Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Structure and Function: Sperm Pathway
Structure and Function: Sperm Pathway
Uploaded by
Jaden BrownOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Structure and Function: Sperm Pathway
Structure and Function: Sperm Pathway
Uploaded by
Jaden BrownCopyright:
Available Formats
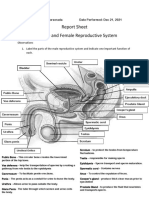
Structure and Function
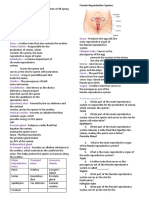
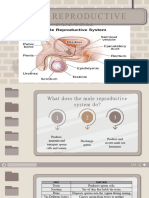
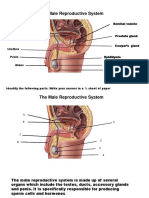
The Male Reproductive System
Urinary bladder Ureter
Symphysis pubis
Vas deferens
Seminal vesicle
Ejaculatory duct
Urethra Prostate
Bulbourethral
gland
Penis gland
Epididymis
Glans penis
Prepuce
Testes
Scrotum 5
The Sperm Pathway Sperm Pathway
Seminal vesicles
Testes
Ejaculatory duct
Sperm
Prostate gland
Epididymis
Urethra
Vas deferens Expulsion
from the body
7
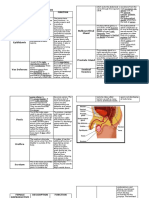
Summary of Parts and their Functions
PARTS FUNCTION
Testis Produces sperm cells
Scrotum Sac of skin that holds the testis
Penis Deposits sperms into the vagina during
mating.
Vas Deferens (tube) Carries sperm from testes to urethra
Urethra Carries sperm and urine out of the body
Glands Provide liquid in which sperm can swim
a. seminal vesicle Secretes a fluid that makes up most of
the components of the semen.
b. Prostate gland Secretes a slightly alkaline milky fluid
that is discharge as part of the semen
c. Bulbourethral gland Secretes a thick and clear mucus that
lubricates and neutralizes the any trace 8
of acidic urine in the urethra.
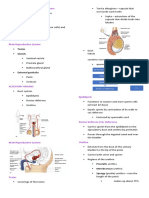
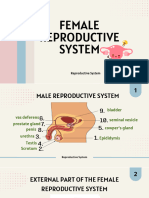
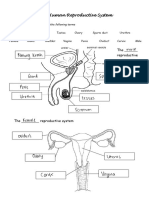
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
A. Functions
1. Oogenesis ( produces female sex cells )
2. Copulation – receive sperm from male
3. Hormone production
4. Provide sites for egg fertilization,
implantation, and development
5. Acts as birth canal
Endocervical canal
Fornix
SUMMARY OF PARTS AND
FUNCTIONS
PARTS FUNCTIONS
Ovary Produces egg cells
Oviduct ( fallopian tube ) Serves as passageway of
eggs from the ovary to
the uterus ; iste of egg
fertilization.
Uterus Serves as site of egg
implantation; is where
the fertilized egg
develops
Vagina Receives the penis of
male during mating ,
What is the menstrual cycle?
• The process in which females
ripen or release one mature egg.
• The average menstrual cycle will
repeat itself about every 28 days,
but normal menstrual cycles can
range from 21 to 40 days.
Hormones
• FSH – Follicle Stimulation - Produced
Hormone in the
• LH - Luteinizing hormone LH – pituitary
gland
signals ovulation
• Estrogen – produced
throughout the menstrual cycle
• Progesterone – produced during -Produced
second half of cycle – by the
follicles in
contributes to thickening of the
the endometrium which is shed ovaries
during the menstrual phase if
fertilization does not take place
You might also like
- 4 Male and Female Reproductive Organs PPTDocument71 pages4 Male and Female Reproductive Organs PPTDanica Marie Sibay100% (2)
- Angeles - Momentum TransferDocument16 pagesAngeles - Momentum TransferJaden BrownNo ratings yet
- Angeles - Momentum TransferDocument16 pagesAngeles - Momentum TransferJaden BrownNo ratings yet
- Angeles - Momentum TransferDocument16 pagesAngeles - Momentum TransferJaden BrownNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child NursingDocument30 pagesMaternal and Child NursingJack Bisarra Sanchez0% (1)
- Basic Obstetrics For The Midwifery Board ExaminationDocument3 pagesBasic Obstetrics For The Midwifery Board ExaminationJoshua Diao94% (16)
- File 0441Document149 pagesFile 0441Kellie ManganNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesReproductive SystemJune PinedaNo ratings yet
- Summary QuestionDocument4 pagesSummary QuestionwagkangtangaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Human Reproduction Education Presentation in Peach Violet Hand Drawn Lightly Textured StyleDocument19 pagesUnderstanding Human Reproduction Education Presentation in Peach Violet Hand Drawn Lightly Textured StylemarcosryanhmaranhaoNo ratings yet
- 4 Male and Female Reproductive Organs PPTDocument71 pages4 Male and Female Reproductive Organs PPTDanica Marie Sibay100% (1)
- Y11 Hum - Rep1 20 3 17Document8 pagesY11 Hum - Rep1 20 3 17Rabia RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Reproductive OrgansDocument24 pagesReproductive OrgansQUEENY CORONELNo ratings yet
- MATERNAL-AND-CHILD-NURSING Notes For BoardsDocument10 pagesMATERNAL-AND-CHILD-NURSING Notes For BoardsJill Margarett BongatoNo ratings yet
- and 2. Lesson 1 and 2 Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDocument50 pagesand 2. Lesson 1 and 2 Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDwinurcholis CholisNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System - Male and FemaleDocument27 pagesReproductive System - Male and FemaleJerome CameroNo ratings yet
- Second Grading LMDocument150 pagesSecond Grading LMALIEZA PAUNILNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesThe Reproductive SystemRichard Castada Guanzon Jr.No ratings yet
- Demo TTL2 - PPT Forda PinalDocument22 pagesDemo TTL2 - PPT Forda PinalkharrenneNo ratings yet
- Biology 12 Worksheet Male Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesBiology 12 Worksheet Male Reproductive SystemMJ VergaraNo ratings yet
- Science 10 NOTESDocument23 pagesScience 10 NOTESnamoramica1No ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesReproductive SystemCHESKA LYKA ASILONo ratings yet
- Report Sheet The Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesReport Sheet The Male and Female Reproductive SystemFelix HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System:: Summary QuestionDocument4 pagesMale Reproductive System:: Summary QuestionwagkangtangaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesMale Reproductive Systemellen_reclaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 3RD QuarterDocument13 pagesScience Reviewer 3RD QuarterKurt John DecenaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System ReproductionDocument9 pagesReproductive System ReproductionDaBestMusicNo ratings yet
- W2 - Human Reproductive SystemDocument35 pagesW2 - Human Reproductive Systemleo manalonNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System ModuleDocument17 pagesReproductive System ModulePATRICIA KAYE RIONo ratings yet
- 3Q Module 1 Male and Female Reproductive Systems 1Document29 pages3Q Module 1 Male and Female Reproductive Systems 1Pau BluzaNo ratings yet
- Ana ReproDocument4 pagesAna ReproFIONA DANE MAURERANo ratings yet
- Fantiyao Reproductive System Group 2Document4 pagesFantiyao Reproductive System Group 2Jushelle Anne Tigoy PilareNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 16Document5 pagesLaboratory 16Jeca InandanNo ratings yet
- LECTURE NO 3 - Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesLECTURE NO 3 - Reproductive SystemRebell AeonNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument41 pagesHuman ReproductionMmabatho Vilakazi100% (1)
- ExtraaaDocument5 pagesExtraaaaviraaworldNo ratings yet
- Topic 17: ReproductionDocument29 pagesTopic 17: ReproductionEva SidhaniNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument39 pagesReproductive SystemCenando Bodanio100% (1)
- Lesson 2. Reproductive SystemDocument31 pagesLesson 2. Reproductive SystemZerene Joy ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Sci 10 - 044447Document12 pagesSci 10 - 044447tefzychiNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Science Periodical Test NotesDocument13 pages3rd Quarter Science Periodical Test Notesmichael enriquezNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesMale Reproductive SystemSarilyn Simon50% (2)
- Sexual Reproduction in HumansDocument14 pagesSexual Reproduction in HumansUnknownKidNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Reproduction - 2023Document62 pagesPlant and Animal Reproduction - 2023TohmNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument13 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemmoroshariekarlaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesReproductive SystemkhakimagdalenaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Module 1.3 Reproductive SystemDocument113 pagesQuarter 3 Module 1.3 Reproductive Systemsano.kthNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document3 pagesScience 10Andrea JimenezNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System v2 - 3rd QuarterDocument20 pagesReproductive System v2 - 3rd QuarterGeromme TudNo ratings yet
- QUARTER 3 Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesQUARTER 3 Reproductive Systemespinajeff07No ratings yet
- Science 5 ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience 5 ReviewerAlexandra Pauline DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesReproductive SystemMARYLOUISE SANDIEGONo ratings yet
- Male & Female Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesMale & Female Reproductive SystemCandly SHi100% (1)
- Third Term s2 BiologyDocument34 pagesThird Term s2 BiologyADEYI KAYODE SAMUELNo ratings yet
- Science 5Document26 pagesScience 5barangay89zone9No ratings yet
- AP2 Lab13 Reproductive System Anatomy Lab SP21finalDocument14 pagesAP2 Lab13 Reproductive System Anatomy Lab SP21finalBella DonnaAriesta LumbanGaolNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Role of Hormones in The Female and Male Reproductive SystemDocument24 pagesLesson 3: Role of Hormones in The Female and Male Reproductive Systemnathanielstanaj.mNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Humans: Chapter - I Reproduction SystemsDocument18 pagesSexual Reproduction in Humans: Chapter - I Reproduction Systemsrajendra110778No ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System - PPTX NewDocument7 pagesMale Reproductive System - PPTX NewSarilyn SimonNo ratings yet
- Reproduction - S3AC - Actividades A Explicar - 2021Document50 pagesReproduction - S3AC - Actividades A Explicar - 2021Villaxx 05No ratings yet
- 3 Human ReproductionDocument89 pages3 Human Reproductionrustama0322No ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument36 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemamyNo ratings yet
- (Template) The Human Reproductive SystemDocument4 pages(Template) The Human Reproductive Systemshakhirafk143No ratings yet
- Science PPT Male Rep System 1.1Document70 pagesScience PPT Male Rep System 1.1Mathel ChavezNo ratings yet
- Day 5 - Two and Three Dimensional KinematicsDocument17 pagesDay 5 - Two and Three Dimensional KinematicsJaden BrownNo ratings yet
- Piaget's Theory of Cognitive DevelopmentDocument19 pagesPiaget's Theory of Cognitive DevelopmentJaden BrownNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Individual DifferencesDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of Individual DifferencesJaden BrownNo ratings yet
- NNMMKLDocument6 pagesNNMMKLJaden BrownNo ratings yet
- Bonding Forces and EnergiesDocument3 pagesBonding Forces and EnergiesJaden BrownNo ratings yet
- What To Do in The PortfolioDocument1 pageWhat To Do in The PortfolioJaden BrownNo ratings yet
- 1DumbEnmyAndPlusDMG Com - Com2us - Smon.normal - Freefull.google - Kr.android - CommonDocument1 page1DumbEnmyAndPlusDMG Com - Com2us - Smon.normal - Freefull.google - Kr.android - CommonJaden BrownNo ratings yet
- Minimum System ReqDocument1 pageMinimum System ReqJaden BrownNo ratings yet
- AsdasdDocument1 pageAsdasdJaden BrownNo ratings yet
- Sched 2019-2020Document1 pageSched 2019-2020Jaden BrownNo ratings yet
- Sched 2019-2020Document1 pageSched 2019-2020Jaden BrownNo ratings yet
- PlathelminthesDocument42 pagesPlathelminthesLuca MincuNo ratings yet
- 858 2060 1 SM PDFDocument10 pages858 2060 1 SM PDFLina JuwairiyahNo ratings yet
- Klinefelter Syndrome in Clinical Practice. Nat Clin Pract Urol 4:192-204Document14 pagesKlinefelter Syndrome in Clinical Practice. Nat Clin Pract Urol 4:192-204Anonymous LAWfm7No ratings yet
- Antenatal & Postnatal Care: 1. General InformationDocument7 pagesAntenatal & Postnatal Care: 1. General InformationanishnithaNo ratings yet
- Oral Contraceptives PDFDocument24 pagesOral Contraceptives PDFSheema TabassumNo ratings yet
- Perineal CareDocument10 pagesPerineal Careoxidalaj100% (11)
- Jadwal Simpo Pit Pogi 2019Document12 pagesJadwal Simpo Pit Pogi 2019Hartanto LieNo ratings yet
- Artificial Propagation Research PaperDocument6 pagesArtificial Propagation Research Paperapi-240613752No ratings yet
- Perinatal Mortality HUKMDocument8 pagesPerinatal Mortality HUKMMuvenn KannanNo ratings yet
- Contraception MethodsDocument22 pagesContraception MethodspghsNo ratings yet
- Biology Q PDFDocument9 pagesBiology Q PDFsumon chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- A History of The Penile Implant To 1974: Sex Med Rev 2016 4:285 E293 285Document9 pagesA History of The Penile Implant To 1974: Sex Med Rev 2016 4:285 E293 285Anonymous S0MyRHNo ratings yet
- Prolapse of The Umbilical CordDocument13 pagesProlapse of The Umbilical CordJm OpolintoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Isolation and Speciation Updated For ApDocument25 pagesReproductive Isolation and Speciation Updated For Apapi-265142071No ratings yet
- രതിവിജ്ഞാനംDocument97 pagesരതിവിജ്ഞാനംChristopher George100% (1)
- The Genetics of MicrocephalyDocument6 pagesThe Genetics of MicrocephalyErsya MuslihNo ratings yet
- Science 5 ST 2Document1 pageScience 5 ST 2jekjek100% (1)
- Article - Yoga For WomenDocument8 pagesArticle - Yoga For WomenDuath Dinen100% (1)
- Labor and DeliveryDocument6 pagesLabor and Deliveryjenryl91% (11)
- GNRH Agonist Trigger For The Induction of Oocyte Maturation in GNRH Antagonist IVF Cycles: A SWOT AnalysisDocument12 pagesGNRH Agonist Trigger For The Induction of Oocyte Maturation in GNRH Antagonist IVF Cycles: A SWOT Analysisgardener10No ratings yet
- There Are Safe Methods To Prevent Pregnancy After Unprotected SexDocument8 pagesThere Are Safe Methods To Prevent Pregnancy After Unprotected SexAnjaliSinhaNo ratings yet
- Lsac Asr 2018 Chap5 Teenagers and Sex PDFDocument11 pagesLsac Asr 2018 Chap5 Teenagers and Sex PDFPriambodo GandhiNo ratings yet
- Stages of LabourDocument43 pagesStages of LabourhaisureshNo ratings yet
- GynegologicalDocument1 pageGynegologicaltristan_adviento32No ratings yet
- Case Study Menstrual Cycle - Middle School LevelDocument3 pagesCase Study Menstrual Cycle - Middle School Levelymaamoun1No ratings yet
- Science F4 Chapter 2 Body Coordination 2.6 NotesDocument4 pagesScience F4 Chapter 2 Body Coordination 2.6 NotesKSSM TSENo ratings yet
- Bacterial Classification, Structure, and Replication - MurrrayDocument34 pagesBacterial Classification, Structure, and Replication - MurrraysebastianNo ratings yet
- Amniotomia para Acortar El Trabajo de PartoDocument87 pagesAmniotomia para Acortar El Trabajo de PartoJohanna Villamarin SilvaNo ratings yet