Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chariezza Lei J. Sanglad BS Chemistry-IV
Chariezza Lei J. Sanglad BS Chemistry-IV
Uploaded by
Yen BumOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chariezza Lei J. Sanglad BS Chemistry-IV
Chariezza Lei J. Sanglad BS Chemistry-IV
Uploaded by
Yen BumCopyright:
Available Formats
Chariezza Lei J.
Sanglad
BS Chemistry-IV
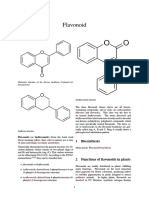
Retronecine
The Chemistry of Retronecine
Retronecine is a pyrrolizidine alkaloid (PA) found in a variety of plants in the genera
Senecio and Crotalaria, and the family Boraginaceae. Retronecine is a heterocyclic organic
compound and an unsaturated base. Unsaturated pyrrolizidine alkaloids are hepatotoxic, that is,
damaging to the liver. It is composed of a necine base (amino alcohols) and one or more necic
acids (mono- or dicarboxylic aliphatic acids), which are responsible for their structural diversity.
It is usually found in the form of tertiary bases or pyrrolizidine alkaloids N-oxides (PANO), which
are water soluble. Amino alcohols, or necines, are derived from pyrrolizidine. The pyrrolizidine
core, comprising two saturated five-membered rings with a nitrogen atom between them,
sometimes displays a double bond which frequently results in enhanced toxicity.
Advantages of Retronecine
Retronecine, a pyrrolizidine alkaloid is known to be used in the production of honey.
Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are produced by plants as a defense mechanism against insect herbivores.
Disadvantages of Retronecine
Retronecine can pose a life threat to humans and animals once they are present in a variety
of foodstuff. This compound has become known for its toxicity, as per several outbreaks that were
registered, mainly in developing countries. Retronecine, a pyrrolizidine alkaloid have little or no
known therapeutic value and are exceptionally toxic. PA were associated to skin cancer and
ultimately trigger the formation of tumors, since they can lead to photosensitization in animals
upon their consumption and metabolism. It has been shown before that this compound induces
liver tumors in rodents via formation of DNA adducts, thus may also be genotoxic and tumorigenic
to humans. The potential role of this compound in diseases such as cancer, pulmonary
hypertension, congenital anomalies and liver diseases has been reviewed before wherein these
alkaloids are genotoxic and can slowly initiate diseases.
Uses
Retronecine as one type of PA is also used as a defense mechanism for some organisms
such as Utetheisa ornatrix. Utetheisa ornatrix caterpillars obtain these toxins from their food
plants and use them as a deterrent for predators. This protect them from most of their natural
enemies. The toxins stay in these organisms even when they metamorphose into adult moths,
continuing to protect them throughout their adult stage.
This compound can also be use in the production of honey.
Effects
Effects on Human Health
The symptoms are characterized by upper abdominal discomfort that develops rapidly and
progresses to swelling of the abdomen resulting in increased girth, sometimes accompanied by a
reduction in the quantity of urine excreted and swelling of the feet. The disease is called veno-
occlusive disease (VOD). There may be vomiting of blood. Some patients may have only vague
symptoms and the only sign of the disease may be persistent enlargement of the liver. The liver is
usually the target organ.
Consumption of crops containing retronecine can cause large-scale outbreaks of toxic
disease in both man and farm animals.
You might also like
- Synthesis of IodoformDocument5 pagesSynthesis of IodoformYen Bum0% (1)
- FAO Fact Sheet Pyrrolizidine AlkaloidsDocument6 pagesFAO Fact Sheet Pyrrolizidine AlkaloidsMammo BerisoNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument4 pagesReview of Related LiteratureLiana GuadizNo ratings yet
- Biochem AssDocument18 pagesBiochem AssIshwar ChandraNo ratings yet
- Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids:Toxicity, Awareness and Regulations Laid by GovernmentDocument11 pagesPyrrolizidine Alkaloids:Toxicity, Awareness and Regulations Laid by GovernmentHadiya FawadNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisruptorsDocument50 pagesEndocrine DisruptorsSnowangeleyes AngelNo ratings yet
- Deletarious Substances in Poultry FeedDocument4 pagesDeletarious Substances in Poultry FeedShah NawazNo ratings yet
- 10 13040@ijpsr 0975-8232 53 690-02Document14 pages10 13040@ijpsr 0975-8232 53 690-02Luluil MunirohNo ratings yet
- RiyaDocument11 pagesRiyaKanishka VermaNo ratings yet
- Plant and Food Toxins: Group 3Document25 pagesPlant and Food Toxins: Group 3Patricia Irene AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Cheeke 1988. Toxicity and Metabolism of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids .Document10 pagesCheeke 1988. Toxicity and Metabolism of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids .Raquel Aravena RiverosNo ratings yet
- 1 Vol. 10 Issue 1 Jan 2019 IJPSR RE 2667Document11 pages1 Vol. 10 Issue 1 Jan 2019 IJPSR RE 2667Armando GemeNo ratings yet
- To Food Hazardous'r-Offood Preservatives: Anterpreet Kaur Arora Shashi Mahajan Pankaj Gupta S Nne Singh KapoorDocument4 pagesTo Food Hazardous'r-Offood Preservatives: Anterpreet Kaur Arora Shashi Mahajan Pankaj Gupta S Nne Singh Kapoordika pujiNo ratings yet
- Food OchratoxinDocument12 pagesFood OchratoxinAntonela ElaNo ratings yet
- Enzymatic Determination of Catechol Oxidase and Protease From Fruits (Orange, Apple) and Vegetables (Carrot, Tomato)Document7 pagesEnzymatic Determination of Catechol Oxidase and Protease From Fruits (Orange, Apple) and Vegetables (Carrot, Tomato)International Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Therapeutic Roles of Medicinal Herbs For The Treatment of Jaundice and Hepatitis BDocument7 pagesTherapeutic Roles of Medicinal Herbs For The Treatment of Jaundice and Hepatitis BEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Velu2016 PDFDocument8 pagesVelu2016 PDFWaqar HassanNo ratings yet
- Caretenoid and Human HealthDocument7 pagesCaretenoid and Human HealthNurul ShahiraNo ratings yet
- Environmental Hazards Component On Food PreparationDocument11 pagesEnvironmental Hazards Component On Food PreparationAivie UntiveroNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNADocument40 pagesRecombinant DNAaymnhssn2020No ratings yet
- Food Toxins KukkuDocument37 pagesFood Toxins Kukkugopika s pillaiNo ratings yet
- Improvement of Lead Acetate-Induced Testicular InjuryDocument11 pagesImprovement of Lead Acetate-Induced Testicular InjuryYeti MaretaNo ratings yet
- Phytochemicals and ScreeningDocument35 pagesPhytochemicals and ScreeningHezekiah Eujhan BuendiaNo ratings yet
- ToxicantsDocument76 pagesToxicantsAnum KhalidNo ratings yet
- Organochlorine Compouds ToxicityDocument39 pagesOrganochlorine Compouds ToxicityAdarshBijapurNo ratings yet
- 7 Komponen Bioaktif Dan Antioksidan Dalam PanganDocument45 pages7 Komponen Bioaktif Dan Antioksidan Dalam PanganFcyshen Lisna Vya CumggoerNo ratings yet
- Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy: ReviewDocument15 pagesBiomedicine & Pharmacotherapy: ReviewMarcus ViniciusNo ratings yet
- J of Food Studies 2014 Food ContaminantsDocument17 pagesJ of Food Studies 2014 Food ContaminantsMylene NapalanNo ratings yet
- Secondary Metabolite ProductionDocument46 pagesSecondary Metabolite ProductionLoidaNo ratings yet
- Antioxidant Hepatoprotective Activities Carica Papaya Loranthus Bengwensis Diclofenac Induced Hepatotoxicity PDFDocument9 pagesAntioxidant Hepatoprotective Activities Carica Papaya Loranthus Bengwensis Diclofenac Induced Hepatotoxicity PDFSSR-IIJLS JournalNo ratings yet
- Extraction 4Document17 pagesExtraction 4Pravin KaleNo ratings yet
- Overviews of Biological Importance of Quercetin: A Bioactive FlavonoidDocument6 pagesOverviews of Biological Importance of Quercetin: A Bioactive FlavonoidDea FauziyyantiNo ratings yet
- Secondary Metabolite - WikipediaDocument4 pagesSecondary Metabolite - WikipediaAttila Tamas100% (1)
- Dietary Polyphenols and Their Biological Significance: Molecular SciencesDocument39 pagesDietary Polyphenols and Their Biological Significance: Molecular SciencesBharti PariharNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologyonline 1 - (2008)Document10 pagesPharmacologyonline 1 - (2008)kahren wayetNo ratings yet
- Food Toxicology 2Document41 pagesFood Toxicology 2Rashid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Rodenticides: Topic Fact SheetDocument7 pagesRodenticides: Topic Fact Sheet152338No ratings yet
- PDF - Pesticides - Types of PesticidesDocument2 pagesPDF - Pesticides - Types of PesticidesomansuNo ratings yet
- Medallion Laboratories Technical Bulletin: Pesticide ResiduesDocument2 pagesMedallion Laboratories Technical Bulletin: Pesticide Residuesdjsp5009No ratings yet
- Therapeutic Agents Toxicity in PoultryDocument20 pagesTherapeutic Agents Toxicity in PoultryMuhammad JameelNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Pyrethroids FactsheetDocument5 pagesSynthetic Pyrethroids FactsheetTheodoor KoenenNo ratings yet
- Rotenone Research AssignmentDocument2 pagesRotenone Research Assignmentderpderp123No ratings yet
- Rodenticide Toxicity - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument13 pagesRodenticide Toxicity - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelfpradeepgullipalli.1089No ratings yet
- Chemistry Project Term 2 Drohan Chakraborty 12 L (A)Document13 pagesChemistry Project Term 2 Drohan Chakraborty 12 L (A)ShreyasiNo ratings yet
- Deleterious Substances in Poultry FeedsDocument14 pagesDeleterious Substances in Poultry FeedsAsfand Ali SheikhNo ratings yet
- Tilapia Melanophores Final'Document37 pagesTilapia Melanophores Final'pawan bNo ratings yet
- Flavonoid: 1 BiosynthesisDocument12 pagesFlavonoid: 1 Biosynthesisసాయిమహేష్రెడ్డిఆవులNo ratings yet
- 154 PDFDocument5 pages154 PDFRusniaty AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Cyanobacteria and Their Toxins: Dave Stone, PHDDocument21 pagesCyanobacteria and Their Toxins: Dave Stone, PHDJaya LekhwaniNo ratings yet
- DessertationDocument68 pagesDessertationapi-3781079100% (3)
- Emerging Contaminants An Concise Overview: A. N. SinghDocument27 pagesEmerging Contaminants An Concise Overview: A. N. Singhansingh123No ratings yet
- Natural Enzymes and ProteinDocument11 pagesNatural Enzymes and ProteinTria Risma100% (1)
- In Vitro Antiplatelet Activity of An Isoflavanone Isolated From MethanolicDocument6 pagesIn Vitro Antiplatelet Activity of An Isoflavanone Isolated From MethanolicvinayNo ratings yet
- Antinutritional Compounds in OilseedsDocument20 pagesAntinutritional Compounds in Oilseedsmohan baluNo ratings yet
- Vitamin KDocument3 pagesVitamin KHiếu BùiNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 - Fishery Preservation Techniques and Food Safety Aspects PDFDocument49 pagesLec 2 - Fishery Preservation Techniques and Food Safety Aspects PDFLarraine Chaste PonteresNo ratings yet
- 14 - Toxicants That Cause FeversDocument9 pages14 - Toxicants That Cause FeversCabinet VeterinarNo ratings yet
- Oloyede 2011Document10 pagesOloyede 2011inayahviNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Polyphenol ResearchFrom EverandRecent Advances in Polyphenol ResearchCelestino Santos-BuelgaNo ratings yet
- Social Studies Fosters StudentsDocument2 pagesSocial Studies Fosters StudentsYen BumNo ratings yet
- 23 Ways To Facilitate StudentDocument11 pages23 Ways To Facilitate StudentYen BumNo ratings yet
- The Two Faces oDocument10 pagesThe Two Faces oYen Bum100% (2)
- Separate Salt ADocument3 pagesSeparate Salt AYen BumNo ratings yet
- Agreement - Singular Subjects 14Document7 pagesAgreement - Singular Subjects 14Yen BumNo ratings yet
- Retronecine IsDocument12 pagesRetronecine IsYen BumNo ratings yet
- Reporter: Sanglad, Chariezza Lei J. Date Submitted: February 20, 2019 Topic: Introduction To Quality Assurance and Quality ControlDocument5 pagesReporter: Sanglad, Chariezza Lei J. Date Submitted: February 20, 2019 Topic: Introduction To Quality Assurance and Quality ControlYen BumNo ratings yet
- 1872 Cavite MutinyDocument13 pages1872 Cavite MutinyYen Bum100% (12)
- Benzoic: Time (S)Document4 pagesBenzoic: Time (S)Yen BumNo ratings yet
- Abbe's RefractoDocument8 pagesAbbe's RefractoYen BumNo ratings yet
- Biosorption of Heavy Metals: Department of Biotechnology and Environmental SciencesDocument25 pagesBiosorption of Heavy Metals: Department of Biotechnology and Environmental SciencesYen BumNo ratings yet
- Name: Chariezza Le J. Sanglad: Experiment No.5Document10 pagesName: Chariezza Le J. Sanglad: Experiment No.5Yen BumNo ratings yet
- Coconut Oil IsDocument2 pagesCoconut Oil IsYen BumNo ratings yet
- Regala, Erlindo Sanglad, Chariezza Lei Talpis, Leziel: Potentiometric Titration of A Weak AcidDocument2 pagesRegala, Erlindo Sanglad, Chariezza Lei Talpis, Leziel: Potentiometric Titration of A Weak AcidYen BumNo ratings yet
- Expt. No. 5 Identification of Organic CompoundsDocument3 pagesExpt. No. 5 Identification of Organic CompoundsYen BumNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination A. Physical State Liquid B. Color Colorless C. Odor Strong and Pungent Odor D. Ignition Test FlammableDocument3 pagesPhysical Examination A. Physical State Liquid B. Color Colorless C. Odor Strong and Pungent Odor D. Ignition Test FlammableYen BumNo ratings yet
- NaphtholDocument1 pageNaphtholYen BumNo ratings yet
- AbbesDocument8 pagesAbbesYen BumNo ratings yet
- Malware 010101Document12 pagesMalware 010101Yen BumNo ratings yet
- QualitativetestforspirinDocument7 pagesQualitativetestforspirinYen BumNo ratings yet