Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 viewsTools, Utensils and Equipment Nutritional Value and Component of Eggs. Characteristics of Quality Fresh Eggs
Tools, Utensils and Equipment Nutritional Value and Component of Eggs. Characteristics of Quality Fresh Eggs
Uploaded by
JohnCzyril Deladia DomensThe document discusses tools, utensils, and equipment needed for cooking eggs including: egg cups for soft boiled eggs, egg slicers to cut off tapered egg ends, electric egg cookers, non-stick skillets for frying eggs, egg beaters for scrambling eggs, and silicone egg rings. It also discusses egg grades from A to C based on quality and nutritional components of eggs such as proteins, vitamins, minerals, and the differences between egg yolks and whites.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Harry Potter - VocabularyDocument11 pagesHarry Potter - VocabularyviniciusmdiasNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in K-12 Bread and Pastry ProductionDocument8 pagesLesson Plan in K-12 Bread and Pastry ProductionGalvez ChaCha96% (269)
- The Master Magician by Charlie N. HolmbergDocument225 pagesThe Master Magician by Charlie N. HolmbergKayla Najma Hidayat100% (1)
- Week 8 PPT EggsDocument37 pagesWeek 8 PPT EggsRINOA KEISHA CORTEZNo ratings yet
- TLECookery10 - Q2 - Mod8 - Cookfishandshellfish Methods of Cooking Fish and Shellfish - v3Document36 pagesTLECookery10 - Q2 - Mod8 - Cookfishandshellfish Methods of Cooking Fish and Shellfish - v3Remy Senabe88% (8)
- LESSON 3 4 Prepare and Cook Egg Dishes Part 1 2Document34 pagesLESSON 3 4 Prepare and Cook Egg Dishes Part 1 2Len Bulgar50% (2)
- Micro-Teaching Fresh BreadDocument2 pagesMicro-Teaching Fresh Breadapi-513510439No ratings yet
- Commodity Analysis CocoaDocument34 pagesCommodity Analysis CocoaSanket Sakpal100% (1)
- Powerpoint Prepareeggdishes 170121050449Document28 pagesPowerpoint Prepareeggdishes 170121050449Glyza Marie CendanaNo ratings yet
- Egg Dishes and ToolsDocument38 pagesEgg Dishes and ToolsSabrina ChuaNo ratings yet
- Egg DishesDocument56 pagesEgg DishesaileenNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Prep Egg DishesDocument35 pagesGrade 10 Prep Egg DishesCharlene obmergaNo ratings yet
- Cookery 11 - Egg DishesDocument12 pagesCookery 11 - Egg Dishesmarylene milanNo ratings yet
- Present and Store Egg Dishes: Cookery 10 Module 4Document26 pagesPresent and Store Egg Dishes: Cookery 10 Module 4Ems BinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Prepare Egg Dishes: Cookery 2Document55 pagesLesson 1 Prepare Egg Dishes: Cookery 2Yaelee SottoNo ratings yet
- Egg and Breakfast PreparationDocument13 pagesEgg and Breakfast PreparationMarvin BuensucesoNo ratings yet
- Egg CookeryDocument15 pagesEgg CookeryIaraCoutoNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document7 pagesModule 2JonardNadelaNo ratings yet
- BF Eggs Revised.2017Document45 pagesBF Eggs Revised.2017Sophia CayabyabNo ratings yet
- EggsDocument13 pagesEggsBonophool Banerjee67% (3)
- Preparing Egg DishesDocument16 pagesPreparing Egg DishesAilyn Grace PantaleonNo ratings yet
- TLE Grade 10 NotesDocument7 pagesTLE Grade 10 NotesLhei Cruz MartinNo ratings yet
- Egg CookeryDocument57 pagesEgg CookeryThefoodiesway100% (3)
- 2.3 Tools Utensils and Equipment Needed inDocument22 pages2.3 Tools Utensils and Equipment Needed inaltheatugade39No ratings yet
- Egg DishesDocument66 pagesEgg DishesEljen MiroNo ratings yet
- Egg CookeryDocument15 pagesEgg CookeryJulie Ann CortezNo ratings yet
- JHS Modules 1ST QuarterDocument11 pagesJHS Modules 1ST QuarterJohnson FernandezNo ratings yet
- Egg Dishes: Prepared By: Joniefe G. SanielDocument57 pagesEgg Dishes: Prepared By: Joniefe G. SanielJoniefe SanielNo ratings yet
- Module 12 EggDocument9 pagesModule 12 Eggirneil H. PepitoNo ratings yet
- Nutritive Value Quality Grading Sizes Market Forms Uses of EggsDocument55 pagesNutritive Value Quality Grading Sizes Market Forms Uses of EggsBRIAR ROSE PARILLANo ratings yet
- Cookery EggDocument18 pagesCookery Eggedmar aguilarNo ratings yet
- TLEDocument53 pagesTLEKa KlasmeytNo ratings yet
- Kit-101 Eggs Station Cooking StylesDocument5 pagesKit-101 Eggs Station Cooking StylesDaliborNo ratings yet
- BF Eggs 3Document19 pagesBF Eggs 3api-317900635No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Composition: Parts of An EggDocument22 pagesLesson 1: Composition: Parts of An Eggjohn michael pagalaNo ratings yet
- Tools and Equipment 23 24Document20 pagesTools and Equipment 23 24hansennichols9No ratings yet
- Breakfast Breakfast Breakfast Breakfast: Week 6 Week 6 Week 6 Week 6Document81 pagesBreakfast Breakfast Breakfast Breakfast: Week 6 Week 6 Week 6 Week 6ponavnitNo ratings yet
- Prepare and Cooked Egg Dishes - 3rd LessonDocument15 pagesPrepare and Cooked Egg Dishes - 3rd LessonElla Cagadas Puzon100% (1)
- Nutritional Values of EggsDocument4 pagesNutritional Values of EggsMickaela Eunice JimenezNo ratings yet
- Lesson8varietyofeggdishes 190220011419Document44 pagesLesson8varietyofeggdishes 190220011419Ronigrace SanchezNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Value: Depart of Food Production Ihm, KolkataDocument12 pagesNutritional Value: Depart of Food Production Ihm, KolkataProbaron BaruahNo ratings yet
- Tle 10 ToolsDocument61 pagesTle 10 ToolsCintoftNo ratings yet
- What Is The Shelf Life of EggsDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Shelf Life of EggsBushra ChuadhryNo ratings yet
- Structure of An EggDocument29 pagesStructure of An EggsheilaNo ratings yet
- Egg Product, Nutritive Value, Quality, and Market FormsDocument19 pagesEgg Product, Nutritive Value, Quality, and Market FormsRosalyn DelfinNo ratings yet
- Variety of Egg DishesDocument37 pagesVariety of Egg DishesEloisa Marie Enriquez BontilaoNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 Q1 W3Document16 pagesCookery 10 Q1 W3Gwyneth Joy CasiquinNo ratings yet
- Egg CookeryDocument4 pagesEgg Cookerygauravkrishana28No ratings yet
- TLECookeryNCII Grade10 QTR1 Module-3Document18 pagesTLECookeryNCII Grade10 QTR1 Module-3Jasmine Pearl WongNo ratings yet
- Egg DishDocument84 pagesEgg DishMarry Jane Lustre CanabalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of An EggDocument57 pagesAnatomy of An EggMARIALYN IBANEZNo ratings yet
- How To Preserve Eggs: Freezing, Pickling, Dehydrating, Larding, Water Glassing, & MoreFrom EverandHow To Preserve Eggs: Freezing, Pickling, Dehydrating, Larding, Water Glassing, & MoreRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- EggsDocument14 pagesEggsLucille PaglingayenNo ratings yet
- Market Forms of EggsDocument49 pagesMarket Forms of Eggsnina051991No ratings yet
- Characteristics of A Fresh Egg:: As Shown in The ShellDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of A Fresh Egg:: As Shown in The ShellValerieAnnVilleroAlvarezValienteNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX Eggs Objectives Describe The Structure of An Egg Explain How To Select andDocument28 pagesVdocuments - MX Eggs Objectives Describe The Structure of An Egg Explain How To Select andMaynard CaspilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document22 pagesLesson 5Nika KatanoNo ratings yet
- First Report in MA - Egg StructureDocument9 pagesFirst Report in MA - Egg StructureIan Keith Revantad SomozaNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 2.2 1 Variety of Egg Dishes EditedDocument7 pagesInformation Sheet 2.2 1 Variety of Egg Dishes EditedKristymel Queen CabugonNo ratings yet
- Definition of An EggDocument3 pagesDefinition of An EggAman BhandariNo ratings yet
- 1.structure of Egg 2.explain Structure of Egg 3.selection of Eggs 4.eggs RecipiesDocument16 pages1.structure of Egg 2.explain Structure of Egg 3.selection of Eggs 4.eggs RecipiesZeon DmelloNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcome 2 Prepare and Cook Egg DishesDocument35 pagesLearning Outcome 2 Prepare and Cook Egg DishesRein Ashlie Gera100% (4)
- Lesson 2 TLEDocument17 pagesLesson 2 TLEJhon Anthony CatinoyNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Learning Outcome 2 Prepare and Cook Egg DishesDocument8 pagesQuarter 1 Learning Outcome 2 Prepare and Cook Egg DishesAdea LucianoNo ratings yet
- Egg DishDocument15 pagesEgg DishThea Jeonieesa GarayNo ratings yet
- Eggs: Fresh, Simple Recipes for Frittatas, Omelets, Scrambles & MoreFrom EverandEggs: Fresh, Simple Recipes for Frittatas, Omelets, Scrambles & MoreRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Img 20221022 214100Document2 pagesImg 20221022 214100JohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- Summative Test QuestionaireDocument2 pagesSummative Test QuestionaireJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- Innovation FormatDocument2 pagesInnovation FormatJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- 150 LandscapingDocument23 pages150 LandscapingJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- What Is The Community Alert Siren System?: Clicking HereDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Community Alert Siren System?: Clicking HereJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- Current Job Position and Workplace No. of Months/yr Took To Land The 1 JobDocument6 pagesCurrent Job Position and Workplace No. of Months/yr Took To Land The 1 JobJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- Weekly School Home Learning Plan For Blended Learning For Roll OutDocument7 pagesWeekly School Home Learning Plan For Blended Learning For Roll OutJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- CRP 506Document174 pagesCRP 506JohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- Lac Plan For Indigenous Groups SampleDocument2 pagesLac Plan For Indigenous Groups SampleJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- Grades 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log School: Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates & Time QuarterDocument5 pagesGrades 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log School: Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates & Time QuarterJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- Active and Inactive FaultsDocument19 pagesActive and Inactive FaultsJohnCzyril Deladia Domens100% (1)
- Prepare Cereals and Starch: A. Perform Mise'en Place BDocument27 pagesPrepare Cereals and Starch: A. Perform Mise'en Place BJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Tle Bread and Pastry ProductionDocument14 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Tle Bread and Pastry ProductionJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- BartendingDocument38 pagesBartendingJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- BreakfastDocument18 pagesBreakfastIasha HussainNo ratings yet
- Tamaya Menu 2019 - 10 Hires Compressed PDFDocument11 pagesTamaya Menu 2019 - 10 Hires Compressed PDFJewyang HuangNo ratings yet
- Hey Friends 1 WB ANSWER KEY - 28-09-18 PDFDocument16 pagesHey Friends 1 WB ANSWER KEY - 28-09-18 PDFbenNo ratings yet
- Parle Products - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesParle Products - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaGaurav LahotiNo ratings yet
- Salads: 300 Salad Recipes For Rapid Weight Loss & Clean Eating (PDFDrive) PDFDocument1,092 pagesSalads: 300 Salad Recipes For Rapid Weight Loss & Clean Eating (PDFDrive) PDFDebora PanzarellaNo ratings yet
- Bibimbap by Oori MenuDocument9 pagesBibimbap by Oori MenuMetroStaycationNo ratings yet
- Cakes Buns Scones Pastry, Biscuits,: Etc. Selected and Tested Recipes and FormulasDocument20 pagesCakes Buns Scones Pastry, Biscuits,: Etc. Selected and Tested Recipes and FormulasJulia BeanNo ratings yet
- III. Business ProponentsDocument6 pagesIII. Business ProponentsJE SingianNo ratings yet
- Homework Names: Rafaela Studies at San Agustin UniversityDocument5 pagesHomework Names: Rafaela Studies at San Agustin UniversityCARLOS JOAQUIN ALVAREZ AMBRONCIONo ratings yet
- Snacks Gain ReportDocument6 pagesSnacks Gain ReportNancy W FaragNo ratings yet
- Rahul Sugar ProductsDocument18 pagesRahul Sugar ProductsSantosh DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Uh Explanation Text 2Document2 pagesUh Explanation Text 2awaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate and Calorie ListDocument9 pagesCarbohydrate and Calorie ListAubrey Dynise C. TorralbaNo ratings yet
- (Multiple Choice Questions) Total Time: 1 Hour Total Marks: 50Document3 pages(Multiple Choice Questions) Total Time: 1 Hour Total Marks: 50GGHS PindoraNo ratings yet
- Bake With Us - Speak English With VanessaDocument5 pagesBake With Us - Speak English With VanessaAbdulmuqtadetr AhmadiNo ratings yet
- Binomial PairsDocument32 pagesBinomial PairsPaul100% (5)
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: ECONOMICS 9708/23Document4 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: ECONOMICS 9708/23santu220875No ratings yet
- Pearson - Roadmap A2+ Workbook With KeyDocument12 pagesPearson - Roadmap A2+ Workbook With Keydanghoi556No ratings yet
- FSM 112 Lecture 1Document6 pagesFSM 112 Lecture 1revilyn reguyalNo ratings yet
- The Thief of Smells - Short StoryDocument3 pagesThe Thief of Smells - Short StoryOlga HazemNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Guidelines To Help Control Nausea and Vomiting During PregnancyDocument16 pagesNutritional Guidelines To Help Control Nausea and Vomiting During PregnancyFitria Ayu AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- I.-Fill in The Correct Connectives and Linking Words From The List. There May Be More Than One Answer in Some SentencesDocument9 pagesI.-Fill in The Correct Connectives and Linking Words From The List. There May Be More Than One Answer in Some SentencesWendy Copaja PortugalNo ratings yet
- Division of Fractions Worksheets Math 6 Q1W3Document8 pagesDivision of Fractions Worksheets Math 6 Q1W3Noemi Rosario SanchezNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Introduction To American CuisineDocument9 pagesTopic 1 - Introduction To American CuisineHoneylyn OlilaNo ratings yet
Tools, Utensils and Equipment Nutritional Value and Component of Eggs. Characteristics of Quality Fresh Eggs
Tools, Utensils and Equipment Nutritional Value and Component of Eggs. Characteristics of Quality Fresh Eggs
Uploaded by
JohnCzyril Deladia Domens0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views28 pagesThe document discusses tools, utensils, and equipment needed for cooking eggs including: egg cups for soft boiled eggs, egg slicers to cut off tapered egg ends, electric egg cookers, non-stick skillets for frying eggs, egg beaters for scrambling eggs, and silicone egg rings. It also discusses egg grades from A to C based on quality and nutritional components of eggs such as proteins, vitamins, minerals, and the differences between egg yolks and whites.
Original Description:
Original Title
powerpoint-prepareeggdishes-170121050449.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses tools, utensils, and equipment needed for cooking eggs including: egg cups for soft boiled eggs, egg slicers to cut off tapered egg ends, electric egg cookers, non-stick skillets for frying eggs, egg beaters for scrambling eggs, and silicone egg rings. It also discusses egg grades from A to C based on quality and nutritional components of eggs such as proteins, vitamins, minerals, and the differences between egg yolks and whites.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views28 pagesTools, Utensils and Equipment Nutritional Value and Component of Eggs. Characteristics of Quality Fresh Eggs
Tools, Utensils and Equipment Nutritional Value and Component of Eggs. Characteristics of Quality Fresh Eggs
Uploaded by
JohnCzyril Deladia DomensThe document discusses tools, utensils, and equipment needed for cooking eggs including: egg cups for soft boiled eggs, egg slicers to cut off tapered egg ends, electric egg cookers, non-stick skillets for frying eggs, egg beaters for scrambling eggs, and silicone egg rings. It also discusses egg grades from A to C based on quality and nutritional components of eggs such as proteins, vitamins, minerals, and the differences between egg yolks and whites.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 28
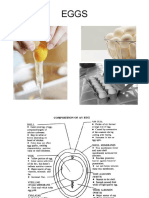
{ Tools, utensils and equipment
Nutritional Value and component of
eggs.
Characteristics of quality fresh eggs
TOOLS AND UTENSILS
NEEDED IN COOKING
EGGS
- For serving and eating
soft-boiled eggs.
They are either
porcelain or stainless
steel.
Some have integrated
plates to hold the
shell pieces.
-For soft-boiled
eggs.
They fit
comfortably inside
an egg without
breaking the shell.
These are
supposed to
cleanly cut the
tapered ends off
the egg so you
can eat out of the
shell.
- Faster than the
hassle of boiling
water on the stove.
Some are
automatic based
on temperature
sensing. Some
have timers.
- They are either
countertop or hold
in your hand
- Usually non-stick,
but plain stainless
steel exists. Most
look similar to
other skillets, but
have sloping sides
to slide the omelet
around.
- For up to three
scrambled eggs.
The shape in
center separates
and beats the
eggs.
- When frying eggs.
Stay cool knock
down handle.
Silicone rings
conform to the
bottom of pan to
reduce egg ooze
out.
- They are used to
separate eggs. They
hold the yolk while
the white drips
through
- Use in cracking eggs
so the shell will not
mix.
Gently slam an egg
down on a razor
blade.
- Flexible silicone
pods that float on the
boiling water. Can
also be used for
baking and molding
- Specialized metal
stove top pans have
been around for a
while. They are
basically double
boilers with one to six
depressions with fixed
or removeable pods.
Quality
&
Grades of Eggs
Changes in Quality Over
Time
Eggs must be stored in the
refrigerator to maintain Grade
A quality. Eggs kept at room
temperature deteriorate as
much in a day as they do in a
week under refrigeration
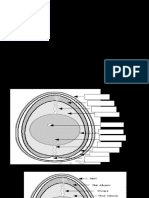
As an egg ages:
• The AIR CELL becomes
larger
• The YOLK becomes flatter,
larger and breaks more easily
• The THICK WHITE
becomes thin and watery
Egg Grades
Grade A
• Thick white
• Round, well centered yolk
• Small air cell (less than 5 mm
deep)
• Clean, uncracked shell with
normal shape
Grade B
• These eggs are mostly used for
commercial baking
• Yolk is slightly flattened; white
is thinner.
• Shell is un-cracked and may
have a rough texture; and/or be
slightly soiled and stained.
Grade C
• The lowest egg grade, these are
used in the production of processed
egg products only. They are not sold
in grocery stores.
• Yolk is flattened and may be
oblong in shape; white is thin and
watery.
• Shell may be cracked and/or
stained.
NUTRITIONAL VALUE
/COMPONENTS OF EGGS
1. high-quality protein
(which contains all essential amino acids
for humans)
2. vitamin A,
3. riboflavin,
4. folic acid,
5. vitamin B6,
6. vitamin B12,
7. Choline
8. Iron
9. calcium
10. phosphorus
11. potassium.
- Contains vitamin A, D and E
- Makes up about 33% of the liquid
weight of the egg
- Contains all of the choline
- High Cholesterol, fat, saturated fat
The egg white consists primarily of
water (87%) and protein (13%) and
contains no cholesterol and little
Contains about 15 calories
You might also like
- Harry Potter - VocabularyDocument11 pagesHarry Potter - VocabularyviniciusmdiasNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in K-12 Bread and Pastry ProductionDocument8 pagesLesson Plan in K-12 Bread and Pastry ProductionGalvez ChaCha96% (269)
- The Master Magician by Charlie N. HolmbergDocument225 pagesThe Master Magician by Charlie N. HolmbergKayla Najma Hidayat100% (1)
- Week 8 PPT EggsDocument37 pagesWeek 8 PPT EggsRINOA KEISHA CORTEZNo ratings yet
- TLECookery10 - Q2 - Mod8 - Cookfishandshellfish Methods of Cooking Fish and Shellfish - v3Document36 pagesTLECookery10 - Q2 - Mod8 - Cookfishandshellfish Methods of Cooking Fish and Shellfish - v3Remy Senabe88% (8)
- LESSON 3 4 Prepare and Cook Egg Dishes Part 1 2Document34 pagesLESSON 3 4 Prepare and Cook Egg Dishes Part 1 2Len Bulgar50% (2)
- Micro-Teaching Fresh BreadDocument2 pagesMicro-Teaching Fresh Breadapi-513510439No ratings yet
- Commodity Analysis CocoaDocument34 pagesCommodity Analysis CocoaSanket Sakpal100% (1)
- Powerpoint Prepareeggdishes 170121050449Document28 pagesPowerpoint Prepareeggdishes 170121050449Glyza Marie CendanaNo ratings yet
- Egg Dishes and ToolsDocument38 pagesEgg Dishes and ToolsSabrina ChuaNo ratings yet
- Egg DishesDocument56 pagesEgg DishesaileenNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Prep Egg DishesDocument35 pagesGrade 10 Prep Egg DishesCharlene obmergaNo ratings yet
- Cookery 11 - Egg DishesDocument12 pagesCookery 11 - Egg Dishesmarylene milanNo ratings yet
- Present and Store Egg Dishes: Cookery 10 Module 4Document26 pagesPresent and Store Egg Dishes: Cookery 10 Module 4Ems BinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Prepare Egg Dishes: Cookery 2Document55 pagesLesson 1 Prepare Egg Dishes: Cookery 2Yaelee SottoNo ratings yet
- Egg and Breakfast PreparationDocument13 pagesEgg and Breakfast PreparationMarvin BuensucesoNo ratings yet
- Egg CookeryDocument15 pagesEgg CookeryIaraCoutoNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document7 pagesModule 2JonardNadelaNo ratings yet
- BF Eggs Revised.2017Document45 pagesBF Eggs Revised.2017Sophia CayabyabNo ratings yet
- EggsDocument13 pagesEggsBonophool Banerjee67% (3)
- Preparing Egg DishesDocument16 pagesPreparing Egg DishesAilyn Grace PantaleonNo ratings yet
- TLE Grade 10 NotesDocument7 pagesTLE Grade 10 NotesLhei Cruz MartinNo ratings yet
- Egg CookeryDocument57 pagesEgg CookeryThefoodiesway100% (3)
- 2.3 Tools Utensils and Equipment Needed inDocument22 pages2.3 Tools Utensils and Equipment Needed inaltheatugade39No ratings yet
- Egg DishesDocument66 pagesEgg DishesEljen MiroNo ratings yet
- Egg CookeryDocument15 pagesEgg CookeryJulie Ann CortezNo ratings yet
- JHS Modules 1ST QuarterDocument11 pagesJHS Modules 1ST QuarterJohnson FernandezNo ratings yet
- Egg Dishes: Prepared By: Joniefe G. SanielDocument57 pagesEgg Dishes: Prepared By: Joniefe G. SanielJoniefe SanielNo ratings yet
- Module 12 EggDocument9 pagesModule 12 Eggirneil H. PepitoNo ratings yet
- Nutritive Value Quality Grading Sizes Market Forms Uses of EggsDocument55 pagesNutritive Value Quality Grading Sizes Market Forms Uses of EggsBRIAR ROSE PARILLANo ratings yet
- Cookery EggDocument18 pagesCookery Eggedmar aguilarNo ratings yet
- TLEDocument53 pagesTLEKa KlasmeytNo ratings yet
- Kit-101 Eggs Station Cooking StylesDocument5 pagesKit-101 Eggs Station Cooking StylesDaliborNo ratings yet
- BF Eggs 3Document19 pagesBF Eggs 3api-317900635No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Composition: Parts of An EggDocument22 pagesLesson 1: Composition: Parts of An Eggjohn michael pagalaNo ratings yet
- Tools and Equipment 23 24Document20 pagesTools and Equipment 23 24hansennichols9No ratings yet
- Breakfast Breakfast Breakfast Breakfast: Week 6 Week 6 Week 6 Week 6Document81 pagesBreakfast Breakfast Breakfast Breakfast: Week 6 Week 6 Week 6 Week 6ponavnitNo ratings yet
- Prepare and Cooked Egg Dishes - 3rd LessonDocument15 pagesPrepare and Cooked Egg Dishes - 3rd LessonElla Cagadas Puzon100% (1)
- Nutritional Values of EggsDocument4 pagesNutritional Values of EggsMickaela Eunice JimenezNo ratings yet
- Lesson8varietyofeggdishes 190220011419Document44 pagesLesson8varietyofeggdishes 190220011419Ronigrace SanchezNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Value: Depart of Food Production Ihm, KolkataDocument12 pagesNutritional Value: Depart of Food Production Ihm, KolkataProbaron BaruahNo ratings yet
- Tle 10 ToolsDocument61 pagesTle 10 ToolsCintoftNo ratings yet
- What Is The Shelf Life of EggsDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Shelf Life of EggsBushra ChuadhryNo ratings yet
- Structure of An EggDocument29 pagesStructure of An EggsheilaNo ratings yet
- Egg Product, Nutritive Value, Quality, and Market FormsDocument19 pagesEgg Product, Nutritive Value, Quality, and Market FormsRosalyn DelfinNo ratings yet
- Variety of Egg DishesDocument37 pagesVariety of Egg DishesEloisa Marie Enriquez BontilaoNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 Q1 W3Document16 pagesCookery 10 Q1 W3Gwyneth Joy CasiquinNo ratings yet
- Egg CookeryDocument4 pagesEgg Cookerygauravkrishana28No ratings yet
- TLECookeryNCII Grade10 QTR1 Module-3Document18 pagesTLECookeryNCII Grade10 QTR1 Module-3Jasmine Pearl WongNo ratings yet
- Egg DishDocument84 pagesEgg DishMarry Jane Lustre CanabalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of An EggDocument57 pagesAnatomy of An EggMARIALYN IBANEZNo ratings yet
- How To Preserve Eggs: Freezing, Pickling, Dehydrating, Larding, Water Glassing, & MoreFrom EverandHow To Preserve Eggs: Freezing, Pickling, Dehydrating, Larding, Water Glassing, & MoreRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- EggsDocument14 pagesEggsLucille PaglingayenNo ratings yet
- Market Forms of EggsDocument49 pagesMarket Forms of Eggsnina051991No ratings yet
- Characteristics of A Fresh Egg:: As Shown in The ShellDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of A Fresh Egg:: As Shown in The ShellValerieAnnVilleroAlvarezValienteNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX Eggs Objectives Describe The Structure of An Egg Explain How To Select andDocument28 pagesVdocuments - MX Eggs Objectives Describe The Structure of An Egg Explain How To Select andMaynard CaspilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document22 pagesLesson 5Nika KatanoNo ratings yet
- First Report in MA - Egg StructureDocument9 pagesFirst Report in MA - Egg StructureIan Keith Revantad SomozaNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 2.2 1 Variety of Egg Dishes EditedDocument7 pagesInformation Sheet 2.2 1 Variety of Egg Dishes EditedKristymel Queen CabugonNo ratings yet
- Definition of An EggDocument3 pagesDefinition of An EggAman BhandariNo ratings yet
- 1.structure of Egg 2.explain Structure of Egg 3.selection of Eggs 4.eggs RecipiesDocument16 pages1.structure of Egg 2.explain Structure of Egg 3.selection of Eggs 4.eggs RecipiesZeon DmelloNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcome 2 Prepare and Cook Egg DishesDocument35 pagesLearning Outcome 2 Prepare and Cook Egg DishesRein Ashlie Gera100% (4)
- Lesson 2 TLEDocument17 pagesLesson 2 TLEJhon Anthony CatinoyNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Learning Outcome 2 Prepare and Cook Egg DishesDocument8 pagesQuarter 1 Learning Outcome 2 Prepare and Cook Egg DishesAdea LucianoNo ratings yet
- Egg DishDocument15 pagesEgg DishThea Jeonieesa GarayNo ratings yet
- Eggs: Fresh, Simple Recipes for Frittatas, Omelets, Scrambles & MoreFrom EverandEggs: Fresh, Simple Recipes for Frittatas, Omelets, Scrambles & MoreRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Img 20221022 214100Document2 pagesImg 20221022 214100JohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- Summative Test QuestionaireDocument2 pagesSummative Test QuestionaireJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- Innovation FormatDocument2 pagesInnovation FormatJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- 150 LandscapingDocument23 pages150 LandscapingJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- What Is The Community Alert Siren System?: Clicking HereDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Community Alert Siren System?: Clicking HereJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- Current Job Position and Workplace No. of Months/yr Took To Land The 1 JobDocument6 pagesCurrent Job Position and Workplace No. of Months/yr Took To Land The 1 JobJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- Weekly School Home Learning Plan For Blended Learning For Roll OutDocument7 pagesWeekly School Home Learning Plan For Blended Learning For Roll OutJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- CRP 506Document174 pagesCRP 506JohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- Lac Plan For Indigenous Groups SampleDocument2 pagesLac Plan For Indigenous Groups SampleJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- Grades 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log School: Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates & Time QuarterDocument5 pagesGrades 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log School: Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates & Time QuarterJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- Active and Inactive FaultsDocument19 pagesActive and Inactive FaultsJohnCzyril Deladia Domens100% (1)
- Prepare Cereals and Starch: A. Perform Mise'en Place BDocument27 pagesPrepare Cereals and Starch: A. Perform Mise'en Place BJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Tle Bread and Pastry ProductionDocument14 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Tle Bread and Pastry ProductionJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- BartendingDocument38 pagesBartendingJohnCzyril Deladia DomensNo ratings yet
- BreakfastDocument18 pagesBreakfastIasha HussainNo ratings yet
- Tamaya Menu 2019 - 10 Hires Compressed PDFDocument11 pagesTamaya Menu 2019 - 10 Hires Compressed PDFJewyang HuangNo ratings yet
- Hey Friends 1 WB ANSWER KEY - 28-09-18 PDFDocument16 pagesHey Friends 1 WB ANSWER KEY - 28-09-18 PDFbenNo ratings yet
- Parle Products - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesParle Products - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaGaurav LahotiNo ratings yet
- Salads: 300 Salad Recipes For Rapid Weight Loss & Clean Eating (PDFDrive) PDFDocument1,092 pagesSalads: 300 Salad Recipes For Rapid Weight Loss & Clean Eating (PDFDrive) PDFDebora PanzarellaNo ratings yet
- Bibimbap by Oori MenuDocument9 pagesBibimbap by Oori MenuMetroStaycationNo ratings yet
- Cakes Buns Scones Pastry, Biscuits,: Etc. Selected and Tested Recipes and FormulasDocument20 pagesCakes Buns Scones Pastry, Biscuits,: Etc. Selected and Tested Recipes and FormulasJulia BeanNo ratings yet
- III. Business ProponentsDocument6 pagesIII. Business ProponentsJE SingianNo ratings yet
- Homework Names: Rafaela Studies at San Agustin UniversityDocument5 pagesHomework Names: Rafaela Studies at San Agustin UniversityCARLOS JOAQUIN ALVAREZ AMBRONCIONo ratings yet
- Snacks Gain ReportDocument6 pagesSnacks Gain ReportNancy W FaragNo ratings yet
- Rahul Sugar ProductsDocument18 pagesRahul Sugar ProductsSantosh DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Uh Explanation Text 2Document2 pagesUh Explanation Text 2awaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate and Calorie ListDocument9 pagesCarbohydrate and Calorie ListAubrey Dynise C. TorralbaNo ratings yet
- (Multiple Choice Questions) Total Time: 1 Hour Total Marks: 50Document3 pages(Multiple Choice Questions) Total Time: 1 Hour Total Marks: 50GGHS PindoraNo ratings yet
- Bake With Us - Speak English With VanessaDocument5 pagesBake With Us - Speak English With VanessaAbdulmuqtadetr AhmadiNo ratings yet
- Binomial PairsDocument32 pagesBinomial PairsPaul100% (5)
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: ECONOMICS 9708/23Document4 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: ECONOMICS 9708/23santu220875No ratings yet
- Pearson - Roadmap A2+ Workbook With KeyDocument12 pagesPearson - Roadmap A2+ Workbook With Keydanghoi556No ratings yet
- FSM 112 Lecture 1Document6 pagesFSM 112 Lecture 1revilyn reguyalNo ratings yet
- The Thief of Smells - Short StoryDocument3 pagesThe Thief of Smells - Short StoryOlga HazemNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Guidelines To Help Control Nausea and Vomiting During PregnancyDocument16 pagesNutritional Guidelines To Help Control Nausea and Vomiting During PregnancyFitria Ayu AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- I.-Fill in The Correct Connectives and Linking Words From The List. There May Be More Than One Answer in Some SentencesDocument9 pagesI.-Fill in The Correct Connectives and Linking Words From The List. There May Be More Than One Answer in Some SentencesWendy Copaja PortugalNo ratings yet
- Division of Fractions Worksheets Math 6 Q1W3Document8 pagesDivision of Fractions Worksheets Math 6 Q1W3Noemi Rosario SanchezNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Introduction To American CuisineDocument9 pagesTopic 1 - Introduction To American CuisineHoneylyn OlilaNo ratings yet