Professional Documents
Culture Documents
E = 1 (wФZ) (P) volts 2∏ A Where: a = 2-for simplex wave-winding = P-for simplex lap-winding For a given d.c. machine, Z, P and a are constant. Hence, putting Ka = ZP/a
E = 1 (wФZ) (P) volts 2∏ A Where: a = 2-for simplex wave-winding = P-for simplex lap-winding For a given d.c. machine, Z, P and a are constant. Hence, putting Ka = ZP/a
Uploaded by
Mark julius garcia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesThe document discusses the principle of electromagnetic induction in generators and provides the formula to calculate the induced emf (Eg) in a generator. It explains that for a given generator, the induced emf is directly proportional to the flux (Φ), number of poles (P), and rotational speed (N). It then provides an example calculation of the voltage generated by a 4-pole, wave-wound generator with 51 slots each containing 20 conductors, rotating at 1500 rpm with a flux of 0.7 webers per pole.
Original Description:
Lecture notes
Original Title
Generator Principle
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the principle of electromagnetic induction in generators and provides the formula to calculate the induced emf (Eg) in a generator. It explains that for a given generator, the induced emf is directly proportional to the flux (Φ), number of poles (P), and rotational speed (N). It then provides an example calculation of the voltage generated by a 4-pole, wave-wound generator with 51 slots each containing 20 conductors, rotating at 1500 rpm with a flux of 0.7 webers per pole.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesE = 1 (wФZ) (P) volts 2∏ A Where: a = 2-for simplex wave-winding = P-for simplex lap-winding For a given d.c. machine, Z, P and a are constant. Hence, putting Ka = ZP/a
E = 1 (wФZ) (P) volts 2∏ A Where: a = 2-for simplex wave-winding = P-for simplex lap-winding For a given d.c. machine, Z, P and a are constant. Hence, putting Ka = ZP/a
Uploaded by
Mark julius garciaThe document discusses the principle of electromagnetic induction in generators and provides the formula to calculate the induced emf (Eg) in a generator. It explains that for a given generator, the induced emf is directly proportional to the flux (Φ), number of poles (P), and rotational speed (N). It then provides an example calculation of the voltage generated by a 4-pole, wave-wound generator with 51 slots each containing 20 conductors, rotating at 1500 rpm with a flux of 0.7 webers per pole.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
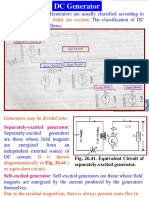
GENERATOR PRINCIPLE
EMF EQUATION OF A GENERATOR
EX. Ф = flux --- per pole, weber
Z = total magnetic coils or conductors
P = no. of generator poles
a = no. of parallel paths
N = armature rotation in rpm.
E = induced emf in any parallel path
Eq = emf generator
By the Law of ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
Average emf generated / cond = dФ/dt volts ( for n = 1 )
Flux cut/cond = dФ = ФP
F = no. of conductor/ sec = N/60 …
.the time per revolution dt = 60 / N
Hence:
EMF generated/ cond = dФ / dt = ФP / 60/N = ФPN / 60 volts
FOR SIMPLEX WAVE - WOUND GENERATOR
No. of parallel path , a = 2
No. of conductor per path = Z/2
Eq = ФPN x Z = ФPNZ volts
60 2 120
FOR SIMPLEX LAP-WOUND GENERATOR
a = P , no. of conductors/ path = Z
P
Eq = ФPN x Z = ФNZ volts
60 P 60
IN GENERAL:
Eq = ФZN x P volts . 2∏
60 a 2∏
= 1 ( 2∏ N ) Ф Z ( P )
2∏ a
Where w = generator angular speed = 2∏ N rad/sec
Eq = 1 ( wФZ ) (P ) volts
2∏ a
Where: a = 2-for simplex wave-winding
= P-for simplex lap-winding
For a given d.c. machine, Z, P and a are constant. Hence, putting
Ka = ZP/a
Eg = Ka Φ N volts - where N is in rps
Problem:
A four pole generator having wave-wound armature winding has 51
slots each slots containing 20 conductors. What will be the voltage
generated in the machine when driven at 1500 rpm assuming the flux
per pole to be 0.7 mWB.
You might also like
- TestDocument361 pagesTestJake Sy100% (1)
- Formula EeDocument8 pagesFormula EeT.Thilagamani100% (2)
- E 240V C 2 P (For Alap Winding) Z 50 (16) 800 WB E C E E 500VDocument12 pagesE 240V C 2 P (For Alap Winding) Z 50 (16) 800 WB E C E E 500VJethro Briza Ganelo100% (2)
- Emf Equation of DC GeneratorDocument2 pagesEmf Equation of DC GeneratorAnonymous pZp8uyNo ratings yet
- Alternators: Working PrincipleDocument7 pagesAlternators: Working PrincipleQasimNo ratings yet
- Ganelo, Jethro B. Bautista, Joanna Marie Z. Gaulit, Carlo J. Bsme 3B May 27, 2021Document16 pagesGanelo, Jethro B. Bautista, Joanna Marie Z. Gaulit, Carlo J. Bsme 3B May 27, 2021jethro ganeloNo ratings yet
- DC Machine Formula CollectionsDocument7 pagesDC Machine Formula Collectionssahulipunku2001No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Topic 5Document4 pagesUnit 3 Topic 5Pika ChuNo ratings yet
- EMF Equation and Types of GeneratorsDocument22 pagesEMF Equation and Types of GeneratorsSrinivas DanduNo ratings yet
- Emf Equation of AlternatorDocument2 pagesEmf Equation of AlternatorThe Engineers EDGE, CoimbatoreNo ratings yet
- Unit 5.2 EMF EquationDocument13 pagesUnit 5.2 EMF EquationArpit Personal 5No ratings yet
- Energy Conversion Module 2Document8 pagesEnergy Conversion Module 2Arvin Palma Dela RocaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 DC MachinesDocument18 pagesLecture 2 DC Machinesee210002004No ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument16 pagesDC MachinesAuthorized EarthlingNo ratings yet
- Emf EquationDocument10 pagesEmf Equationtejashraj93No ratings yet
- Emf Equation of An AlternatorDocument1 pageEmf Equation of An AlternatorPrem SagarNo ratings yet
- Induction and Synchronous Machines PDFDocument23 pagesInduction and Synchronous Machines PDFedara1234No ratings yet
- Speed of A DC MotorDocument4 pagesSpeed of A DC MotorMateo, Dale Vincent A.No ratings yet
- DC GeneratorsDocument35 pagesDC Generatorssayed Tamir janNo ratings yet
- EMF Equation For DC GeneratorDocument2 pagesEMF Equation For DC GeneratorparallaxNo ratings yet
- Emf GeneratorDocument1 pageEmf GeneratorAlex B. MolinaNo ratings yet
- 12 CycloconvertersDocument16 pages12 CycloconvertersAbdallah LotfyNo ratings yet
- Lect 10 - 2machineDocument3 pagesLect 10 - 2machinemohamed shalabyNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine K-NotesDocument38 pagesElectrical Machine K-NotesAkashGauravNo ratings yet
- Alternator PresentationDocument30 pagesAlternator PresentationfarukbiswasNo ratings yet
- 5th Year DiscussionDocument22 pages5th Year DiscussionSymon Miranda Sioson100% (1)
- Synchronous Generator and Alternator FormulasDocument7 pagesSynchronous Generator and Alternator FormulasJosephNo ratings yet
- Polyphase Induction MachinesDocument7 pagesPolyphase Induction Machinespurushg62No ratings yet
- DC Machines: Saikrishna Dasari Dept. of EEE PvkkitDocument38 pagesDC Machines: Saikrishna Dasari Dept. of EEE Pvkkitsai krishnaNo ratings yet
- Sardar Vallabhbhai Institute of Technology, VasadDocument15 pagesSardar Vallabhbhai Institute of Technology, VasadSANJAYNo ratings yet
- Emf Equation of DC GeneratorDocument5 pagesEmf Equation of DC Generatordilja aravindanNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument24 pagesDC Machineskeshab pandeyNo ratings yet
- Eletrical Machines (K-Wiki - Synchronous Machines)Document59 pagesEletrical Machines (K-Wiki - Synchronous Machines)qwer100% (1)
- Exp2 SheetDocument8 pagesExp2 SheetMajdy gamingNo ratings yet
- Module 4 DC Motor GeneratorDocument15 pagesModule 4 DC Motor GeneratorNivedita Acharyya 2035No ratings yet
- Full-Wave Rectifier Circuit With An RL LoadDocument5 pagesFull-Wave Rectifier Circuit With An RL Loadhamza abdo mohamoudNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines II Atif Iqbal PDFDocument52 pagesElectrical Machines II Atif Iqbal PDFSantosh VarshneyNo ratings yet
- EL-225 Electronic Devices and Circuits: National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, FASTDocument5 pagesEL-225 Electronic Devices and Circuits: National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, FASTTanzeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- 17 Alternating Currents SolutionsDocument6 pages17 Alternating Currents SolutionssqhaaNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Alternating Current Level 1 Questions: B 4.5 V R.M.S 50 HZ AC (V) /R (4.5) /2 10.1 WDocument6 pagesSolutions To Alternating Current Level 1 Questions: B 4.5 V R.M.S 50 HZ AC (V) /R (4.5) /2 10.1 WYan Shen TanNo ratings yet
- Rohini 98391871821Document5 pagesRohini 98391871821Aneena ThasneemNo ratings yet
- 2 Converter AnalysisDocument36 pages2 Converter AnalysismurthyNo ratings yet
- Time Constant Inductance/ Resistance X: Time Constants From Equivalent CircuitsDocument154 pagesTime Constant Inductance/ Resistance X: Time Constants From Equivalent Circuitsanoopingle9No ratings yet
- Power Supply Lecture For CpEDocument82 pagesPower Supply Lecture For CpEvj hernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document31 pagesChapter 2Nicholas JyrwaNo ratings yet
- Formula 9Document1 pageFormula 9Raj SakariaNo ratings yet
- AD-DC MotorDocument7 pagesAD-DC MotorJay Mark BalaneNo ratings yet
- Ex. No. 7 Date: 28-04-2021 Design of Single-Phase Half Wave and Full Wave RectifiersDocument5 pagesEx. No. 7 Date: 28-04-2021 Design of Single-Phase Half Wave and Full Wave RectifiersR B SHARANNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 4: Name: Sonu Kumar Keshri Roll No: 1904026 Section:ECE 1 Course Code: ECL3501Document10 pagesExperiment - 4: Name: Sonu Kumar Keshri Roll No: 1904026 Section:ECE 1 Course Code: ECL3501Sonu Kumar KeshriNo ratings yet
- Gandhinagar Institute of Technology 1Document10 pagesGandhinagar Institute of Technology 1muqthiarNo ratings yet
- Module 4 2Document9 pagesModule 4 2Atharva KhadseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Three Phase Induction MotorsDocument46 pagesChapter 3 - Three Phase Induction MotorsiyufikirteNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current NotesDocument5 pagesAlternating Current Noteskamali.v777No ratings yet
- BEE Small Signl ModelDocument13 pagesBEE Small Signl ModelalysonmicheaalaNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Materials EngineeringDocument9 pagesMaterials EngineeringMark julius garciaNo ratings yet
- DC & AC Machinery ADocument9 pagesDC & AC Machinery AMark julius garciaNo ratings yet
- Processes Affecting Changes in PropertiesDocument13 pagesProcesses Affecting Changes in PropertiesMark julius garciaNo ratings yet
- Me Laws and Code ChichuDocument25 pagesMe Laws and Code ChichuMark julius garciaNo ratings yet
- MPS5a - GrindingDocument2 pagesMPS5a - GrindingMark julius garciaNo ratings yet