced in various areas and having diverse regulatory roles; and (4) examples within each category along with their specific locations, functions, and implications if deficient or in excess.
Original Description:
n/a
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes different types of neurotransmitters, including their locations, effects, functions, and related disorders. It discusses four main categories: (1) acetylcholine and monoamines like dopamine and serotonin, found throughout the central and peripheral nervous systems; (2) amino acid neurotransmitters such as glutamate and GABA, the most prevalent in the brain; (3) neuropeptides produced in various areas and having diverse regulatory roles; and (4) examples within each category along with their specific locations, functions, and implications if deficient or in excess.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
105 views4 pagesTypes of Neurotransmitters
Types of Neurotransmitters
Uploaded by
sophia0agulto-1This document summarizes different types of neurotransmitters, including their locations, effects, functions, and related disorders. It discusses four main categories: (1) acetylcholine and monoamines like dopamine and serotonin, found throughout the central and peripheral nervous systems; (2) amino acid neurotransmitters such as glutamate and GABA, the most prevalent in the brain; (3) neuropeptides produced in various areas and having diverse regulatory roles; and (4) examples within each category along with their specific locations, functions, and implications if deficient or in excess.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
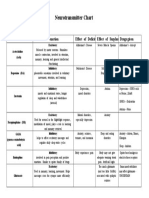
Types of Location Effects Functions Related Disorders
Neurotransmitters and Symptoms
A. Acetylcholine A small molecule neurotransmitter created by adding an acetyl group to
a choline molecule. A neurotransmitter at neuromuscular junctions at
many of the synapses of the autonomic nervous system and at synapses
in several parts of central nervous system.
Acetylcholine Brain, spinal Excitatory in Cognitive Deficiency:
cord, PNS, brain and functioning Alzheimer’s disease;
especially autonomic (learning and delusion; paralysis
some organs nervous memory) Excess: convulsions;
of the system; Skeletal muscle spasms; tremors
parasympathe Inhibitory in movement
tic nervous cardiovascular contraction
system muscles
B. Monoamine Synthesized from a single amino acid hence the name monoamine (one
amine) and slightly larger than amino acid neurotransmitters and their
effect tend to be more diffuse.
1. Dopamine brain Excitatory/inhi Motor activity Deficiency;
bitory and Parkinson’s disease;
coordination; mood disorders;
learning and manic depression
memory; Excess:
attention; Schizophrenic
emotional reactions;
response aggression
2. Epinephrine Brain stem excitatory Alertness and Deficiency:
wakefulness(sl Depression; bipolar
eep and eating disorder; fatigue;
behavior memory
regulator) impairment
Excess: anxiety;
schizophrenia,
hyperactivity
3. Norephinephrine Brain stem excitatory Alertness and Deficiency:
(NE) wakefulness(sl Depression; bipolar
eep and eating disorder; fatigue;
behavior memory
regulator) impairment
Excess: anxiety;
schizophrenia,
hyperactivity
4. Serotonin Brain, spinal Inhibitory Regulates Deficiency:
cord mood, sleep, Insomnia;
impulsivity and depression(usually
pain, found in suicidal
aggression, and patients);
appetite
alcoholism; eating
disorder; aggression
Excess: sleepiness;
lack of motivation
C. Amino Acid The neurotransmitters in the vast majority of fast-acting, directed
synapses in the central nervous system and the molecular building
blocks of protein.
1. Glutamate Brain, spinal Primary Learning, Mood
cord Excitatory memory,
anxiety,
emotions
2. Aspartate Brain, spinal Stimulatory promote a Huntington's
cord robust disease; liver
metabolism; disease;
promotes a cardiovascular
transportation disease
of minerals to
the cells, which
are essential to
form healthy
RNA and DNA;
stimulating an
increased
production of
immunoglobuli
ns and
antibodies.
3. Glycine Brain, spinal Inhibitory regulate the Hyperglycinemia;
cord synthesis of the Lethargy; Muscle
bile acid Hypotonia;
utilized to help Apnea
you digest fats;
help create
muscle tissues;
convert
glucose into
energy
4. Gamma Brain, spinal Primary Facilitates the Deficiency: Anxiety;
Amino-butyric cord Inhibitory control of panic depression;
Acid (GABA) anxiety and epilepsy/seizures;
arousal; Huntington’s chorea
learning Excess: sluggish;
lack of motivation
D. Neuropeptides Functions in multiple capacities and not just as neurotransmitters.
Small protein-like molecules (peptides) used by neurons to communicate
with each other. They are neuronal signaling molecules that influence
the activity of the brain and the body in specific ways.
1. Pituitary peptides Brain Inhibitory Contains Craniopharyngioma;
neuropeptides Cushing's Disease;
that were first Diabetes Insipidus;
identified as Hypopituitarism;
hormones Non-functioning
released by tumors;
pituitary Prolactinoma
2. Hypothalamic Brain Inhibitory Contains sensitivity to cold;
peptides neuropeptides depression;
that were first tiredness;
identified as impotence;
hormones hair loss;
released by menstrual cycle
hypothalamus changes;
constipation;
lower mental
capacity;
weight gain
3. Brain-gut peptides Brain Inhibitory Contains Anxiety; depression;
neuropeptides addictive behaviors
that were first
discovered in
the gut
4. Opioid peptides Brain Inhibitory Contains Alzheimer's disease;
neuropeptides Huntington's
that are similar disease
in structure to
the active
ingredients of
opium
5. Miscellaneous Brain Inhibitory Contains all of Diabetes
peptides the
neuropeptides
transmitters
that do not fit
into one of the
four categories
E. Unconventional Produced in neural cytoplasm and immediately diffused through the cell
Neurotransmitters membrane into the extracellular fluid and then into nearby cells.
1. Soluble gas synaptic Stimulatory Involve in Chronic obstructive
neurotransmitters vesicles, retrograde pulmonary disease
(nitric oxide and clustered transmission;
carbon monoxide) close to the transmit
cell feedback
membrane at signals from
the axon the post
terminal of synaptic
the neuron back to
presynaptic the presynaptic
neuron neuron
2. Endocannabinoids central and Inhibitory Inhibits Struggle with
peripheral subsequent insomnia to the
nervous synaptic point of taking
systems transmission medication;
Anxiety;
Anger management
issues;
Depression;
Conditions
associated with
heightened
inflammation
throughout your
body like arthritis;
Bone loss
3. Anandamide Cell Inhibitory Synthesize Fibromyalgia;
membrane fatty Pain;
compounds Anorexia;
Depression;
Irritable Bowel
Syndrome (IBS)
Migraines;
Multiple Sclerosis
(MS);
Post-Traumatic
Stress Disorder
(PTSD);
Huntington’s;
Parkinson’s;
Motion Sickness;
Autism
You might also like
- Neurobiology A Functional ApproachDocument644 pagesNeurobiology A Functional Approachpeppino Wuver100% (2)
- SAB HLTAAP001 Recognise Healthy Body SystemsDocument67 pagesSAB HLTAAP001 Recognise Healthy Body SystemsBbas T.95% (20)
- Neurotransmitter ChartDocument1 pageNeurotransmitter Chartmonster40lbs100% (2)
- Get Ripped RotationDocument19 pagesGet Ripped Rotationmandyaquarius0% (1)
- Ghost SyndromesDocument7 pagesGhost Syndromespeter911x2134No ratings yet
- Approach To Patients With Altered ConsciousnessDocument54 pagesApproach To Patients With Altered ConsciousnessEidri MoralesNo ratings yet
- Biological Bases Study GuideDocument13 pagesBiological Bases Study Guideapi-421695293No ratings yet
- MCQ - MuscleDocument10 pagesMCQ - Musclebiruk GNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters Cuadro PDFDocument2 pagesNeurotransmitters Cuadro PDFCarina Castillo ValdiviezoNo ratings yet
- Psychy Supplement For Regular & Foundation 2020 PDFDocument2 pagesPsychy Supplement For Regular & Foundation 2020 PDFRAM KUMARNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitter Cheat Sheet AP ReviewDocument2 pagesNeurotransmitter Cheat Sheet AP ReviewNathania DawitNo ratings yet
- CHP 3 PSYCHDocument8 pagesCHP 3 PSYCHEmma Mahoney100% (1)
- NeurotransmittersDocument1 pageNeurotransmittersmegs13045No ratings yet
- Neurotransmitter Final2023Document72 pagesNeurotransmitter Final2023WongelNo ratings yet
- Neurobiologic Theories AND Psychopharmacology: BY Group 1Document15 pagesNeurobiologic Theories AND Psychopharmacology: BY Group 1PALEN, DONNA GRACE B.No ratings yet
- Cerebellum & Brain-Stem AnatomyDocument23 pagesCerebellum & Brain-Stem AnatomyMuhammad ShahzaibNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves TableDocument2 pagesCranial Nerves TableKim Ocampo RojasNo ratings yet
- Description of Location Description of FunctionDocument2 pagesDescription of Location Description of FunctionbrendaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Memory: Introduction To PsychologyDocument6 pagesChapter 5: Memory: Introduction To PsychologyRoseNo ratings yet
- Motor System FinalDocument79 pagesMotor System FinalNdor BariboloNo ratings yet
- 1102 Neurons and NeurotransmittersDocument28 pages1102 Neurons and NeurotransmittersDawud MuhammadNo ratings yet
- NeuronDocument4 pagesNeuroniris danielle barolaNo ratings yet
- 7 NeurotransmittersDocument15 pages7 Neurotransmittershana77777100% (1)
- 9 PsychopathologyDocument2 pages9 PsychopathologyMonchee YusonNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitter Pathway in PsychiatryDocument22 pagesNeurotransmitter Pathway in PsychiatryameerNo ratings yet
- Delirium: DR A.Vijaya Chandra Reddy Associate Professor of Psychaitry Dept. of Psychiatry Rims, KadapaDocument20 pagesDelirium: DR A.Vijaya Chandra Reddy Associate Professor of Psychaitry Dept. of Psychiatry Rims, KadapaPraveen Pravii100% (1)
- Cerebral CortexDocument26 pagesCerebral CortexAkila AkinsNo ratings yet
- Phenomenology Yr4Document52 pagesPhenomenology Yr4Mohd ImranNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument48 pagesAutonomic Nervous Systembasgsr100% (1)
- Psychotherapeutic Drugs: Pam Pam LamDocument7 pagesPsychotherapeutic Drugs: Pam Pam Lamchubbygunny_29776413No ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument8 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorLaine DerainNo ratings yet
- Bio-Phy Psy Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesBio-Phy Psy Lecture NotesakaneNo ratings yet
- NeurotransmittersDocument92 pagesNeurotransmittersClare Ducut100% (1)
- Temporal LobeDocument68 pagesTemporal LobeRupinder GillNo ratings yet
- Psychology The Mind 2016Document30 pagesPsychology The Mind 2016Johan Alejandro Gamez AfonsoNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics PDFDocument10 pagesMnemonics PDFAhmed HamidNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Endocrine System NotesDocument12 pagesIntroduction To The Endocrine System NotesJulioNo ratings yet
- Functional Areas of BrainDocument8 pagesFunctional Areas of BrainirfanzukriNo ratings yet
- Review of Endocrine SystemDocument32 pagesReview of Endocrine SystemJames FNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters: A. Paracrine Regulators (Tissue Hormones)Document11 pagesNeurotransmitters: A. Paracrine Regulators (Tissue Hormones)Prasana100% (1)
- 1.7 Introduction To Neuroanatomy PDFDocument80 pages1.7 Introduction To Neuroanatomy PDFCarina SuarezNo ratings yet
- Mental Status ExamDocument1 pageMental Status Examjnyg008No ratings yet
- Physiology FC PainDocument4 pagesPhysiology FC Painiqz saniomeNo ratings yet
- First Seizure: EEG and Neuroimaging Following An Epileptic SeizureDocument7 pagesFirst Seizure: EEG and Neuroimaging Following An Epileptic SeizureheribertoNo ratings yet
- Brain CellsDocument4 pagesBrain CellsJulius RicardeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of BrainDocument9 pagesAnatomy of Brainfever_159100% (1)
- Cognitive Disorders PresentationDocument70 pagesCognitive Disorders PresentationWasiu AfoloabiNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience Pre-Midterm Pathways: Fall 2012Document46 pagesNeuroscience Pre-Midterm Pathways: Fall 2012Yezin ShamoonNo ratings yet
- Memory FormativeDocument10 pagesMemory FormativeNatalie HoltNo ratings yet
- Vertigo DavidsonDocument13 pagesVertigo DavidsonifahInayahNo ratings yet
- Anxiety and Panic DisordersDocument6 pagesAnxiety and Panic DisordersNo OneNo ratings yet
- NeurobiologyDocument66 pagesNeurobiologybcastle1No ratings yet
- Posture and EquilibriumDocument26 pagesPosture and Equilibriumshwetha pc100% (1)
- Temporal LobeDocument15 pagesTemporal LobeManya KrishnaNo ratings yet
- VEM5384 Clincial Neurology DisordersDocument62 pagesVEM5384 Clincial Neurology DisordersdeadnarwhalNo ratings yet
- Terms in The Field of PsychiatryDocument18 pagesTerms in The Field of PsychiatryOchie YecyecanNo ratings yet
- Significant Functional ImpairmentDocument4 pagesSignificant Functional Impairmentxcupcakex122006No ratings yet
- Post-Seclusion And/or Restraint Review in Psychiatry: A Scoping Review Article OutlineDocument27 pagesPost-Seclusion And/or Restraint Review in Psychiatry: A Scoping Review Article OutlineStudentnurseMjNo ratings yet
- What Are Extrapyramidal SymptomsDocument2 pagesWhat Are Extrapyramidal SymptomscristieristiieNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves (Association & Motor Neurons)Document2 pagesCranial Nerves (Association & Motor Neurons)Ernie G. Bautista II, RN, MD100% (3)
- Seizures and The Epilepsies in Infants, Children, and AdolescentsDocument12 pagesSeizures and The Epilepsies in Infants, Children, and AdolescentsCecille Ann CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing: TH THDocument9 pagesPsychiatric Nursing: TH THrockstoneyNo ratings yet
- PsychoneuroimmunologyDocument23 pagesPsychoneuroimmunologyMohmmadRjab SederNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument7 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorAsma Tariq JavedNo ratings yet
- Full Text 01Document86 pagesFull Text 01bogdan anghelNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Unit 4 - Unit 5: Section ADocument8 pagesQuestion Bank Unit 4 - Unit 5: Section AJamhari SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Jacob Gutierrez - Virtual Bioman PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesJacob Gutierrez - Virtual Bioman PhotosynthesisJacob GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Shock Case StudyDocument2 pagesShock Case StudyDonna LLerandiNo ratings yet
- Retdem 6 MarchDocument2 pagesRetdem 6 MarchCurtney PedriaNo ratings yet
- Wilkins Clinical Assessment in Respiratory Care 7th Edition by Heuer - Test BankDocument37 pagesWilkins Clinical Assessment in Respiratory Care 7th Edition by Heuer - Test BankalishcathrinNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Asthma PDFDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Diagram of Asthma PDFYhenlee Rhizelle MarquezNo ratings yet
- Progressive Resisted Exercise BPTDocument24 pagesProgressive Resisted Exercise BPTWraith GAMING100% (1)
- Acute Manifestations of Neuromuscular DiseaseDocument10 pagesAcute Manifestations of Neuromuscular DiseasetsyrahmaniNo ratings yet
- Makalah BBLRDocument1 pageMakalah BBLRrizky100% (1)
- Chapter 39 AntihypertensivesDocument4 pagesChapter 39 AntihypertensivesErika Joy Cabison TamayoNo ratings yet
- Spinal ReflexesDocument4 pagesSpinal Reflexesjp100% (1)
- Differential Diagnosis of PULMONARY EDEMADocument3 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of PULMONARY EDEMAHY Hong YiNo ratings yet
- HematopoiesisDocument3 pagesHematopoiesisVino OrajayNo ratings yet
- בלי תשובות מבחן בפסיכולוגיה פיזיולוגית א - רביד דורון - המכללת האקדמית תל אביב יפוDocument6 pagesבלי תשובות מבחן בפסיכולוגיה פיזיולוגית א - רביד דורון - המכללת האקדמית תל אביב יפוTali KasisNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology 14Th Edition Fox Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument37 pagesHuman Physiology 14Th Edition Fox Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFletitiaestheru3hnxz100% (12)
- Carbon Monoxide Poisoning in ChildrenDocument10 pagesCarbon Monoxide Poisoning in ChildrenSubash PaudealNo ratings yet
- A Patient With Oedema PresentationDocument35 pagesA Patient With Oedema PresentationWasswaNo ratings yet
- Sleep and Its Disturbances: Submitted To Ms. Ranganayaki L (Professor)Document83 pagesSleep and Its Disturbances: Submitted To Ms. Ranganayaki L (Professor)Satbir GillNo ratings yet
- Iii. Clinical Discussion of The Disease A. Pathophysiology of Fracture I. (Book Based)Document4 pagesIii. Clinical Discussion of The Disease A. Pathophysiology of Fracture I. (Book Based)Lemuel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Lech in New Article 121208Document10 pagesLech in New Article 121208Saidah SaidNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument117 pagesMuscular SystemAiman Bañaga Arabain100% (1)
- Hypertension ReviewerDocument9 pagesHypertension Reviewermecleo93No ratings yet
- Cell Communication NotesDocument3 pagesCell Communication NoteselyssaNo ratings yet
- COPD Case StudyDocument10 pagesCOPD Case Studyskylineco4No ratings yet
- Acid Base Balance Fluid BalanceDocument32 pagesAcid Base Balance Fluid BalanceLIDIYA MOL P VNo ratings yet