Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 viewsSpecies of Homo: S S Sapiens
Species of Homo: S S Sapiens
Uploaded by
AloyThere were three known species of Homo: Homo habilis, Homo erectus, and Homo sapiens. Homo habilis lived around 2.5 million years ago in Africa and was the first to use stone tools. Homo erectus emerged between 1.8-300,000 years ago and was the first early human to migrate out of Africa. Homo sapiens, the last in the human evolutionary path, developed a large cranium size around 120,000 years ago and was the only surviving human species after 30,000 years ago. Brain size increased over time and was linked to greater intelligence and tool usage, helping humans adapt.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Investigatory ProjectDocument21 pagesInvestigatory ProjectDiya 2788% (86)
- Thesis Proposal (Final)Document22 pagesThesis Proposal (Final)Geneva Katug80% (10)
- Yellow Modern History Timeline InfographicDocument1 pageYellow Modern History Timeline Infographiclamar.w.a.b2010No ratings yet
- Human EvolutionDocument3 pagesHuman EvolutionEMPRON ALVIE JEAN I.No ratings yet
- Ucsp FinalsDocument10 pagesUcsp FinalsMhaica GalagataNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Reviewer Quiz 1Document8 pagesUcsp Reviewer Quiz 1koriNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Anthropology ReportDocument21 pagesGroup 1 - Anthropology ReportJR BetonioNo ratings yet
- Human EvolutionDocument6 pagesHuman EvolutionMichi Leah RobinahNo ratings yet
- Intro To EveloutionDocument9 pagesIntro To EveloutionJerik GarciaNo ratings yet
- Homo ErectusDocument27 pagesHomo ErectusPlanet CscNo ratings yet
- Pequeños Restos Grandes Problemas Nature 2014Document3 pagesPequeños Restos Grandes Problemas Nature 2014Ares PumaNo ratings yet
- Species of Human: Group 2Document31 pagesSpecies of Human: Group 2Lakesha MarshallNo ratings yet
- Luxury Hotels KutaDocument4 pagesLuxury Hotels KutaEdithya EffendiNo ratings yet
- G1 AustralopithecusandHomoerectus 206239472350308Document6 pagesG1 AustralopithecusandHomoerectus 206239472350308john TabonNo ratings yet
- Biological EvolutionDocument1 pageBiological EvolutionJamielle SanchezNo ratings yet
- In Search of The First Hominids: Image Not Available For Online UseDocument6 pagesIn Search of The First Hominids: Image Not Available For Online UseDRagonrougeNo ratings yet
- Part-1 Early SocietiesDocument89 pagesPart-1 Early SocietiesZafar AkhtarNo ratings yet
- HumanEvolution READ 2Document6 pagesHumanEvolution READ 2odinsonNo ratings yet
- FLORES 11B - UCSP 21-22 Worksheet 7Document2 pagesFLORES 11B - UCSP 21-22 Worksheet 7Jabriel Zeth Realista FloresNo ratings yet
- Human Capacity For CultureDocument2 pagesHuman Capacity For Cultureyaji FerellaNo ratings yet
- Human Origin Report SocscieDocument7 pagesHuman Origin Report SocscieKurt BashNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xi History Study Notes English - Sujith-2023Document50 pagesHsslive-Xi History Study Notes English - Sujith-2023ifshaussunna313No ratings yet
- Documentary NotesDocument3 pagesDocumentary NotesMy Roses Are RosèNo ratings yet
- Different Stages of Human EvolutionDocument2 pagesDifferent Stages of Human EvolutionMAREEZ E ISHQ MAREEZ E ISHQNo ratings yet
- Evolution of ManDocument1 pageEvolution of ManKamalito El CaballeroNo ratings yet
- HominisationDocument16 pagesHominisationDaniela Ruiz ZúñigaNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument8 pagesChapter TwotamiratNo ratings yet
- Stages of Human EvolutionDocument3 pagesStages of Human EvolutionHonot OnorNo ratings yet
- EUGENEDocument10 pagesEUGENEeugenekylecabbab26No ratings yet
- TIMELINE-The Evolution of ManDocument2 pagesTIMELINE-The Evolution of Manrm0099216No ratings yet
- Homo ErectusDocument8 pagesHomo ErectusKristelNo ratings yet
- 1585815003human Evolution TIMELINEDocument3 pages1585815003human Evolution TIMELINEShieny Dayanap GulleNo ratings yet
- Infos Ape To ManDocument8 pagesInfos Ape To Manjosh salahidNo ratings yet
- Stages of Evolution of ManDocument3 pagesStages of Evolution of ManAbdus samiNo ratings yet
- أحفورة تعيد ترتيب التطور البشريDocument3 pagesأحفورة تعيد ترتيب التطور البشريAbu HashimNo ratings yet
- Out of Africa Modern Human Origins Special FeatureDocument5 pagesOut of Africa Modern Human Origins Special FeatureDariebel Sab-itNo ratings yet
- Homo Habilis H. Habilis Homo, H. HabilisDocument12 pagesHomo Habilis H. Habilis Homo, H. HabilisDerick BrinNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Atom 5. Electrons in AtomsDocument17 pagesThe Structure of The Atom 5. Electrons in AtomsLore WheelockNo ratings yet
- Human EvolutionDocument7 pagesHuman EvolutionCatherine Faye BalderamaNo ratings yet
- Bio-Cultural Evolution of HumansDocument8 pagesBio-Cultural Evolution of Humanstyagiishika216No ratings yet
- HOMÍNIDSDocument8 pagesHOMÍNIDSjosema2No ratings yet
- Stages of Evolution of ManDocument3 pagesStages of Evolution of ManTristan Nialler100% (1)
- Anth Project PWeeksDocument18 pagesAnth Project PWeekspjf_weeksNo ratings yet
- Evidence From The Fossil Record: Replica of Fossil Skull of - Fossil Number KNM ER 1813, Found At, KenyaDocument3 pagesEvidence From The Fossil Record: Replica of Fossil Skull of - Fossil Number KNM ER 1813, Found At, KenyaSanket PatilNo ratings yet
- Evolucion HDocument7 pagesEvolucion HAmygaty Escobar ParedesNo ratings yet
- Homo Erectus - Definition, Characteristics, Skull, Diet, Tools, & Facts - BritannicaDocument9 pagesHomo Erectus - Definition, Characteristics, Skull, Diet, Tools, & Facts - Britannicakenneth kwakyeNo ratings yet
- Looking Back at Human Biocultural and Social EvolutionDocument63 pagesLooking Back at Human Biocultural and Social EvolutionraymondNo ratings yet
- Archaic HomoDocument12 pagesArchaic HomoJussel Catalo IINo ratings yet
- Eed 6 Unit 1 Part 3 StudentsDocument11 pagesEed 6 Unit 1 Part 3 StudentsMhaebilyn DizonNo ratings yet
- Human Remains (KENYA)Document7 pagesHuman Remains (KENYA)Rowan LoveriaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Human EvolutionDocument3 pagesStages of Human EvolutionHarley AdanzaNo ratings yet
- List Human Ancesters DetailsDocument1 pageList Human Ancesters DetailsVenkatesan RamalingamNo ratings yet
- Name - Yash Narayan Patil STD-X Div-D Roll No - 19 Project Name - Human Evolution Subject - ScienceDocument7 pagesName - Yash Narayan Patil STD-X Div-D Roll No - 19 Project Name - Human Evolution Subject - SciencePrachi PatilNo ratings yet
- Handoutucspg2 247710491157022Document4 pagesHandoutucspg2 247710491157022john TabonNo ratings yet
- Origin of Huan RaceDocument6 pagesOrigin of Huan RaceJenell F. LumaluNo ratings yet
- Homo HabilisDocument5 pagesHomo HabilisJay R ChivaNo ratings yet
- "The Upright Man": Human Capacity For CultureDocument5 pages"The Upright Man": Human Capacity For Culturefernando tamayoNo ratings yet
- SS - G7 U1-L3 Early HomininsDocument27 pagesSS - G7 U1-L3 Early HomininsJai du ToitNo ratings yet
- M1L2SDocument3 pagesM1L2SRhianna TetlowNo ratings yet
- About the Little People: Fairies, Elves, Dwarfs, and LeprechaunsFrom EverandAbout the Little People: Fairies, Elves, Dwarfs, and LeprechaunsNo ratings yet
- Ancient Giants of the Americas: Suppressed Evidence and the Hidden History of a Lost RaceFrom EverandAncient Giants of the Americas: Suppressed Evidence and the Hidden History of a Lost RaceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Community EngagementDocument21 pagesCommunity EngagementAloyNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate and International TradeDocument3 pagesExchange Rate and International TradeAloyNo ratings yet
- The Bases of International Trade The Concept of Absolute AdvantageDocument7 pagesThe Bases of International Trade The Concept of Absolute AdvantageAloyNo ratings yet
- The Trend Towards Globalization: PrivatizationDocument7 pagesThe Trend Towards Globalization: PrivatizationAloyNo ratings yet
- Micro and Macro Economics: Submitted By: Joshua J. ValeteDocument3 pagesMicro and Macro Economics: Submitted By: Joshua J. ValeteAloyNo ratings yet
- The Agrarian ReformDocument5 pagesThe Agrarian ReformAloyNo ratings yet
- AP7 B R E A K: 7:15am - 7:30am 7:30am - 8:30am 8:30am - 9:30amDocument1 pageAP7 B R E A K: 7:15am - 7:30am 7:30am - 8:30am 8:30am - 9:30amAloyNo ratings yet
- ScheduleDocument1 pageScheduleAloyNo ratings yet
- Palash Agrawal ResumeDocument1 pagePalash Agrawal ResumesgbhuNo ratings yet
- Events of Disputes AnswersDocument7 pagesEvents of Disputes AnswersMohamed AliNo ratings yet
- 10th English Model Test Paper General Students 2023-24Document6 pages10th English Model Test Paper General Students 2023-24gursewaksinghmaahuNo ratings yet
- Marc Rolli Gilles Deleuzes Transcendental Empiricism From Tradition To DifferenceDocument329 pagesMarc Rolli Gilles Deleuzes Transcendental Empiricism From Tradition To DifferenceleonardobahamondesNo ratings yet
- 31 MySQL QuestionsDocument13 pages31 MySQL QuestionsAmit_mahajanNo ratings yet
- Educ4000 Curriculum Integration and Differentiation Semester 2 2018 Bentley Campus IntDocument20 pagesEduc4000 Curriculum Integration and Differentiation Semester 2 2018 Bentley Campus Intapi-314401095No ratings yet
- Ped 201 Lab 5 sp14Document7 pagesPed 201 Lab 5 sp14api-241632865No ratings yet
- What Is Critical Pedagogy?: A Summary of The Work of Paulo Freire & His ContemporariesDocument38 pagesWhat Is Critical Pedagogy?: A Summary of The Work of Paulo Freire & His ContemporariesS. Ma. Elisabeth Ngewi,rvmNo ratings yet
- Pratibha Revankar PDFDocument2 pagesPratibha Revankar PDFrajasekharsnetxcellNo ratings yet
- Never Pitch Again by Alina Medina PDFDocument9 pagesNever Pitch Again by Alina Medina PDFIt's Just MeNo ratings yet
- Certificates For Project ReportDocument11 pagesCertificates For Project ReportFiroz KachhiNo ratings yet
- Stawirway To HeavenDocument2 pagesStawirway To HeavenMarcos ViníciusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document7 pagesChapter 1Freziel Ann Marbebe DarongNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Huawei UMTS Radio Network Dimensioning (RND)Document61 pagesIntroduction To Huawei UMTS Radio Network Dimensioning (RND)darkmesiahNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea in ChildrenDocument6 pagesDiarrhea in ChildrenAdeola AdegboyegaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Basketball Lesson PlansDocument6 pagesWeek 2 Basketball Lesson PlansMayra Carrera100% (1)
- American Atheist Magazine April 1980Document48 pagesAmerican Atheist Magazine April 1980American Atheists, Inc.No ratings yet
- Wildlife CurriculumDocument70 pagesWildlife Curriculumapi-240926941100% (1)
- Reparando Boot ServerDocument6 pagesReparando Boot ServerErlon TroianoNo ratings yet
- NP OKC Find Nosey ParkerDocument14 pagesNP OKC Find Nosey ParkernoseyparkerguideNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ClonidineDocument2 pagesDrug Study ClonidineCezanne CruzNo ratings yet
- Pak Study Notes For First Semester Examination of Mechanical Engineering F-16 BatchDocument70 pagesPak Study Notes For First Semester Examination of Mechanical Engineering F-16 Batchfatima vohraNo ratings yet
- (Blogchuyenanh) - Cornucopia 2 Answer KeyDocument4 pages(Blogchuyenanh) - Cornucopia 2 Answer KeyteivcouqNo ratings yet
- Tgfu Peer Teach AssignmentDocument2 pagesTgfu Peer Teach Assignmentapi-282302964No ratings yet
- 03 Answer Sheet Talking AboutDocument8 pages03 Answer Sheet Talking AboutQuinterito QuizNo ratings yet
- Corpo Digest Set 1Document8 pagesCorpo Digest Set 1Darlene Ganub100% (1)
- El Mahdy2013Document9 pagesEl Mahdy2013prakharNo ratings yet
- English 2-01-Structure Subject Verb AgreementDocument10 pagesEnglish 2-01-Structure Subject Verb Agreementweni wijatmokoNo ratings yet
- Reese, Cox, and Koop Sand ModelDocument18 pagesReese, Cox, and Koop Sand Modelv100% (3)
Species of Homo: S S Sapiens
Species of Homo: S S Sapiens
Uploaded by
Aloy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views4 pagesThere were three known species of Homo: Homo habilis, Homo erectus, and Homo sapiens. Homo habilis lived around 2.5 million years ago in Africa and was the first to use stone tools. Homo erectus emerged between 1.8-300,000 years ago and was the first early human to migrate out of Africa. Homo sapiens, the last in the human evolutionary path, developed a large cranium size around 120,000 years ago and was the only surviving human species after 30,000 years ago. Brain size increased over time and was linked to greater intelligence and tool usage, helping humans adapt.
Original Description:
Biological Evolution
Original Title
Handouts
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThere were three known species of Homo: Homo habilis, Homo erectus, and Homo sapiens. Homo habilis lived around 2.5 million years ago in Africa and was the first to use stone tools. Homo erectus emerged between 1.8-300,000 years ago and was the first early human to migrate out of Africa. Homo sapiens, the last in the human evolutionary path, developed a large cranium size around 120,000 years ago and was the only surviving human species after 30,000 years ago. Brain size increased over time and was linked to greater intelligence and tool usage, helping humans adapt.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views4 pagesSpecies of Homo: S S Sapiens
Species of Homo: S S Sapiens
Uploaded by
AloyThere were three known species of Homo: Homo habilis, Homo erectus, and Homo sapiens. Homo habilis lived around 2.5 million years ago in Africa and was the first to use stone tools. Homo erectus emerged between 1.8-300,000 years ago and was the first early human to migrate out of Africa. Homo sapiens, the last in the human evolutionary path, developed a large cranium size around 120,000 years ago and was the only surviving human species after 30,000 years ago. Brain size increased over time and was linked to greater intelligence and tool usage, helping humans adapt.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
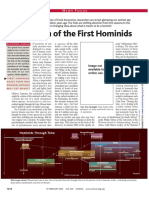
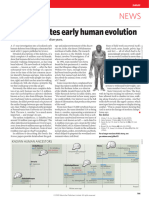
Species of Homo - In the case of Asia, assumed that a large
the very first brain would
The term Homo was taken in a Latin word which means “man” evidence of a correspond to the
Homo erectus was development of
- It is believed that the homo species had a large cranium size relative to the the so-called “Java complex thinking
australopithecines and was definitely bipedal. Man,” discovered processes, which is
by the Dutch turn enable humans
Based on the fossil there are three known species of Homo today; doctor Eugene to improve their way
Dubois in Trinil, of life such as by
- Homo habilis Java, Indonesia in working with tools.
- Homo erectus 1891. Dubois
- Homo sapiens pegged the dating - Archaic Homo
of his fossil to sapiens live about
Homo habilis Homo erectus Homo sapiens about 700,000 500,000-200,000
- Also known among - It name was - The last species in the years old. years ago in the
physical derived from its human evolutionary continent of Africa,
Anthropologist as the distinct feature path is the Homo - In 1920 another Europe and Asia.
“able man” or the which is ability to sapiens or the so- Homo erectus
“Handy man” because walk in an upright called “thinking man” fossil was found in - Meanwhile, the
it was the first to posture. cave in Homo
manufacture stone - Fossil evidence Have several types Zhoukoudian in nearthenthalensis
tools. suggest that it had China. (Neanderthals) is
existed between Archaic Homo sapiens believed to have
- It had a large brain 1.8 – 300,000 Homo heidelbergensis - The Human roamed Europe and
compared to the million years ago. Homo neanderthalencies remains, known as part of Asia
Australopithecines Homo sapiens-sapiens the “Peking man” sometime 230,000-
and measured three - These Homo dates about 30,000 years ago.
to four feet in height. erectus were - A crucial 420,000 years ago.
discovered in a development in the The fossils - They had a large
- This fossil was wide range of area emergence of the described as brain, which
discovered in Olduvai – e.g. Africa, Homo family was the having a large measures 1,740 cc.
Gorge, Tazania, and China, Java – formation of a large skull and heavy and is larger than an
Lake Turkana in which indicate cranium. brow ridges, average modern
Kenya. that this species which are features human being.
may have been the - Scientist equate typical of any
- They are believed to first early human brain size with erectus found. - There were also
have existed circa 2.5 to go out of Africa. intelligence. For reports of
million years ago. instance, it is - In 1984, an almost discoveries of
complete Homo Neanderthals burial
erectus fossil sites in places such remain of a female
belonging to as Israel, which Homo erectus.
young a male adult suggest that the
was found in Neanderthals may - They named her
Nariokotome in had a sense of Homo Florisiensis
Kenya, Africa. religion. or simply habbit.
This individual, - The modern Homo Excavated in the
named by scientist sapiens emerge only island of Flores,
as the “Turkana about 120,000 years Indonesia, Hobbit
Boy” is believe by ago. was unusual for a
some scientist as Homo erectus
belonging to a - The very first because she only
separate species -- evidence of this kind stood half as tall as
- the Homo was discovered in modern adults.
ergaster. 1868and which is She weighed only
popularly known 55 pounds and her
- The Homo erectus today as the “Cro- brain was only a
in general stood Magnon Man”. third of the size of
taller than the modern human’s.
Homo Habilis - Using they tools, Seven excavated
since it measured they manufactured remains show that
over five feet. fine implements such they were all tiny
as blades fashioned individuals who
- There is also out of stone, bones, lived between
evidence to antlers, ivory, wood 95,000 to 13,000
suggest that this and shells. years ago.
species was the
first in several - Later, Homo sapiens
aspects of sapiens would create The March of Humanity
primitive life’s. works of art such as
They had use of cave paintings clay Underlying the story behind the march of humanity, is
fire, used caves as sculpture. adaptation. It can be remembered that Darwin explained this
dwelling place and phenomenon in terms of natural selection.
hunted for food. According to this principle, nature favors the species who adapts
best to a given environment; therefore, those who could not cope
- A recent find, In with the environment would eventually die out and their genes
2004, archeologist would not be preserved for posterity.
excavated an
almost full skeletal
The period of time covering most of the changes in the human The brain need a large amount of energy to perform effectively,
evolutionary history spanned different epochs in the last 2 so human must select their food carefully in such a way that it
million to 10,000 years ago. It should be recalled that the will satisfy the energy requirements of the of brain.
environment was not as stable as today so nature itself posed a
great challenge for humanity to solve. Changes in the hand and the Use of Tools
In the end, the story of evolution tells us how precisely humans
diverged their primate roots. Adapting biologically was man’s
response to the changes in nature. The hand also underwent changes to adapt to the changing
environment.
Bipedalism The palm and the fingers develop in such a way that it can holds
object better.
Bipedalism is ability to walk on two feet. Human develop “opposing thumb”, which enabled them to
precise and power gripping task.
This feat is largely attribute to humans alone, as primates are
generally quadruped, that is, walking on all fours. Incidentally, the oldest stone tool is flake tool found in Ethiopia
Bipedalism was borne out of the need to explore man’s new and dated about 2.5 million years old. Though this particular
changing environment. development is associated mainly with the Homo habilis.
However, wood does not preserve well there is no evidence of
this kind of primitive tools.
Increase in Cranial Capacity
The Dental Evidence the Canine and Molar.
The average size of the brain Australopithecus was only about
400-500 cc.
The size and shape of the teeth tell us something about the diet
Archaic Homo sapiens’ brains measured about 600-750 cc.
of the ancient early human.
While the modern Homo sapiens has a 1,500 cc.
For example, sharp and protruding canines are commonly
There was an increase in the cranial capacity of human species observed in Australopithecines species such as the A. afarensis.
because natured favored it.
Meanwhile, the large jaw bone and sagittal crest are often seen
Those who have bigger brains meant they were able to think in the fossilized remains of A. boises and A. robustos.
better. They all developed this kind of dental features to enable them to
There are still many other functions of the brain such as the cut, chew and mince fibrous and raw food sources from savanna.
capacity for symbolic language. When the Homo line emerge, their set of teeth had a different
Human are able to decode signs or symbols by created other structure.
members of their group – an ability which can be passed on to For example, the pre-molar, molar and canine decrease in size.
future generations by way of education.
There were also no protruding canines.
The relationship may not obvious, but having a bigger brain
influenced by the way we do things, like eating. The sagittal crest as well as the strong muscles in the chin
vanished.
Overall, the mouth receded in most Homo species, which gave Therefore, people who inhabit places near the equator developed
this family a better facial appearance. darker skin, while those who live farther from the equator
developed lighter skin.
Africa: Cradle of Evolution As a whole, man’s physical appearance is a result of adaptation
to the environment, it is not a gauge of intelligence and ability.
Africa is cradle of human evolution.
East and South Africa appeared to be the most ideal location
three million years ago because the warmer savanna
environment here was a cry from the cruel cold environs of the
Plio-Pleistocene epoch.
Recent genetic evidence (mitochondrial DNA evidence) also
point to Africa as the home of the ancestors of all modern Homo
sapiens sapiens living in the world today.
It is estimated that the Homo sapiens emerge in Africa some
150,000 years ago.
It is generally accepted among scientist that the Homo was the
first human species to walk out Africa – beginning from the
Homo erectus whose fossil remains were found in Africa, China
and South-East Asia.
Eventually, the modern Homo sapiens replaced all the others
Homo species and became the only surviving human species in
the world.
The modern Homo sapiens is presumed to have not only superior
physical attributes compared to the early humans, but they also
had a better cultural adaptation.
The human race belongs to single human species – Homo
sapiens sapiens. But not all human look the same because
different environmental niches affected their physical
appearance. This is due to adaptation of their part.
They underwent biological change to enable them to survive in
their respective location in the world. One of these adaptation is
the color of the skin.
The melanin, the substance in the human body responsible for
the color of the skin, decrease or increase depending on the
skin’s exposure to sunlight that contains ultra violet reaction.
You might also like
- Investigatory ProjectDocument21 pagesInvestigatory ProjectDiya 2788% (86)
- Thesis Proposal (Final)Document22 pagesThesis Proposal (Final)Geneva Katug80% (10)
- Yellow Modern History Timeline InfographicDocument1 pageYellow Modern History Timeline Infographiclamar.w.a.b2010No ratings yet
- Human EvolutionDocument3 pagesHuman EvolutionEMPRON ALVIE JEAN I.No ratings yet
- Ucsp FinalsDocument10 pagesUcsp FinalsMhaica GalagataNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Reviewer Quiz 1Document8 pagesUcsp Reviewer Quiz 1koriNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Anthropology ReportDocument21 pagesGroup 1 - Anthropology ReportJR BetonioNo ratings yet
- Human EvolutionDocument6 pagesHuman EvolutionMichi Leah RobinahNo ratings yet
- Intro To EveloutionDocument9 pagesIntro To EveloutionJerik GarciaNo ratings yet
- Homo ErectusDocument27 pagesHomo ErectusPlanet CscNo ratings yet
- Pequeños Restos Grandes Problemas Nature 2014Document3 pagesPequeños Restos Grandes Problemas Nature 2014Ares PumaNo ratings yet
- Species of Human: Group 2Document31 pagesSpecies of Human: Group 2Lakesha MarshallNo ratings yet
- Luxury Hotels KutaDocument4 pagesLuxury Hotels KutaEdithya EffendiNo ratings yet
- G1 AustralopithecusandHomoerectus 206239472350308Document6 pagesG1 AustralopithecusandHomoerectus 206239472350308john TabonNo ratings yet
- Biological EvolutionDocument1 pageBiological EvolutionJamielle SanchezNo ratings yet
- In Search of The First Hominids: Image Not Available For Online UseDocument6 pagesIn Search of The First Hominids: Image Not Available For Online UseDRagonrougeNo ratings yet
- Part-1 Early SocietiesDocument89 pagesPart-1 Early SocietiesZafar AkhtarNo ratings yet
- HumanEvolution READ 2Document6 pagesHumanEvolution READ 2odinsonNo ratings yet
- FLORES 11B - UCSP 21-22 Worksheet 7Document2 pagesFLORES 11B - UCSP 21-22 Worksheet 7Jabriel Zeth Realista FloresNo ratings yet
- Human Capacity For CultureDocument2 pagesHuman Capacity For Cultureyaji FerellaNo ratings yet
- Human Origin Report SocscieDocument7 pagesHuman Origin Report SocscieKurt BashNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xi History Study Notes English - Sujith-2023Document50 pagesHsslive-Xi History Study Notes English - Sujith-2023ifshaussunna313No ratings yet
- Documentary NotesDocument3 pagesDocumentary NotesMy Roses Are RosèNo ratings yet
- Different Stages of Human EvolutionDocument2 pagesDifferent Stages of Human EvolutionMAREEZ E ISHQ MAREEZ E ISHQNo ratings yet
- Evolution of ManDocument1 pageEvolution of ManKamalito El CaballeroNo ratings yet
- HominisationDocument16 pagesHominisationDaniela Ruiz ZúñigaNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument8 pagesChapter TwotamiratNo ratings yet
- Stages of Human EvolutionDocument3 pagesStages of Human EvolutionHonot OnorNo ratings yet
- EUGENEDocument10 pagesEUGENEeugenekylecabbab26No ratings yet
- TIMELINE-The Evolution of ManDocument2 pagesTIMELINE-The Evolution of Manrm0099216No ratings yet
- Homo ErectusDocument8 pagesHomo ErectusKristelNo ratings yet
- 1585815003human Evolution TIMELINEDocument3 pages1585815003human Evolution TIMELINEShieny Dayanap GulleNo ratings yet
- Infos Ape To ManDocument8 pagesInfos Ape To Manjosh salahidNo ratings yet
- Stages of Evolution of ManDocument3 pagesStages of Evolution of ManAbdus samiNo ratings yet
- أحفورة تعيد ترتيب التطور البشريDocument3 pagesأحفورة تعيد ترتيب التطور البشريAbu HashimNo ratings yet
- Out of Africa Modern Human Origins Special FeatureDocument5 pagesOut of Africa Modern Human Origins Special FeatureDariebel Sab-itNo ratings yet
- Homo Habilis H. Habilis Homo, H. HabilisDocument12 pagesHomo Habilis H. Habilis Homo, H. HabilisDerick BrinNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Atom 5. Electrons in AtomsDocument17 pagesThe Structure of The Atom 5. Electrons in AtomsLore WheelockNo ratings yet
- Human EvolutionDocument7 pagesHuman EvolutionCatherine Faye BalderamaNo ratings yet
- Bio-Cultural Evolution of HumansDocument8 pagesBio-Cultural Evolution of Humanstyagiishika216No ratings yet
- HOMÍNIDSDocument8 pagesHOMÍNIDSjosema2No ratings yet
- Stages of Evolution of ManDocument3 pagesStages of Evolution of ManTristan Nialler100% (1)
- Anth Project PWeeksDocument18 pagesAnth Project PWeekspjf_weeksNo ratings yet
- Evidence From The Fossil Record: Replica of Fossil Skull of - Fossil Number KNM ER 1813, Found At, KenyaDocument3 pagesEvidence From The Fossil Record: Replica of Fossil Skull of - Fossil Number KNM ER 1813, Found At, KenyaSanket PatilNo ratings yet
- Evolucion HDocument7 pagesEvolucion HAmygaty Escobar ParedesNo ratings yet
- Homo Erectus - Definition, Characteristics, Skull, Diet, Tools, & Facts - BritannicaDocument9 pagesHomo Erectus - Definition, Characteristics, Skull, Diet, Tools, & Facts - Britannicakenneth kwakyeNo ratings yet
- Looking Back at Human Biocultural and Social EvolutionDocument63 pagesLooking Back at Human Biocultural and Social EvolutionraymondNo ratings yet
- Archaic HomoDocument12 pagesArchaic HomoJussel Catalo IINo ratings yet
- Eed 6 Unit 1 Part 3 StudentsDocument11 pagesEed 6 Unit 1 Part 3 StudentsMhaebilyn DizonNo ratings yet
- Human Remains (KENYA)Document7 pagesHuman Remains (KENYA)Rowan LoveriaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Human EvolutionDocument3 pagesStages of Human EvolutionHarley AdanzaNo ratings yet
- List Human Ancesters DetailsDocument1 pageList Human Ancesters DetailsVenkatesan RamalingamNo ratings yet
- Name - Yash Narayan Patil STD-X Div-D Roll No - 19 Project Name - Human Evolution Subject - ScienceDocument7 pagesName - Yash Narayan Patil STD-X Div-D Roll No - 19 Project Name - Human Evolution Subject - SciencePrachi PatilNo ratings yet
- Handoutucspg2 247710491157022Document4 pagesHandoutucspg2 247710491157022john TabonNo ratings yet
- Origin of Huan RaceDocument6 pagesOrigin of Huan RaceJenell F. LumaluNo ratings yet
- Homo HabilisDocument5 pagesHomo HabilisJay R ChivaNo ratings yet
- "The Upright Man": Human Capacity For CultureDocument5 pages"The Upright Man": Human Capacity For Culturefernando tamayoNo ratings yet
- SS - G7 U1-L3 Early HomininsDocument27 pagesSS - G7 U1-L3 Early HomininsJai du ToitNo ratings yet
- M1L2SDocument3 pagesM1L2SRhianna TetlowNo ratings yet
- About the Little People: Fairies, Elves, Dwarfs, and LeprechaunsFrom EverandAbout the Little People: Fairies, Elves, Dwarfs, and LeprechaunsNo ratings yet
- Ancient Giants of the Americas: Suppressed Evidence and the Hidden History of a Lost RaceFrom EverandAncient Giants of the Americas: Suppressed Evidence and the Hidden History of a Lost RaceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Community EngagementDocument21 pagesCommunity EngagementAloyNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate and International TradeDocument3 pagesExchange Rate and International TradeAloyNo ratings yet
- The Bases of International Trade The Concept of Absolute AdvantageDocument7 pagesThe Bases of International Trade The Concept of Absolute AdvantageAloyNo ratings yet
- The Trend Towards Globalization: PrivatizationDocument7 pagesThe Trend Towards Globalization: PrivatizationAloyNo ratings yet
- Micro and Macro Economics: Submitted By: Joshua J. ValeteDocument3 pagesMicro and Macro Economics: Submitted By: Joshua J. ValeteAloyNo ratings yet
- The Agrarian ReformDocument5 pagesThe Agrarian ReformAloyNo ratings yet
- AP7 B R E A K: 7:15am - 7:30am 7:30am - 8:30am 8:30am - 9:30amDocument1 pageAP7 B R E A K: 7:15am - 7:30am 7:30am - 8:30am 8:30am - 9:30amAloyNo ratings yet
- ScheduleDocument1 pageScheduleAloyNo ratings yet
- Palash Agrawal ResumeDocument1 pagePalash Agrawal ResumesgbhuNo ratings yet
- Events of Disputes AnswersDocument7 pagesEvents of Disputes AnswersMohamed AliNo ratings yet
- 10th English Model Test Paper General Students 2023-24Document6 pages10th English Model Test Paper General Students 2023-24gursewaksinghmaahuNo ratings yet
- Marc Rolli Gilles Deleuzes Transcendental Empiricism From Tradition To DifferenceDocument329 pagesMarc Rolli Gilles Deleuzes Transcendental Empiricism From Tradition To DifferenceleonardobahamondesNo ratings yet
- 31 MySQL QuestionsDocument13 pages31 MySQL QuestionsAmit_mahajanNo ratings yet
- Educ4000 Curriculum Integration and Differentiation Semester 2 2018 Bentley Campus IntDocument20 pagesEduc4000 Curriculum Integration and Differentiation Semester 2 2018 Bentley Campus Intapi-314401095No ratings yet
- Ped 201 Lab 5 sp14Document7 pagesPed 201 Lab 5 sp14api-241632865No ratings yet
- What Is Critical Pedagogy?: A Summary of The Work of Paulo Freire & His ContemporariesDocument38 pagesWhat Is Critical Pedagogy?: A Summary of The Work of Paulo Freire & His ContemporariesS. Ma. Elisabeth Ngewi,rvmNo ratings yet
- Pratibha Revankar PDFDocument2 pagesPratibha Revankar PDFrajasekharsnetxcellNo ratings yet
- Never Pitch Again by Alina Medina PDFDocument9 pagesNever Pitch Again by Alina Medina PDFIt's Just MeNo ratings yet
- Certificates For Project ReportDocument11 pagesCertificates For Project ReportFiroz KachhiNo ratings yet
- Stawirway To HeavenDocument2 pagesStawirway To HeavenMarcos ViníciusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document7 pagesChapter 1Freziel Ann Marbebe DarongNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Huawei UMTS Radio Network Dimensioning (RND)Document61 pagesIntroduction To Huawei UMTS Radio Network Dimensioning (RND)darkmesiahNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea in ChildrenDocument6 pagesDiarrhea in ChildrenAdeola AdegboyegaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Basketball Lesson PlansDocument6 pagesWeek 2 Basketball Lesson PlansMayra Carrera100% (1)
- American Atheist Magazine April 1980Document48 pagesAmerican Atheist Magazine April 1980American Atheists, Inc.No ratings yet
- Wildlife CurriculumDocument70 pagesWildlife Curriculumapi-240926941100% (1)
- Reparando Boot ServerDocument6 pagesReparando Boot ServerErlon TroianoNo ratings yet
- NP OKC Find Nosey ParkerDocument14 pagesNP OKC Find Nosey ParkernoseyparkerguideNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ClonidineDocument2 pagesDrug Study ClonidineCezanne CruzNo ratings yet
- Pak Study Notes For First Semester Examination of Mechanical Engineering F-16 BatchDocument70 pagesPak Study Notes For First Semester Examination of Mechanical Engineering F-16 Batchfatima vohraNo ratings yet
- (Blogchuyenanh) - Cornucopia 2 Answer KeyDocument4 pages(Blogchuyenanh) - Cornucopia 2 Answer KeyteivcouqNo ratings yet
- Tgfu Peer Teach AssignmentDocument2 pagesTgfu Peer Teach Assignmentapi-282302964No ratings yet
- 03 Answer Sheet Talking AboutDocument8 pages03 Answer Sheet Talking AboutQuinterito QuizNo ratings yet
- Corpo Digest Set 1Document8 pagesCorpo Digest Set 1Darlene Ganub100% (1)
- El Mahdy2013Document9 pagesEl Mahdy2013prakharNo ratings yet
- English 2-01-Structure Subject Verb AgreementDocument10 pagesEnglish 2-01-Structure Subject Verb Agreementweni wijatmokoNo ratings yet
- Reese, Cox, and Koop Sand ModelDocument18 pagesReese, Cox, and Koop Sand Modelv100% (3)