Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
140 viewsIS - LM Model
IS - LM Model
Uploaded by
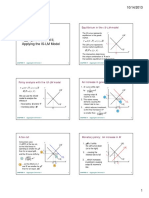
Abhishek SinhaThe IS-LM model shows the simultaneous workings of the goods (product) market and money market. The IS curve depicts combinations of national income and interest rates that balance the goods market. It slopes downward. The LM curve shows the combinations that balance the money market, where money demand equals supply. It slopes upward. The overall equilibrium occurs where the IS and LM curves intersect, balancing both markets simultaneously and determining the equilibrium interest rate and level of national income.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Chapter 6 Mankiw (Macroeconomics)Document36 pagesChapter 6 Mankiw (Macroeconomics)andrew myintmyat100% (1)
- Interview Questions EconomicsDocument1 pageInterview Questions EconomicsManoj KNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money Formulas SheetDocument1 pageTime Value of Money Formulas SheetBilal HussainNo ratings yet
- Inside Job TermsDocument8 pagesInside Job TermsKavita SinghNo ratings yet
- Barre CombinationDocument3 pagesBarre CombinationAlli ANo ratings yet
- The Is-Lm Model: ECON 2123: MacroeconomicsDocument56 pagesThe Is-Lm Model: ECON 2123: MacroeconomicskatecwsNo ratings yet
- IS-LM FrameworkDocument54 pagesIS-LM FrameworkLakshmi NairNo ratings yet
- Offer Curves & Terms of TradeDocument19 pagesOffer Curves & Terms of Tradedranita@yahoo.com0% (1)
- Chapter16 by Group CDocument33 pagesChapter16 by Group CMohamedAli AbdulleNo ratings yet
- Consumption Function and MultiplierDocument24 pagesConsumption Function and MultiplierVikku AgarwalNo ratings yet
- IS LM, AD AS (Closed Economy)Document16 pagesIS LM, AD AS (Closed Economy)hishamsaukNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet - CHE374Document26 pagesCheat Sheet - CHE374JoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Is - LM Model Econ - 102 2Document28 pagesChapter - 5 Is - LM Model Econ - 102 2abhishekNo ratings yet
- Coach Huber AP Macroeconomics: Gross Domestic ProductDocument18 pagesCoach Huber AP Macroeconomics: Gross Domestic Productapi-255899090No ratings yet
- Notes - EconomicsDocument69 pagesNotes - EconomicsHaktan OdabasiNo ratings yet
- 9.6 Keynesian MultiplierDocument23 pages9.6 Keynesian MultiplierkimmoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 The Money Supply ProcessDocument34 pagesLecture 9 The Money Supply Processmusaraza890No ratings yet
- Partial Equilibrium: EconomicsDocument5 pagesPartial Equilibrium: EconomicsSamantha SamdayNo ratings yet
- Economics General Price LevelDocument15 pagesEconomics General Price LevelNeelam FartyalNo ratings yet
- Cost of Production: The Isoquant-Isocost Approach/ Least CostDocument33 pagesCost of Production: The Isoquant-Isocost Approach/ Least CostKhizer SikanderNo ratings yet
- Cost & Cost CurvesDocument46 pagesCost & Cost CurvesManoj Kumar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- Kaldor Model - Group 3Document12 pagesKaldor Model - Group 3Dairy Of PeaceNo ratings yet
- 2 - International Parity ConditionsDocument116 pages2 - International Parity ConditionsMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Recession FinalDocument40 pagesRecession FinalMehwish JavedNo ratings yet
- Lectures 4 and 5 Modern Trade TheoriesDocument33 pagesLectures 4 and 5 Modern Trade TheoriesChenxi LiuNo ratings yet
- Macro-Economics Lecture (BBA)Document262 pagesMacro-Economics Lecture (BBA)Sahil NoorzaiNo ratings yet
- Monopoly MarketDocument29 pagesMonopoly MarketSanjay .. SanjuNo ratings yet
- Is LM PDFDocument9 pagesIs LM PDFShivam SoniNo ratings yet
- RBI Monetary Policy FinalDocument28 pagesRBI Monetary Policy FinaltejassuraNo ratings yet
- Mundell Fleming ModelDocument22 pagesMundell Fleming ModelDhruv BhandariNo ratings yet
- Elesticity of DemandDocument48 pagesElesticity of DemandDr.Ashok Kumar Panigrahi100% (1)
- TOPIC 3 - Exchange Rates and The Foreign Exchange Market-An Asset ApproachDocument42 pagesTOPIC 3 - Exchange Rates and The Foreign Exchange Market-An Asset ApproachYiFeiNo ratings yet
- Cost & Production FinalDocument109 pagesCost & Production Finalsamrulezzz100% (1)
- The Heckscher-Ohlin Model: Appleyard & Field (& Cobb) : Chapters 8 & 9Document16 pagesThe Heckscher-Ohlin Model: Appleyard & Field (& Cobb) : Chapters 8 & 9सरल जीवनNo ratings yet
- Monetary PolicyDocument23 pagesMonetary PolicyManjunath ShettigarNo ratings yet
- National Income & Price DeterminationDocument6 pagesNational Income & Price DeterminationPinkyNo ratings yet
- Price Determined Under OligopolyDocument19 pagesPrice Determined Under Oligopolyss_love_8750% (2)
- Two-Variable Regression Model - The Problem of EstimationDocument35 pagesTwo-Variable Regression Model - The Problem of EstimationAyesha RehmanNo ratings yet
- 3Document19 pages3Erica CraneNo ratings yet
- Econ 201 Mid Term ReviewDocument7 pagesEcon 201 Mid Term ReviewGeorge DhimaNo ratings yet
- Mundell-Fleming ModelDocument32 pagesMundell-Fleming ModelMarce Tabares Herrera100% (1)
- Chapter 01 - OutputDocument39 pagesChapter 01 - Outputrabbani haque100% (1)
- Chapter 9 - The Is-Lm/Ad-As ModelDocument20 pagesChapter 9 - The Is-Lm/Ad-As Modelvivianguo23No ratings yet
- The Circular Flow of Income Lesson 1 and 2Document16 pagesThe Circular Flow of Income Lesson 1 and 2api-53255207No ratings yet
- Input Output AnalysisDocument17 pagesInput Output AnalysisAmal Datta100% (1)
- The Phillips Curve: Relation Between Unemployment and The Rate of Money Wage ChangesDocument16 pagesThe Phillips Curve: Relation Between Unemployment and The Rate of Money Wage ChangesShashank Shekhar SinghNo ratings yet
- Numericals On National Income Accounting 2019-20Document2 pagesNumericals On National Income Accounting 2019-20NIKITA SONINo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics National Income AccountingDocument62 pagesMacroeconomics National Income AccountingCikgu Poli0% (1)
- Ch16 Salvatore PPPDocument40 pagesCh16 Salvatore PPPRyan J Anward0% (1)
- Chapter 12 Exchange-Rate DeterminationDocument56 pagesChapter 12 Exchange-Rate DeterminationSashi VelnatiNo ratings yet
- Econ 181 Lecture 2 BDocument72 pagesEcon 181 Lecture 2 BJYJB WangNo ratings yet
- Theory of National Income DeterminationDocument50 pagesTheory of National Income DeterminationKunal KunduNo ratings yet
- Macro Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesMacro Cheat SheetMei SongNo ratings yet
- Excess and Deficient Demand HandoutDocument3 pagesExcess and Deficient Demand HandoutTashiTamangNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 NATIONAL INCOMEDocument42 pagesChapter-2 NATIONAL INCOMEDr-Abu Hasan Sonai SheikhNo ratings yet
- Homework Assignment 3 Answer: Econ 512 Yili Chien Intermediate Economics Spring 2006Document7 pagesHomework Assignment 3 Answer: Econ 512 Yili Chien Intermediate Economics Spring 2006Asif KhanNo ratings yet
- Reserve Requirement/Deposit Expansion AND BANK BALANCE SHEET PRACTICE Questions - Show Your Work and Answer in The Space ProvidedDocument6 pagesReserve Requirement/Deposit Expansion AND BANK BALANCE SHEET PRACTICE Questions - Show Your Work and Answer in The Space ProvidedRingle JobNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium and Disequilibrium in Balance of PaymentDocument9 pagesEquilibrium and Disequilibrium in Balance of PaymentDari ThangkhiewNo ratings yet
- S5M IS-LM ModelDocument34 pagesS5M IS-LM ModelManoranjan DashNo ratings yet
- ECOM3201 Problems and Solutions - IS LMDocument18 pagesECOM3201 Problems and Solutions - IS LMKume BuverlNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting: An Investment Decision MethodDocument23 pagesCapital Budgeting: An Investment Decision MethodAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- PRODUCTDocument6 pagesPRODUCTAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument7 pagesProduct Life CycleAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- Threats To Computer System & Control MeasuresDocument3 pagesThreats To Computer System & Control MeasuresAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- Illustrate in Brief Human Resource PlanningDocument2 pagesIllustrate in Brief Human Resource PlanningAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Income DeterminationDocument4 pagesTheory of Income DeterminationAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy - 2Document4 pagesFiscal Policy - 2Abhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- A) Not Understanding The Environment or Focusing On ResultsDocument2 pagesA) Not Understanding The Environment or Focusing On ResultsAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals OF Accounting: Accounting by Meigs, Williams, Haka, BettnerDocument64 pagesFundamentals OF Accounting: Accounting by Meigs, Williams, Haka, BettnerAliya SaeedNo ratings yet
- 12cheat Sheet - IntegersDocument2 pages12cheat Sheet - IntegersshagogalNo ratings yet
- AOFS - The Simiax Legion 1.0Document1 pageAOFS - The Simiax Legion 1.0angelofmenothNo ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals: AppellantDocument64 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals: AppellantEquality Case FilesNo ratings yet
- (LBYCVW3) EXPT #1 Calibration of The Weir Hydrology ApparatusDocument8 pages(LBYCVW3) EXPT #1 Calibration of The Weir Hydrology ApparatusJoshua James DyNo ratings yet
- GAD When Did GAD Came Into Being?Document3 pagesGAD When Did GAD Came Into Being?John Alvin de LaraNo ratings yet
- Lifestyle Upper Intermediate CB 2012 177p PDFDocument177 pagesLifestyle Upper Intermediate CB 2012 177p PDFԿորյուն ՕհանյանNo ratings yet
- K5 - PPT Trematodes BbsDocument23 pagesK5 - PPT Trematodes Bbsrinaaa20000% (1)
- Compuware DCRUM Intro 2012 Version 12.00Document142 pagesCompuware DCRUM Intro 2012 Version 12.00JanNo ratings yet
- Asem0909 PDFDocument14 pagesAsem0909 PDFTROY2ARCHILLESNo ratings yet
- Ebook World Civilizations Volume Ii Since 1500 8Th Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook World Civilizations Volume Ii Since 1500 8Th Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFtracey.ogletree521100% (40)
- Median and ModeDocument24 pagesMedian and Modemayra kshyapNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document47 pagesChapter 4Lyka Mariz AricayosNo ratings yet
- Buckling of Column: Saifulnizan JamianDocument24 pagesBuckling of Column: Saifulnizan JamianNazhan HaziqNo ratings yet
- Benefits of EDTA Chelation Therapy in Arterioscler PDFDocument11 pagesBenefits of EDTA Chelation Therapy in Arterioscler PDFNéstor Mata RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Grade-8 (Science) Third QuarterDocument1 pageGrade-8 (Science) Third Quartertrexia autidaNo ratings yet
- "Analysis of Marketing Strategies of Nestle Maggi: Winter ReportDocument51 pages"Analysis of Marketing Strategies of Nestle Maggi: Winter ReportAnonymous PbMgeIvKNo ratings yet
- Laguna Tayabas Bus Co V The Public Service CommissionDocument1 pageLaguna Tayabas Bus Co V The Public Service CommissionAnonymous byhgZINo ratings yet
- Exibições: Chandelier Cifra: Principal 412.396 TomDocument7 pagesExibições: Chandelier Cifra: Principal 412.396 TomAnonymous kgBjU5Qp8No ratings yet
- Knowledge Base Article: 000517728:: Dsa-2018-018: Dell Emc Isilon Onefs Multiple Vulnerabilities. (000517728)Document3 pagesKnowledge Base Article: 000517728:: Dsa-2018-018: Dell Emc Isilon Onefs Multiple Vulnerabilities. (000517728)Prakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- Job Mismatch in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesJob Mismatch in The Philippinesjovelyn c. aronNo ratings yet
- Transport Across Cell MembraneDocument38 pagesTransport Across Cell MembraneViswadeep DasNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Copper (II) Sulfate Solution PDFDocument3 pagesElectrolysis of Copper (II) Sulfate Solution PDFJoko SusiloNo ratings yet
- What Is Swar VigyanDocument28 pagesWhat Is Swar VigyanNarendra BhogalNo ratings yet
- 15 Life Changing Lessons From Wayne DyerDocument6 pages15 Life Changing Lessons From Wayne Dyersaikumar selaNo ratings yet
- Write The Days in The Correct OrderDocument7 pagesWrite The Days in The Correct OrderRuth Yánez PadillaNo ratings yet
- Configuration For High Availability (HA) Best Practices GuideDocument19 pagesConfiguration For High Availability (HA) Best Practices GuideAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Users Manual For VRP Spreadsheet Solver v3Document18 pagesUsers Manual For VRP Spreadsheet Solver v3Hernandez Miguel AngelNo ratings yet
IS - LM Model
IS - LM Model
Uploaded by
Abhishek Sinha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
140 views5 pagesThe IS-LM model shows the simultaneous workings of the goods (product) market and money market. The IS curve depicts combinations of national income and interest rates that balance the goods market. It slopes downward. The LM curve shows the combinations that balance the money market, where money demand equals supply. It slopes upward. The overall equilibrium occurs where the IS and LM curves intersect, balancing both markets simultaneously and determining the equilibrium interest rate and level of national income.
Original Description:
IS LM DETAILS
Original Title
IS - LM model
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe IS-LM model shows the simultaneous workings of the goods (product) market and money market. The IS curve depicts combinations of national income and interest rates that balance the goods market. It slopes downward. The LM curve shows the combinations that balance the money market, where money demand equals supply. It slopes upward. The overall equilibrium occurs where the IS and LM curves intersect, balancing both markets simultaneously and determining the equilibrium interest rate and level of national income.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
140 views5 pagesIS - LM Model
IS - LM Model
Uploaded by
Abhishek SinhaThe IS-LM model shows the simultaneous workings of the goods (product) market and money market. The IS curve depicts combinations of national income and interest rates that balance the goods market. It slopes downward. The LM curve shows the combinations that balance the money market, where money demand equals supply. It slopes upward. The overall equilibrium occurs where the IS and LM curves intersect, balancing both markets simultaneously and determining the equilibrium interest rate and level of national income.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
IS-LM MODEL
Inclusion of the money sector and showing the
simultaneous working of the product and money
markets.
IS curve: a curve showing the eqlb situation in the
goods market
It is the locus of combinations of national income
and rate of interest for which the goods market is in
eqlb.
Eqlb is achieved when demand for goods is equal to
supply of goods
Demand for goods = C + I + G ………(1)
Supply of goods = C + S + T ………..(2)
Equating 1 & 2 C+I+G = C+S+T
Or, I+G = S+T
Assumptions:
1. Savings is dependent on national income
or S = S(Y) and dS / dY > 0
2. Investment is dependent on rate of interest
or, I = I(r) and dI / dr < 0
3. Govt. expenses and taxes are autonomous.
4. When savings and investments are equal then we
have eqlb in the goods market.
5. The combination of national income and rate of
interest for which S = I brings about eqlb in
goods market.
Properties of IS curve :
o It is downward sloping.
o Its slope depends on the interest sensitivity of
investment and marginal propensity to save
o At all the points savings is equal to investments
Shifts of IS curve :
The IS curve will shift rightwards if there is an increase
in Govt. expenditure or decrease in taxes.
The slope of the curve will change if either mps
changes or interest sensitivity of investment changes.
Eqn. of IS curve:
Y = C(Y) + I(r) + G
LM Curve: shows eqlb in money market.
The combination of national income and rate of
interest, which brings eqlb in the money market, is
shown by the LM curve.
Eqlb in money market is obtained when demand for
money is equal to supply of money.
Supply of money is determined by the Central Bank
of a country, so it is autonomous. Ms =
M(constant)
Demand for money depends on three motives
Transaction motive : T.D. = K = k(Y) and dK/dY >
0
Precautionary motive
Speculative motive : S.D. = L = l(r) and dl/dr <
0
Md = k(Y) + l(r)
Thus the combination of Y and r for which Md will
equal Ms gives the LM curve.
Assumptions :
The transaction and precautionary demand depend on
the level of income.
Speculative demand is inversely proportional to the
rate of interest.
The prices of bonds remain constant.
The bond prices are inversely proportional to the rate
of interest.
For every combination of Income and rate of interest
we get a level of money demand. The level of money
demand which is equal to money supply gives money
market eqlb.
Properties of LM curve :
o It is upward rising.
o At every point, money demand is equal to money
supply.
o Slope of LM curve depends on the responsiveness
of transaction demand to changes in income and
that of speculative demand to rate of interest.
Shifts of LM curve :
The LM curve will shift right if money supply
increases and
shift left if money supply decreases.
There will be change in the slope of LM curve if the
value of ‘k’ or ‘l’ changes.
Eqn. of LM curve :
Ms = k(Y) + l(r)
GENERAL EQLB. OF PRODUT AND MONEY
MARKETS
The general eqlb of the economy is when the
product and money markets are in eqlb jointly.
It is obtained as a combination of income and rate
of interest which will bring eqlb simultaneously in
the product and money markets.
We have,
Y = C(Y) + I(r) + G ……(1)
Ms = k(Y) + l(r) …….(2)
The values of Y and r which will solve these eqns.
brings about general eqlb.
You might also like
- Chapter 6 Mankiw (Macroeconomics)Document36 pagesChapter 6 Mankiw (Macroeconomics)andrew myintmyat100% (1)
- Interview Questions EconomicsDocument1 pageInterview Questions EconomicsManoj KNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money Formulas SheetDocument1 pageTime Value of Money Formulas SheetBilal HussainNo ratings yet
- Inside Job TermsDocument8 pagesInside Job TermsKavita SinghNo ratings yet
- Barre CombinationDocument3 pagesBarre CombinationAlli ANo ratings yet
- The Is-Lm Model: ECON 2123: MacroeconomicsDocument56 pagesThe Is-Lm Model: ECON 2123: MacroeconomicskatecwsNo ratings yet
- IS-LM FrameworkDocument54 pagesIS-LM FrameworkLakshmi NairNo ratings yet
- Offer Curves & Terms of TradeDocument19 pagesOffer Curves & Terms of Tradedranita@yahoo.com0% (1)
- Chapter16 by Group CDocument33 pagesChapter16 by Group CMohamedAli AbdulleNo ratings yet
- Consumption Function and MultiplierDocument24 pagesConsumption Function and MultiplierVikku AgarwalNo ratings yet
- IS LM, AD AS (Closed Economy)Document16 pagesIS LM, AD AS (Closed Economy)hishamsaukNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet - CHE374Document26 pagesCheat Sheet - CHE374JoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Is - LM Model Econ - 102 2Document28 pagesChapter - 5 Is - LM Model Econ - 102 2abhishekNo ratings yet
- Coach Huber AP Macroeconomics: Gross Domestic ProductDocument18 pagesCoach Huber AP Macroeconomics: Gross Domestic Productapi-255899090No ratings yet
- Notes - EconomicsDocument69 pagesNotes - EconomicsHaktan OdabasiNo ratings yet
- 9.6 Keynesian MultiplierDocument23 pages9.6 Keynesian MultiplierkimmoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 The Money Supply ProcessDocument34 pagesLecture 9 The Money Supply Processmusaraza890No ratings yet
- Partial Equilibrium: EconomicsDocument5 pagesPartial Equilibrium: EconomicsSamantha SamdayNo ratings yet
- Economics General Price LevelDocument15 pagesEconomics General Price LevelNeelam FartyalNo ratings yet
- Cost of Production: The Isoquant-Isocost Approach/ Least CostDocument33 pagesCost of Production: The Isoquant-Isocost Approach/ Least CostKhizer SikanderNo ratings yet
- Cost & Cost CurvesDocument46 pagesCost & Cost CurvesManoj Kumar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- Kaldor Model - Group 3Document12 pagesKaldor Model - Group 3Dairy Of PeaceNo ratings yet
- 2 - International Parity ConditionsDocument116 pages2 - International Parity ConditionsMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Recession FinalDocument40 pagesRecession FinalMehwish JavedNo ratings yet
- Lectures 4 and 5 Modern Trade TheoriesDocument33 pagesLectures 4 and 5 Modern Trade TheoriesChenxi LiuNo ratings yet
- Macro-Economics Lecture (BBA)Document262 pagesMacro-Economics Lecture (BBA)Sahil NoorzaiNo ratings yet
- Monopoly MarketDocument29 pagesMonopoly MarketSanjay .. SanjuNo ratings yet
- Is LM PDFDocument9 pagesIs LM PDFShivam SoniNo ratings yet
- RBI Monetary Policy FinalDocument28 pagesRBI Monetary Policy FinaltejassuraNo ratings yet
- Mundell Fleming ModelDocument22 pagesMundell Fleming ModelDhruv BhandariNo ratings yet
- Elesticity of DemandDocument48 pagesElesticity of DemandDr.Ashok Kumar Panigrahi100% (1)
- TOPIC 3 - Exchange Rates and The Foreign Exchange Market-An Asset ApproachDocument42 pagesTOPIC 3 - Exchange Rates and The Foreign Exchange Market-An Asset ApproachYiFeiNo ratings yet
- Cost & Production FinalDocument109 pagesCost & Production Finalsamrulezzz100% (1)
- The Heckscher-Ohlin Model: Appleyard & Field (& Cobb) : Chapters 8 & 9Document16 pagesThe Heckscher-Ohlin Model: Appleyard & Field (& Cobb) : Chapters 8 & 9सरल जीवनNo ratings yet
- Monetary PolicyDocument23 pagesMonetary PolicyManjunath ShettigarNo ratings yet
- National Income & Price DeterminationDocument6 pagesNational Income & Price DeterminationPinkyNo ratings yet
- Price Determined Under OligopolyDocument19 pagesPrice Determined Under Oligopolyss_love_8750% (2)
- Two-Variable Regression Model - The Problem of EstimationDocument35 pagesTwo-Variable Regression Model - The Problem of EstimationAyesha RehmanNo ratings yet
- 3Document19 pages3Erica CraneNo ratings yet
- Econ 201 Mid Term ReviewDocument7 pagesEcon 201 Mid Term ReviewGeorge DhimaNo ratings yet
- Mundell-Fleming ModelDocument32 pagesMundell-Fleming ModelMarce Tabares Herrera100% (1)
- Chapter 01 - OutputDocument39 pagesChapter 01 - Outputrabbani haque100% (1)
- Chapter 9 - The Is-Lm/Ad-As ModelDocument20 pagesChapter 9 - The Is-Lm/Ad-As Modelvivianguo23No ratings yet
- The Circular Flow of Income Lesson 1 and 2Document16 pagesThe Circular Flow of Income Lesson 1 and 2api-53255207No ratings yet
- Input Output AnalysisDocument17 pagesInput Output AnalysisAmal Datta100% (1)
- The Phillips Curve: Relation Between Unemployment and The Rate of Money Wage ChangesDocument16 pagesThe Phillips Curve: Relation Between Unemployment and The Rate of Money Wage ChangesShashank Shekhar SinghNo ratings yet
- Numericals On National Income Accounting 2019-20Document2 pagesNumericals On National Income Accounting 2019-20NIKITA SONINo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics National Income AccountingDocument62 pagesMacroeconomics National Income AccountingCikgu Poli0% (1)
- Ch16 Salvatore PPPDocument40 pagesCh16 Salvatore PPPRyan J Anward0% (1)
- Chapter 12 Exchange-Rate DeterminationDocument56 pagesChapter 12 Exchange-Rate DeterminationSashi VelnatiNo ratings yet
- Econ 181 Lecture 2 BDocument72 pagesEcon 181 Lecture 2 BJYJB WangNo ratings yet
- Theory of National Income DeterminationDocument50 pagesTheory of National Income DeterminationKunal KunduNo ratings yet
- Macro Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesMacro Cheat SheetMei SongNo ratings yet
- Excess and Deficient Demand HandoutDocument3 pagesExcess and Deficient Demand HandoutTashiTamangNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 NATIONAL INCOMEDocument42 pagesChapter-2 NATIONAL INCOMEDr-Abu Hasan Sonai SheikhNo ratings yet
- Homework Assignment 3 Answer: Econ 512 Yili Chien Intermediate Economics Spring 2006Document7 pagesHomework Assignment 3 Answer: Econ 512 Yili Chien Intermediate Economics Spring 2006Asif KhanNo ratings yet
- Reserve Requirement/Deposit Expansion AND BANK BALANCE SHEET PRACTICE Questions - Show Your Work and Answer in The Space ProvidedDocument6 pagesReserve Requirement/Deposit Expansion AND BANK BALANCE SHEET PRACTICE Questions - Show Your Work and Answer in The Space ProvidedRingle JobNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium and Disequilibrium in Balance of PaymentDocument9 pagesEquilibrium and Disequilibrium in Balance of PaymentDari ThangkhiewNo ratings yet
- S5M IS-LM ModelDocument34 pagesS5M IS-LM ModelManoranjan DashNo ratings yet
- ECOM3201 Problems and Solutions - IS LMDocument18 pagesECOM3201 Problems and Solutions - IS LMKume BuverlNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting: An Investment Decision MethodDocument23 pagesCapital Budgeting: An Investment Decision MethodAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- PRODUCTDocument6 pagesPRODUCTAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument7 pagesProduct Life CycleAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- Threats To Computer System & Control MeasuresDocument3 pagesThreats To Computer System & Control MeasuresAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- Illustrate in Brief Human Resource PlanningDocument2 pagesIllustrate in Brief Human Resource PlanningAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Income DeterminationDocument4 pagesTheory of Income DeterminationAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy - 2Document4 pagesFiscal Policy - 2Abhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- A) Not Understanding The Environment or Focusing On ResultsDocument2 pagesA) Not Understanding The Environment or Focusing On ResultsAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals OF Accounting: Accounting by Meigs, Williams, Haka, BettnerDocument64 pagesFundamentals OF Accounting: Accounting by Meigs, Williams, Haka, BettnerAliya SaeedNo ratings yet
- 12cheat Sheet - IntegersDocument2 pages12cheat Sheet - IntegersshagogalNo ratings yet
- AOFS - The Simiax Legion 1.0Document1 pageAOFS - The Simiax Legion 1.0angelofmenothNo ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals: AppellantDocument64 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals: AppellantEquality Case FilesNo ratings yet
- (LBYCVW3) EXPT #1 Calibration of The Weir Hydrology ApparatusDocument8 pages(LBYCVW3) EXPT #1 Calibration of The Weir Hydrology ApparatusJoshua James DyNo ratings yet
- GAD When Did GAD Came Into Being?Document3 pagesGAD When Did GAD Came Into Being?John Alvin de LaraNo ratings yet
- Lifestyle Upper Intermediate CB 2012 177p PDFDocument177 pagesLifestyle Upper Intermediate CB 2012 177p PDFԿորյուն ՕհանյանNo ratings yet
- K5 - PPT Trematodes BbsDocument23 pagesK5 - PPT Trematodes Bbsrinaaa20000% (1)
- Compuware DCRUM Intro 2012 Version 12.00Document142 pagesCompuware DCRUM Intro 2012 Version 12.00JanNo ratings yet
- Asem0909 PDFDocument14 pagesAsem0909 PDFTROY2ARCHILLESNo ratings yet
- Ebook World Civilizations Volume Ii Since 1500 8Th Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook World Civilizations Volume Ii Since 1500 8Th Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFtracey.ogletree521100% (40)
- Median and ModeDocument24 pagesMedian and Modemayra kshyapNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document47 pagesChapter 4Lyka Mariz AricayosNo ratings yet
- Buckling of Column: Saifulnizan JamianDocument24 pagesBuckling of Column: Saifulnizan JamianNazhan HaziqNo ratings yet
- Benefits of EDTA Chelation Therapy in Arterioscler PDFDocument11 pagesBenefits of EDTA Chelation Therapy in Arterioscler PDFNéstor Mata RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Grade-8 (Science) Third QuarterDocument1 pageGrade-8 (Science) Third Quartertrexia autidaNo ratings yet
- "Analysis of Marketing Strategies of Nestle Maggi: Winter ReportDocument51 pages"Analysis of Marketing Strategies of Nestle Maggi: Winter ReportAnonymous PbMgeIvKNo ratings yet
- Laguna Tayabas Bus Co V The Public Service CommissionDocument1 pageLaguna Tayabas Bus Co V The Public Service CommissionAnonymous byhgZINo ratings yet
- Exibições: Chandelier Cifra: Principal 412.396 TomDocument7 pagesExibições: Chandelier Cifra: Principal 412.396 TomAnonymous kgBjU5Qp8No ratings yet
- Knowledge Base Article: 000517728:: Dsa-2018-018: Dell Emc Isilon Onefs Multiple Vulnerabilities. (000517728)Document3 pagesKnowledge Base Article: 000517728:: Dsa-2018-018: Dell Emc Isilon Onefs Multiple Vulnerabilities. (000517728)Prakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- Job Mismatch in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesJob Mismatch in The Philippinesjovelyn c. aronNo ratings yet
- Transport Across Cell MembraneDocument38 pagesTransport Across Cell MembraneViswadeep DasNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Copper (II) Sulfate Solution PDFDocument3 pagesElectrolysis of Copper (II) Sulfate Solution PDFJoko SusiloNo ratings yet
- What Is Swar VigyanDocument28 pagesWhat Is Swar VigyanNarendra BhogalNo ratings yet
- 15 Life Changing Lessons From Wayne DyerDocument6 pages15 Life Changing Lessons From Wayne Dyersaikumar selaNo ratings yet
- Write The Days in The Correct OrderDocument7 pagesWrite The Days in The Correct OrderRuth Yánez PadillaNo ratings yet
- Configuration For High Availability (HA) Best Practices GuideDocument19 pagesConfiguration For High Availability (HA) Best Practices GuideAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Users Manual For VRP Spreadsheet Solver v3Document18 pagesUsers Manual For VRP Spreadsheet Solver v3Hernandez Miguel AngelNo ratings yet