Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lease Financing: Lessor Lessee
Lease Financing: Lessor Lessee
Uploaded by
alialim.Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lease Financing: Lessor Lessee
Lease Financing: Lessor Lessee
Uploaded by
alialim.Copyright:
Available Formats
Leasing or Lease Financing is one of the most important and most flexible financial
service.
A Lease is a contractual arrangement or transaction between two or more
parties, in which one party owning an asset or equipment (les- sor) provides an
asset to another party (lessee) for use or transfers the right to use the asset,
over a certain or agreed period of time for consideration in form of periodic
payment (rentals) with or without charging a premium. At the end of the
period (lease period) the asset or equip reverts back to the lessor
Lease Financing
Lease Financing or Leasing is a process where one party (lessor) transfers
the right of economic use of an asset to another party (les- see).
Lease Financing essentially involves the divorce of ownership from the
economic use of the asset for the lessor i.e. The Lessor is the owner of
the capital asset and the ownership of the asset always remains with him,
but the right to use the asset is transferred to the lessee. Lessee is the
party who takes the asset or equipment for a specified period and has to
pay lease rentals throughout the lease period.
Leasing or Lease Financing is generally used to finance fixed asset
having high value.
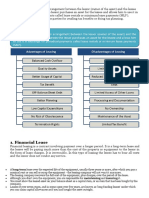
Advantages of Lease Financing
• It helps is reducing the financial burden on lessee.
• It is a device of financing the cost of an asset.
• It is an important financial service as it provides benefit to both
parties.
Types of Lease – Leasing
There are various types of lease as shown in the diagram below
(i) Financial Lease or Capital Lease –
A financial Lease involves payment of lease rentals over one obliga-
tory, non-cancelable lease period sufficient in total to amortize the
capital invested by the lessor and also leave some profit. It involves
the transfer of all risks and rewards associated with the ownership of
the asset to the lessee, but the title of ownership may or may not be
transferred after the completion of lease period. Financial Lease may
be of two types:
Full pay out lease – A Full Payout Lease covers the total
value/cost of the asset through Lease rentals and scrap value. The
lease period usually covers the entire economic life of the asset.
True lease – A true lease only involves only taxation benefits for
the lessor as he bears all the risks and rewards associated with
owner- ship of asset and the lessee only gets the right to use the
asset.
Eg. Ships, air crafts, railway wagon, land, heavy machinery.
(ii) Operating Lease
An Operating lease has the following features:
• It does not transfer all the risks and rewards associated
with ownership of the asset
• The cost of asset is not fully amortized during the primary
lease period
• It consists of a cancellation clause
• Responsibility of maintenance and repair, insurance lies
with the lessor
• The asset is provided on lease for a short period only,
usually less than the useful life of the asset
• It is a high risk lease
• The Lease can be renewed after the expiry of term period
Eg. computer operator, taxi, printers.
Difference Between Operating Lease and
Financial Lease:
Operating Lease Financing Lease
More than one lease
A single lessee is
The number of contract is undertaken
contracted under a
lease contracts and there are several
single agreement
lessees
The cost of asset is not Fully pay out lease –
fully amortized The asset is
Amortization of because the asset is amortized through a
cost of asset leased many times single lease as it is
with different lessees provided for a long
over a period of time term
Equipment or asset is Asset is for the
Specific Use for general purpose specific use of the
use lessee
Risk associated with
It is transferred to
ownership is borne by
the lessee and the
Ownership risk the lessor and the
lessor only retains
lessee only gets the
the title of ownership
right to use the asset
Undertaken for a short Long time, entire
Lease period time period hours or days
Cancellation clause Can be canceled at any It is not revocable in
point before the expiry the primary lease
of the lease period by period
notice to the lessor
Lessor has to bear the Lessee has to bear
Risk of obsolesce
risk the risk
The lessor is
Lessor is a financial
specialized in services
investor and does not
Specialized services of handling the asset
provide any
or equip and
additional services
maintaining it
On the basis of number and nature of parties involved in a
transaction there may be the following types of lease:
(i) Sale and Lease back –
Under this type of lease the owner of the asset sells the asset to the
lessor and takes it back on lease under the lease agreement i.e. the
lessee is the owner of the asset. This type of lease helps in transfer-
ring the ownership from true owner to the lessor. This exchange of
title helps (previous owner) the lessee in liquidating the funds tied up
in a particular asset.
Hence, the seller of the asset becomes the lessee and the buyer of the
asset becomes the lessor. The seller (lessee) receives the cost of
asset and the right to use the asset, while the buyer enjoys the
ownership of asset and lease rentals for the agreed period.
It is generally used in cases where assets are not subjected to depreci-
ation and in industries where free finance is provided to the leasing
company.
E.g. Bank Lockers
(ii) Direct Lease –
In a Direct Lease, the lessee and owner of asset are different entities.
It can be of two types:
Bipartite Lease – In a Bipartite Lease, two parties are involved in a
lease transaction i.e. equipment supplier or lessor and lessee. It is
structured as an operating lease with inbuilt facilities like –
Upgrade lease – It provides an option to upgrade the equipment in
future
Swap lease – It provides an option to replace an equipment with
a similar equipment in working condition.
Tripartite Lease – In a Tripartite Lease the equipment supplier,
lessor, lessee are different entities i.e. three parties are involved in a
lease transaction.
It is a sales aid lease under which the equipment supplier arranges
for lease finance in by –
• Providing reference about the customer to the leasing
company
• Negotiating the terms with the customer
• Writing lease on his own account and discounting the lease
receivables with designated leasing company
On the basis of the domicile of the equipment manufac-
turer there are three types of lease:
(i) Domestic lease – A lease in which all the parties under the
lease contract are of the same country i.e. the equipment supplier, the
lessor and lessee are domiciled in the same country, it is a domestic
lease.
(ii) International or Cross border lease – In a cross border
lease, the lessor and lessee are domiciled in different countries
(iii) Import Lease – In an import lease, mainly the equipment sup-
plier is from a foreign country, the lessor and lessee may be in the
same country.
Other types of Lease:
Leverage lease
In such a lease agreement, the lessor buys an asset through borrowed
funds. Since huge capital is involved in purchase of heavy machiner- ies
and equipment, therefore, borrowed funds are used to finance an asset.
Generally there are three parties involved – a lessee (user), a lessor
(leasing company) and a financer (Banks and Financial institu- tions).
The lessor (leasing company) provides 20%-40% of the pur- chase
value of the asset through equity capital and the remaining amount is
borrowed from commercial bank or financial institutions (financer).
Hence it is financed partly by debt and partly by equity.
• Owner and user or lessor and lessee – They may be
individuals, partners, joint stock companies, corporation or
financial institutions
• Joint lessor or lessee
• Lease broker – merchant banker, subsidiaries, private
merchant
• Lease financier
Parties involved in Lease Financing –
(ii) Asset – The asset, property, equipment is the subject matter of
the contract. It may be an automobile, plant and machinery, equip-
ment, land and building, factory, business, aircraft etc. Ownership of
asset is separated from use of asset during the lease period.
(iii) Term Period – The time period for which the asset is taken on
lease is called lease period. Every lease has a specified or definite
period after which it expires. On the basis on contact between the les-
sor and lessee the lease period may be of two types:
• Primary lease period – Time in which investor wants the
interest on investment
• Secondary ease period – Time for charging nominal rental
(iv) Consideration – Lease Financing involves consideration in form of
lease rentals to be paid by the lessee to the lessor for a speci- fied term period.
The amount of lease rental is decided by taking into account –
• the cost of investment
• cost of repair and maintenance
• depreciation
• taxes
• and adjusted value of cash flows (time value of money).
Modes of terminating Lease
At the end of the lease period, There can be four possible outcomes of lease
expiration:
1. The lease is renewed on a perpetual basis or extended for a definite
period
2. The asset reverts back to the lessor
3. The lessor sells the asset to a third party
4. Lessor sells asset to the lessee
Parties may mutually agree to any one of the following alternatives at the
beginning of the lease term.
You might also like
- 6.3.2 Providing Inspiration and DirectionDocument648 pages6.3.2 Providing Inspiration and Directiontyra banks100% (1)
- Leasing and Hire PurchaseDocument48 pagesLeasing and Hire PurchasePreeti Sharma100% (1)
- Solutions in AppendixDocument13 pagesSolutions in Appendixtfytf70% (2)
- Leasing Hire PurchaseDocument50 pagesLeasing Hire PurchaseRajjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Leasing: Presented By-Ahmed Gulzar Roll No. - 17 Mba 4 SemDocument22 pagesLeasing: Presented By-Ahmed Gulzar Roll No. - 17 Mba 4 SemGulzarNo ratings yet
- Unit-4Leasing and Hire PurchaseDocument25 pagesUnit-4Leasing and Hire Purchasetanishq8807No ratings yet
- New LeasingDocument56 pagesNew LeasingChirag Goyal100% (1)
- Leasing and Hire Purchase (Autosaved)Document72 pagesLeasing and Hire Purchase (Autosaved)medha_mehtaNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial System M. Com Semester Ii Leasing and Hire PurchaseDocument26 pagesIndian Financial System M. Com Semester Ii Leasing and Hire PurchaseAjayNo ratings yet
- Leasing 1Document41 pagesLeasing 1Aaryan SinghNo ratings yet
- Material Unit 3Document14 pagesMaterial Unit 3Pranjay PoddarNo ratings yet
- Group2 Lease FinancingDocument24 pagesGroup2 Lease FinancingMohit Motwani100% (1)
- Leasing:: The Advantages From The Viewpoint of The LesseDocument3 pagesLeasing:: The Advantages From The Viewpoint of The LesseKUNAL KISHOR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Concept of Lease ContractDocument7 pagesConcept of Lease ContractSah AnuNo ratings yet
- Types of LeasingDocument7 pagesTypes of LeasingsanjuNo ratings yet
- Lease Financing and Hire Purchase: Presented by Ashish .K A Maria - Joseph Megha .M Sneha .MDocument70 pagesLease Financing and Hire Purchase: Presented by Ashish .K A Maria - Joseph Megha .M Sneha .MmelvinmeghaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 PDFDocument11 pagesChapter 8 PDFsabbir ahmedNo ratings yet
- 7.lease Vs FinanceDocument6 pages7.lease Vs FinanceShiva AroraNo ratings yet
- Khushigadiya LeasingDocument10 pagesKhushigadiya Leasingkilling machineNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document29 pagesUnit 4123kasaragod123No ratings yet
- LeasingDocument7 pagesLeasingavishkar kaleNo ratings yet
- Theoretical and Regulatory Framework of Leasing: Management of Financial Services - MY KhanDocument28 pagesTheoretical and Regulatory Framework of Leasing: Management of Financial Services - MY KhanSuraj Rajpurohit50% (2)
- Leasing AND Hire PurchaseDocument37 pagesLeasing AND Hire PurchaseDgnfdckckNo ratings yet
- Lease Financing: Presentation By: Mohammed Akbar KhanDocument30 pagesLease Financing: Presentation By: Mohammed Akbar KhanMohammed Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- Leasing: Definitions, Types, Merits and Demerits: AdvertisementsDocument5 pagesLeasing: Definitions, Types, Merits and Demerits: AdvertisementsShivani GogiaNo ratings yet
- Leasing, Hire Purchase & Consumer Credit: Unit-2Document60 pagesLeasing, Hire Purchase & Consumer Credit: Unit-2Feeroj PathanNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: Leasing and HirepurchaseDocument28 pagesObjectives:: Leasing and HirepurchaseviveksansonNo ratings yet
- Financial Services: Topic:-LeasingDocument11 pagesFinancial Services: Topic:-LeasingUtkarsh RajputNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Accounting For LeasesDocument11 pagesLesson 3 Accounting For LeasesKurrent Toy100% (1)
- Lea Se Fin Anc IngDocument22 pagesLea Se Fin Anc IngrachealllNo ratings yet
- Lease PDFDocument13 pagesLease PDFAsma HatamNo ratings yet
- On LeaseDocument12 pagesOn Leasesonam sharmaNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Richa GuptaDocument18 pagesPrepared By: Richa GuptaRicha GuptaNo ratings yet
- All Types of Leasing NewDocument6 pagesAll Types of Leasing NewsanjuNo ratings yet
- A667849305 22264 20 2019 LeaseDocument26 pagesA667849305 22264 20 2019 LeaseChinmai SaiNo ratings yet
- Lease FinancingDocument36 pagesLease Financingssahni15No ratings yet
- Unit FourDocument28 pagesUnit FourTesfaye Megiso BegajoNo ratings yet
- Notes of MFBSDocument23 pagesNotes of MFBSScroll with deepriyaNo ratings yet
- Law of PropertyDocument10 pagesLaw of Propertyshubhankar negiNo ratings yet
- 202004021945300501vasudha Kumar Finance Management 1Document7 pages202004021945300501vasudha Kumar Finance Management 1StarboyNo ratings yet
- Arrangement Between Two Parties For A Specified PeriodDocument11 pagesArrangement Between Two Parties For A Specified PeriodPatel JayeshNo ratings yet
- LeasingDocument10 pagesLeasingSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Building EconomicsDocument13 pagesBuilding EconomicsRiya VermaNo ratings yet
- LeaseDocument7 pagesLeaseSeenu SeenuNo ratings yet
- Lease Financing & Higher Purchase Finance: Submitted byDocument25 pagesLease Financing & Higher Purchase Finance: Submitted byHitesh ChopraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Medium Term FinanceDocument5 pagesChapter 9 - Medium Term FinanceTAN YUN YUNNo ratings yet
- LEASE_FINANCING[1]Document11 pagesLEASE_FINANCING[1]ratnadeeprd16No ratings yet
- F.services Notes-2Document1 pageF.services Notes-2ravindranathNo ratings yet
- LeasingDocument14 pagesLeasingmotvivred1No ratings yet
- By Otmar, B.A: Leasing PreparedDocument53 pagesBy Otmar, B.A: Leasing PreparedAnna Mwita100% (1)
- Types of LeasesDocument4 pagesTypes of LeasesPui YanNo ratings yet
- Non Banking Financial Institutions: by Sudev Jyothisi FN-92 Scms-CochinDocument18 pagesNon Banking Financial Institutions: by Sudev Jyothisi FN-92 Scms-CochinSUDEVJYOTHISINo ratings yet
- Types of LeaseDocument3 pagesTypes of LeaseAmit KainthNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Financial Services in India: LeasingDocument15 pagesUnit - 3 Financial Services in India: Leasingcmmounika1998gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Leasing and HPDocument21 pagesLeasing and HPshivakumar NNo ratings yet
- Leasing: Hitesh GuptaDocument28 pagesLeasing: Hitesh Guptaaqas_khanNo ratings yet
- Financial Accountancy Unit: 4 Leasing and Hire Purchase LeasingDocument3 pagesFinancial Accountancy Unit: 4 Leasing and Hire Purchase LeasingPrakash RNo ratings yet
- LeasingDocument6 pagesLeasingShubham DhimaanNo ratings yet
- LeasesDocument1 pageLeasesRazzaqeeeNo ratings yet
- Real Estate Terminology: Property Management, Financing, Construction, Agents and Brokers TermsFrom EverandReal Estate Terminology: Property Management, Financing, Construction, Agents and Brokers TermsNo ratings yet
- Zerfe Paper RevisedDocument38 pagesZerfe Paper Revisedkassahun mesele100% (1)
- SBR SD21 Examiner's ReportDocument18 pagesSBR SD21 Examiner's ReportIanNo ratings yet
- Indian Restaurant Business PlanDocument23 pagesIndian Restaurant Business PlanAjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Ifrs 14 From EyDocument17 pagesIfrs 14 From EyObisike EmeziNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 2: Financial LiabilitiesDocument63 pagesIntermediate Accounting 2: Financial LiabilitiesLyca Mae CubangbangNo ratings yet
- Joe O Business PlanDocument21 pagesJoe O Business PlanZamri NasirNo ratings yet
- Accounting Concepts and ConventionsDocument4 pagesAccounting Concepts and ConventionsakhilNo ratings yet
- ACCA F7 - Financial Reporting INT UK PasscardsDocument145 pagesACCA F7 - Financial Reporting INT UK Passcardsoleksandr.jobNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Chapter 13 - Acctg For BotDocument3 pagesQuiz - Chapter 13 - Acctg For BotMark CanoNo ratings yet
- Module 11 - Employee BenefitsDocument8 pagesModule 11 - Employee BenefitsLuiNo ratings yet
- AC551 MidtermDocument10 pagesAC551 MidtermAbigail GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Paper 16Document71 pagesPaper 16pkaul1No ratings yet
- The Air Rules 1982Document20 pagesThe Air Rules 1982visutsiNo ratings yet
- Accounts Paper TodayDocument37 pagesAccounts Paper TodayMANMEET MALKOTRANo ratings yet
- BUSINESS PLAN-AY OKAY - FinalDocument39 pagesBUSINESS PLAN-AY OKAY - FinalAlbert Jun Piquero AlegadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Ratio AnalysisDocument6 pagesChapter 4 - Ratio AnalysisLysss EpssssNo ratings yet
- Inter Accounts Revision - Part 1Document317 pagesInter Accounts Revision - Part 1311812922nishanthininkNo ratings yet
- Just Balance Sheet FinalDocument7 pagesJust Balance Sheet Finalsantosh hugarNo ratings yet
- Tech Mahindra P&L StatmentDocument6 pagesTech Mahindra P&L StatmentBharat RajputNo ratings yet
- Small Business Plan TemplateDocument21 pagesSmall Business Plan TemplateSeth JayNo ratings yet
- ACCT 4200 Project Solution - Final Posting 2022Document14 pagesACCT 4200 Project Solution - Final Posting 2022Jaspal SinghNo ratings yet
- Acct-1 Chap-1-1Document11 pagesAcct-1 Chap-1-1Natnael GetahunNo ratings yet
- SPM Slides 10Document28 pagesSPM Slides 10FantayNo ratings yet
- Emilio Aguinaldo College - Cavite Campus School of Business AdministrationDocument9 pagesEmilio Aguinaldo College - Cavite Campus School of Business AdministrationKarlayaan50% (2)
- Sears Vs Walmart - ExcelDocument11 pagesSears Vs Walmart - ExcelTamas OberoiNo ratings yet
- Seatwork 01 Audit of Intangible Assets - ReviewDocument4 pagesSeatwork 01 Audit of Intangible Assets - ReviewDan Andrei BongoNo ratings yet
- International Business Competing in The Global Marketplace 12Th Edition Hill Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesInternational Business Competing in The Global Marketplace 12Th Edition Hill Test Bank Full Chapter PDFbeyradicantdays100% (11)
- Tire City, Inc - Examen FinalDocument3 pagesTire City, Inc - Examen Finalmacro_jNo ratings yet














































![LEASE_FINANCING[1]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/747553681/149x198/b0e8dd3c62/1720003853?v=1)