Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Water Resource Engineering: Cebu Technological University - Main Campus
Water Resource Engineering: Cebu Technological University - Main Campus
Uploaded by
Dench Noel Baclado0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views5 pagesThe document discusses several key concepts in water resource engineering including riparian rights, groundwater law, and drainage law. It then provides recommendations from an engineering perspective on how to address issues related to water scarcity, solid waste management, and flood reduction. Specifically, it recommends increasing water catchment and treatment, establishing localized waste management systems, clearing drainage systems, and relocating homes near rivers to reduce flooding risk. For drainage projects, it recommends using culverts due to their ability to safely direct water flow while being a low-cost and low-maintenance option.
Original Description:
aaa
Original Title
I
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses several key concepts in water resource engineering including riparian rights, groundwater law, and drainage law. It then provides recommendations from an engineering perspective on how to address issues related to water scarcity, solid waste management, and flood reduction. Specifically, it recommends increasing water catchment and treatment, establishing localized waste management systems, clearing drainage systems, and relocating homes near rivers to reduce flooding risk. For drainage projects, it recommends using culverts due to their ability to safely direct water flow while being a low-cost and low-maintenance option.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views5 pagesWater Resource Engineering: Cebu Technological University - Main Campus
Water Resource Engineering: Cebu Technological University - Main Campus
Uploaded by
Dench Noel BacladoThe document discusses several key concepts in water resource engineering including riparian rights, groundwater law, and drainage law. It then provides recommendations from an engineering perspective on how to address issues related to water scarcity, solid waste management, and flood reduction. Specifically, it recommends increasing water catchment and treatment, establishing localized waste management systems, clearing drainage systems, and relocating homes near rivers to reduce flooding risk. For drainage projects, it recommends using culverts due to their ability to safely direct water flow while being a low-cost and low-maintenance option.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
CEBU TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY - MAIN CAMPUS
M.J. CUENCO R. PALMA STREET, CEBU CITY
WATER
RESOURCE ENGINEERING
SUBMMITTED BY:
LAPAS, JACLYN FAITH
SUBMMITTED TO:
ENGR. NIMFA RODRIGUEZ
I. Identify
RIPARIAN RIGHT
In a property law, doctrine pertaining to properties
next to a waterway that governs the use of surface water
and gives all owners of land contiguous to rivers, streams,
lakes, and ponds equal rights to the water, whether the
right is exercised or not. The riparian right is
usufructuary, meaning that the landowner does not own the
water itself but instead enjoys a right to use the water
and its surface. Riparian rights are not ownership rights
but rights of access to the water such as for drinking
water, bathing, or irrigation.
GROUNDWATER LAW
Ground water Law involves many issues, including the
distinction between percolating groundwater and surface
water, the definition of basin boundaries, the interrelated
concepts of safe yield and overdraft, and the different
categories of groundwater rights. On the other hand, it is
closely connected to land and ownership of land it is also
often vital for public water supply systems and supporting
ecosystems of high public value. The amount of groundwater
right is based on the size of the surface area where each
landowner gets a corresponding amount of the available
water. Once adjudicated, the maximum amount of the water
right is set, but the right can be decreased if the total
amount of available water decreases as is likely during a
drought. Landowners may sue others for encroaching upon
their groundwater rights, and water pumped for use on the
overlying land takes preference over water pumped for use
off the land. The Rule of Capture provides each landowner
the ability to capture as much groundwater as they can put
to a beneficial use, but they are not guaranteed any set
amount of water. As a result, well-owners are not liable to
other landowners for taking water from beneath their land.
State laws or regulations will often define "beneficial
use", and sometimes place other limits, such as disallowing
groundwater extraction which causes subsidence on
neighboring property.
DRAINAGE LAW
In drainage law it is a specific area of water
law related to drainage of surface water on real property.
It is particularly important in areas where freshwater is
scarce, flooding is common, or water is in high demand for
agricultural or commercial purposes. They tackle about how
and what are the rules of having a freshwater in your area
and how it should be used. It means that a neighboring
property has the right to use any pipes and drains on the
property for the flow of water and drainage. There is
probably a drain and pipe that runs over the property
leading to the neighboring property and the property owner
is obliged to allow the neighbor to use this drain and
water supply pipe and is not permitted to cut off this
supply to the neighbor.
II. Applying Engineering Knowledge
I. Solving Scarcity of Water
Since water treatment is hard to have, the scarcity of
water can be prevented through usage control of water to
community. The localized barangay must be guided properly
in commercial use. Collection of waste water should have
water treatment to increase water consumption of
communities. Every house should have water catchment and be
directed to water treatment plant.
II. Solid Waste Management
The common problem that our communities have been
facing right now is uncontrolled disposal of waste. As an
engineer, I suggest having a small landfill in every
barangay, enough garbage trucks to collect the waste,
scheduled collection of waste, proper segregation and
disposal of waste must be strictly monitor and maintain.
Proper use of plastic material must be applied. Recyclable
materials should be used as eco-friendly materials.
Monitoring of drainages must be done to prevent clogging
during flood. A strict implementation of the rules would
make a community better and disciplined.
III. Flood Reduction
Common flood problems are happened in crowded area and
many establishments like cities. Improper disposal of
garbage’s is the first subject in dealing flooding. The
canals were clogged due to garbage’s. I suggest that the
drainages should be monitored in case of clogging to
maintain the flow of waste water to the discharge area. In
streams and rivers, the dwellers near the river should be
relocated or must be away 10-20 meters to prevent damages
and secure human lives during flooding. Proper concrete
drainages in every house must be installed to prevent
contamination of groundwater.
III. In Handling Drainage Project, As an Engineer,
which is advisable to have?
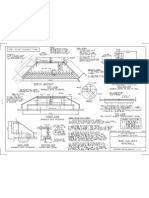
CULVERT
The function of culvert is an important part in controlling
waterways and waste waters. This is most commonly used in
roads, bridges, tunnels and etc. Some advantages are:
Safe and stable method for stream crossing.
Can accommodate wildlife and protect stream health.
Can reduce expensive erosion and structural damage.
Low cost.
Low maintenance.
Prevent ErosionPrevent Flooding
Allow Water to Flow
UnobstructedDivert Water for Farming/Engineering Purposes
Maintenance considerations are applied to avoid
disfunction of the structure:
Keep culvert inlets free of debris to allow water
passage.
Check culvert bodies periodically and remove sediment.
Check culvert outlets for erosion
You might also like
- Work Method Statement FOR Laying of Box Culvert and Sump ConstructionDocument3 pagesWork Method Statement FOR Laying of Box Culvert and Sump ConstructionLynn Mail100% (3)
- Box Culvert PPT SVDocument46 pagesBox Culvert PPT SVChandini Suman Sahoo75% (4)
- Progress ReportDocument45 pagesProgress ReportAnonymous Of0C4d100% (1)
- HEC-RAS 5.0 Reference ManualDocument538 pagesHEC-RAS 5.0 Reference ManualRcambillo S. CidhmaNo ratings yet
- Lot 1 BoQDocument8 pagesLot 1 BoQelbaraniNo ratings yet
- Water LawDocument51 pagesWater LawRick CoyleNo ratings yet
- Presidential Decree 1067Document7 pagesPresidential Decree 1067Vincent Dioshua YambaoNo ratings yet
- 255 Water Law Outline1Document23 pages255 Water Law Outline1James N. HansonNo ratings yet
- Water Code of The PhilippinesDocument28 pagesWater Code of The PhilippinespicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Rainwater Harvesting-A Study - by Gangu R KeswaniDocument30 pagesRainwater Harvesting-A Study - by Gangu R KeswaniGangu Keswani100% (1)
- Rainwater HarvestingDocument3 pagesRainwater HarvestingJohnreeNo ratings yet
- Ijcas 2016 3 (2) 335 338a PDFDocument4 pagesIjcas 2016 3 (2) 335 338a PDFVENKATESHNo ratings yet
- 1.1-Basic Environmental Engineering (MNB)Document40 pages1.1-Basic Environmental Engineering (MNB)shakibNo ratings yet
- SHOUKATH SEMINAR FinalDocument27 pagesSHOUKATH SEMINAR Finalgreeshma cNo ratings yet
- Water-Resources Engineering - Parte 6Document50 pagesWater-Resources Engineering - Parte 6Jose Suarez100% (1)
- 2022 Ceor Module 8Document9 pages2022 Ceor Module 8Justine OnzagaNo ratings yet
- Water Resources Management 2023 QueQueDocument18 pagesWater Resources Management 2023 QueQuemukoro ejiroNo ratings yet
- Water Management FeaturesDocument5 pagesWater Management FeaturesSaketh VuppalapatiNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument11 pagesWater ResourcesGerrold RamosNo ratings yet
- Hydro EngineeringDocument5 pagesHydro EngineeringAce WoodsNo ratings yet
- Integrated Water ManagementDocument16 pagesIntegrated Water Managementadit.shet23100% (1)
- Dam and Other Water Control Structures: Good or Evil?Document8 pagesDam and Other Water Control Structures: Good or Evil?aabhash bhattaraiNo ratings yet
- WRE IntroductionDocument15 pagesWRE IntroductionKalidas A KNo ratings yet
- Water Code of The PhilippinesDocument44 pagesWater Code of The PhilippinesSarah Jean SiloterioNo ratings yet
- Coastal ReservoirDocument5 pagesCoastal Reservoirhram_phdNo ratings yet
- Concepts For Planning Water Resources DevelopmentDocument43 pagesConcepts For Planning Water Resources DevelopmentLo[da LimpagNo ratings yet
- Answers 1Document7 pagesAnswers 1mariyaNo ratings yet
- Water Code of The PhilippinesDocument23 pagesWater Code of The PhilippinesKesTerJeeeNo ratings yet
- Chap01 IntroductionDocument8 pagesChap01 IntroductionTanjim IrtizaNo ratings yet
- Enviromental ManagmentDocument14 pagesEnviromental ManagmentAbrilisamargiotta2008 hNo ratings yet
- Rain Water HarvestingDocument7 pagesRain Water HarvestingMithil KotwalNo ratings yet
- Water Conservation Guidelines and Plans in ZambiaDocument56 pagesWater Conservation Guidelines and Plans in ZambiaCharles ChisangaNo ratings yet
- Case Study No. 12-Presidential Decree No. 1067Document25 pagesCase Study No. 12-Presidential Decree No. 1067picefeatiNo ratings yet
- Problems Associated With Philippine Clean Water Act of 2004Document84 pagesProblems Associated With Philippine Clean Water Act of 2004NICO OBEJERONo ratings yet
- Priyadarshini Institute & of Engineering, Technology NagpurDocument26 pagesPriyadarshini Institute & of Engineering, Technology NagpurNikhil ladiNo ratings yet
- Water Conservation: Tips To Save WaterDocument9 pagesWater Conservation: Tips To Save WaterGaurav YadavNo ratings yet
- Abe 171 Hw1 Paper Report Water Code of The PhilippinesDocument12 pagesAbe 171 Hw1 Paper Report Water Code of The PhilippinesEarl Dominic PorcinculaNo ratings yet
- Interview Guide-1Document17 pagesInterview Guide-1Anonymous hgpfWOOJ0No ratings yet
- Sources of Water SupplyDocument27 pagesSources of Water SupplySreelakshmi CJNo ratings yet
- Water Law CE 4-4Document4 pagesWater Law CE 4-4LienardNo ratings yet
- En Integrated Use Water 2007Document8 pagesEn Integrated Use Water 2007hbifxfgpNo ratings yet
- 4ème Cours - Irrigation and DrainageDocument4 pages4ème Cours - Irrigation and DrainageBroomNo ratings yet
- Water Resources and EngineeringDocument6 pagesWater Resources and EngineeringJoery Jr EsperonNo ratings yet
- Water Resource EngineeringDocument32 pagesWater Resource EngineeringS. M. FARZIN HASAN 1801078No ratings yet
- WatershedsDocument6 pagesWatershedsreaderWorm01No ratings yet
- Wsud 090315185906 Phpapp02Document85 pagesWsud 090315185906 Phpapp02Tri WahyuningsihNo ratings yet
- ERD - BJD PDFDocument167 pagesERD - BJD PDFDipanjal DasNo ratings yet
- Part II Water SupplyDocument15 pagesPart II Water SupplymariyaNo ratings yet
- Water Sensitive Design-ShashiDocument9 pagesWater Sensitive Design-ShashiShashikant Nishant SharmaNo ratings yet
- " ": Rainwater HarvestingDocument15 pages" ": Rainwater HarvestingLucifer100% (1)
- PD 1067 - The Water Code of The Philippines The Philippine Clean Water Act of 2004 - (RA 9275)Document44 pagesPD 1067 - The Water Code of The Philippines The Philippine Clean Water Act of 2004 - (RA 9275)PIKACHUCHIENo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology Cabanatuan CityDocument8 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology Cabanatuan CityJosiah CruzNo ratings yet
- Ass 1Document68 pagesAss 1Anusmita MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document42 pagesLecture 1Mahmudul Hasan PathikNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Chapter TwoDocument26 pagesLecture - Chapter TwoHabtie Habtie ZewduNo ratings yet
- Water Conservation PracticesDocument53 pagesWater Conservation PracticesCarol TumanengNo ratings yet
- HYDROLOGY PrelimsDocument17 pagesHYDROLOGY PrelimsLeea Anne MalitNo ratings yet
- Water Resources Engineering: Presented byDocument28 pagesWater Resources Engineering: Presented byAlex TajoraNo ratings yet
- CVS 445 Assignment 2Document8 pagesCVS 445 Assignment 2Bavaria Latimore BLNo ratings yet
- Water Resources Engineering 3Document53 pagesWater Resources Engineering 3Angela Mae VelardeNo ratings yet
- Harvesting RainwaterDocument17 pagesHarvesting RainwateralagarhemaNo ratings yet
- Issues of Large Dams - Case StudyDocument35 pagesIssues of Large Dams - Case StudybhuvaneshkmrsNo ratings yet
- Watershed Management 56880c65119c9Document27 pagesWatershed Management 56880c65119c9Uttam BiswasarmaNo ratings yet
- 2004 Connecticut Conservation Times NewsletterDocument4 pages2004 Connecticut Conservation Times NewsletterConnecticut Nonpoint Pollution EducationNo ratings yet
- 5 Construction Method Statement: 5.1 General DescriptionDocument12 pages5 Construction Method Statement: 5.1 General DescriptionUpali Karunarathne100% (1)
- Typical Box CulvertDocument1 pageTypical Box CulvertDeepak Pandey100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Drainage DesignDocument47 pagesChapter 4 Drainage DesignNasredeenAhmadNo ratings yet
- India Country Kit Documentation 2022Document34 pagesIndia Country Kit Documentation 2022MGL RAJKOTNo ratings yet
- Stormwater Drainage: DesignDocument31 pagesStormwater Drainage: DesignMihretu AbrhamNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Reinforced Concrete CulvertDocument49 pagesAnalysis and Design of Reinforced Concrete Culvertسجى وليدNo ratings yet
- Erosion Control ProcedureDocument10 pagesErosion Control ProcedureozerNo ratings yet
- Typical Section of RCC Road Rigid Pavement: SCALE 1:50Document4 pagesTypical Section of RCC Road Rigid Pavement: SCALE 1:50Swopnil KalikaNo ratings yet
- Scour in Bottomless Culvert FHWADocument80 pagesScour in Bottomless Culvert FHWAGUido JUarezNo ratings yet
- Transport For NSW (TFNSW) Qa Specification R11 Stormwater DrainageDocument45 pagesTransport For NSW (TFNSW) Qa Specification R11 Stormwater DrainageHenry HNo ratings yet
- Interim Revisions To: The Manual For Bridge EvaluationDocument57 pagesInterim Revisions To: The Manual For Bridge EvaluationAna Maria OlayaNo ratings yet
- 1.4 - Mr. Prasanna Kangara - Resident Engineer (Kegalle)Document16 pages1.4 - Mr. Prasanna Kangara - Resident Engineer (Kegalle)mpchanakaNo ratings yet
- Bridge Inspection Manual Version 19Document145 pagesBridge Inspection Manual Version 19atac101100% (1)
- Making HEC-RAS Models Run FasterDocument27 pagesMaking HEC-RAS Models Run FasterAaron NicholsNo ratings yet
- Drain PLNDocument2 pagesDrain PLNDaniel AuriNo ratings yet
- 09 (Spojnice U Betonskim Konstrukcijama I Mostovima)Document28 pages09 (Spojnice U Betonskim Konstrukcijama I Mostovima)Vladimir MilicevicNo ratings yet
- Cross-Drainage Culvert Design by Using GIS: M. Günal, M. Ay and A.Y. GünalDocument4 pagesCross-Drainage Culvert Design by Using GIS: M. Günal, M. Ay and A.Y. GünalLXN 6176No ratings yet
- Geotech Buried PipesDocument54 pagesGeotech Buried Pipeserleos100% (2)
- Part 6 - Sec 6.08.2.1 RC Pipe CulvertsDocument2 pagesPart 6 - Sec 6.08.2.1 RC Pipe CulvertsAbdul Wahab JamilNo ratings yet
- Hydrological and Drainage Investigation ReportDocument45 pagesHydrological and Drainage Investigation Reportmarting69No ratings yet
- Aw Ma CatalogueDocument23 pagesAw Ma CatalogueTuan NgoNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal - Green RoadDocument11 pagesResearch Proposal - Green RoadSunil ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Foothills Solar & SubstationDocument49 pagesFoothills Solar & SubstationfazyroshanNo ratings yet
- Arema Mre 2013 Toc-Vol1 Ch1Document3 pagesArema Mre 2013 Toc-Vol1 Ch1Ndoro Bei0% (1)
- Chapter 14 Proposed Road Operation and Maintenance PlanDocument48 pagesChapter 14 Proposed Road Operation and Maintenance PlanrobinNo ratings yet